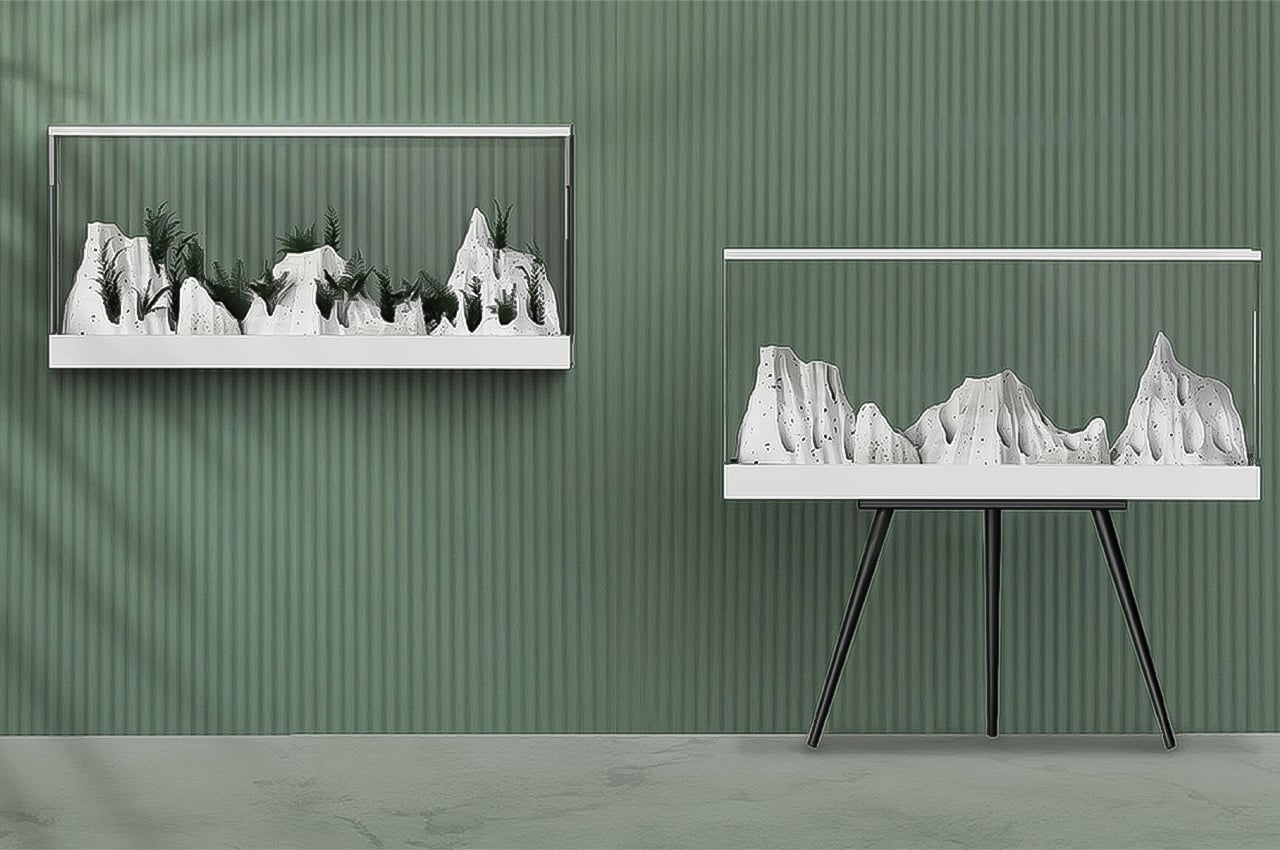
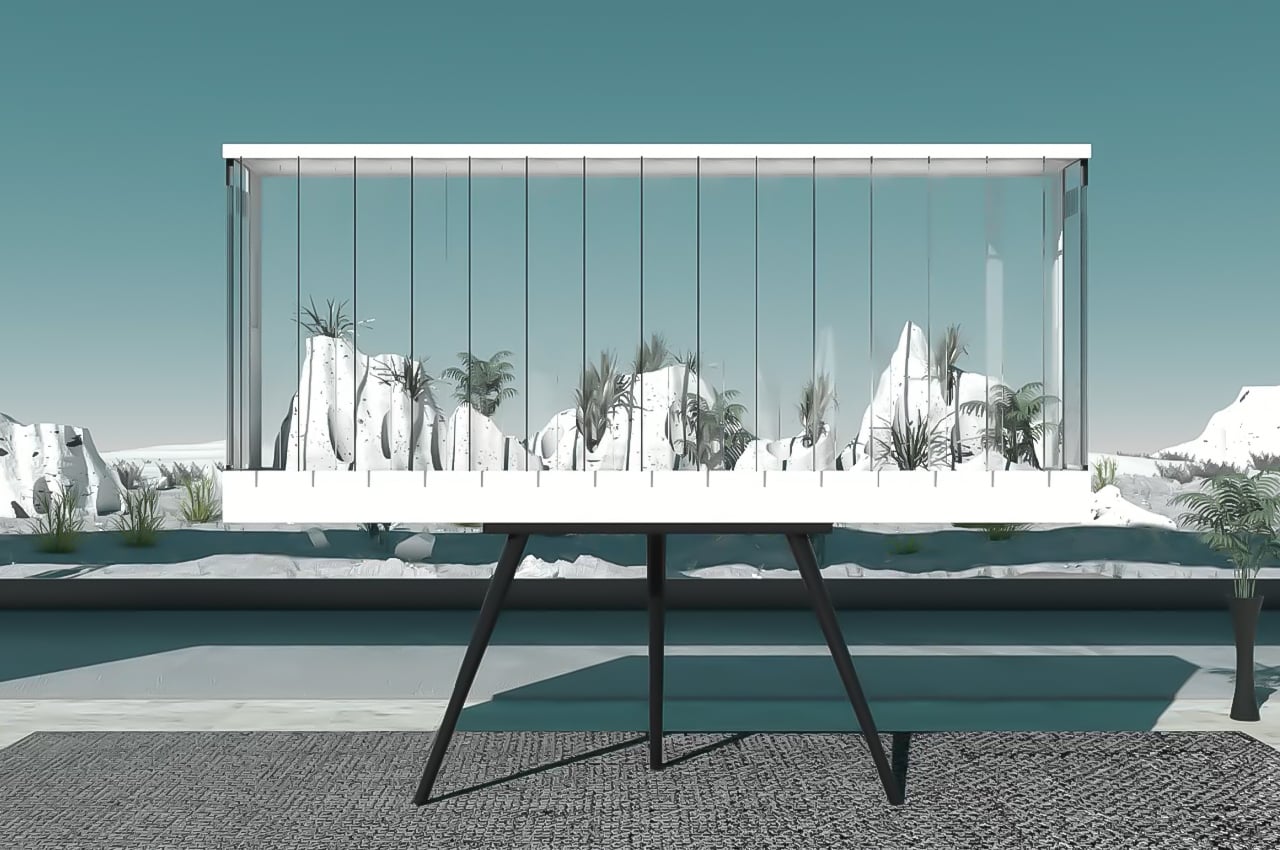
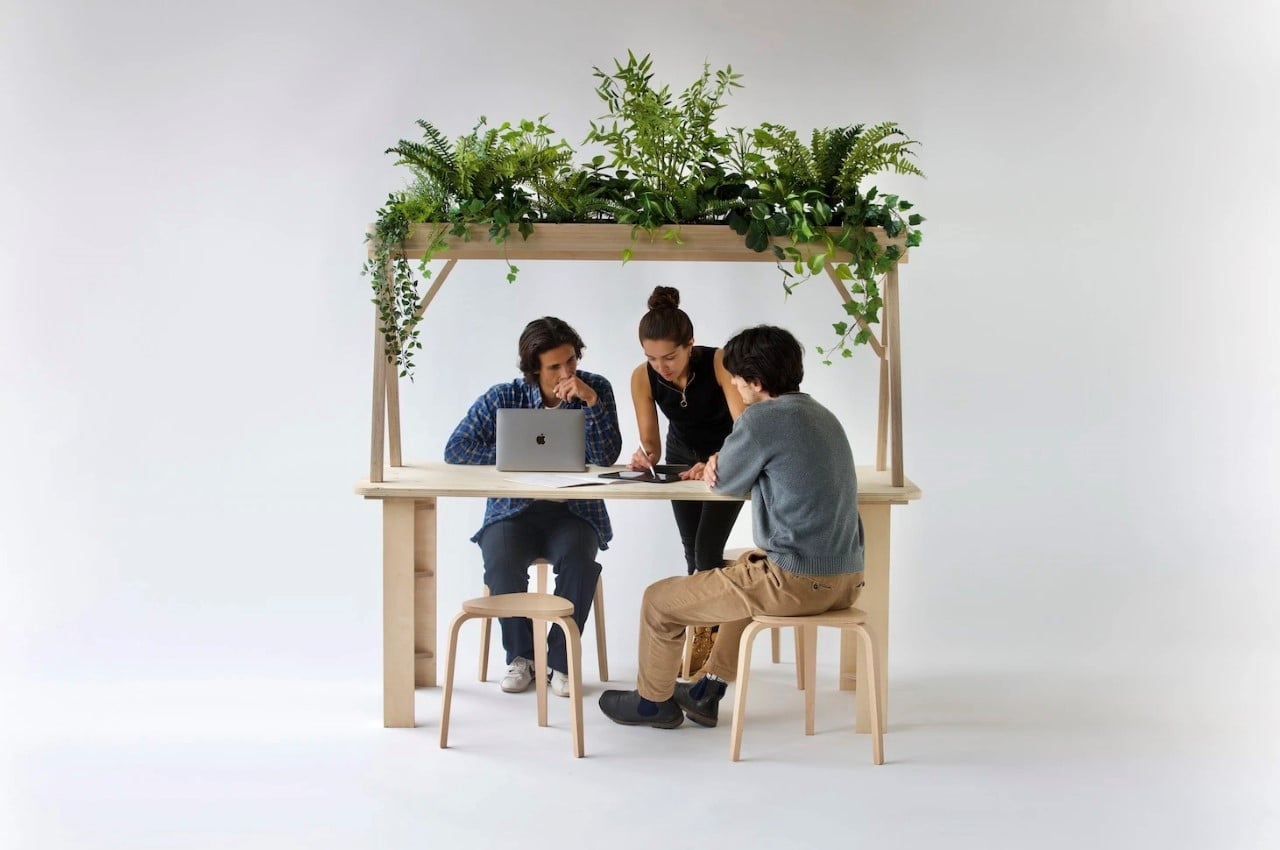
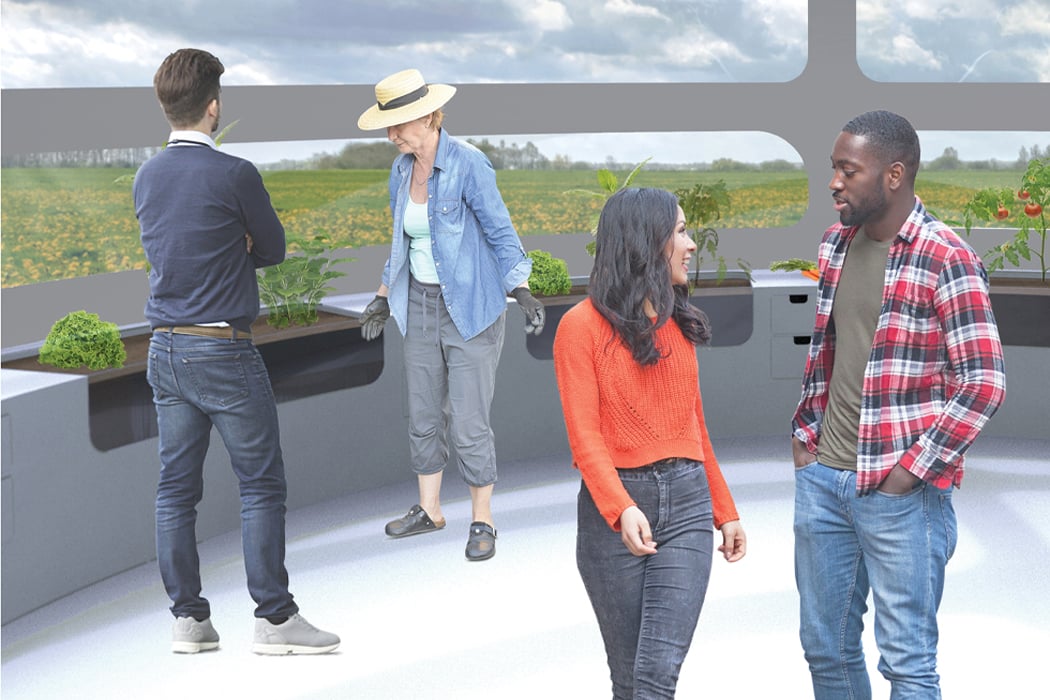
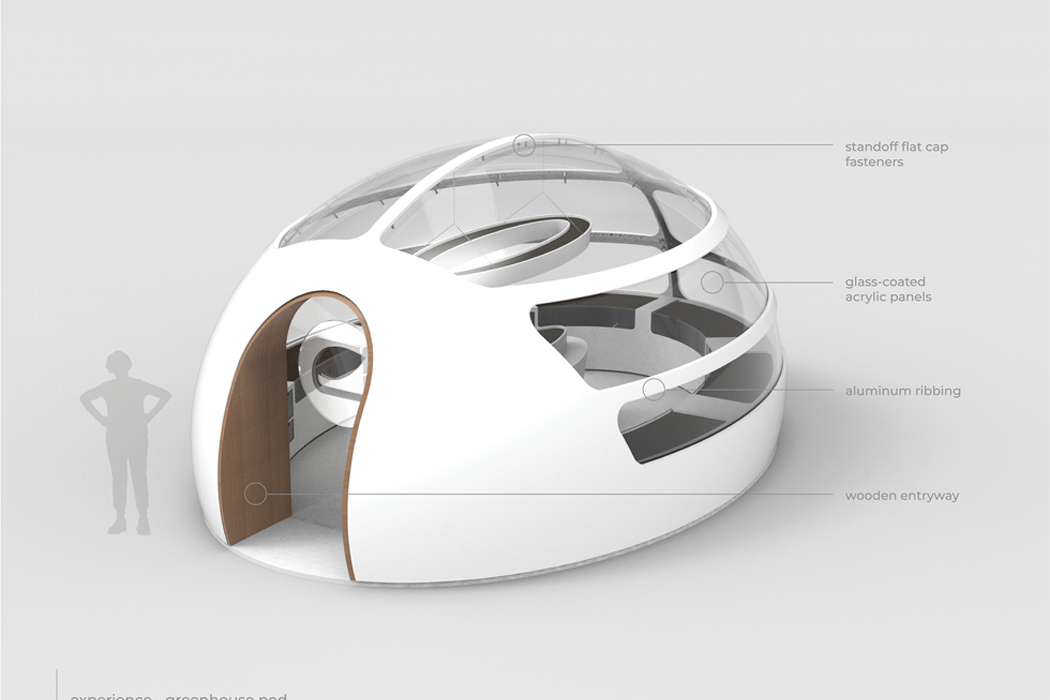
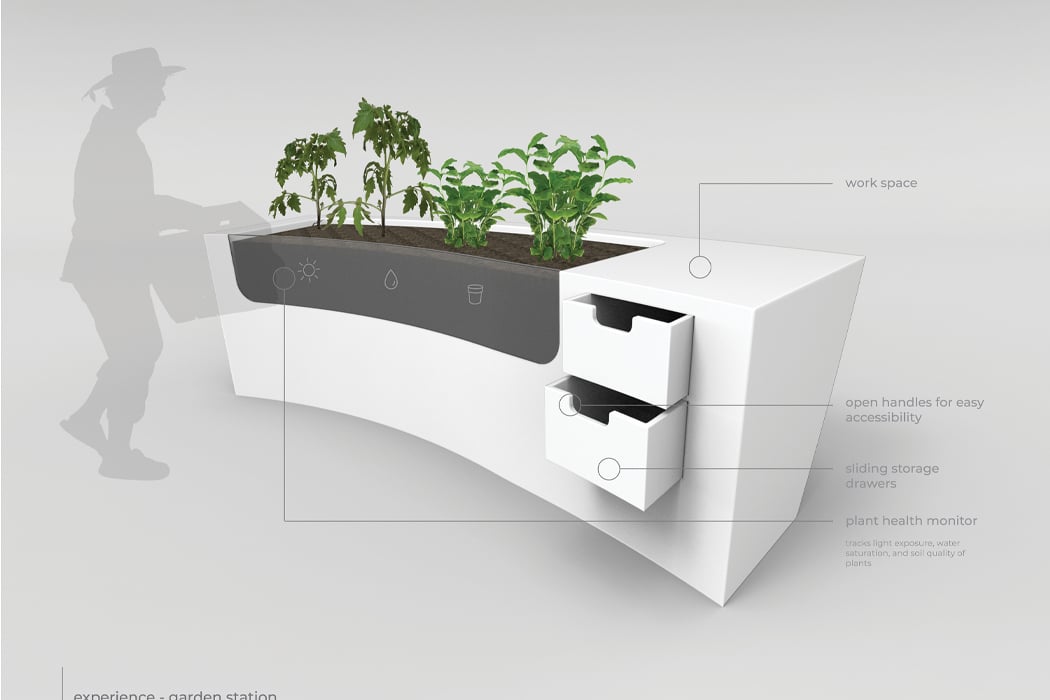
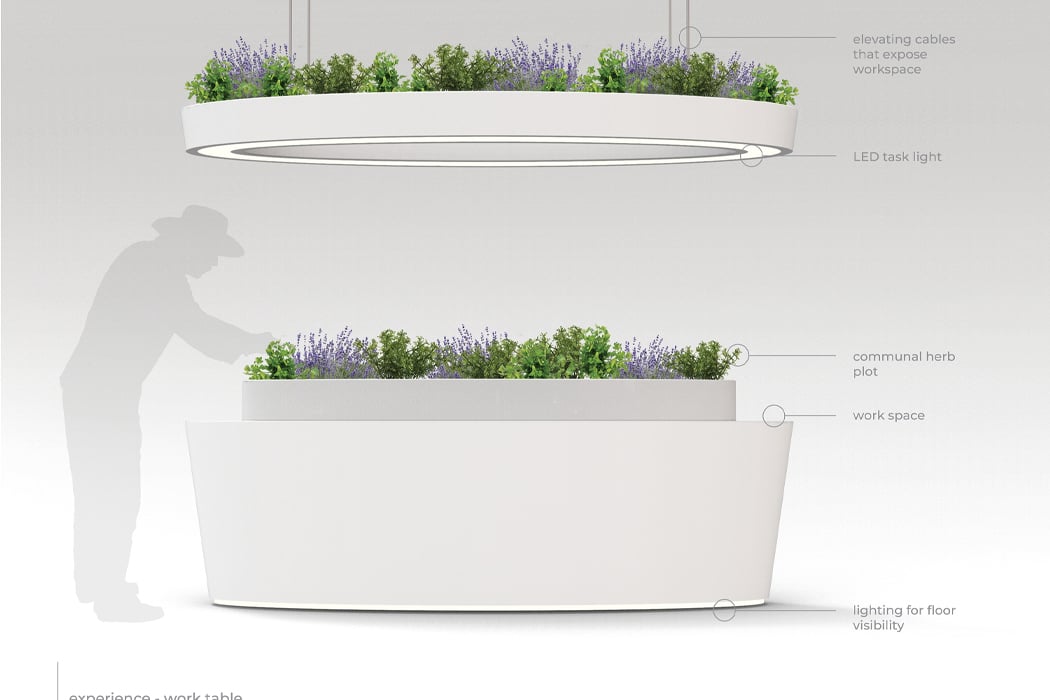
Permaculture gardening is deeply rooted in the principles of sustainability and aims to harmonize the growth of plants with the local environment. In 1978, Australian ecologist