
Industrial designer Mary Lempres has unveiled a groundbreaking bio-cement structure named Reef Rocket, inspired by the intricate and resilient nature of oyster reefs. Designed to combat coastal flooding, filter seawater, and foster biodiversity, Reef Rocket utilizes biomimicry principles to mimic the functionalities of naturally occurring oyster reefs.
Designers: Mary Lempres, Ahmed Miftah
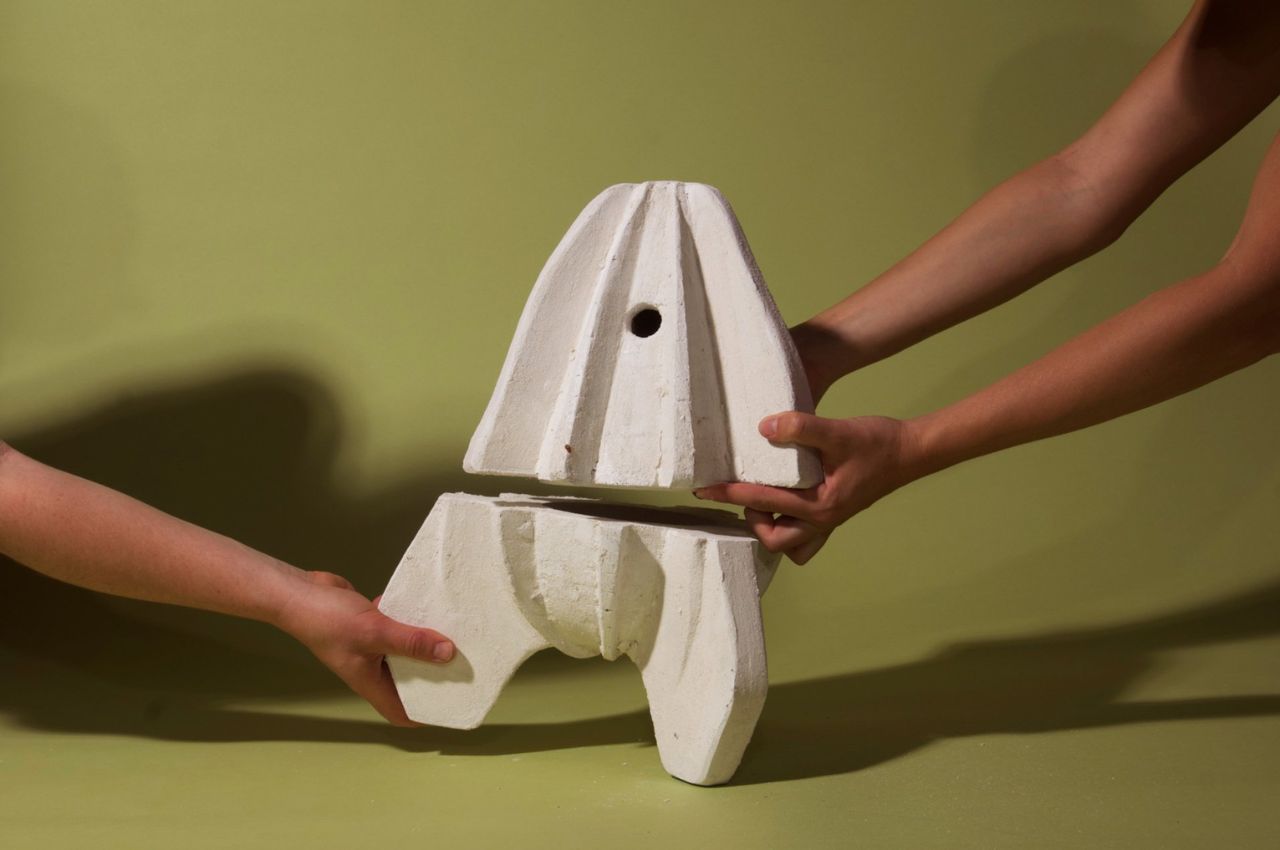

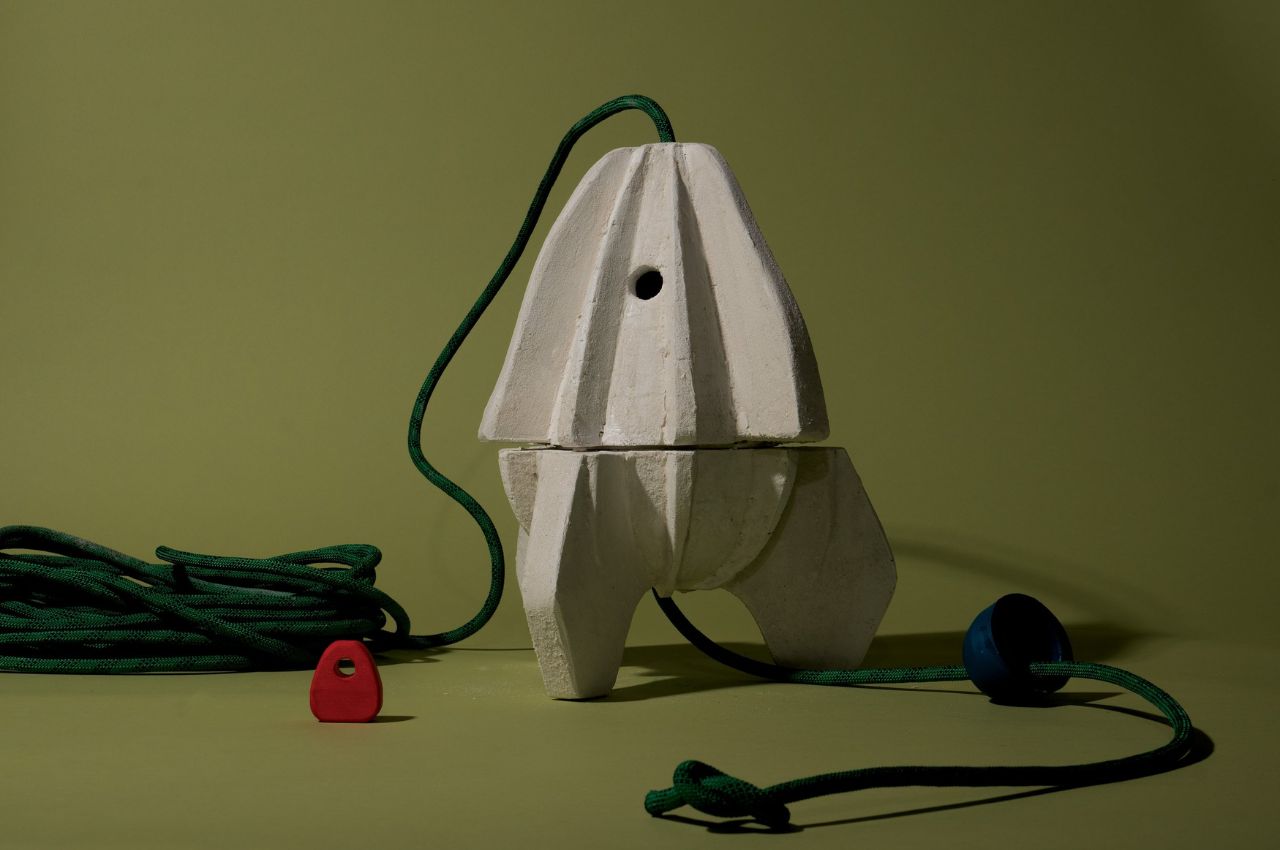
The structure comprises two bio-cement modules with ridged surfaces that can be stacked to form a distinctive rocket-like shape when assembled underwater. Lempres collaborated with bio-geotechnical specialist Ahmed Miftah to develop a unique method for growing plant-derived cement, drawing parallels to the irrigation systems used for plant cultivation.
Biomimicry, the practice of seeking solutions to human design challenges in nature, guided Lempres in creating ridged modules that emulate coastal oyster reefs. These reefs naturally filter algae from seawater, attract aquatic organisms, dissipate wave energy, mitigate storm surges, and manage eroding coastlines.
