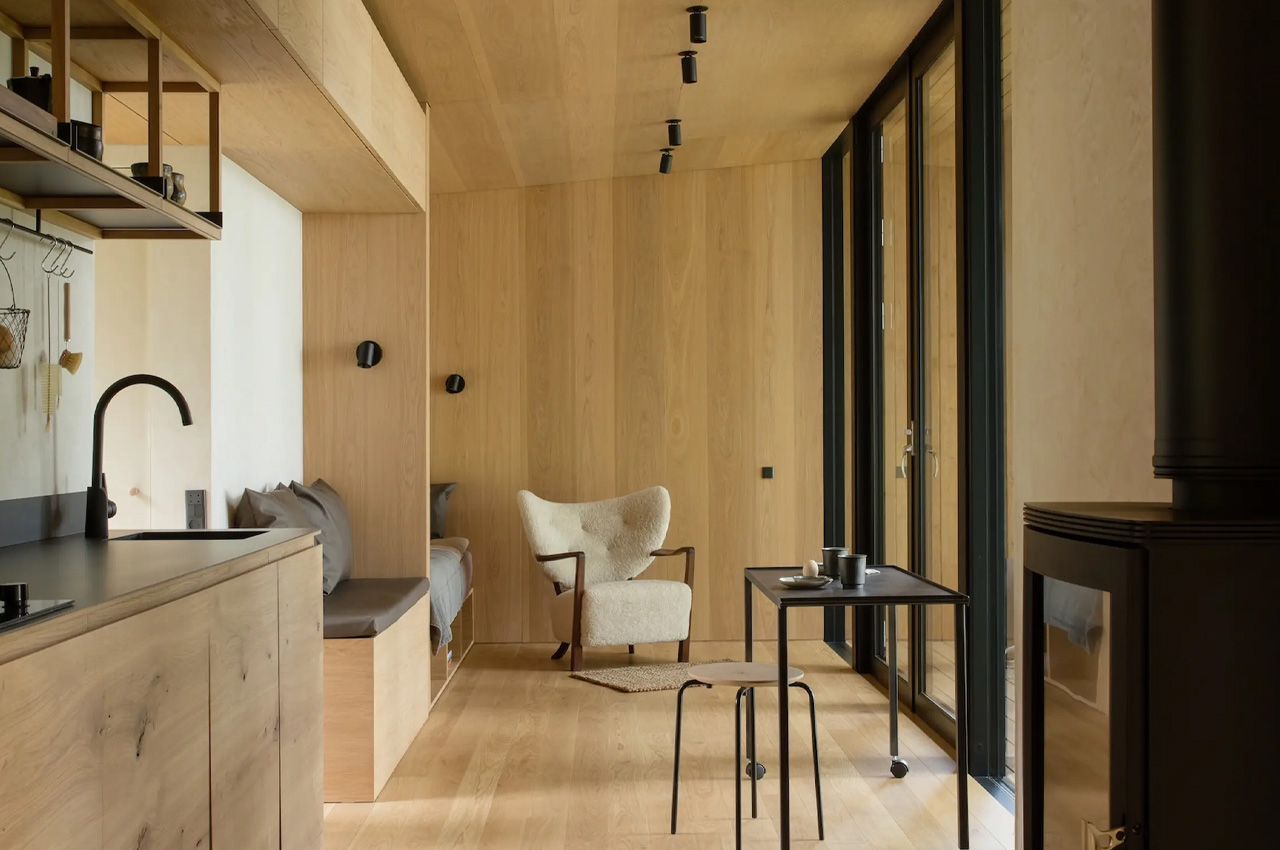
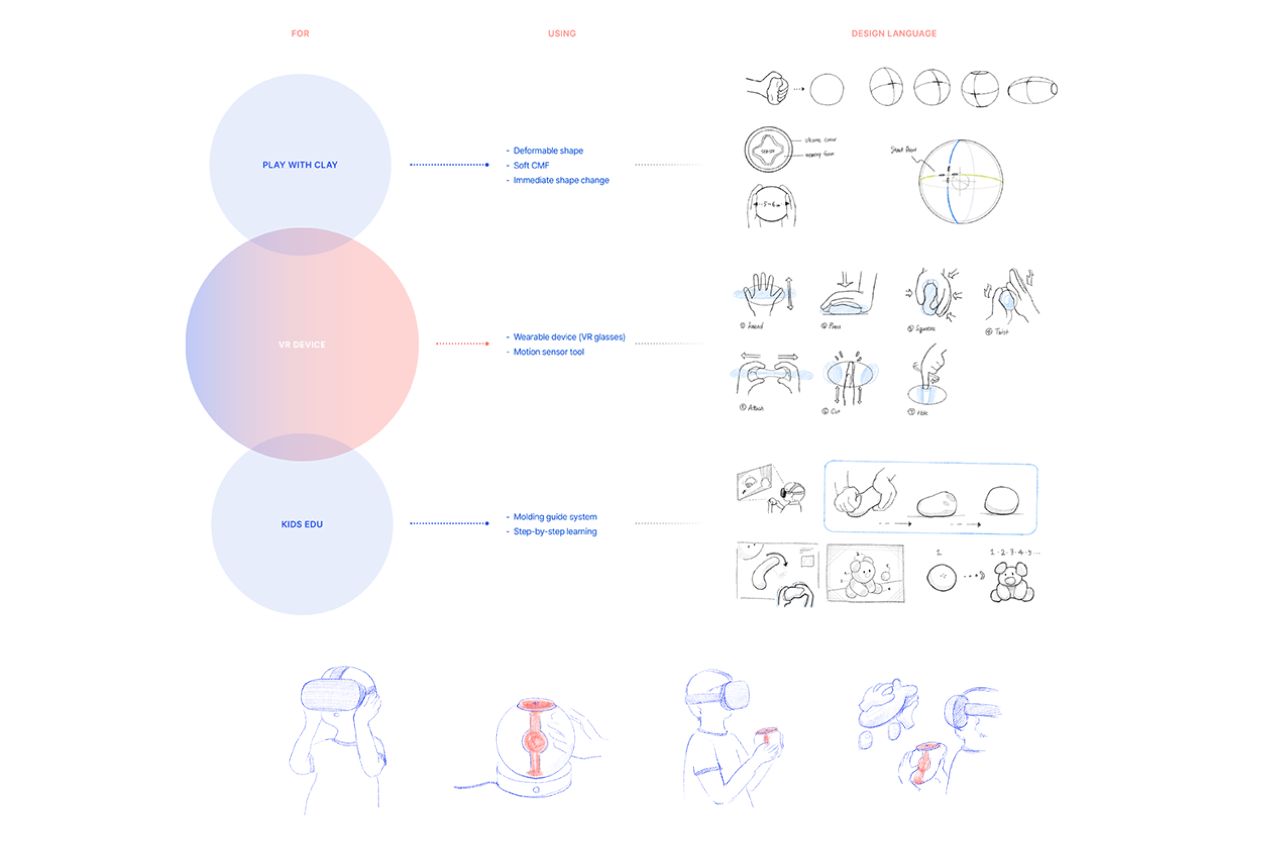
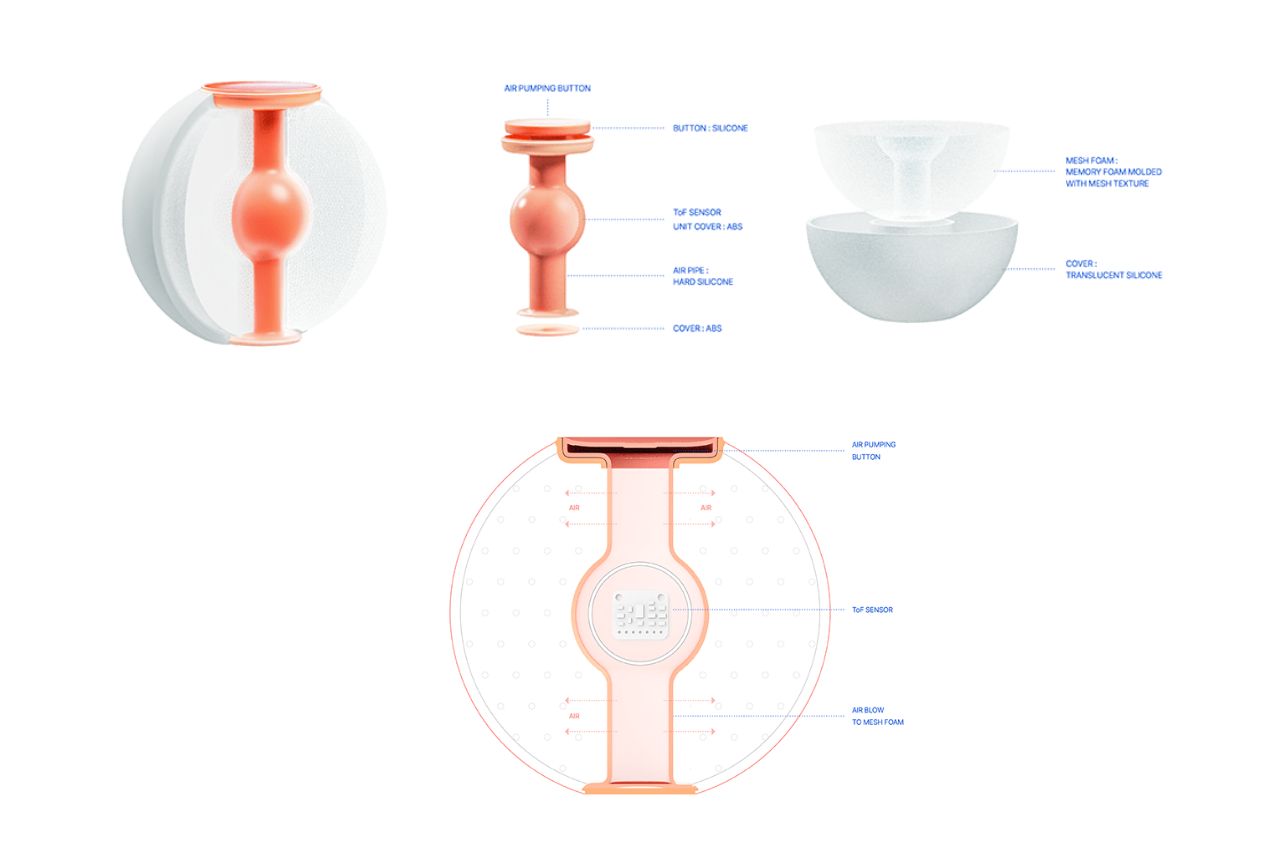
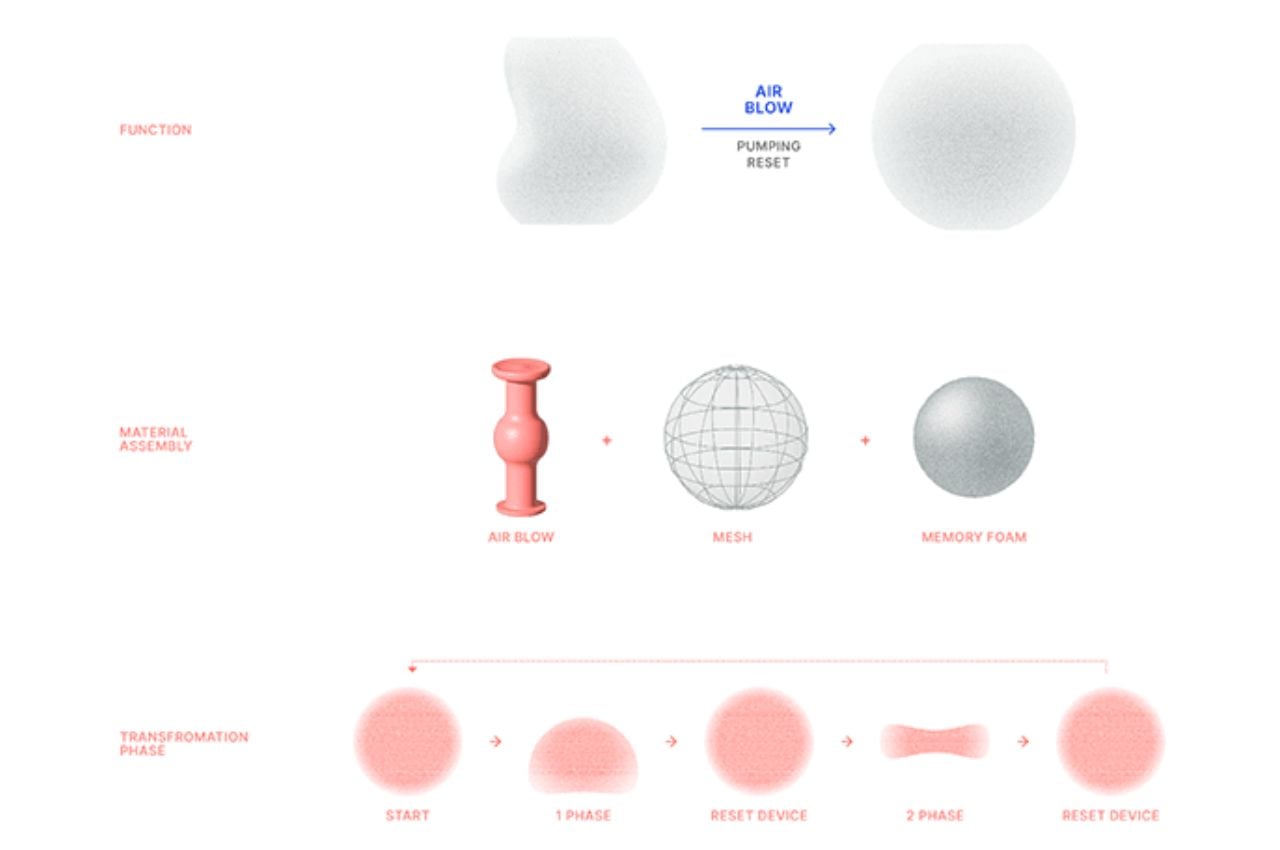
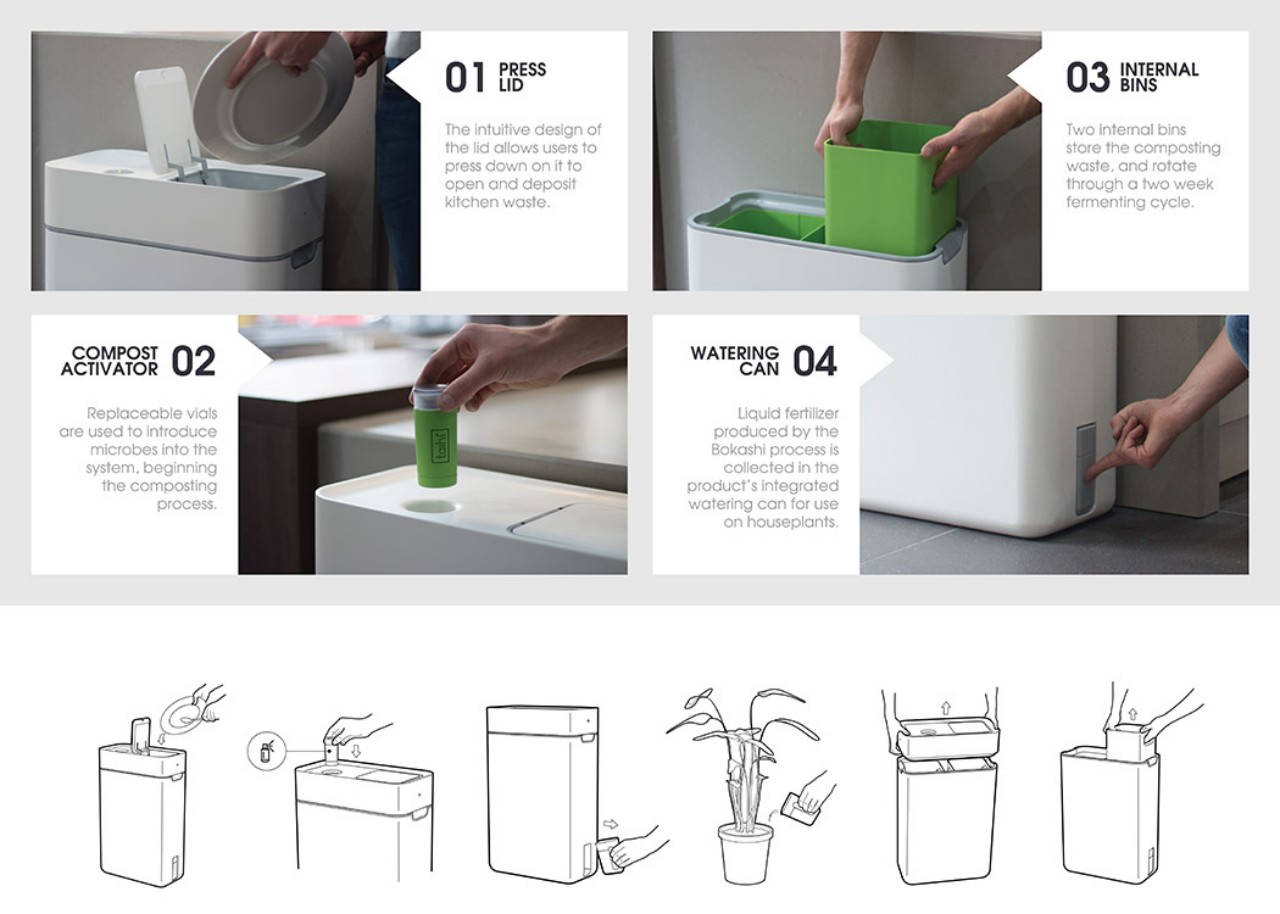
The primary purpose of kitchen flooring is to offer a flat, comfortable surface for walking and standing for extended periods, facilitating easy movement around the space. It’s crucial to choose durable materials that can withstand daily wear and tear, considering that kitchens often require frequent cleaning due to food spills. Here are the top flooring materials suitable for kitchens, emphasizing resistance to heat, moisture, staining, and impact damage to ensure longevity.
Designer: Konga

1. Ceramic Tile

Image courtesy of: dit26978
Pros:
Ceramic tile is crafted from clay and natural ingredients, shaped, glazed, and fired at high temperatures. Resistant to water and stains, it’s an ideal choice for kitchen flooring, also withstanding heat and breakage. While it can last indefinitely under optimal conditions, it may develop cracks and chipping if the top layer wears off. Ceramic tiles are resistant to water and heat.
Cons:
Ceramic tile, while exceptionally hard, may be uncomfortable to stand on for extended periods. Improper installation can lead to cracking and chipping, resulting in the top layer peeling off.
2. Porcelain tile

Designer: Horizon Italian Tile
Pros:
Porcelain tiles, made from baked natural clay at high temperatures and pressure, are exceptionally strong, durable, and long-lasting. Their non-porous surface makes them resistant to stains and scratches. Available in a variety of colors, textures, and patterns, including designs resembling natural stone and wood, they are easy to maintain.
Cons:
The biggest disadvantage of porcelain tiles is that they possess a dense and hard composition, resulting in considerable weight.