David Holmgren and environmental psychology professor Bill Mollison coined “permaculture” from “permanent agriculture,” later expanding its meaning to include “permanent culture.” Permaculture gardening primarily emphasizes the gradual enhancement of soil quality with nutrients, aiming to continually revitalize the earth while nurturing plant health. Its core ethics include prioritizing care for the Earth, for people, and ensuring equitable sharing, returning any surplus.
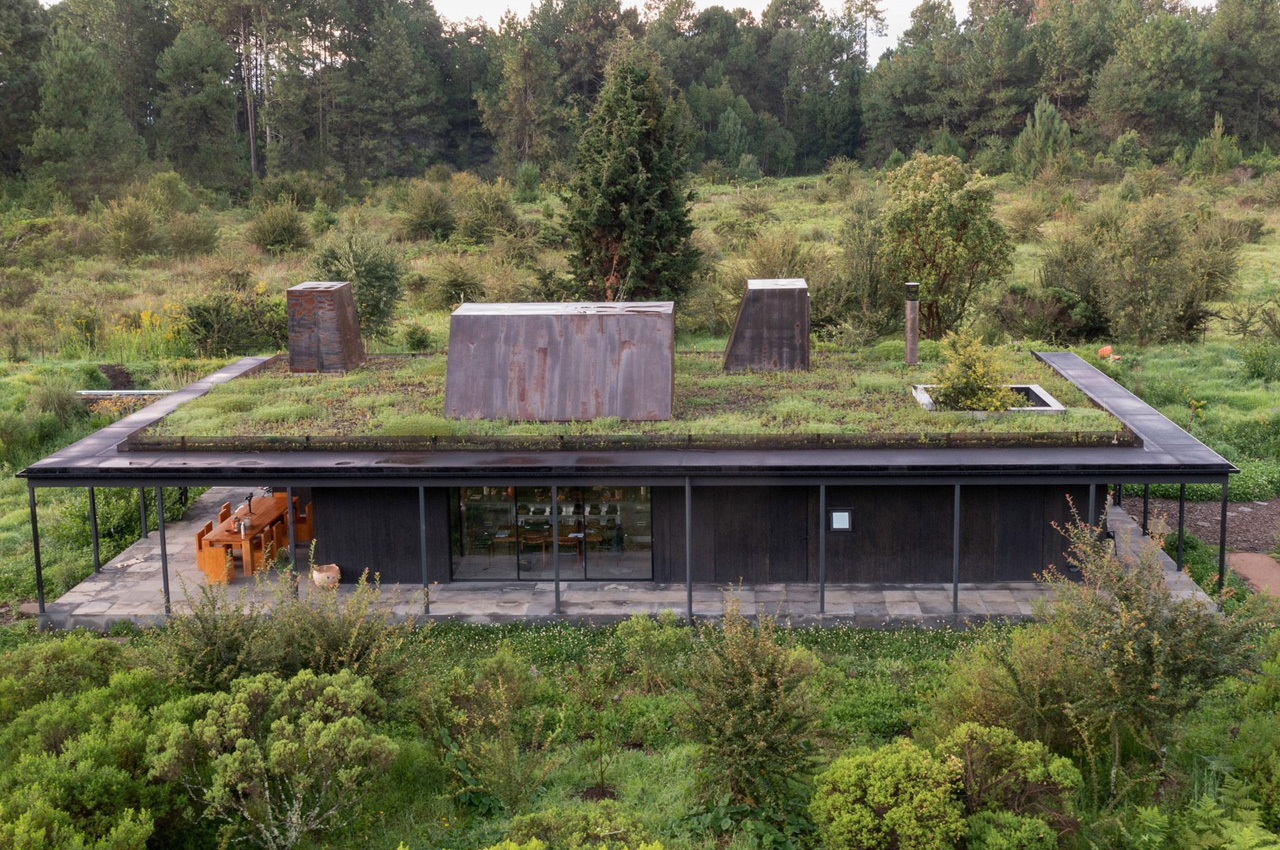
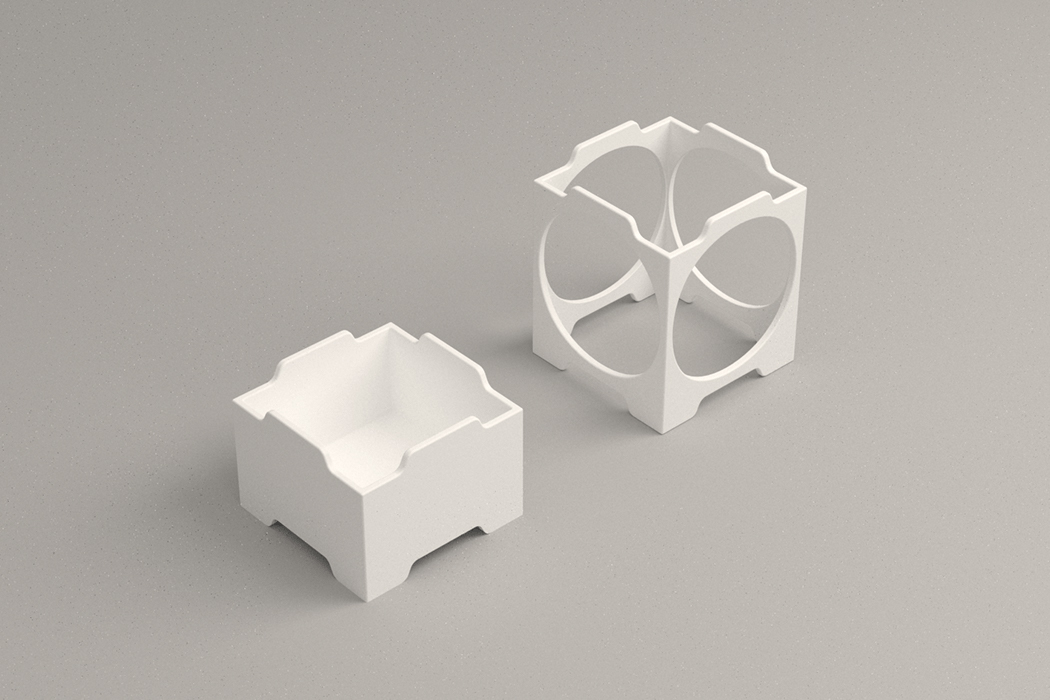
Designer: Robert Hutchison Architecture and Javier Sanchez Arquitectos
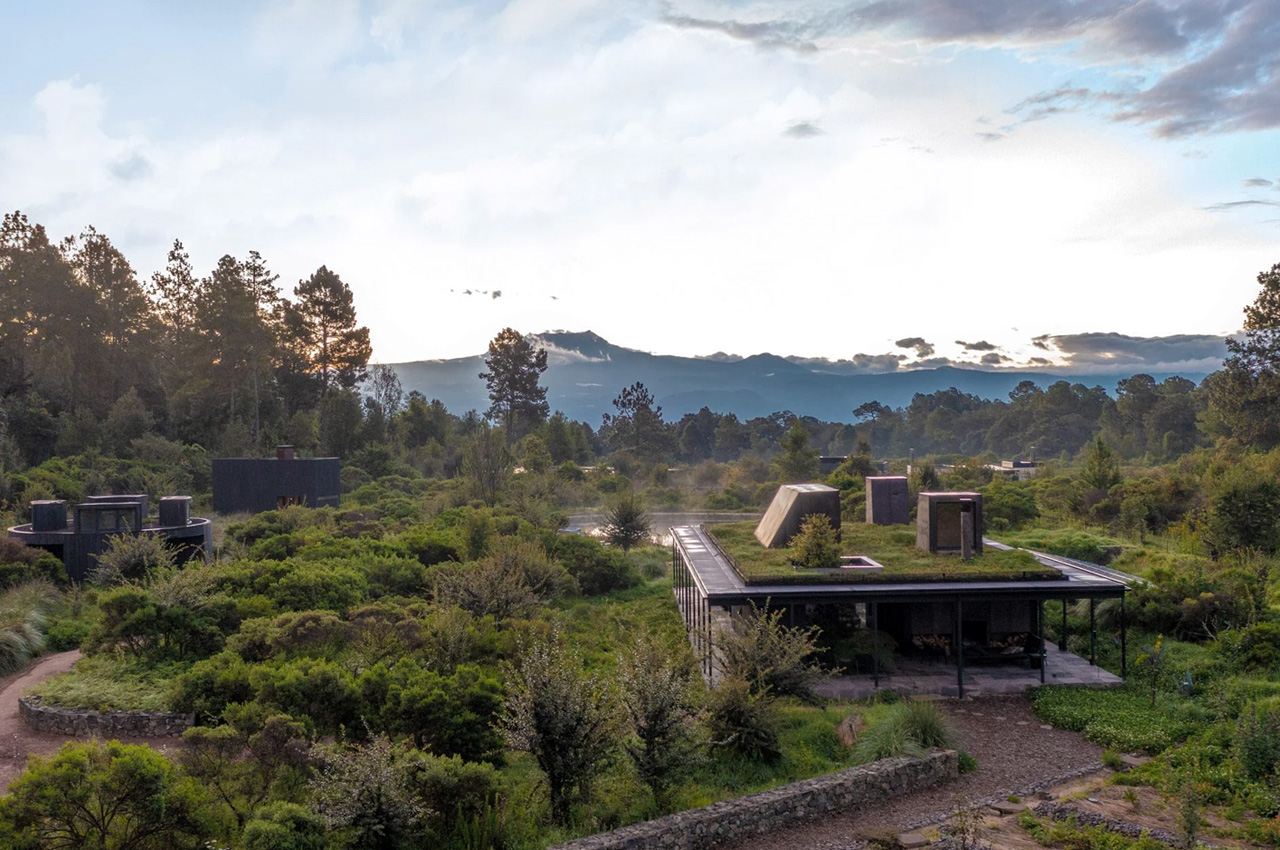

What is the primary goal of Permaculture?
Permaculture advocates aligning with nature, emphasizing mindful actions to avoid widespread negative impacts. It stresses preserving and restoring natural systems and settlements, highlighting their irreplaceable