The bio-cement modules are formed by pouring a non-toxic solution containing a crude extract from globally grown plants over crushed aggregate. The aggregate, sourced in New York City, consists of crushed glass and oyster shells recovered from local restaurants and New York Harbour.
Lempres explained that the substrate, saturated for three to nine days, becomes natural concrete as the extracted biocatalyst causes minerals to form “mineral bridges” between the glass and shell waste. The resulting product is water-resistant, durable, and comparable to standard concrete but with the added benefit of being environmentally friendly and sustainable.
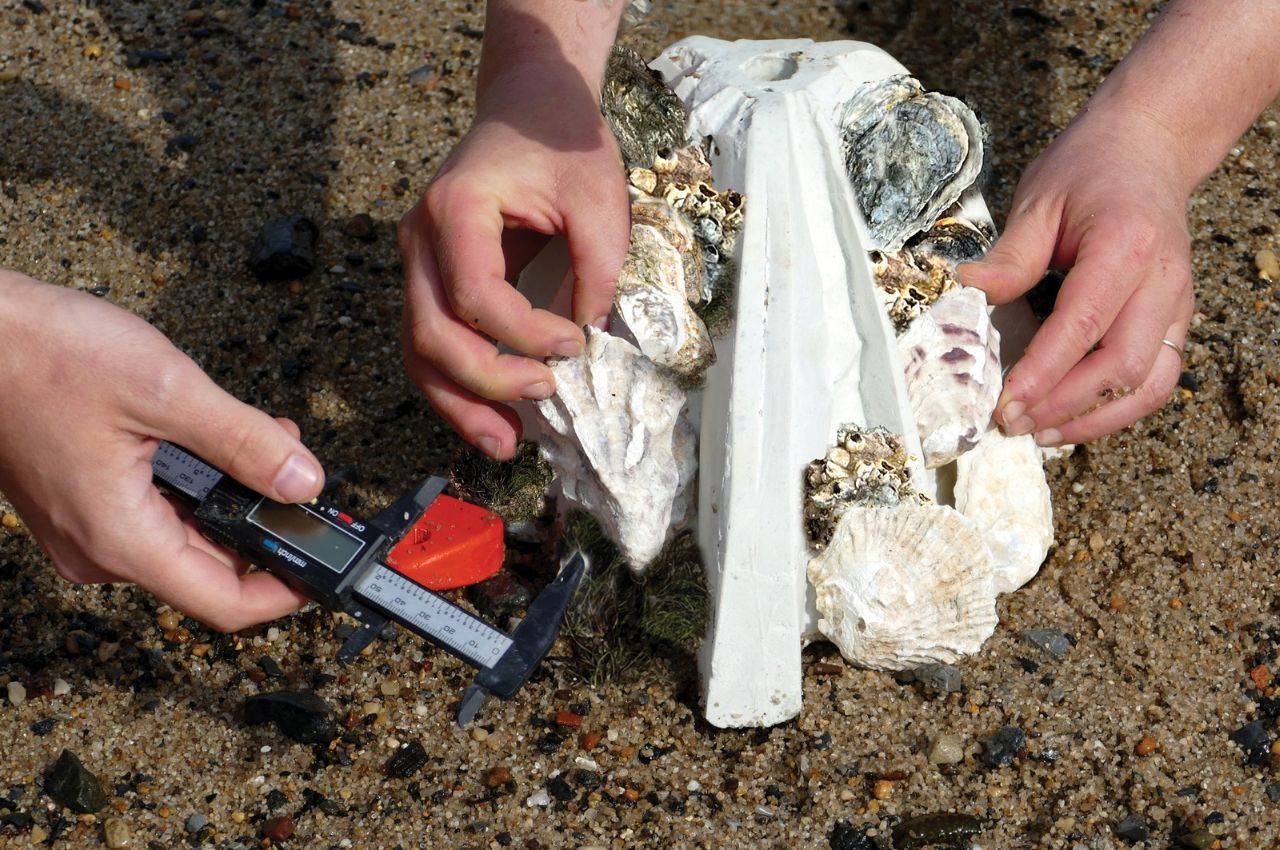

What sets Reef Rocket apart is its ability to grow in any environment without the need for heat or burning fossil fuels. Lempres emphasized its affordability and scalability as a sustainable alternative to traditional cement. The bio-concrete shares chemical similarities with the material oysters use to grow their reefs, but the key difference lies in the speed of growth, with Reef Rocket taking only several days compared to millennia for natural oyster reefs.
