Primed goes in-depth on the technobabble you hear on Engadget every day -- we dig deep into each topic's history and how it benefits our lives. You can follow the series here. Looking to suggest a piece of technology for us to break down? Drop us a line at primed *at* engadget *dawt* com.

Long before the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) could smash its first atoms, researchers manning the Tevatron collider at Fermilab, in a quiet suburb 40 miles west of Chicago, raced to find evidence that the Higgs boson exists. After roughly three decades of service, the Tevatron shut down for good in late 2011, dealing the city of Batavia's largest employer a significant blow. Less than 18 months later, the LHC (the Tevatron's technological successor) also went offline - albeit temporarily. Only four years after recording its first proton collisions, the team at CERN is already scrambling to upgrade the staggering LHC, which lies under parts of no less than five cities in both France and Switzerland. With the world's largest particle colliders smashing a whole lot of nothing together for the next two years at least, the field of high-energy physics research is starting to look resource-starved. Of course, many might ask why exactly we need giant atom smashers like this, or even how they work. It turns out that first part is quite a bit easier to answer than the second.
During the last several decades, particle accelerators have revealed the existence of elementary particles such as quarks, led to the discovery of antimatter and generally helped us unlock the mysteries of the universe. And once they were done splitting atoms and probing the darkest corners of theoretical physics, accelerators often led to breakthroughs in medical imaging and cancer research. So, as massive colliders seem ready to land on the endangered species list, it seems as good a time as any to explain what a particle collider is, how it works and what we as a society have to gain from the research.
Filed under: Science
Comments
 In scientific pursuits, like the search for dark matter, researchers sometimes use high-power particle accelerators. But these giant machines are extremely expensive and only a handful of them exist, so teams must travel to places like the SLAC Natio...
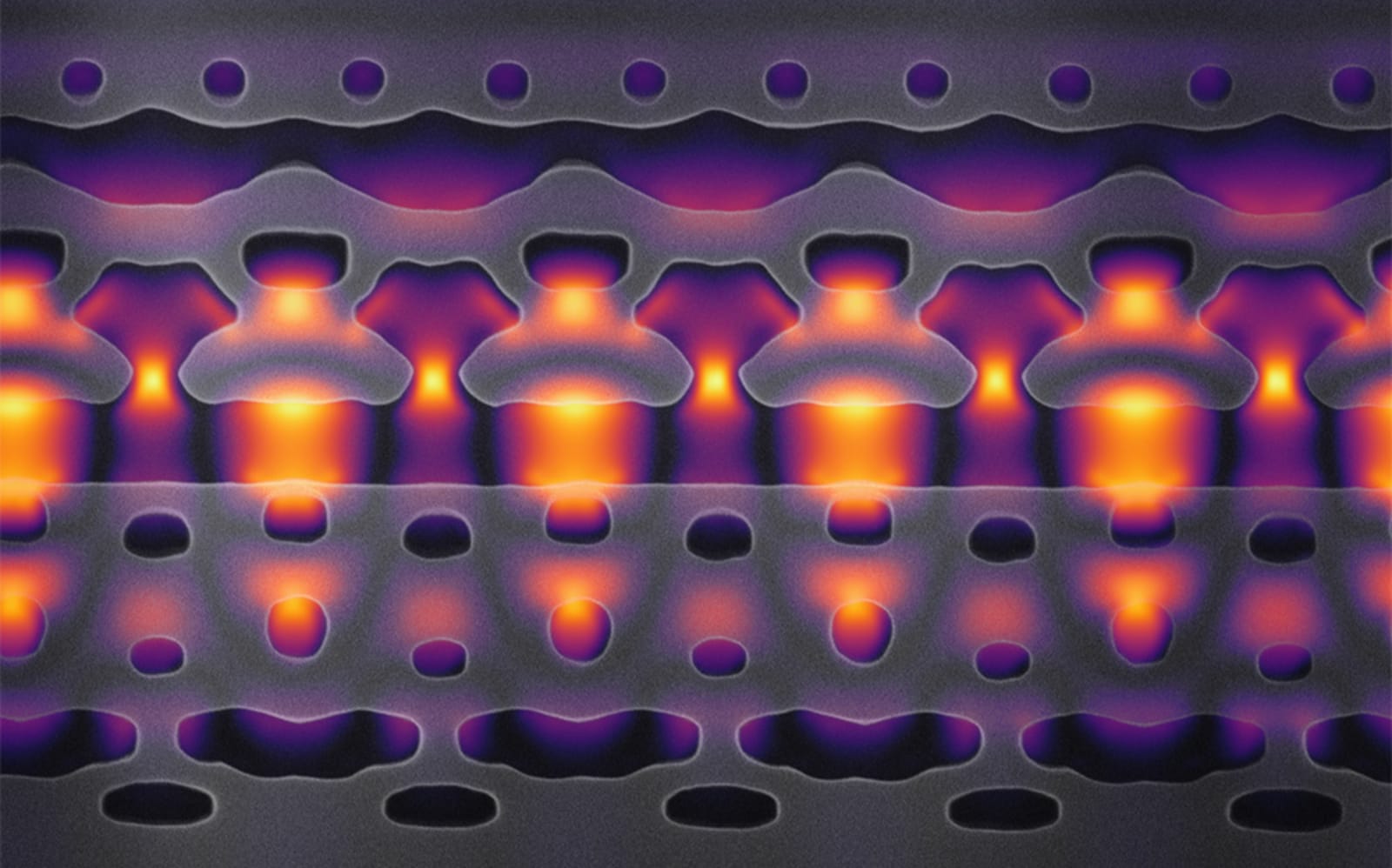
In scientific pursuits, like the search for dark matter, researchers sometimes use high-power particle accelerators. But these giant machines are extremely expensive and only a handful of them exist, so teams must travel to places like the SLAC Natio...
 In scientific pursuits, like the search for dark matter, researchers sometimes use high-power particle accelerators. But these giant machines are extremely expensive and only a handful of them exist, so teams must travel to places like the SLAC Natio...
In scientific pursuits, like the search for dark matter, researchers sometimes use high-power particle accelerators. But these giant machines are extremely expensive and only a handful of them exist, so teams must travel to places like the SLAC Natio...









