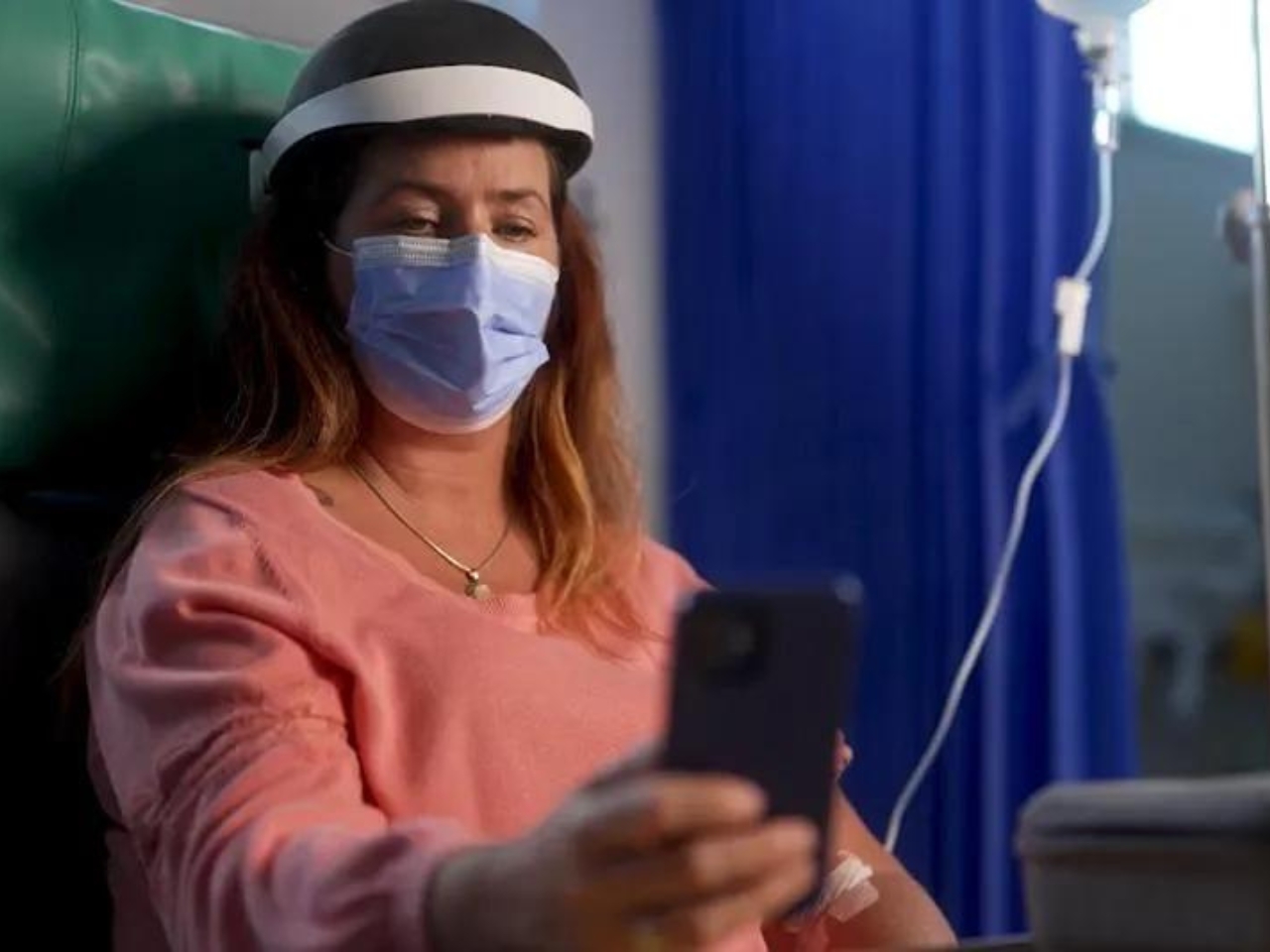

One of the most common side effects on patients undergoing chemotherapy is the loss of hair. It may seem like not a big deal anymore these days because people are more “accepting” of baldness, but there is still of course an effect on self-esteem and self-image of the patient. They say that hair loss is one of the most traumatic parts for them when it comes to their cancer treatment. A new product that will help them prevent this chemotherapy side effect will soon be available for commercial purchase.