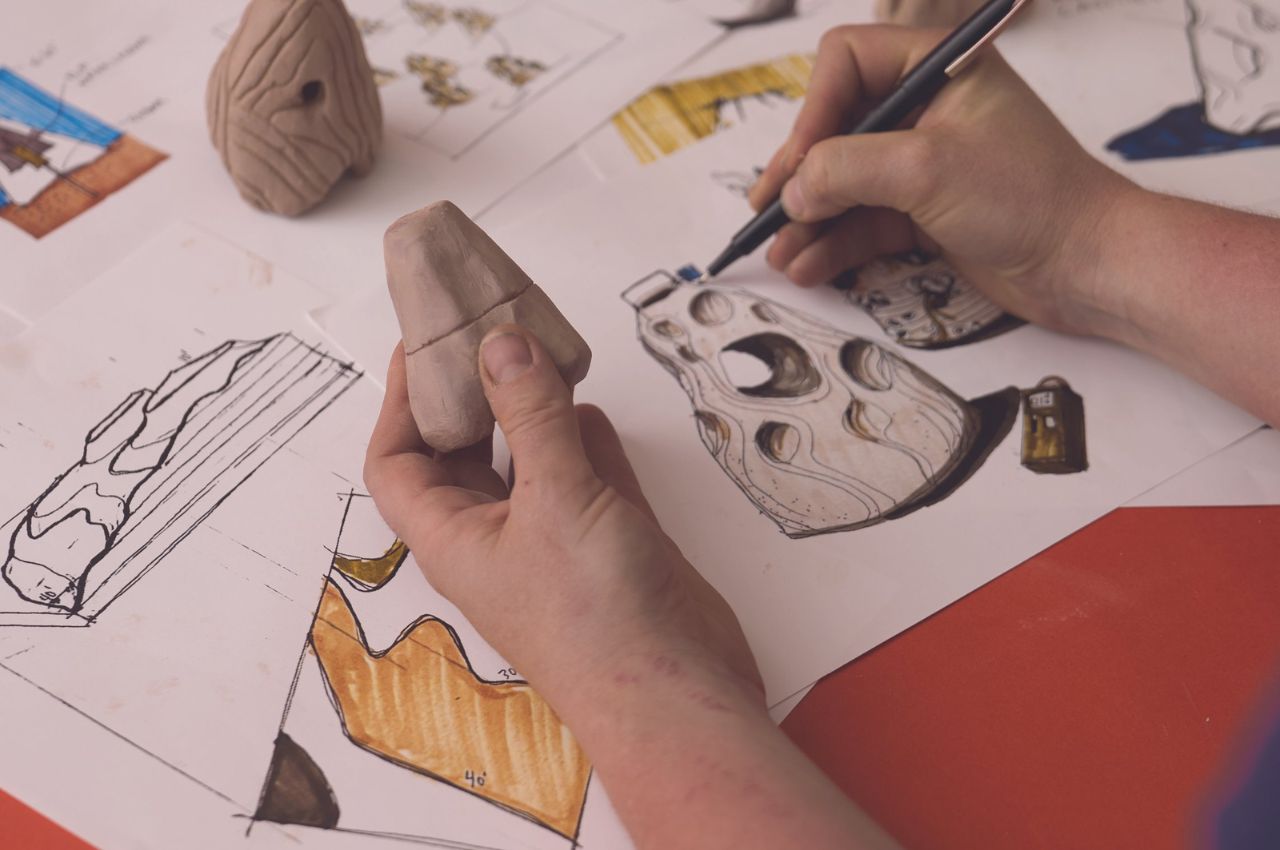

Lempres and her team experimented with “hundreds” of prototypes before settling on prefabricated molds for the modules. These molds allow the bio-cement to be packed and set without the need for heat or chemicals, offering an accessible and efficient assembly process.
