
If you've been paying attention, you know the quantum computing revolution is coming -- and so far the world has a mini quantum network, not to mention the $10,000 D-Wave One, to show for it. Researchers from the University of Melbourne and University College, London, have now developed the "first working quantum bit based on a single atom of silicon." By measuring and manipulating the magnetic orientation, or spin, of an electron bound to a phosphorus atom embedded in a silicon chip, the scientists were able to both read and write information, forming a qubit, the basic unit of data for quantum computing.
The team used a silicon transistor, which detects the electron's spin and captures its energy when the spin's direction is "up." Once the electron is in the transistor, scientists can change its spin state any way they choose, effectively "writing" information and giving them control of the quantum bit. The next step will be combing two qubits into a logic step, with the ultimate goal being a full-fledged quantum computer capable of crunching numbers, cracking encryption codes and modeling molecules that would put even supercomputers to shame. But, you know, baby steps.
Filed under: Science, Alt
Researchers create working quantum bit in silicon, pave way for PCs of the future originally appeared on Engadget on Fri, 21 Sep 2012 00:47:00 EDT. Please see our terms for use of feeds.
Permalink  The Register
The Register |
 UNSW Australia
UNSW Australia |
Email this |
Comments
 In addition to penning 37 plays, William Shakespeare was a prolific composer of sonnets -- crafting 154 of them during his life. Now, more than 400 years after his death, the Bard's words are influencing a new generation of poets. It's just that thes...
In addition to penning 37 plays, William Shakespeare was a prolific composer of sonnets -- crafting 154 of them during his life. Now, more than 400 years after his death, the Bard's words are influencing a new generation of poets. It's just that thes...
 In addition to penning 37 plays, William Shakespeare was a prolific composer of sonnets -- crafting 154 of them during his life. Now, more than 400 years after his death, the Bard's words are influencing a new generation of poets. It's just that thes...
In addition to penning 37 plays, William Shakespeare was a prolific composer of sonnets -- crafting 154 of them during his life. Now, more than 400 years after his death, the Bard's words are influencing a new generation of poets. It's just that thes...
 Scientists are clearly picking up the pace in their quest to kill antibiotic-resistant "superbugs." Teams at the Universty of Melbourne and UT Southwestern Medical Center have developed composite molecules that overcome the defenses of stubborn bact...
Scientists are clearly picking up the pace in their quest to kill antibiotic-resistant "superbugs." Teams at the Universty of Melbourne and UT Southwestern Medical Center have developed composite molecules that overcome the defenses of stubborn bact...
 Today on In Case You Missed It: University of Melbourne researchers studying non-sized crystals (that might one day be used to store greenhouse gases) needed to know what the nanoparticles would do in low-gravity, so they jumped off a plane while...
Today on In Case You Missed It: University of Melbourne researchers studying non-sized crystals (that might one day be used to store greenhouse gases) needed to know what the nanoparticles would do in low-gravity, so they jumped off a plane while...
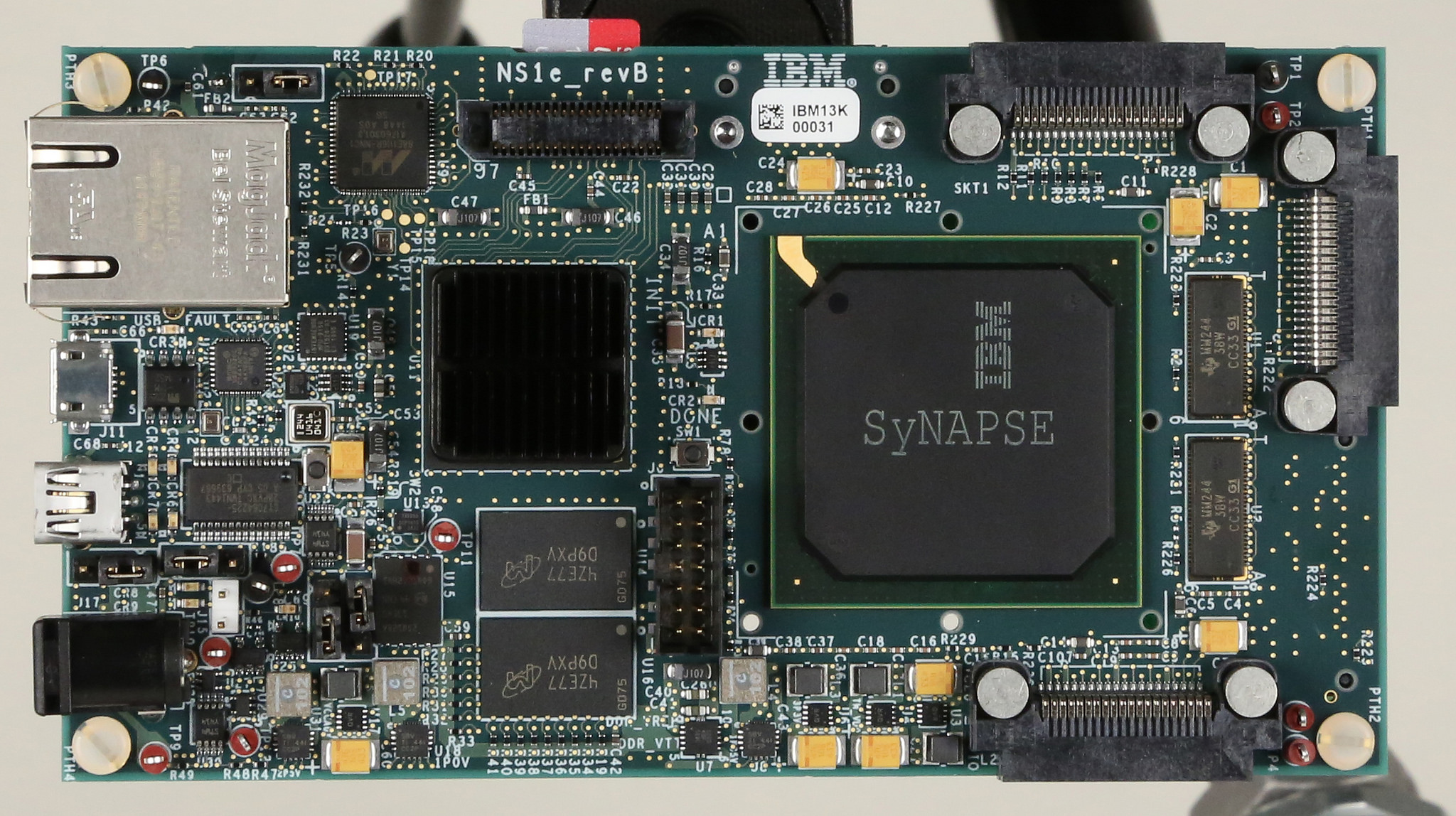 Researchers from the University of Melbourne have teamed with IBM to develop an implantable computer chip capable of constantly monitoring the patient's brain activity and, hopefully, predict when they'll suffer an epileptic seizure. The chip is base...