3. Concrete Flooring
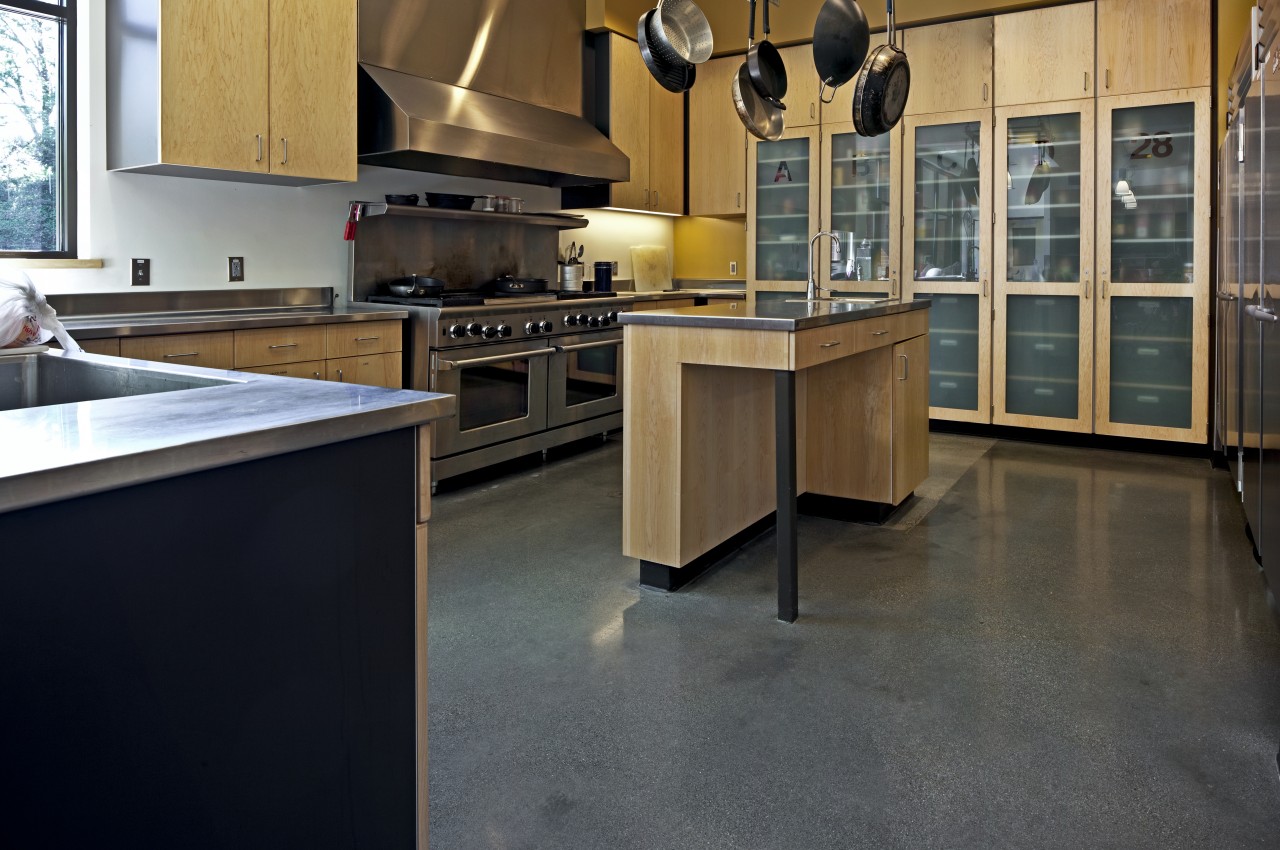

Image courtesy of: Mint_Images
Pros:
Concrete floors are a highly cost-effective flooring option for industrial-themed kitchens. One of the best aspects of concrete is that it is versatile and can be stained, polished, or can be treated creatively into stylish works of art. Concrete floors are particularly suitable for modern kitchens. Concrete floors are resistant to impact and heat.
Cons:
Due to its porous nature, concrete requires periodic sealing to safeguard against staining and water damage. Additionally, it can feel hard and cold underfoot. Moreover, while concrete offers an urban or industrial aesthetic, its appearance may not be unique.
4. Natural Stone
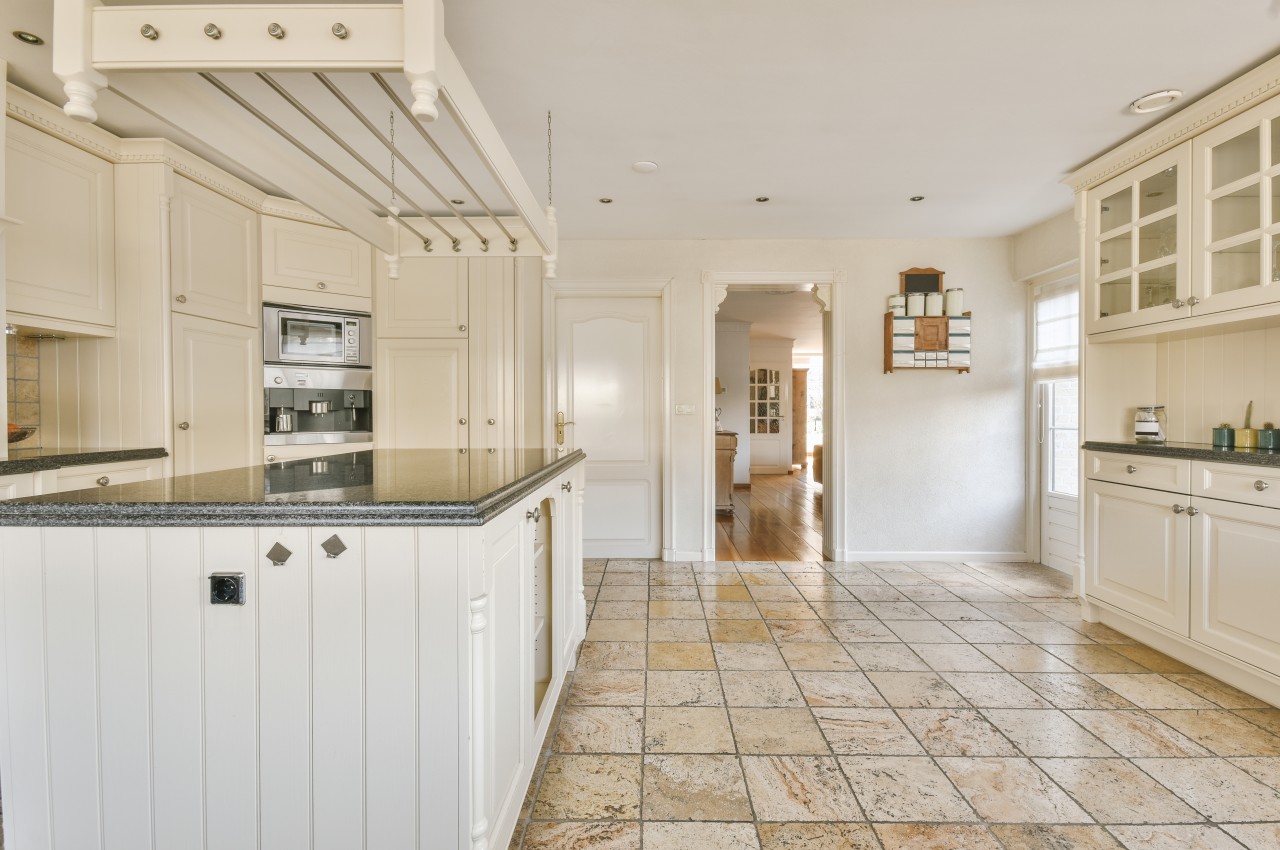

Image courtesy of: pro_creator
Pros:
Natural stone is a popular choice for durable kitchen flooring, offering various options with distinct properties. Granite is sturdy and versatile, suitable for both tiles and countertops. Limestone adds aesthetic appeal but is softer and better suited for accents. Marble is elegant but prone to scratching and staining. Sandstone offers a soft, multicolored look ideal for kitchens. Slate is durable and sophisticated, lasting for decades with proper maintenance while travertine provides Old World style, though it’s less durable than other options. Overall, natural stone enhances the kitchen’s appearance while ensuring long-lasting functionality. Also, its natural vein patterns provide a unique look, and no two tiles or slabs look alike.