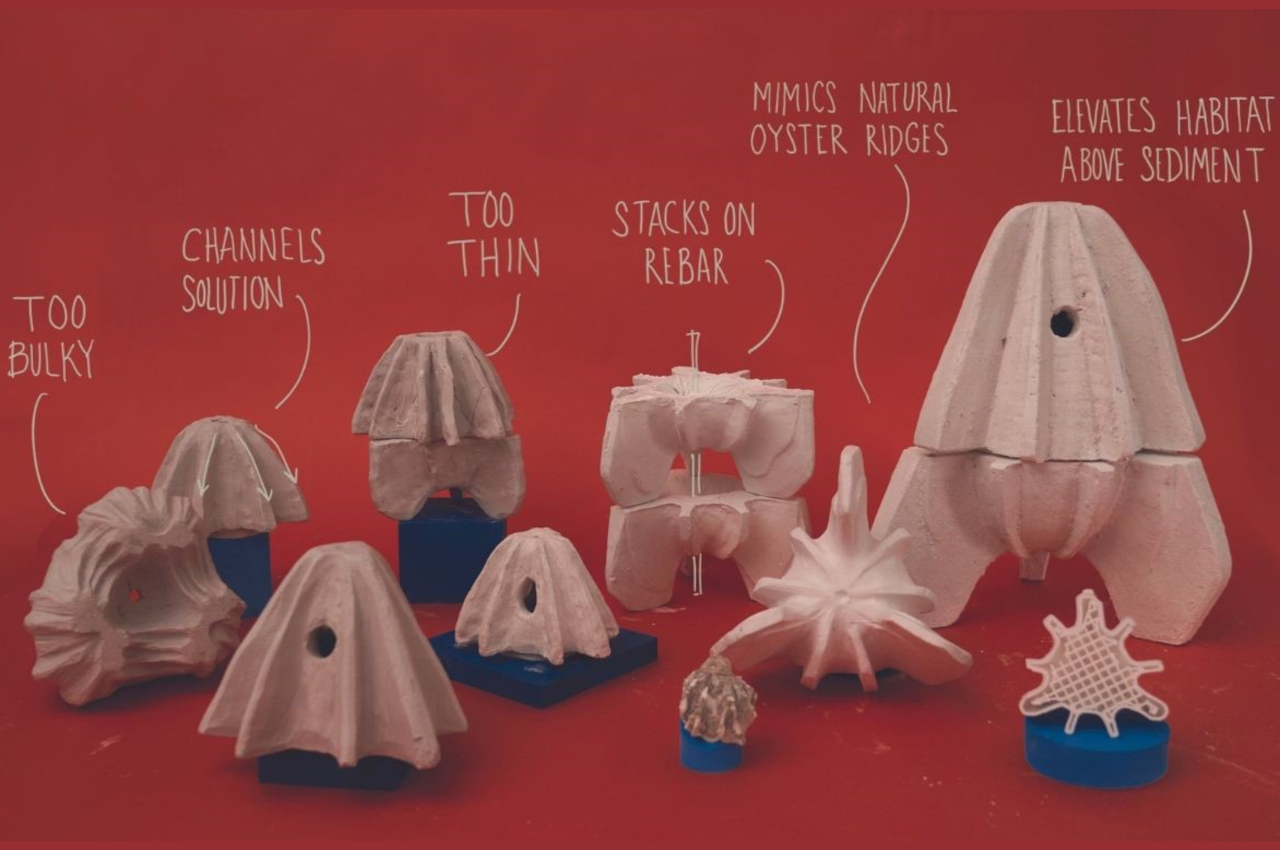
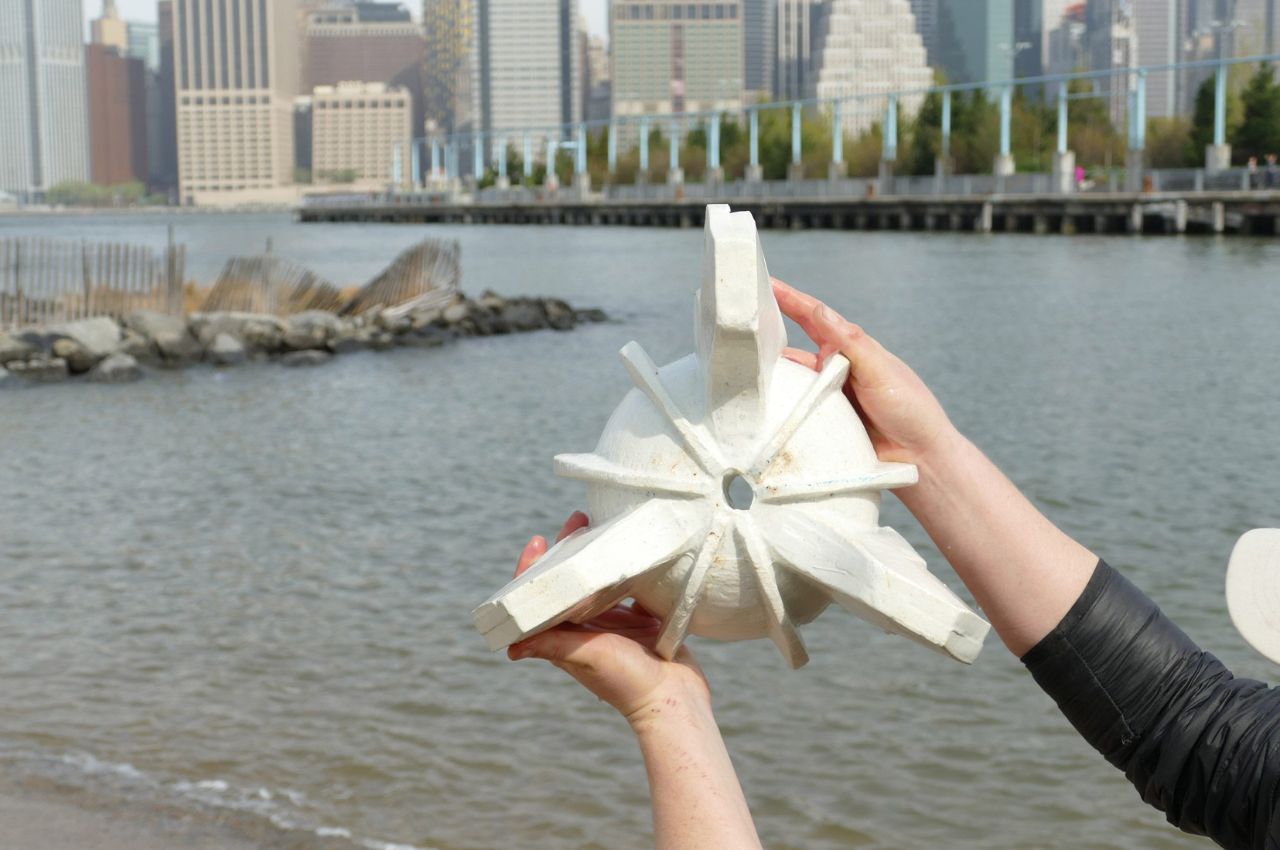


Reef Rocket’s deliberate design prioritizes small size, lightweight construction, and ease of assembly, aiming to make the innovative solution accessible to a broad audience. Lempres envisions a future where durable materials can be grown like crops, regenerating waste and mitigating environmental pollution. The project stands as a testament to the potential of biomimicry and sustainable design in addressing the challenges posed by climate change and coastal resilience. Reef Rocket represents a significant step towards harmonizing human infrastructure with the resilient and regenerative capacities of the natural world.

The post Bio-Cement: A Potential Material That May Replace Regular Cement first appeared on Yanko Design.