
While we've seen supercomputers break records before, rarely have we seen the barrier smashed quite so thoroughly as by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory's Sequoia supercomputer. Researchers at both LLNL and Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute have used planet-scale calculations on the Blue Gene/Q-based cluster to set an all-time simulation speed record of 504 billion events per second -- a staggering 41 times better than the 2009 record of 12.2 billion. The partnership also set a record for parallelism, too, by making the supercomputer's 1.97 million cores juggle 7.86 million tasks at once. If there's a catch to that blistering performance, it's not knowing if Sequoia reached its full potential. LLNL and RPI conducted their speed run during an integration phase, when Sequoia could be used for public experiments; now that it's running classified nuclear simulations, we can only guess at what's possible.
Filed under: Science, Alt
Comments
Source: Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
 Jupiter's ancient name really is well-deserved: according to a new study, the king of the planets isn't just the largest in the Solar System, it's also the oldest. A team of researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in California and th...
Jupiter's ancient name really is well-deserved: according to a new study, the king of the planets isn't just the largest in the Solar System, it's also the oldest. A team of researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in California and th...
 Jupiter's ancient name really is well-deserved: according to a new study, the king of the planets isn't just the largest in the Solar System, it's also the oldest. A team of researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in California and th...
Jupiter's ancient name really is well-deserved: according to a new study, the king of the planets isn't just the largest in the Solar System, it's also the oldest. A team of researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in California and th...
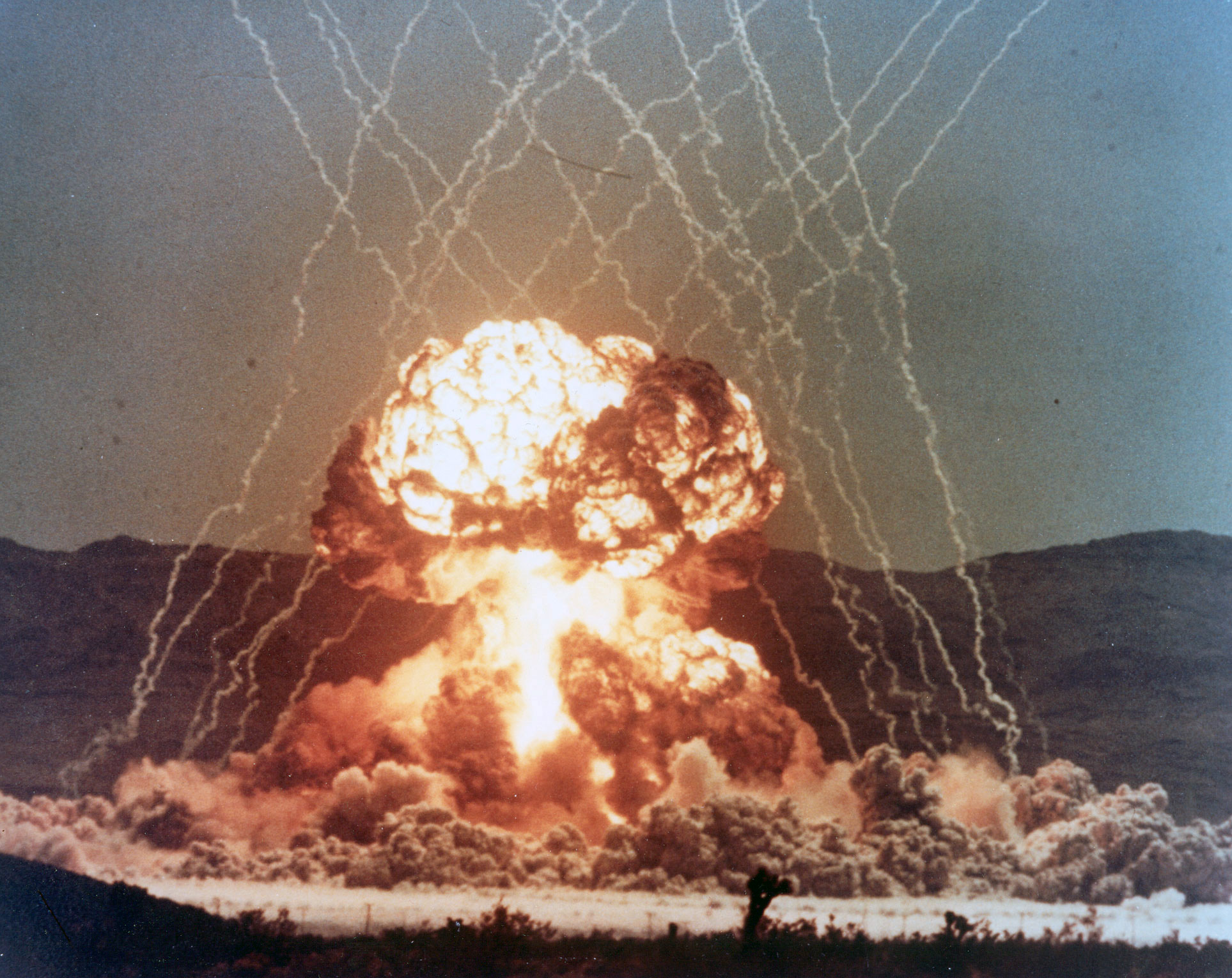 There's something both beautiful and unnerving about a mushroom cloud. The United States conducted around 216 atmospheric nuclear tests between 1945 and 1992, many taking place in Nevada and the Pacific Proving Grounds. Now, rare videos of those deto...