Designer: Luminate
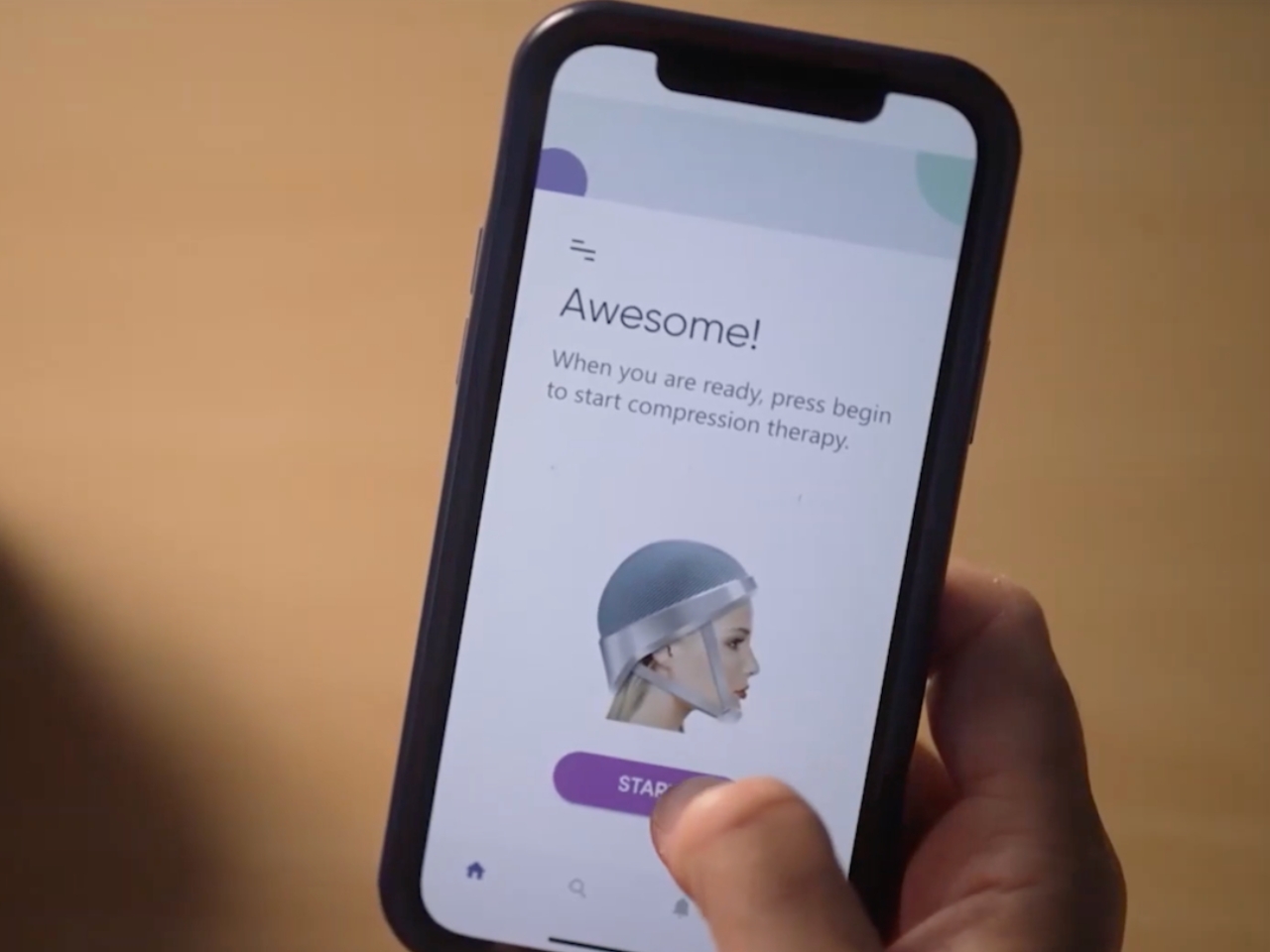
Lily is a helmet created by cancer treatment tech startup Luminate. The basic idea for the device is that when worn during chemotherapy sessions, the helmet applies pressure across the scalp that stops the chemicals from getting into the patient’s hair follicles. The helmet is also made from soft materials so it’s still comfortable when worn and will not add to the common discomfort patients experience when having their chemotherapy session. Just think of the helmet as a compression garment for the head.

