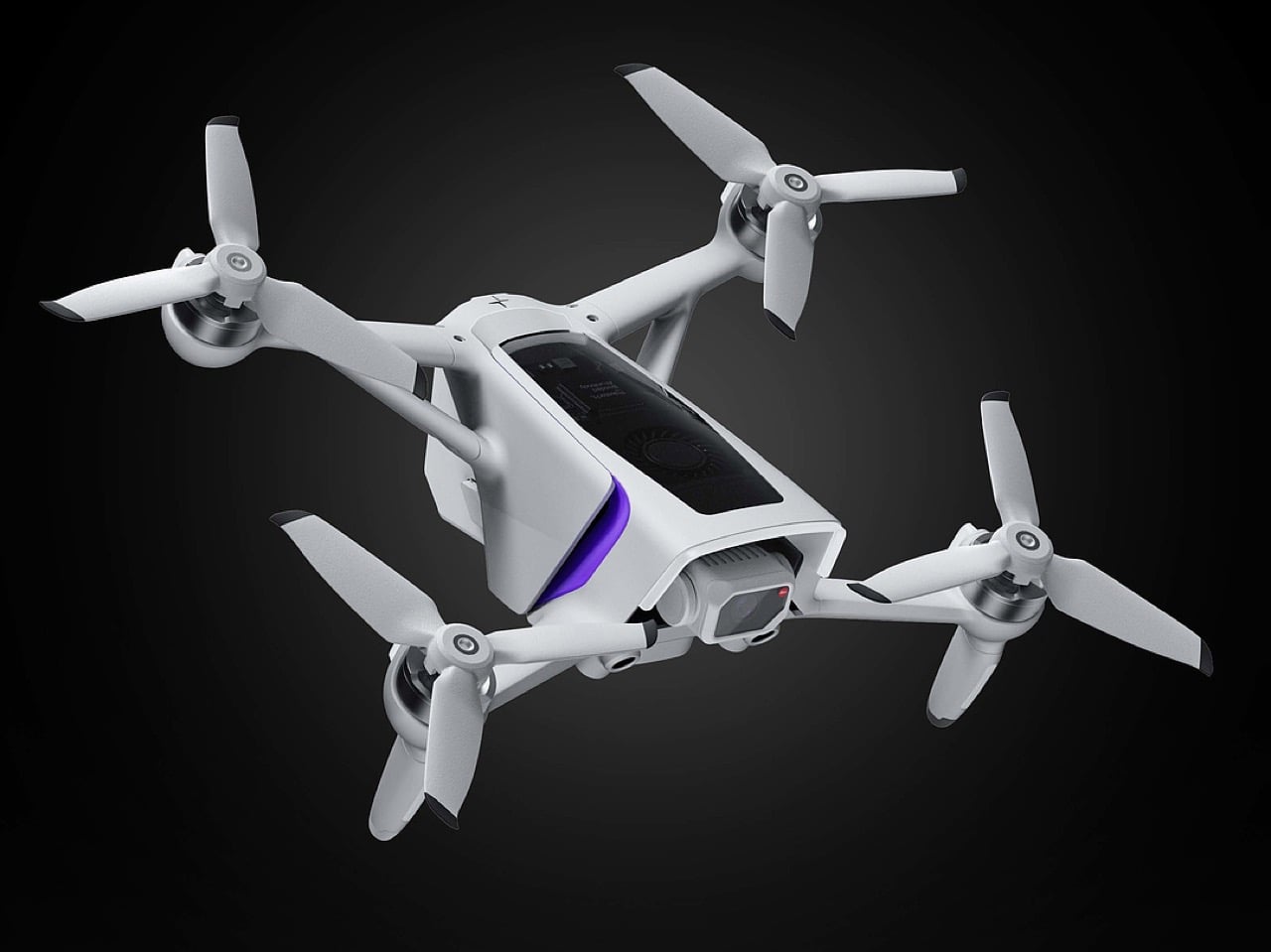