There's something both beautiful and unnerving about a mushroom cloud. The United States conducted around 216 atmospheric nuclear tests between 1945 and 1992, many taking place in Nevada and the Pacific Proving Grounds. Now, rare videos of those deto...
 Microsoft isn't the only big-name tech company using AI to fight cancer. NVIDIA is partnering with the US Department of Energy and the National Cancer Institute to develop CANDLE (Cancer Distributed Learning Environment), an AI-based "common discover...
Microsoft isn't the only big-name tech company using AI to fight cancer. NVIDIA is partnering with the US Department of Energy and the National Cancer Institute to develop CANDLE (Cancer Distributed Learning Environment), an AI-based "common discover...
 Police and archaeologists regularly depend on DNA evidence for identification, but it has a serious flaw. DNA degrades under environmental conditions like heat and light, so it may be useless even if you have a ton of samples. However, Lawrence Live...
Police and archaeologists regularly depend on DNA evidence for identification, but it has a serious flaw. DNA degrades under environmental conditions like heat and light, so it may be useless even if you have a ton of samples. However, Lawrence Live...
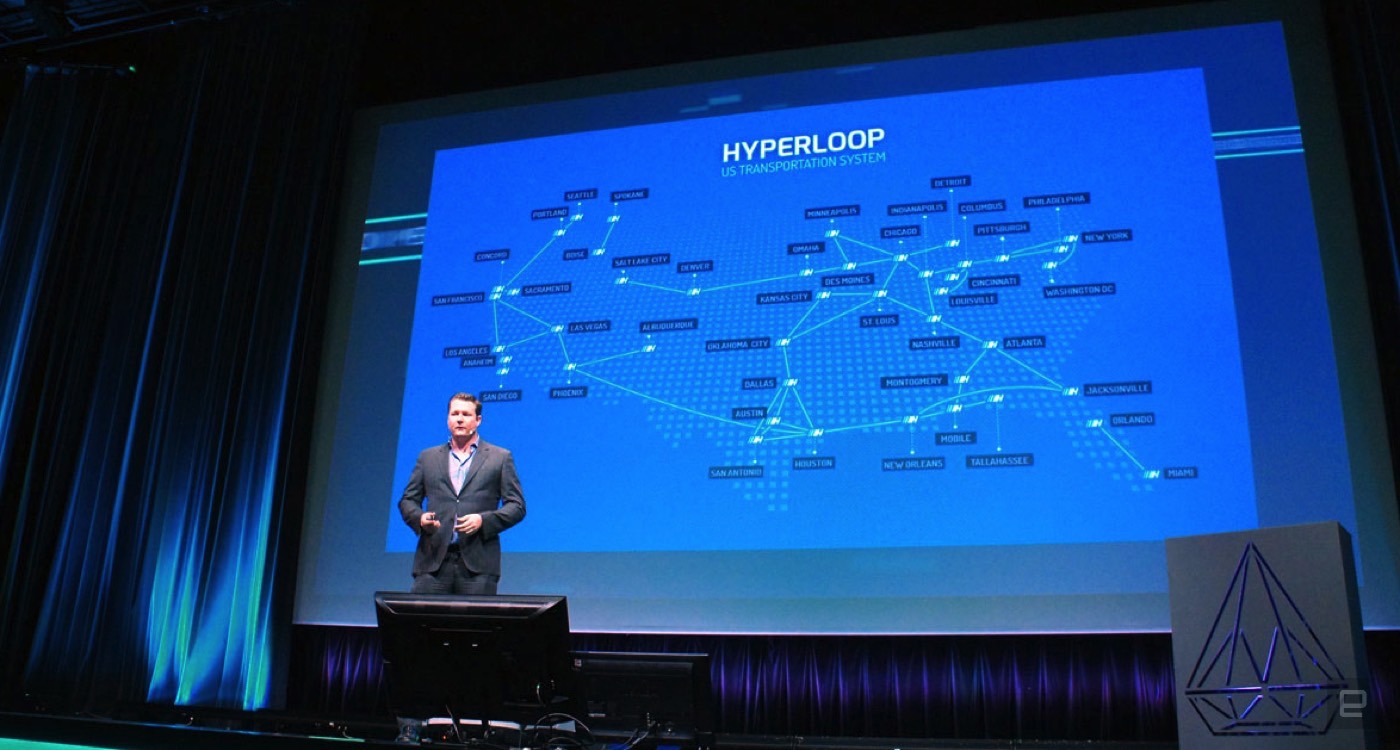 One of the two competing Hyperloop companies has made a major announcement concerning how it's going to make high speed transport a reality. Hyperloop Transportation Technologies has signed a deal with the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory to ha...
One of the two competing Hyperloop companies has made a major announcement concerning how it's going to make high speed transport a reality. Hyperloop Transportation Technologies has signed a deal with the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory to ha...
 It's no longer a rare feat to 3D print blood vessels. Printing vessels that act like the real deal, however, has been tricky... until now. Lawrence Livermore researchers have successfully 3D printed blood vessels that deliver nutrients and self-ass...
It's no longer a rare feat to 3D print blood vessels. Printing vessels that act like the real deal, however, has been tricky... until now. Lawrence Livermore researchers have successfully 3D printed blood vessels that deliver nutrients and self-ass...