value. The goal is to achieve objectives with minimal environmental disruption.
What is Permaculture farming?
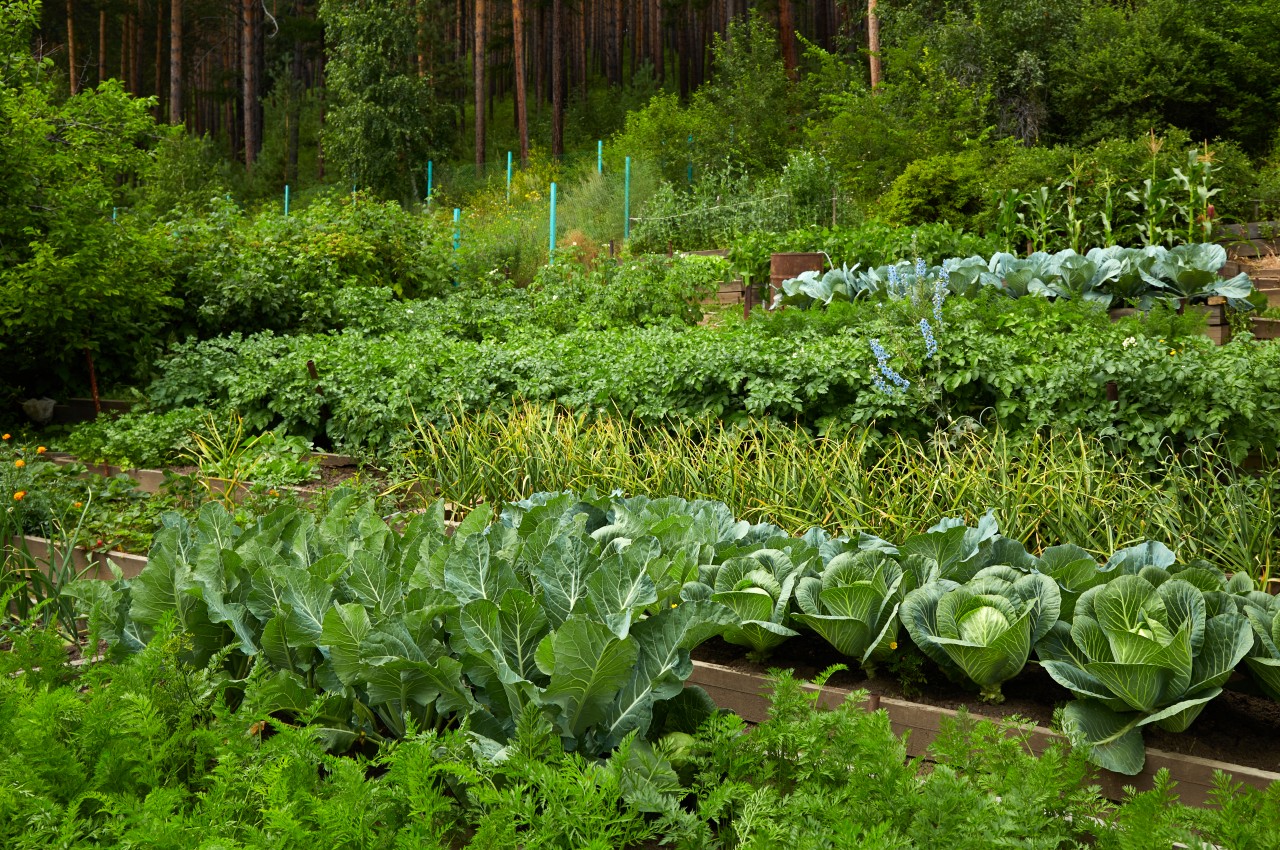

Image courtesy of: viktelminova
Permaculture farming means growing crops in a way that takes care of itself and the environment. It learns from nature and creates farming systems where different crops help each other grow. This way of farming is diverse, strong, and lasts a long time, just like nature does.