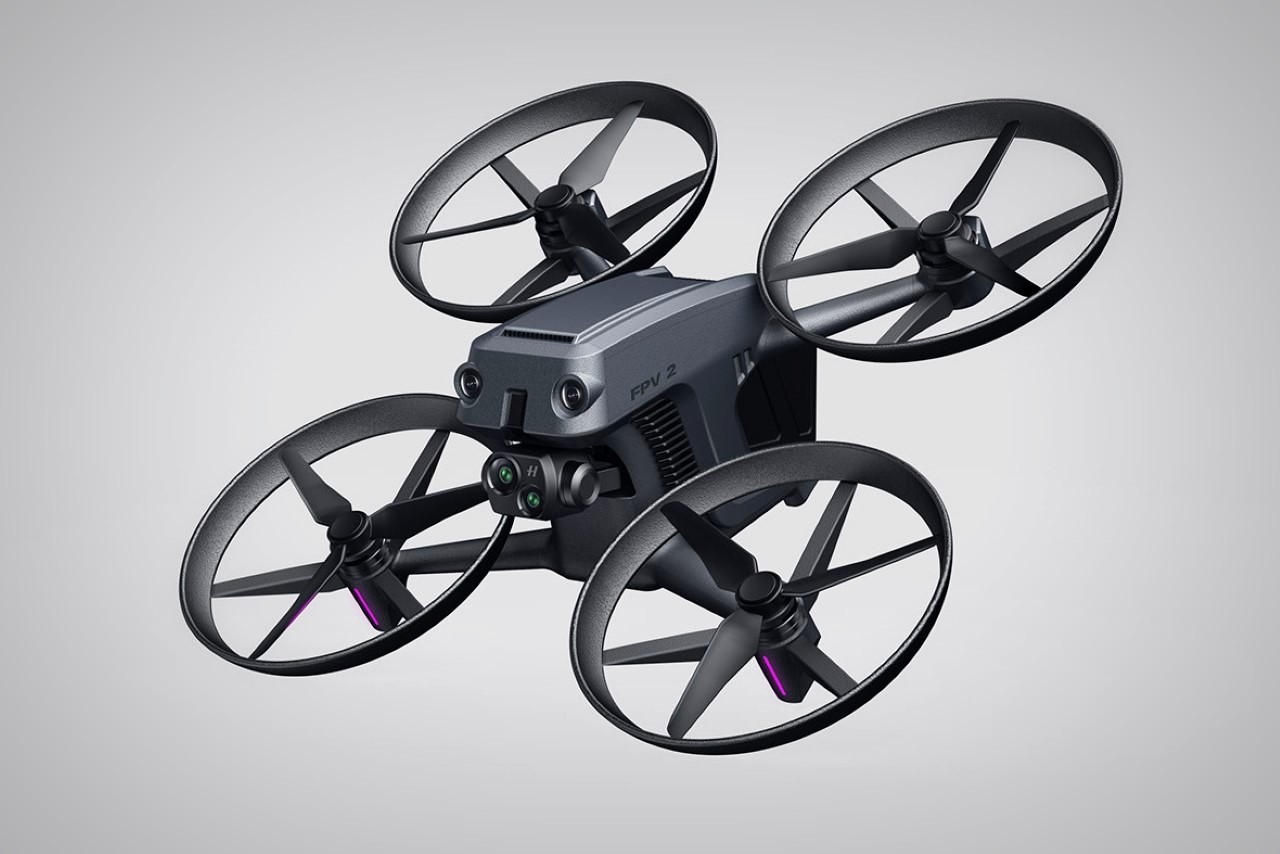