Cons:
Stone installation is time-consuming, involving cutting and handling heavy materials. Its main drawback is its porous nature, making it susceptible to water and liquid stains, particularly in the kitchen. Applying a quality penetrating stone sealer annually can provide invisible protection, but reapplication is necessary at regular intervals.
5. Vitrified Tiles
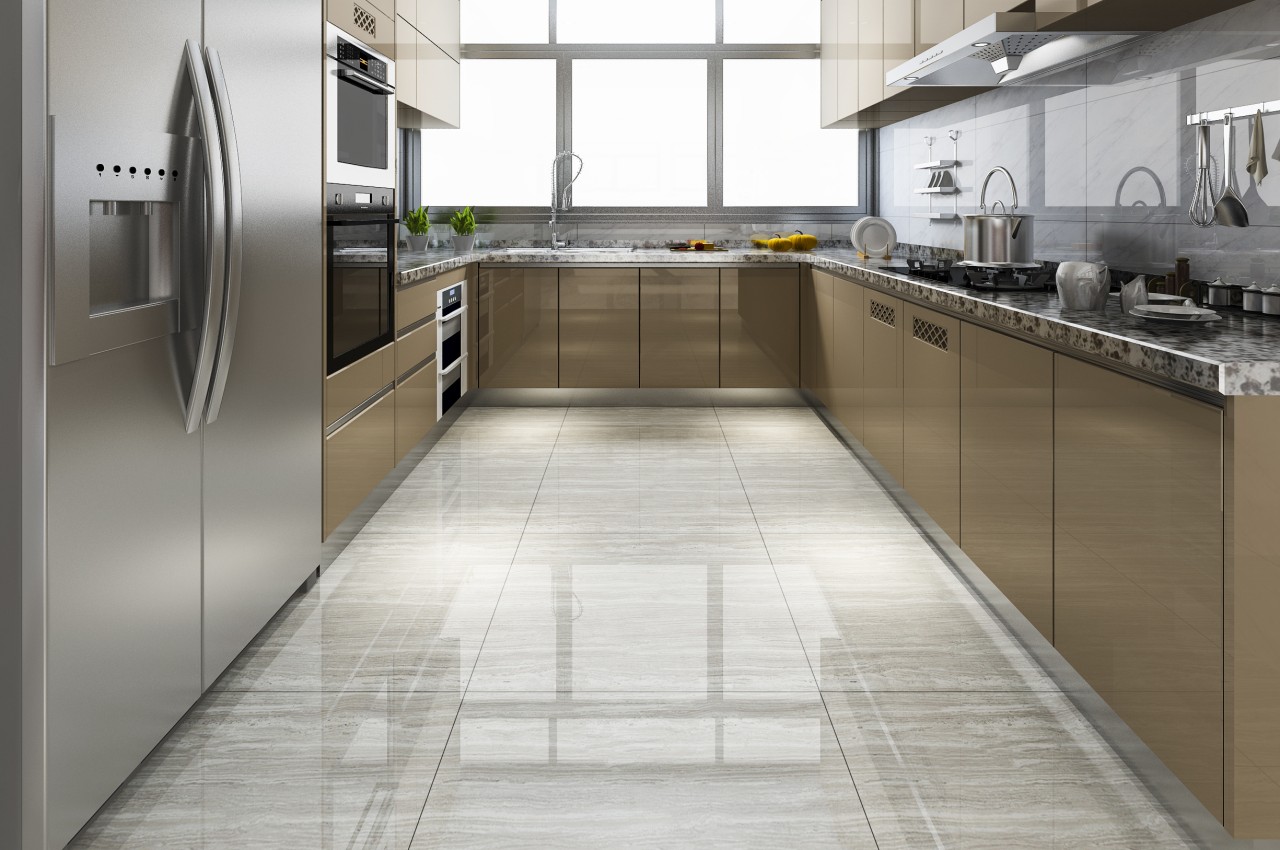

Image courtesy of: dit26978
Pros:
Vitrified tiles are highly favored as a flooring choice for kitchens due to their numerous advantages. These tiles are renowned for their exceptional hardness, density, and strength, making them resistant to stains, scratches, and acids, which are common in kitchen environments. Available in a diverse array of colors, designs, and sizes, including glazed, full-body, and double-charged varieties, vitrified tiles offer versatility to suit different aesthetic preferences. Moreover, their ability to withstand heavy foot traffic ensures long-lasting durability, making them an ideal option for busy kitchen spaces.
Cons:
The biggest disadvantage is that vitrified tiles can become slippery when wet.