What are the benefits of creating a Permaculture Garden?
The benefits of creating a Permaculture Garden includes:
Protects Natural Resources

Image courtesy of: Sangiao_photography
We can optimize natural resources by harvesting wild medicinal plants, growing anti-pollutant plants for indoor air quality, and strategically planting trees for summer shade. It’s essential to minimize waste and promote material reuse.
Avoid Tilling the Soil
In permaculture, it’s preferred to avoid tilling vegetable garden soil. Instead, natural insect processes, aided by mulch, are encouraged, as tillers or cultivators can harm underground insect populations.
Promotes Biodiversity

Image courtesy of: YuriArcursPeopleimages
Unlike conventional agriculture, permaculture embraces nature, drawing inspiration from its diversity and working in harmony with it to derive benefits.
Connects Humans with Nature
Permaculture links humans with nature, fostering harmony by working in tandem with natural processes. This approach to gardening can deeply affect our spiritual well-being.
Low Maintenance
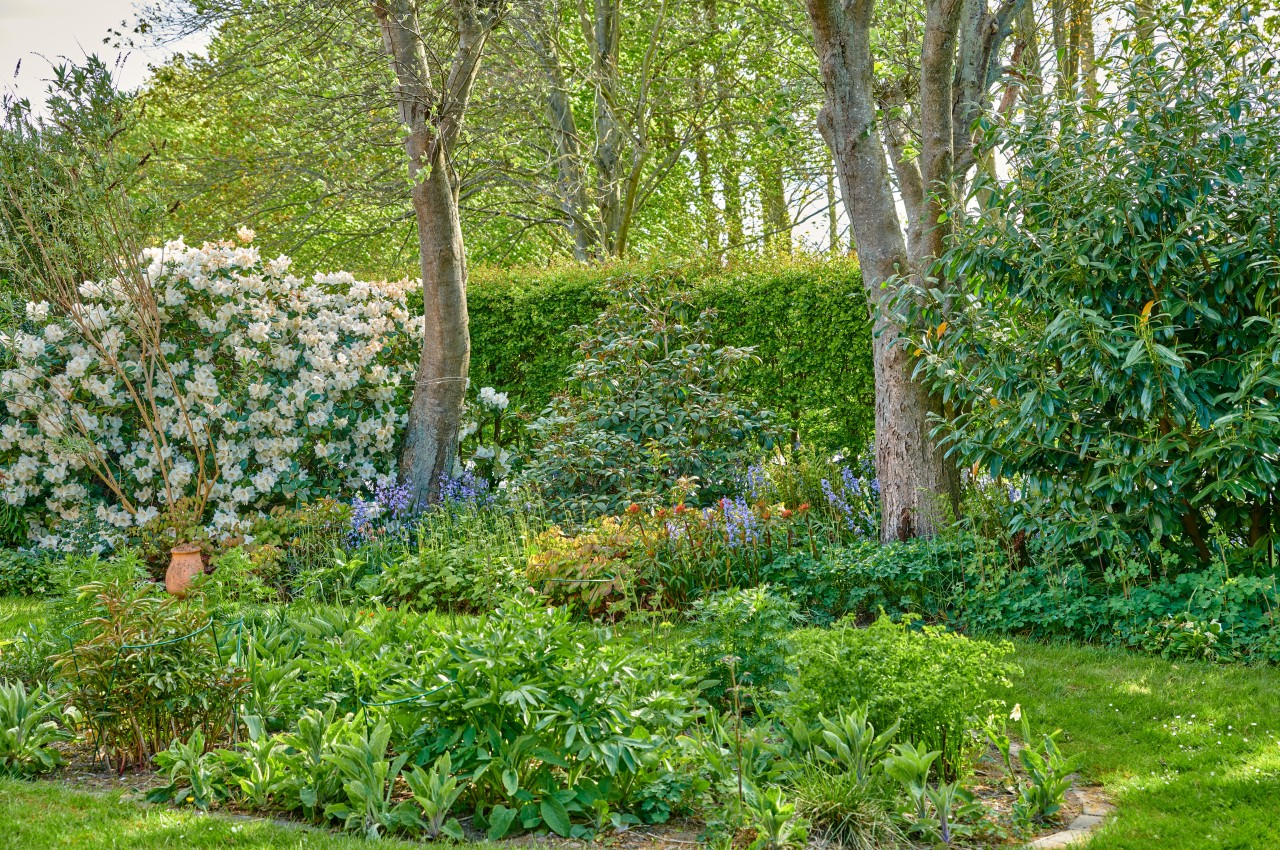

Image courtesy of: YuriArcursPeopleimages
Permaculture gardening offers low-maintenance benefits, making it ideal for those with limited time or less gardening experience.
Avoids Use of Pesticides
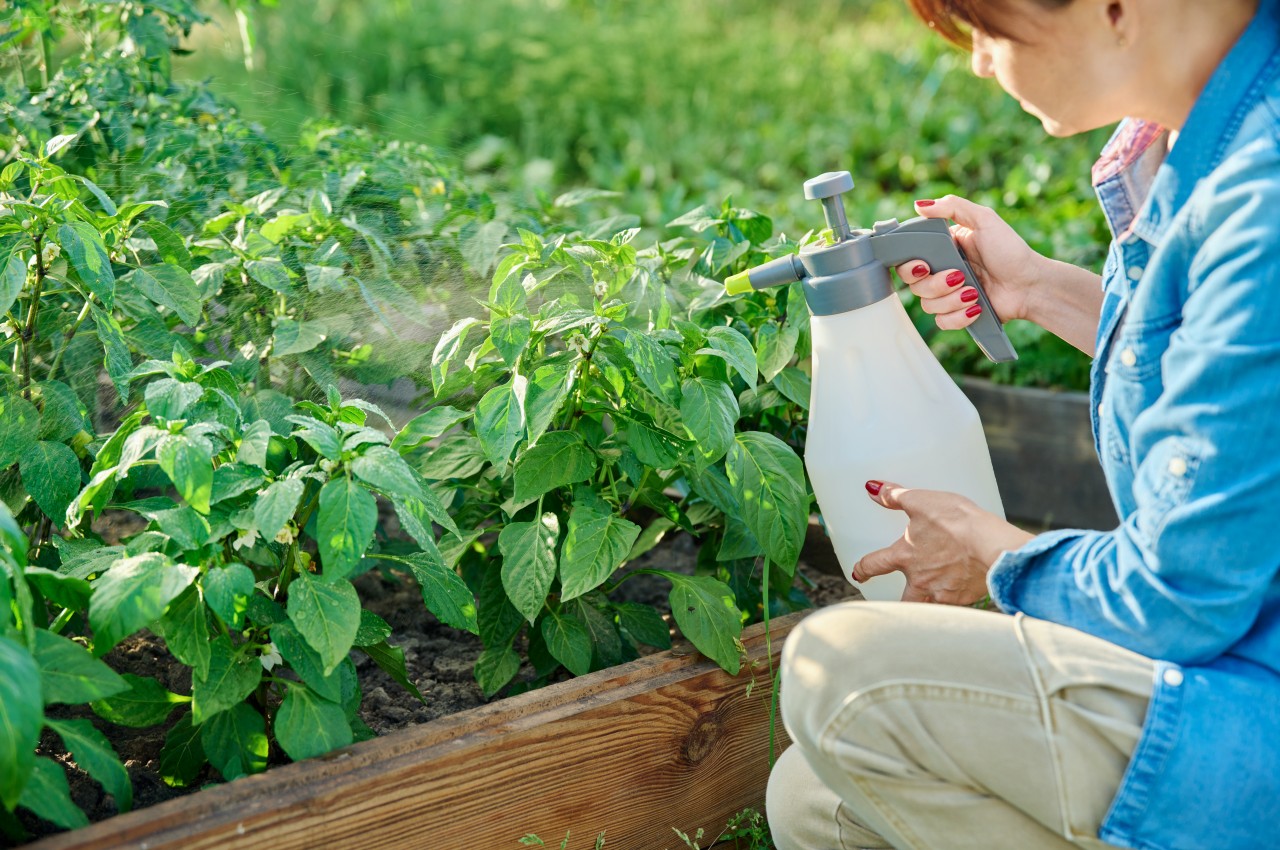

Image courtesy of: valeriygoncharukphoto
Permaculture avoids all pesticides and insecticides, organic or not, to protect biodiversity, relying on natural self-regulation and abstaining from herbicides and chemical fertilizers. Gardeners may accept some crop loss to pests rather than resorting to chemicals.