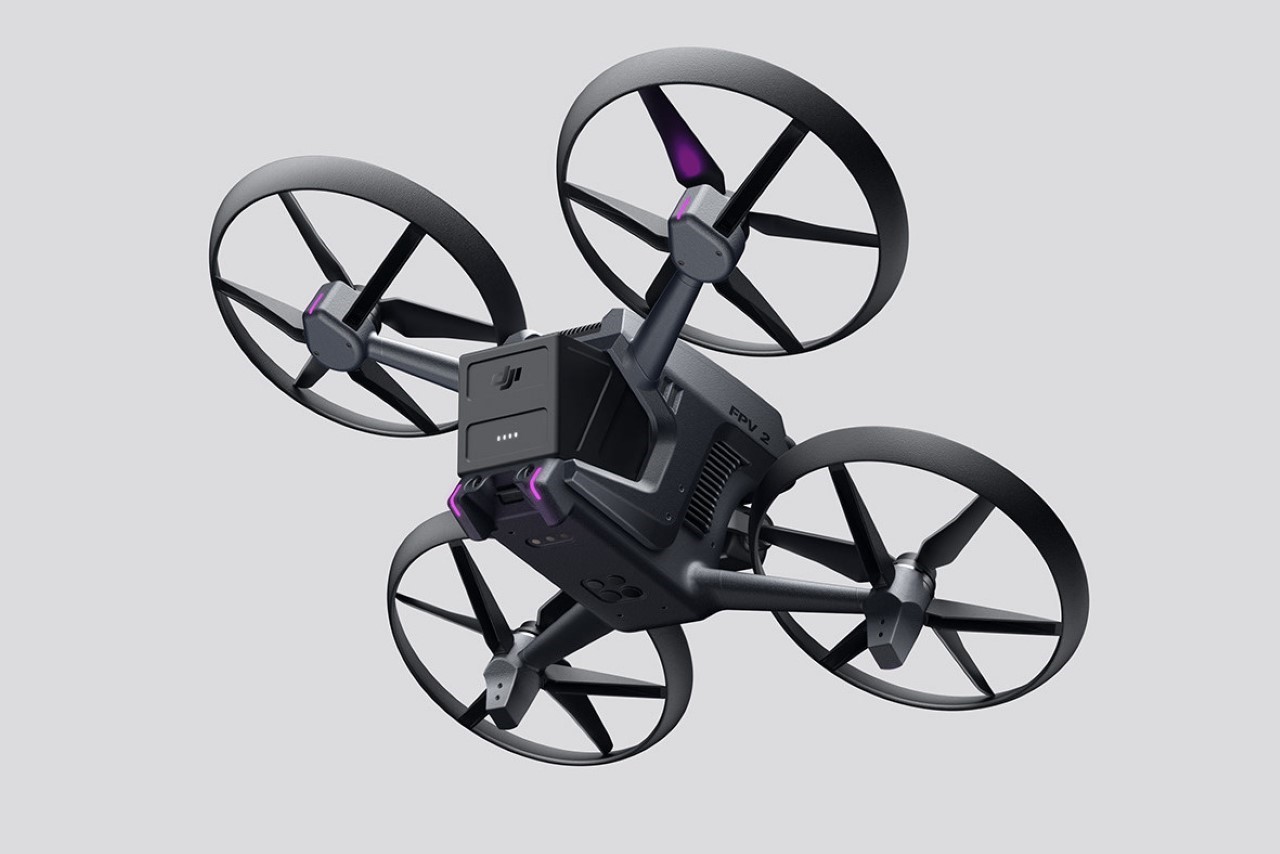