6. Bamboo Flooring
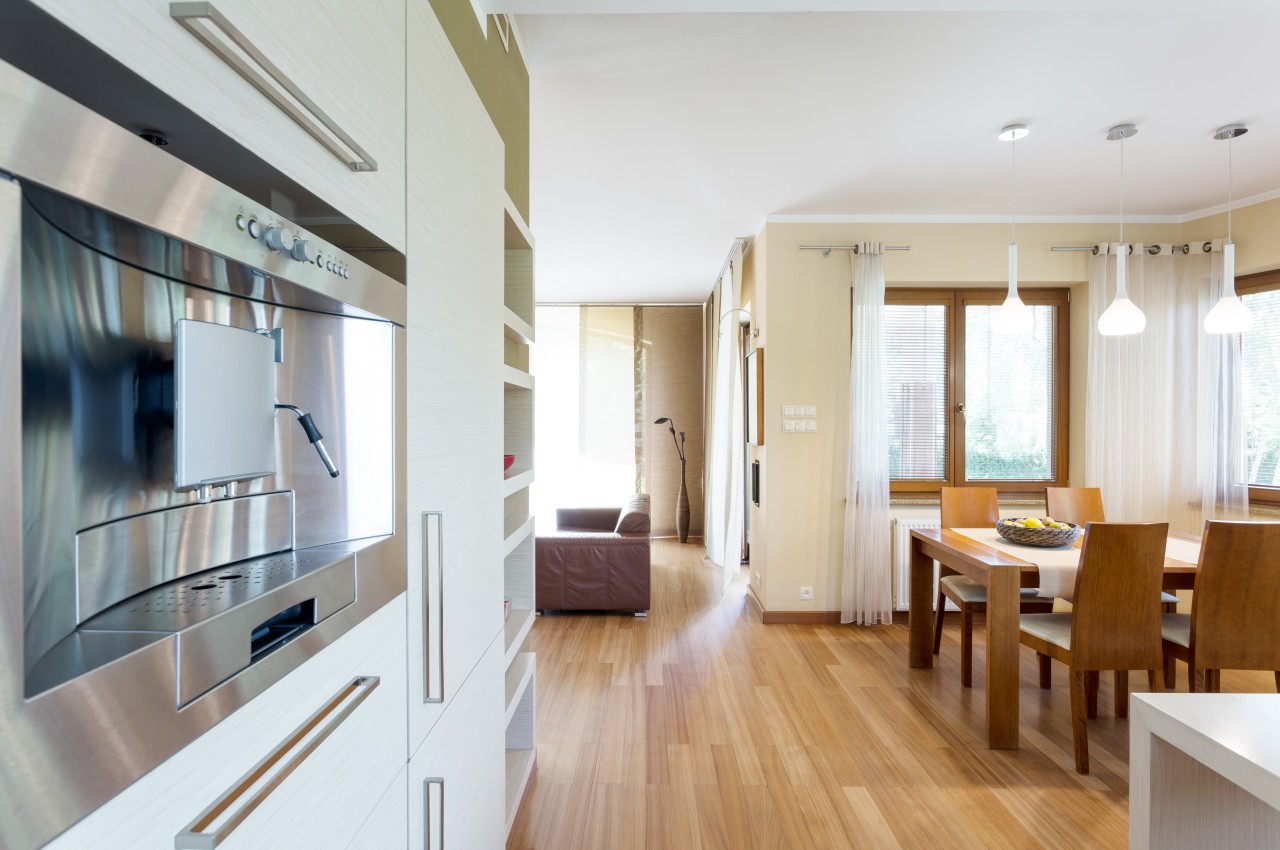

Image courtesy of: bialasiewicz
Pros:
A recent innovation is bamboo flooring which is becoming increasingly popular for kitchens due to its durability and enhanced moisture resistance from the manufacturing process. It offers the look of hardwood with greater durability. There are three types: strand woven, engineered, and solid bamboo, each offering varying levels of durability and cost.
Cons:
The drawback is that this flooring type can vary in appearance based on color, grain, and pattern. Solid bamboo may not be suitable for kitchens with moisture present.
7. Cork Flooring
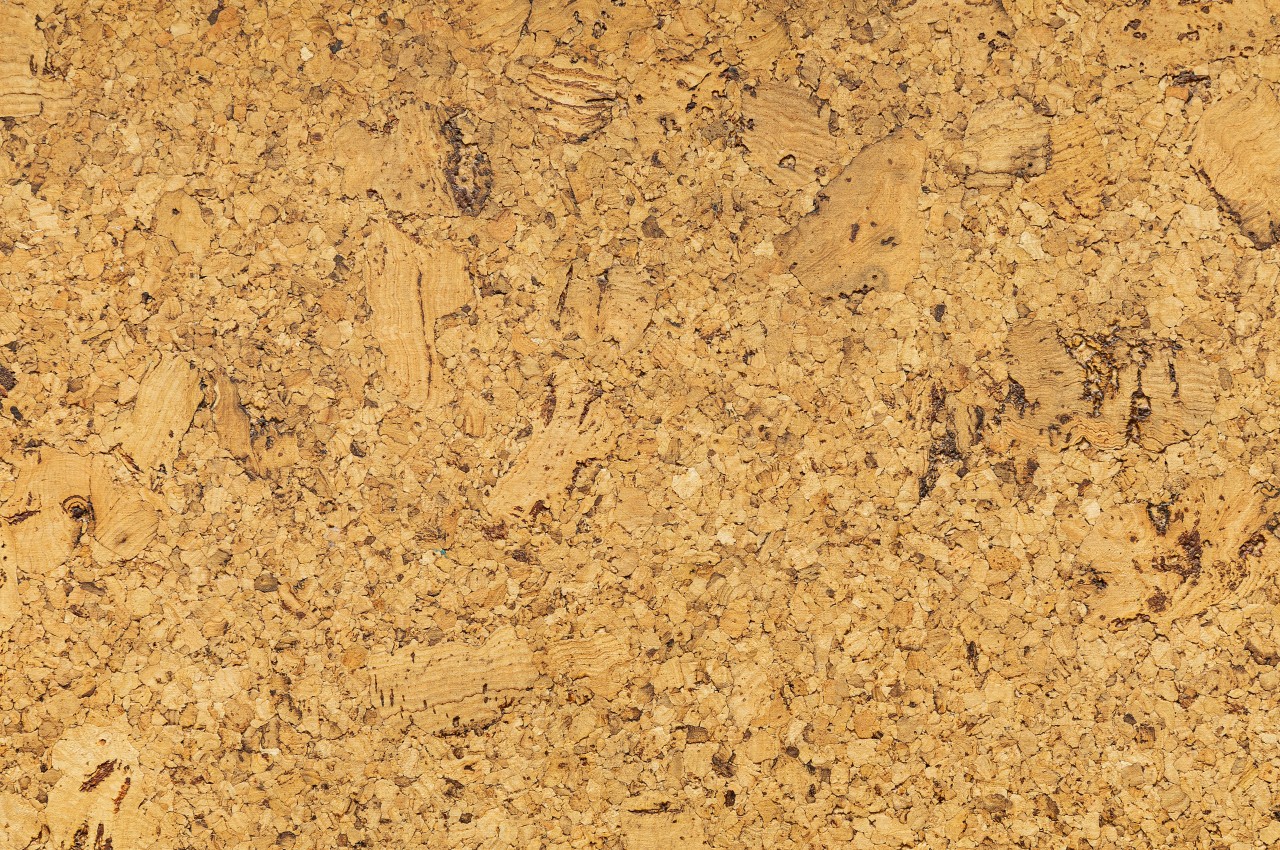

Image courtesy of: traimakivan
Pros:
Cork flooring seeks to improve the comfort of the user with a soft construction that reduces fatigue and strain from walking and standing during food preparation. This material has a unique appearance that can add to the home’s aesthetic, and it is made from sustainable materials, harvested from the bark of cork oak trees.