Saves Space
Producing ample yields in a confined space reduces the need for more area, allowing for extra activities. An essential element of permaculture gardening is maximizing space efficiency. Permaculture gardens vary in size, but in limited spaces, employing strategies to uphold permaculture principles is key. For instance, consider cultivating plants vertically using trellises or similar structures.
Supports Local Wildlife
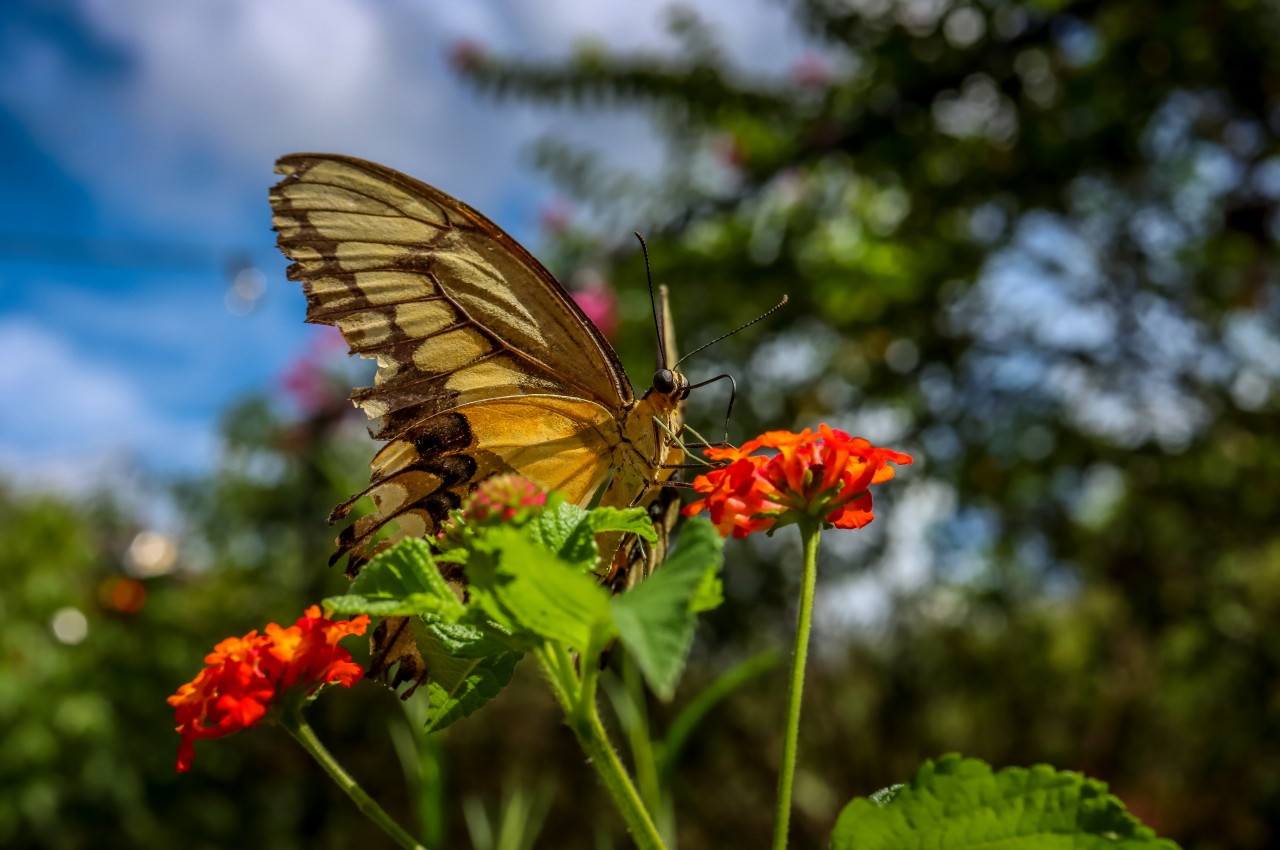

Image courtesy of: cannonapril
Permaculture’s ethics and practices naturally draw wildlife to outdoor spaces. Follow permaculture guidelines to turn your backyard into a flourishing haven for birds, pollinating insects, and other creatures. Tips include avoiding pesticides, using vegetation to attract specific animals, hanging bird feeders, keeping dead logs and leaf litter, and planting trees and shrubs for wildlife shelter.
However, there are a few downsides to permaculture gardening. It can initially be more expensive to implement its practices. Although, the upfront costs are usually justified by long-term benefits. Some may find the initial workload overwhelming, despite its eventual rewards. Moreover, there may be concerns about potential odors from composting, managing a garden that utilizes all resources, and dealing with pests and bacteria without pesticides.
How to design a Permaculture Garden?
Use these tips to create your own Permaculture Garden:
Know your Surroundings
Get to know your environment by familiarizing yourself with the native flora, fauna, and predators in your area, while also noting the sunny and shady spots in your garden. Identify any unique features that could be advantageous for your permaculture garden.
Choose Your Plants Wisely
Select plants suited to your local conditions, researching which species thrive annually and perennially. Utilize companion planting to attract beneficial insects, deter pests, and enrich soil naturally. Opt for butterfly-attracting flowers, pest-repelling herbs for fruit trees, and nitrogen-fixing green manure crops to gradually enhance soil fertility. Opt for edible crops like fruits, veggies, herbs, seeds, and fruit trees, as they provide sustenance with minimal resource use.
Design the Garden
Once you’re familiar with your surroundings and the existing plant life, you can better design your garden. Consider light, water sources, and landscape when situating plants. Utilize plant stacking for efficient space use, with ground cover herbs, shrubs, and trees organized accordingly.