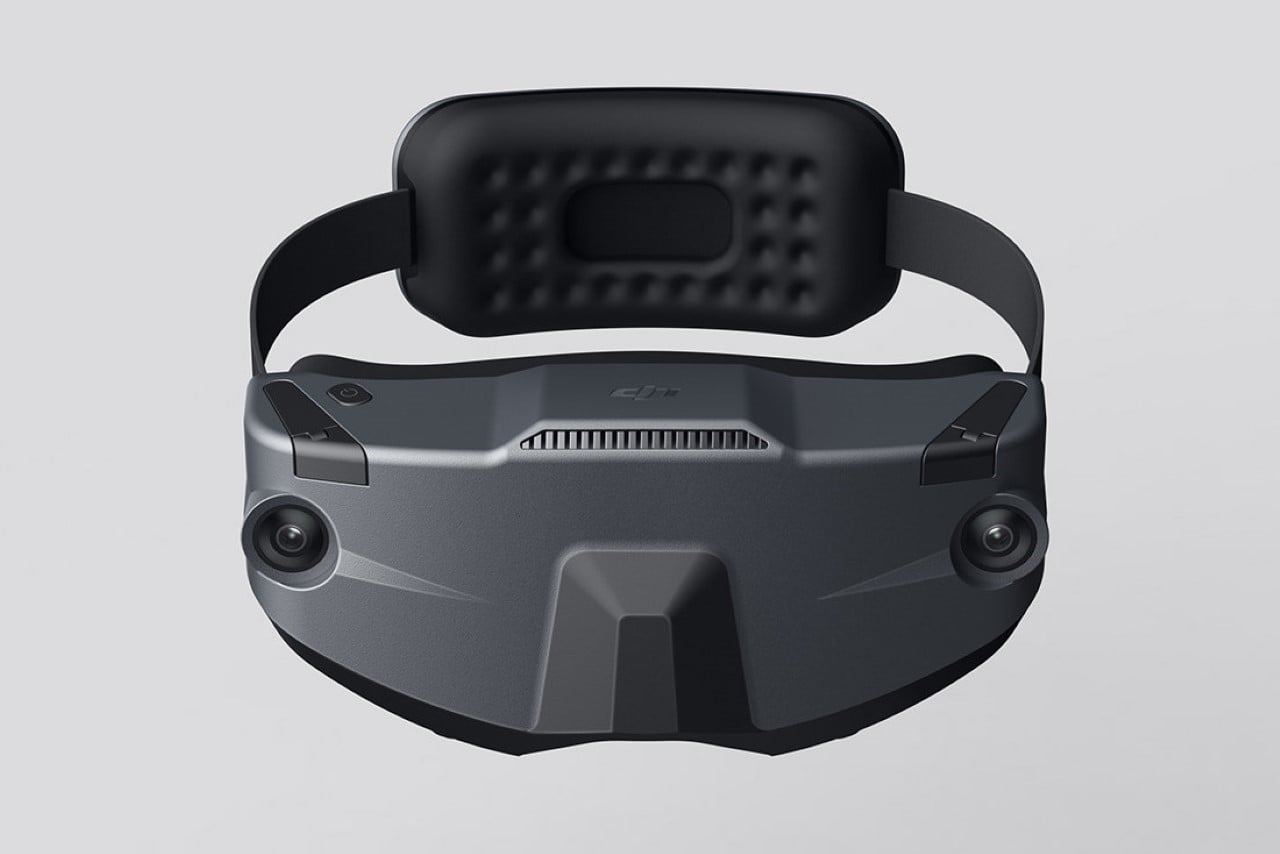
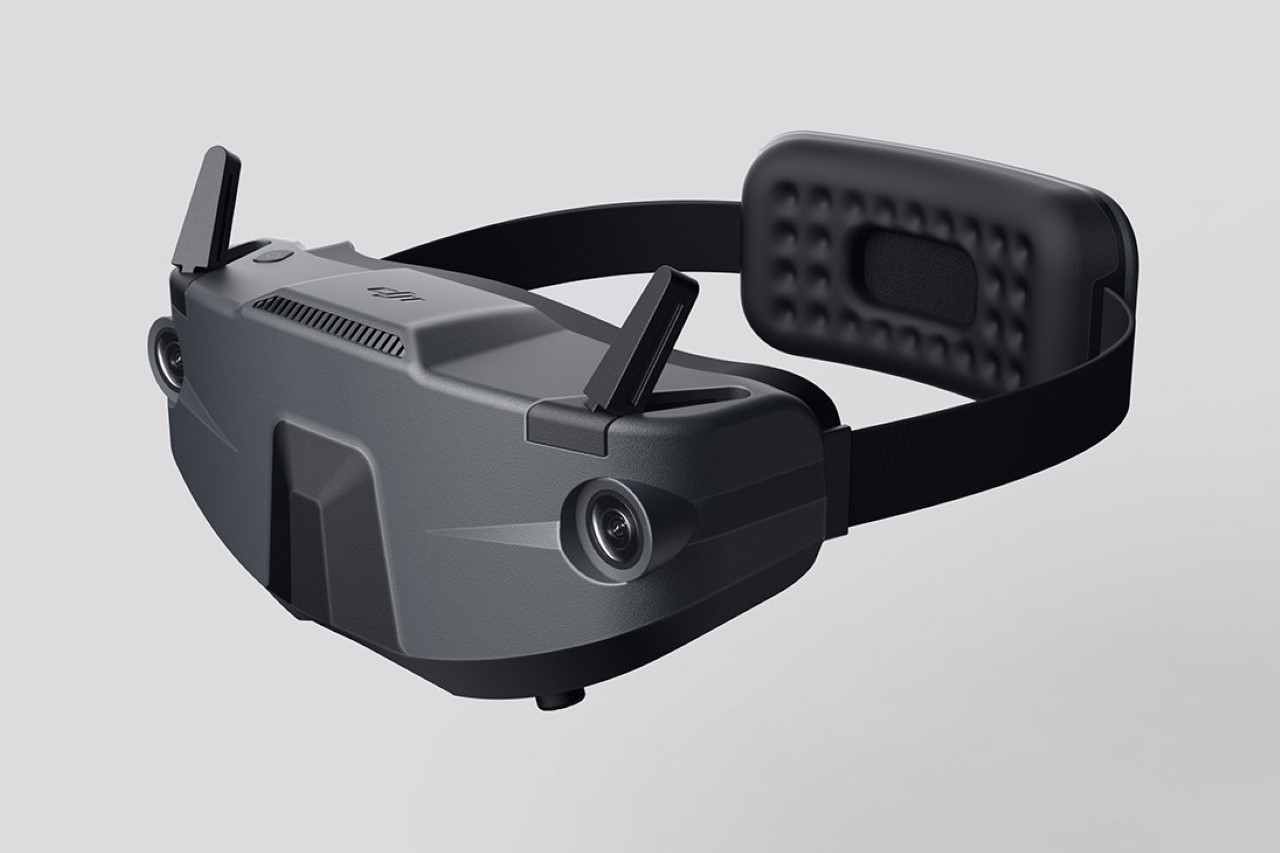