Researchers from the University of Melbourne have teamed with IBM to develop an implantable computer chip capable of constantly monitoring the patient's brain activity and, hopefully, predict when they'll suffer an epileptic seizure. The chip is base...
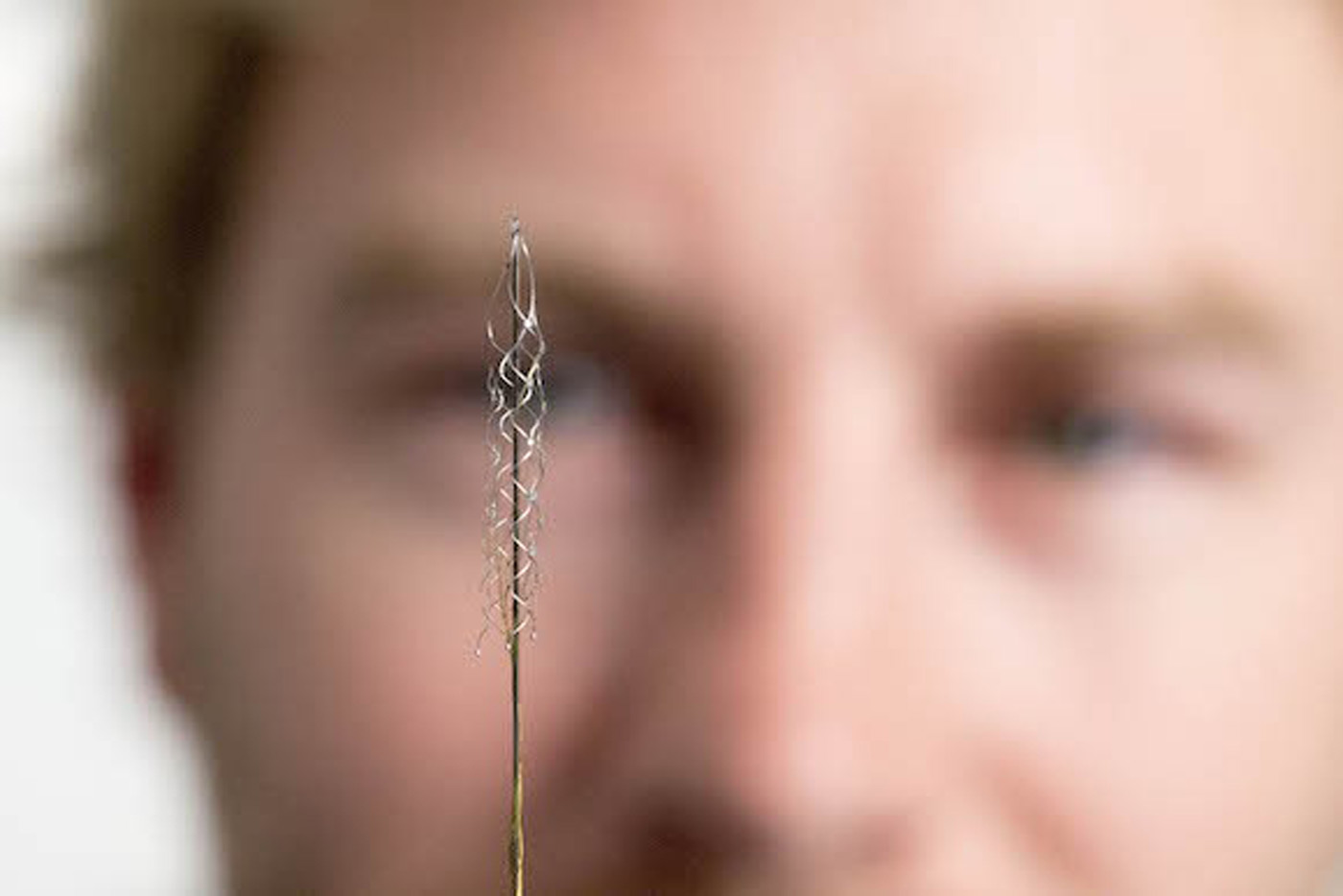 Right now, mind-controlling a machine isn't pretty: you typically wear a silly cap or headset, or else subject yourself to open brain surgery to get a deeper link. Australian scientists might have a better way, though. They've developed a brain-mac...
Right now, mind-controlling a machine isn't pretty: you typically wear a silly cap or headset, or else subject yourself to open brain surgery to get a deeper link. Australian scientists might have a better way, though. They've developed a brain-mac...