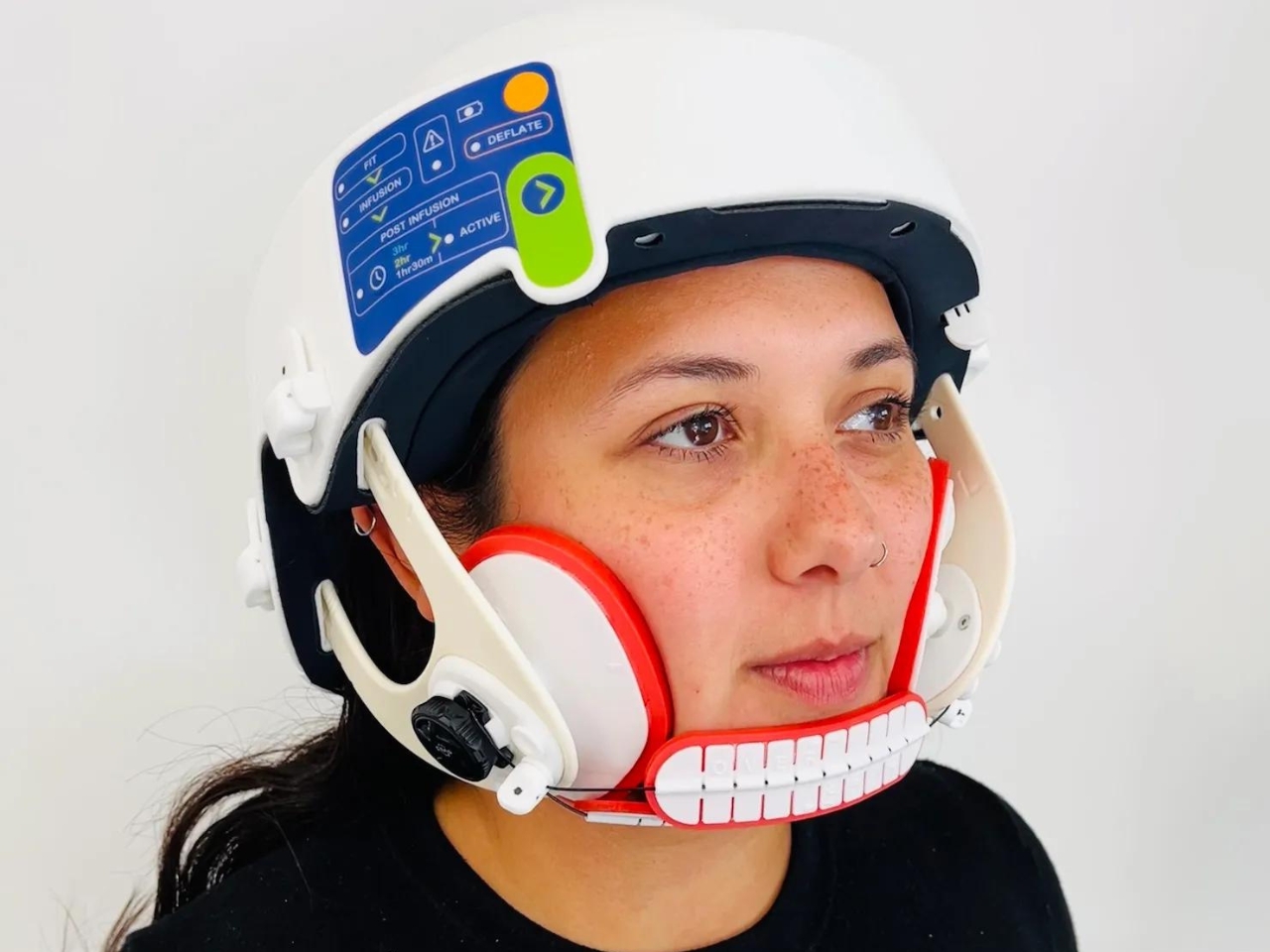
The wearable device looks like your typical helmet but with additional paddings on the cheek and under the chin. The way it’s built and designed is to bock off the capillaries to prevent the toxic chemo cocktail from affecting the patient’s hair. In their initial trials, 75% of the participants retained their hair while undergoing chemotherapy while wearing the Lily helmet. There will be another trial this November involving 85 patients across the U.S.
Luminate is also developing a glove and boot set called Lilac that will help prevent neuropathy, another side effect of chemotherapy. The company’s goal is to make cancer treatments more comfortable for patients by creating products that will address the side effects.

The post Helmet helps mitigate hair loss for cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy first appeared on Yanko Design.