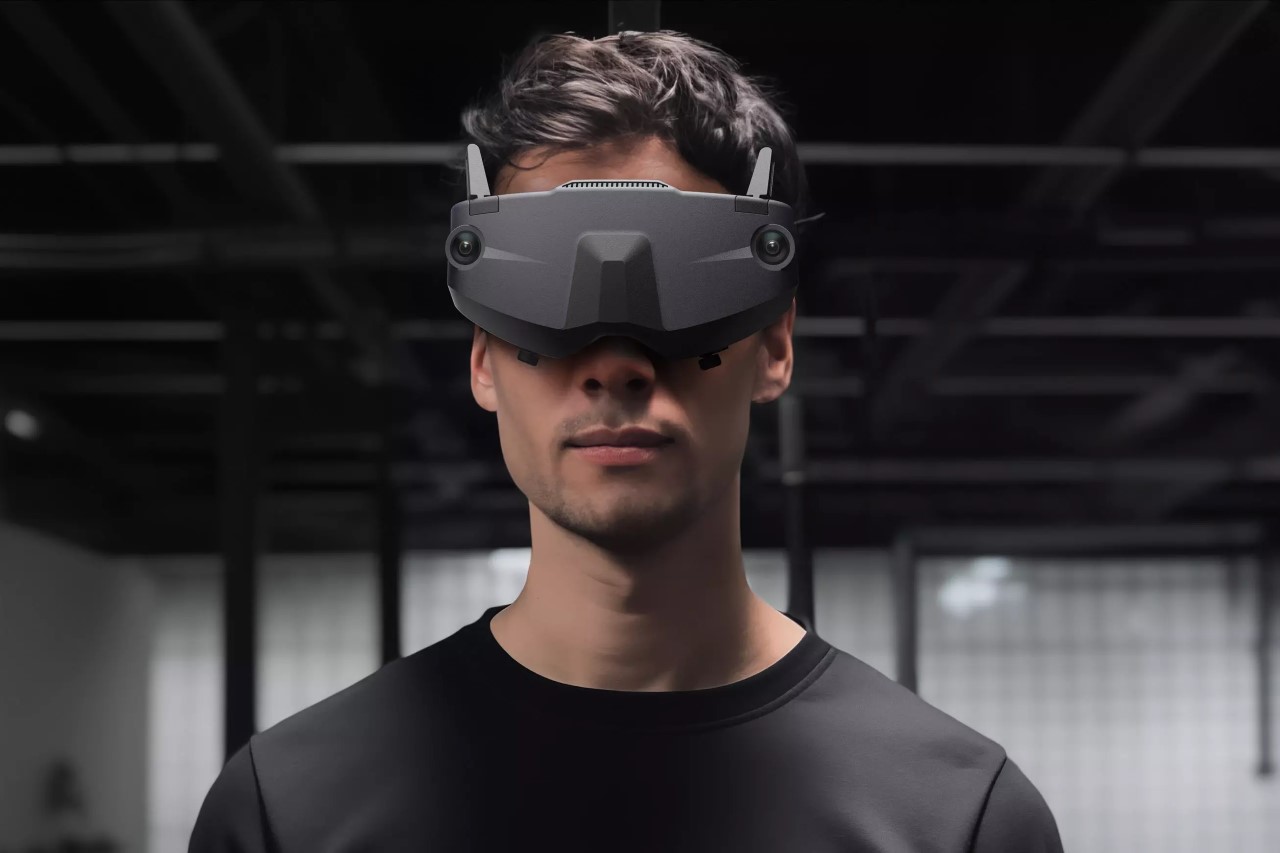