Cons:
Cork offers a warm and soft underfoot experience, but it’s less durable than most flooring options and susceptible to scratches and moisture. To prevent staining and water damage, sealing the flooring every one to two years is recommended.
8. Laminate Flooring
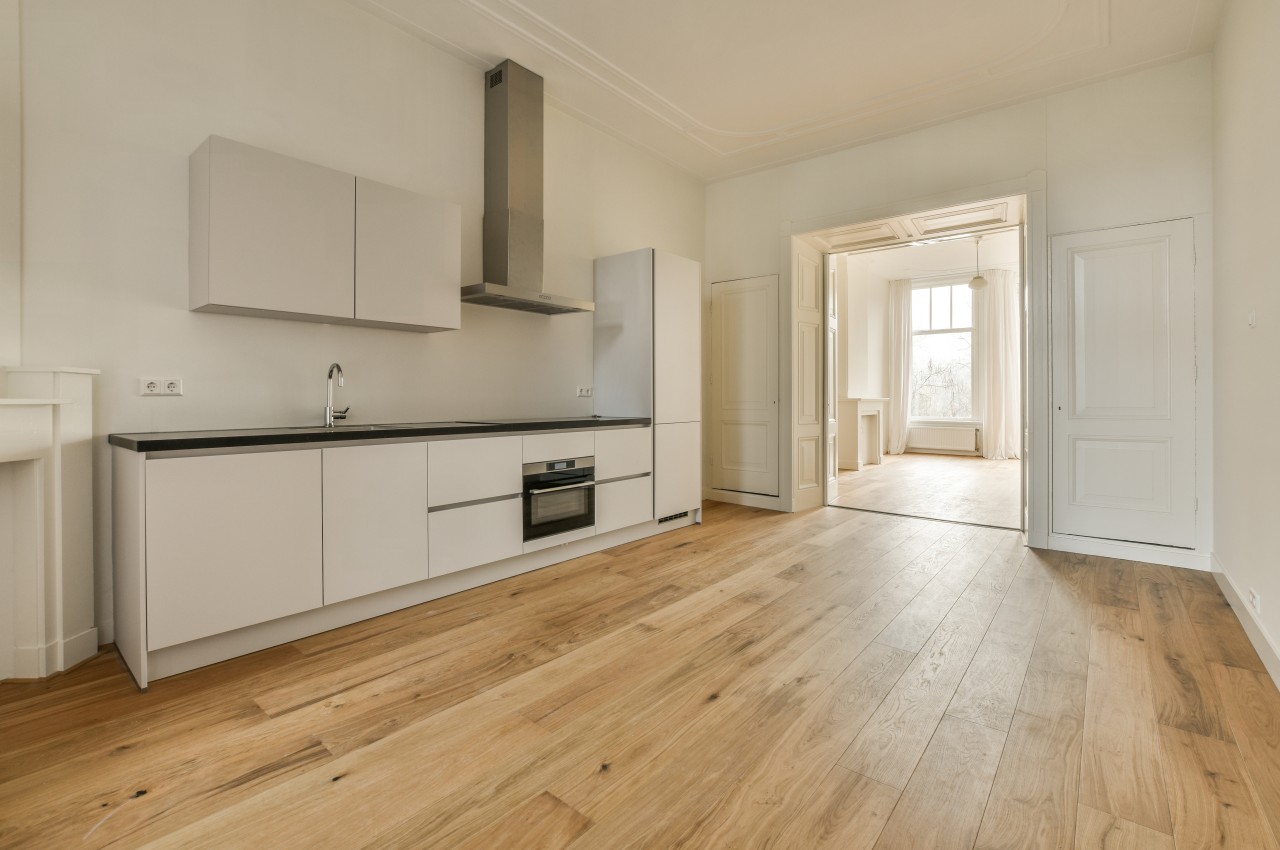

Image courtesy of: pro_creator
Pros:
Laminate wood flooring presents an affordable option for flooring, offering a cost-effective means to elevate the aesthetic of a kitchen compared to hardwood. Its superior scratch resistance against regular foot traffic makes it an attractive choice. Additionally, laminate serves as a practical alternative to hardwood floors and is available in a variety of styles and finishes.
Cons:
Laminate flooring isn’t as well-suited for handling moisture, which can make maintenance more challenging when used in kitchens. If you choose to install laminate in this space, it’s essential to employ a proper moisture barrier. Additionally, laminate doesn’t offer the same longevity as hardwood, tile, and vinyl flooring options.
9. Vinyl Flooring
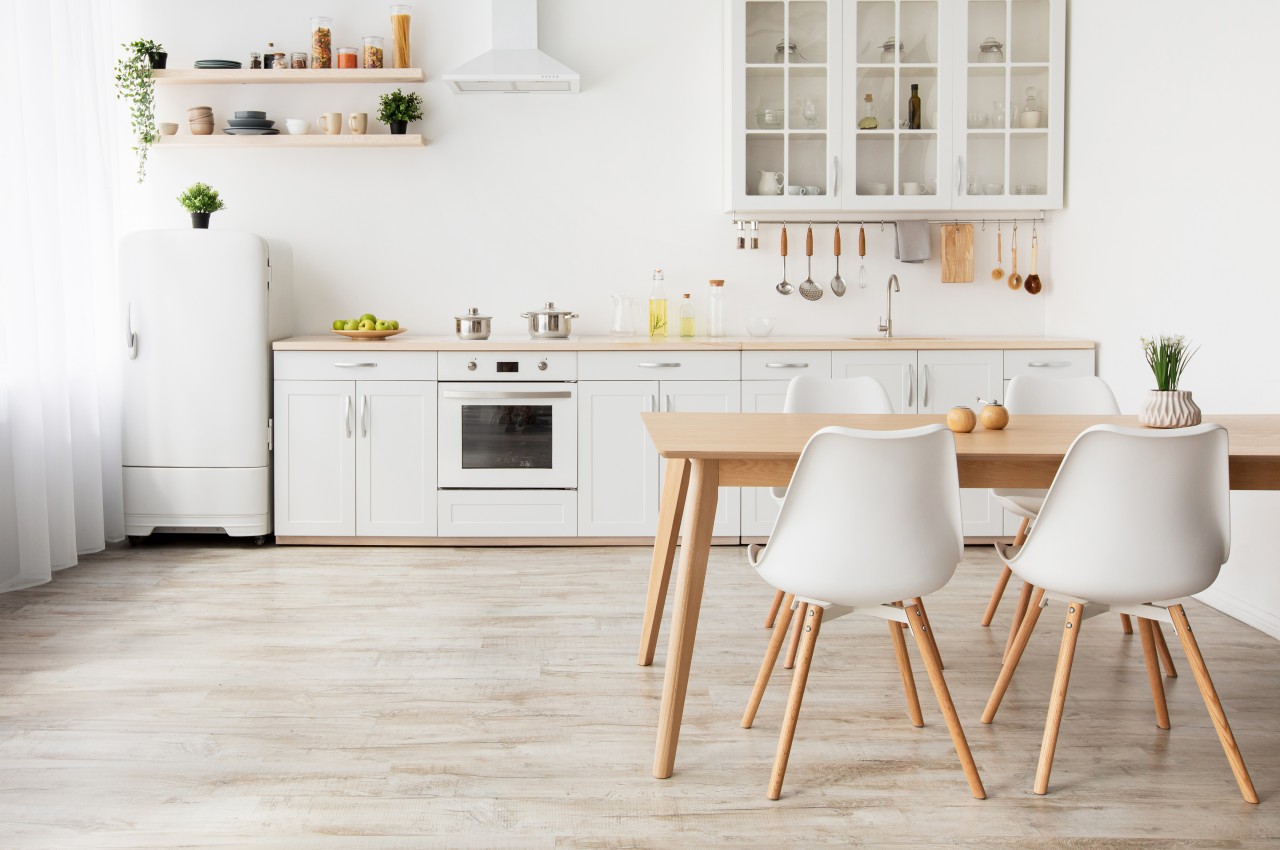

Image courtesy of: studio
Pros:
Vinyl flooring offers numerous benefits specifically tailored for kitchen environments. Its durability, with a lifespan ranging from 10 to 20 years, can be further extended through proper maintenance and careful use. With its water-resistant and anti-slip features, vinyl flooring is an ideal option for moisture-prone spaces like kitchens, offering easy maintenance and effective stain resistance. The softness underfoot, thanks to its foam or felt backing layer, ensures comfort during prolonged periods of standing while reducing fatigue. Moreover, vinyl flooring comes in a wide range of colors and designs, providing options that mimic the appearance of natural materials like stone and wood.