Create Garden Beds
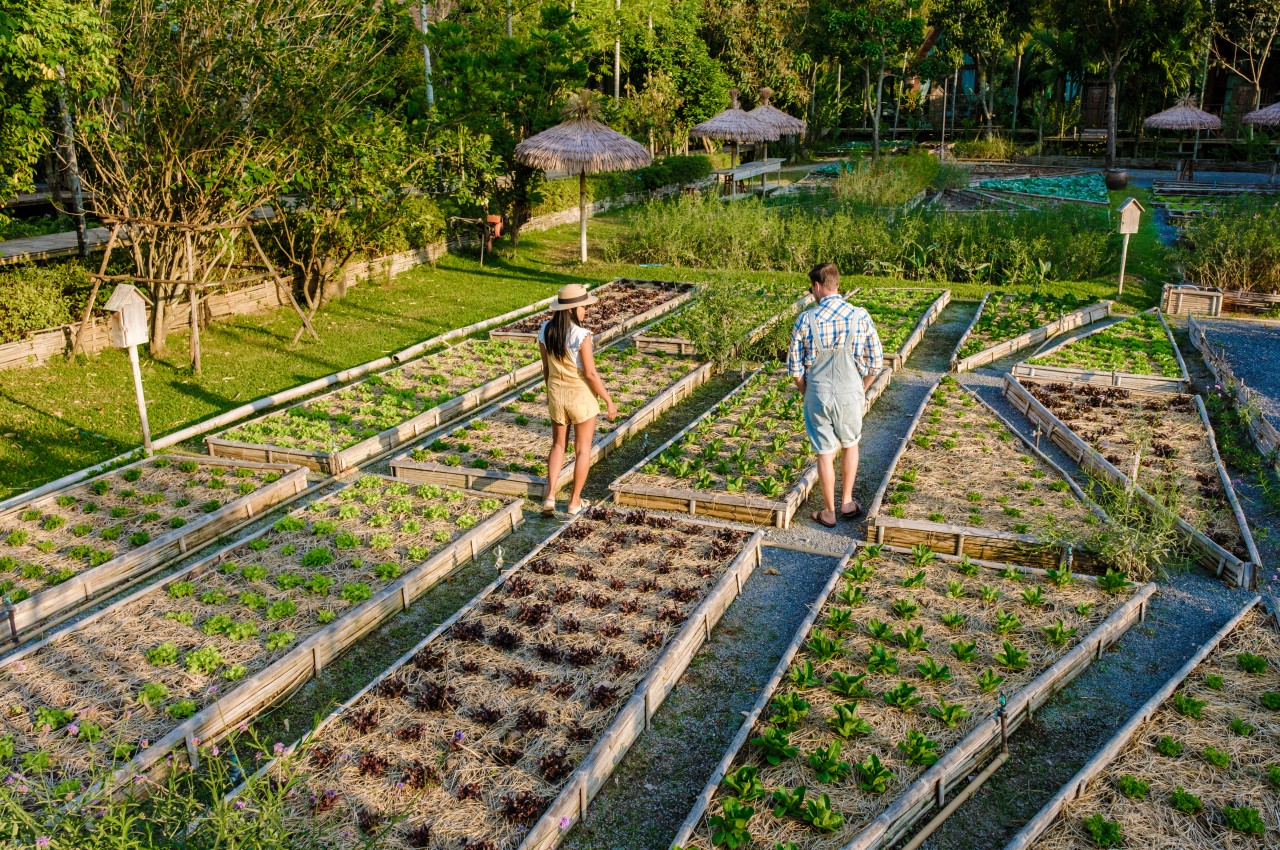

Image courtesy of: fokkebok
Build raised beds, ideal for permaculture gardening as they preserve soil nutrients without tilling, placed six to 12 inches above ground. Alternatively, use sheet mulching, and layering compostable materials over grass to build soil without disturbing tillage.
Plant the Permaculture Garden
Plant your permaculture garden, prioritizing taller plants to offer shade for sun-sensitive ones. Group together plants with similar water and sunlight requirements for optimal growth.
Add Mulch
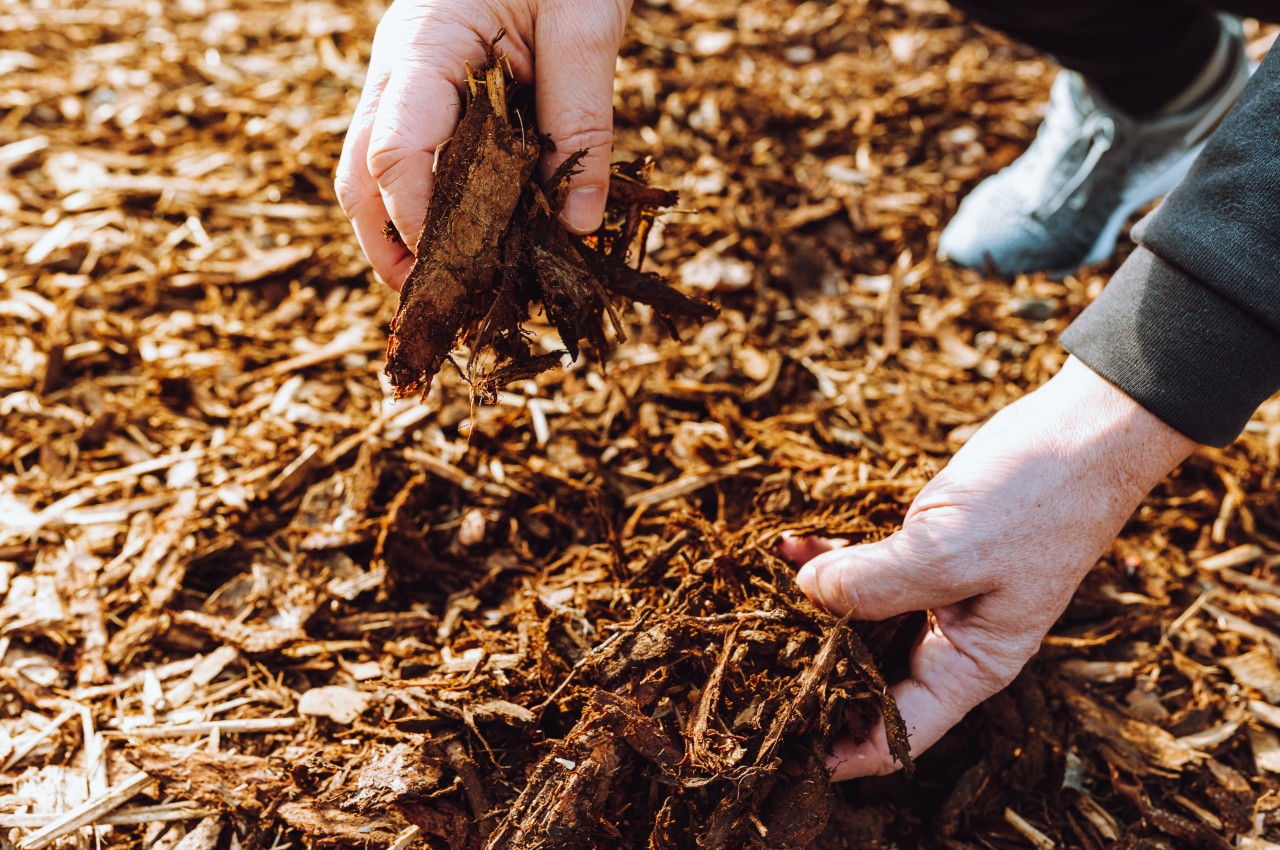

Image courtesy of: larisikstefania
Use organic mulch on topsoil instead of chemical weed killers in line with permaculture principles. Apply it after planting to suppress weeds and retain soil moisture. Options include leaves, newspaper, straw, wood chips, shredded bark, and grass clippings.