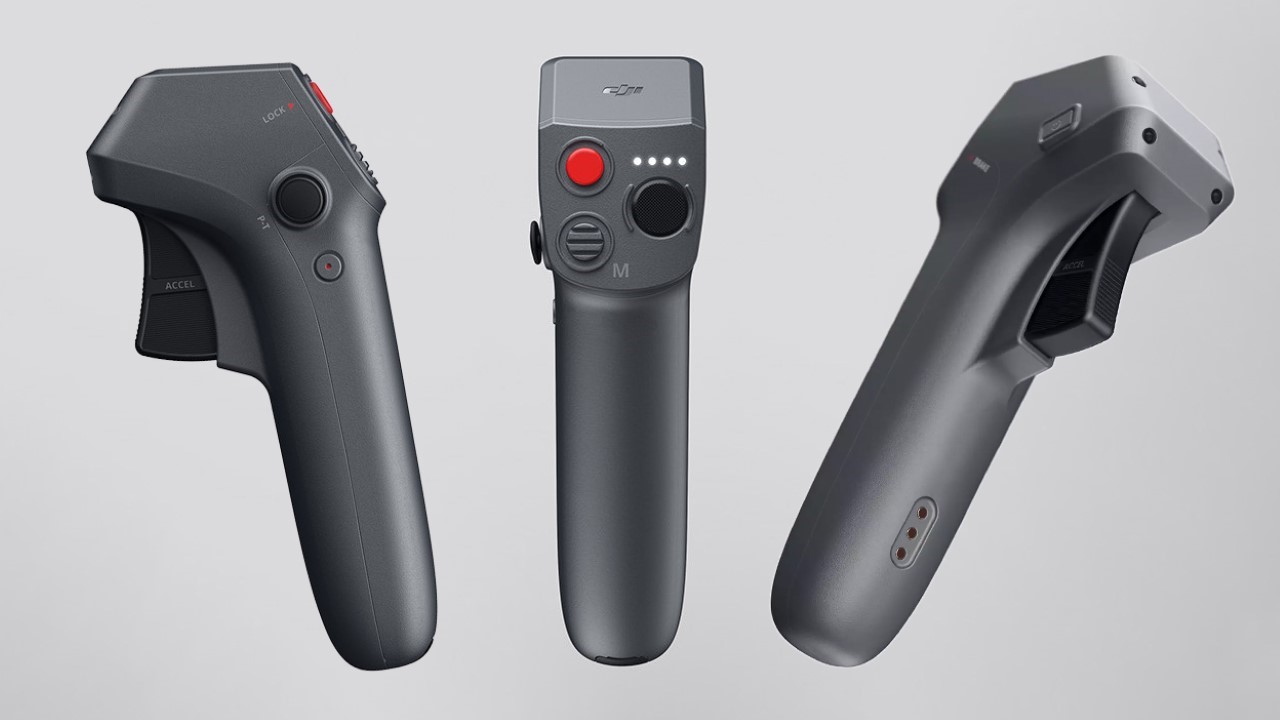