Cons:
Vinyl flooring emits high levels of VOCs (volatile organic compounds) and may have a noticeable odor upon installation. Additionally, it is not resistant to strong chemicals, which can cause permanent discoloration and damage. Outdoor use is not recommended as prolonged sunlight exposure can lead to fading. Furthermore, an uneven subfloor can result in lumps and damage over time, while sharp objects can cause cuts and dents that are challenging to repair.
10. Hardwood Flooring
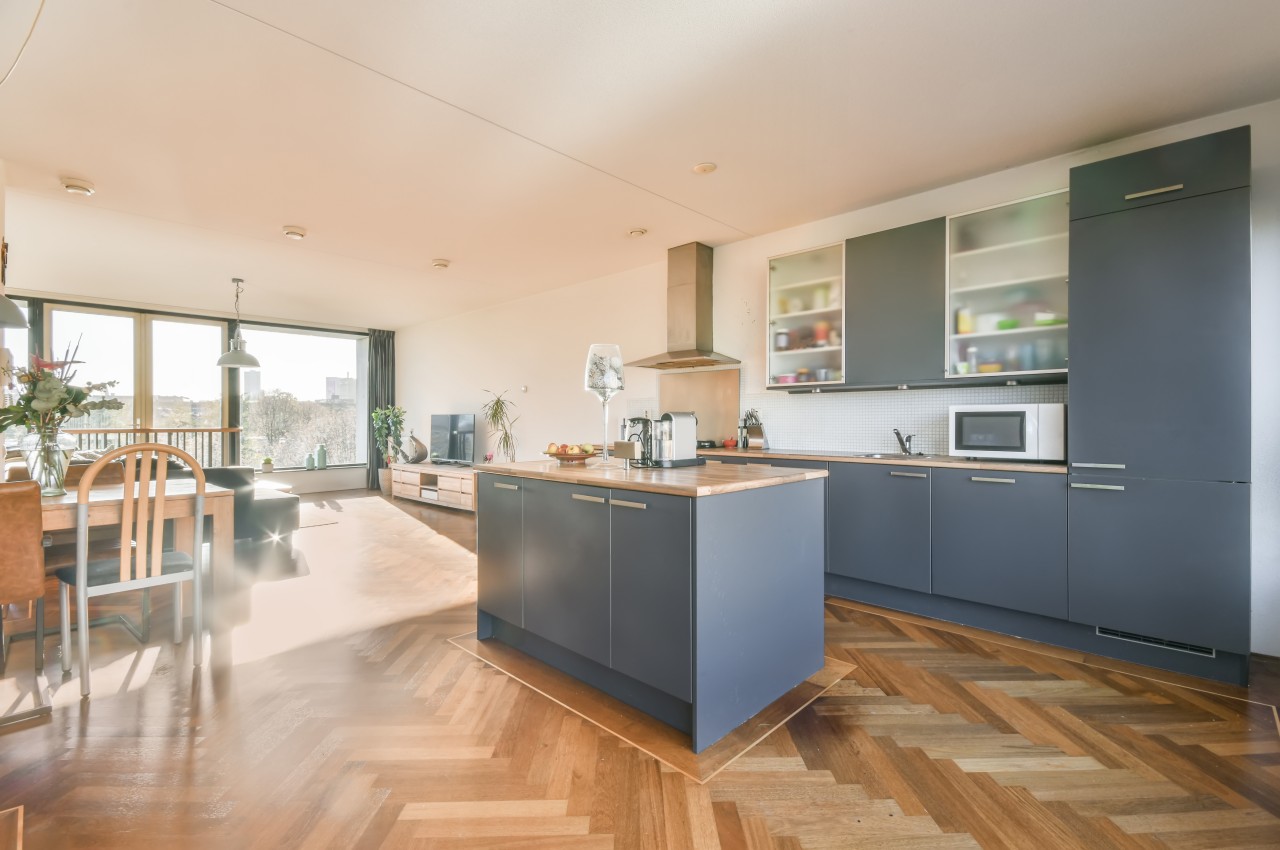

Image courtesy of: studio
Pros:
Hardwood flooring is known for its durability as it offers good longevity with proper care and maintenance. With a diverse array of styles available, it can suit any decor. It is easy to maintain as it requires only regular sweeping and vacuuming, although it’s essential to avoid wet-mopping and promptly clean up spills to prevent damage.
Cons:
While engineered hardwood is typically more affordable, solid hardwood remains costly. Both types are susceptible to moisture damage, with solid hardwood being especially vulnerable. Moreover, hardwood floors are susceptible to scratches, dents, and photosensitivity, prompting the need for more durable species or alternative materials like laminate or vinyl, especially in sunlit rooms.
The post 10 Most Popular Kitchen Flooring Materials: Their Pros and Cons first appeared on Yanko Design.