Add Compost
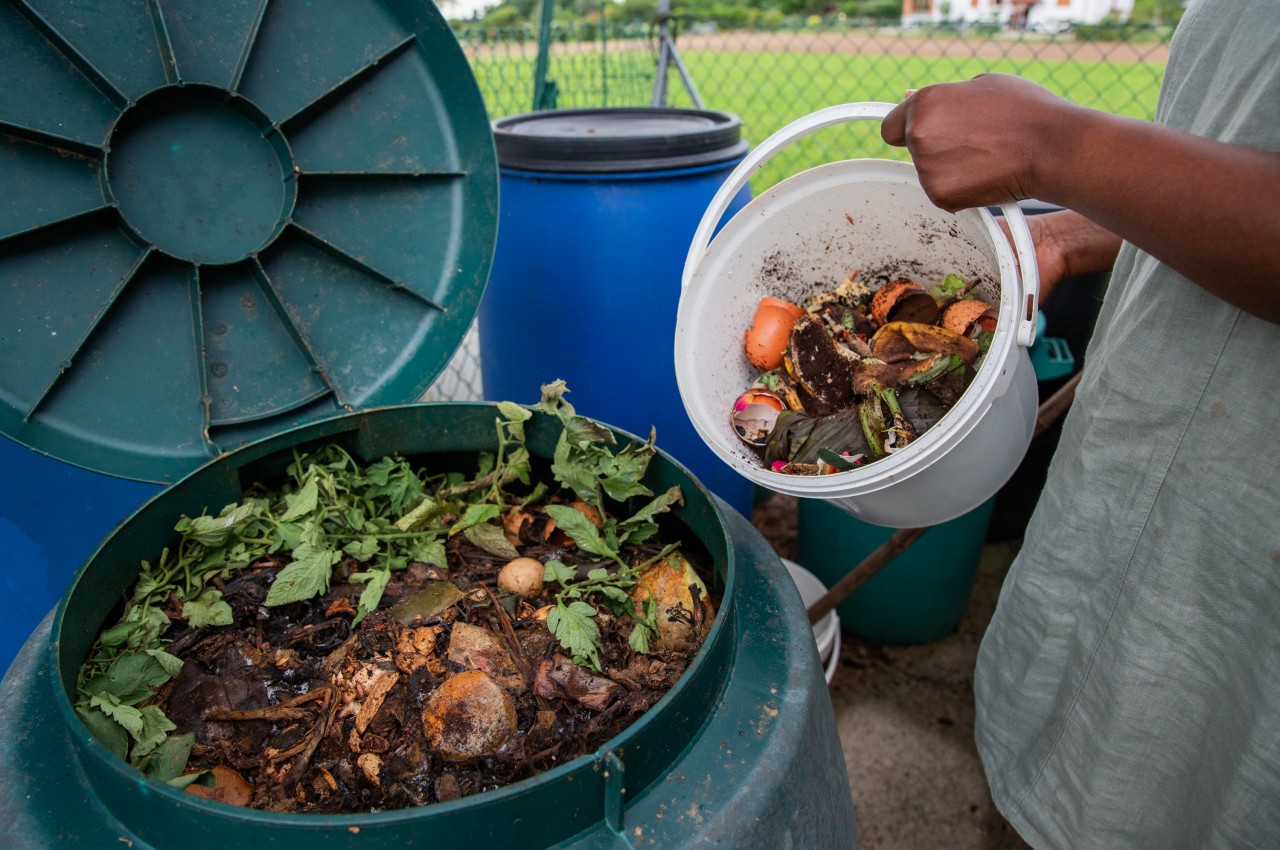

Image courtesy of: medialensking
Add compost without disturbing the soil, favoring natural options over chemical fertilizers. Utilize materials like manure, kitchen scraps, earthworm castings, and worm tea to enrich the soil with organic matter and beneficial microbes.
Efficient Water Irrigation System
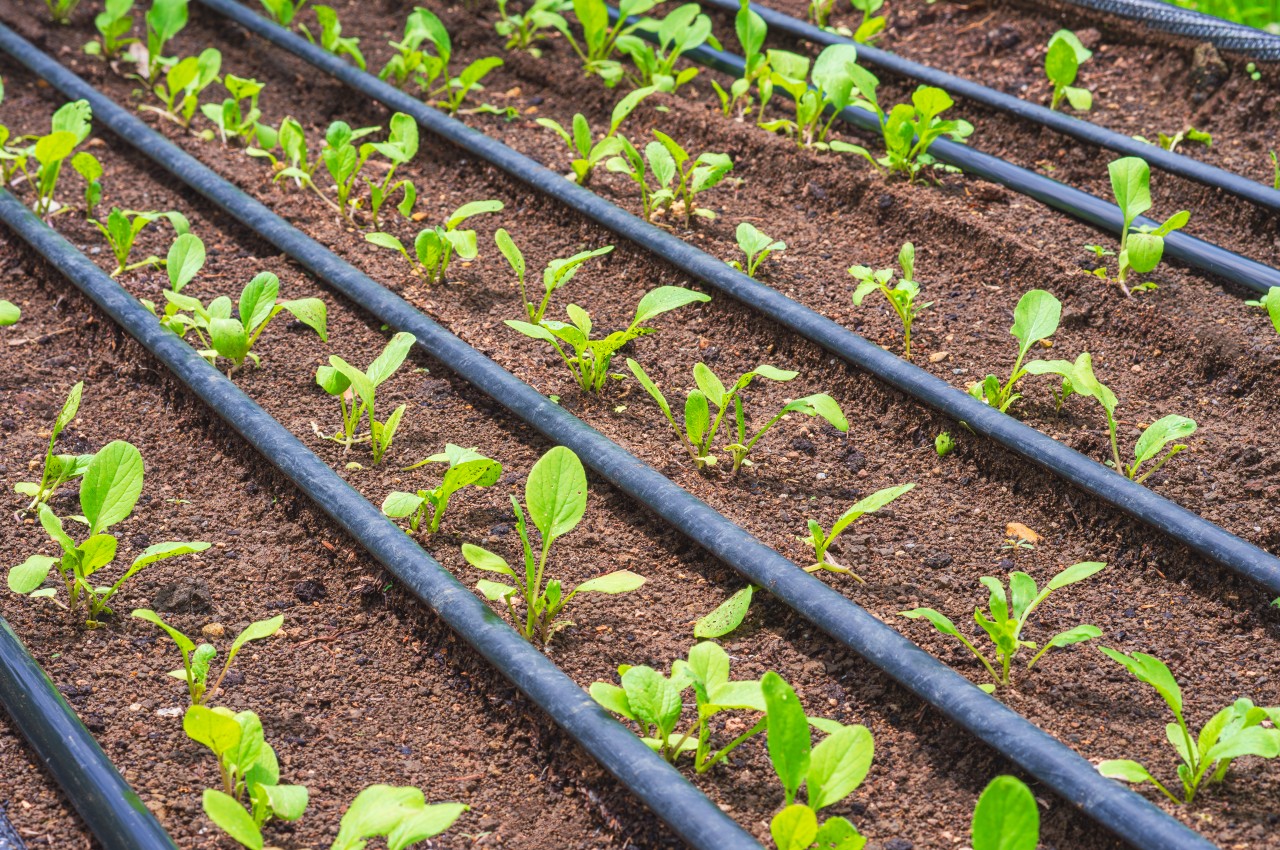

Image courtesy of: aowsakornprapat
Use a sustainable watering system, minimizing water consumption for optimal garden health. Choose a low-waste drip irrigation method to directly hydrate soil and collect rain runoff from roof gutters for recycling into your watering system.
What is the difference between Permaculture and Organic Farming?
Organic Farming

Image courtesy of: monkeybusiness
Organic farming, initiated in the 1940s, is denoted by the term “organic,” indicating products grown or raised without synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, antibiotics, and growth regulators, spurred by J. I. Rodale.
Permaculture Farming
In the 1970s, Bill Mollison and David Holmgren introduced permaculture design, an agricultural system mirroring nature and addressing human needs like food, shelter, and energy consumption.
Here is how Permaculture differs from Organic Farming
• The primary difference between organic farming and permaculture is their approach to sustainable practices. Permaculture centers on preserving natural resources and conserving the planet, ensuring current needs are met without compromising those of future generations.
• Permaculture prioritizes energy conservation by locally growing and selling food, minimizing carbon footprints, while organic-labeled produce is often transported globally.
• In organic farming, the focus is on eliminating chemical residue from the food supply while protecting pollinators, while in permaculture, it’s environmental protection, ultimately benefiting humans.
• Permaculture farming promotes zero waste through recycling and reusable packaging, while organic food often uses disposable containers, contributing to landfill waste.
• Permaculture emphasizes integrated design, where each element serves multiple functions, contrasting with organic farming’s focus on a limited range of commodities. For example, chickens in permaculture not only provide eggs but also help control pests, fertilize the soil, and contribute to soil aeration.
In conclusion, permaculture yields numerous benefits: waste reduction, efficient resource utilization, and pollution prevention. It fosters ethical land management, enhancing both homeowners’ lives and ecosystems. Moreover, permaculture paves the way for sustainable systems that safeguard habitats for humans, animals, and plants, ensuring a healthy planet for the future.
The post What is Permaculture? Exploring the Basics of Permaculture Gardening first appeared on Yanko Design.