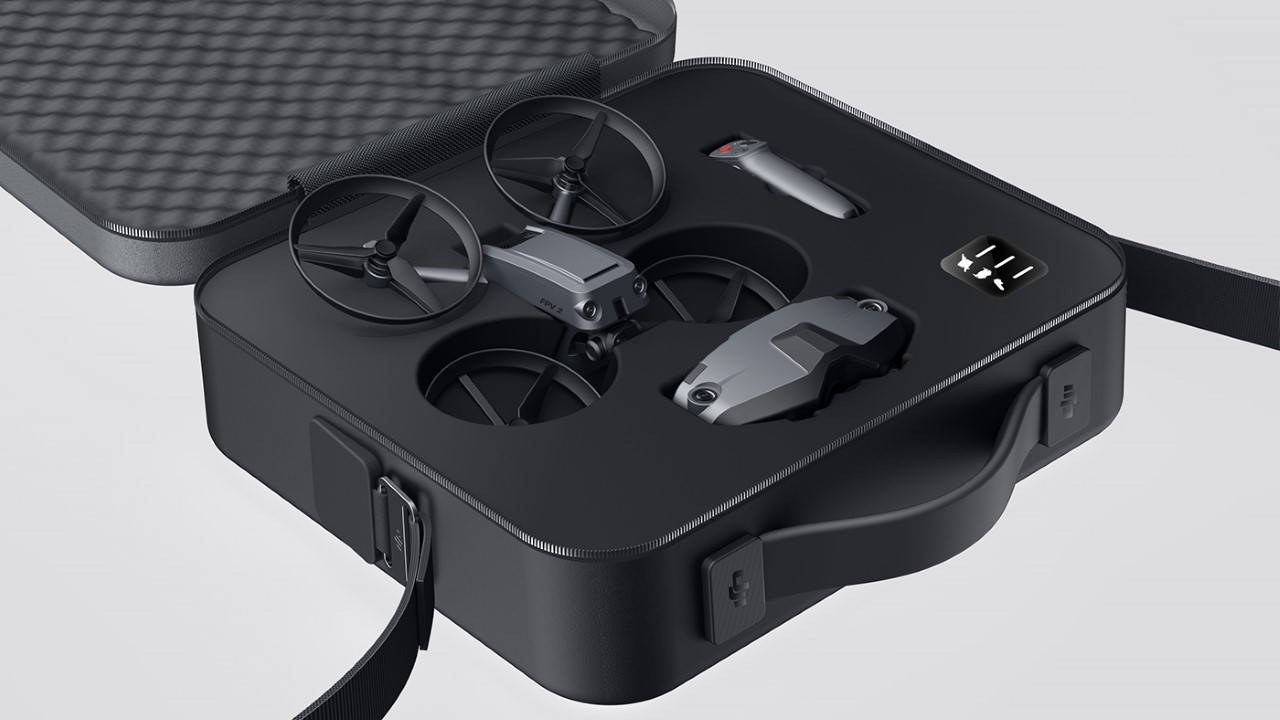
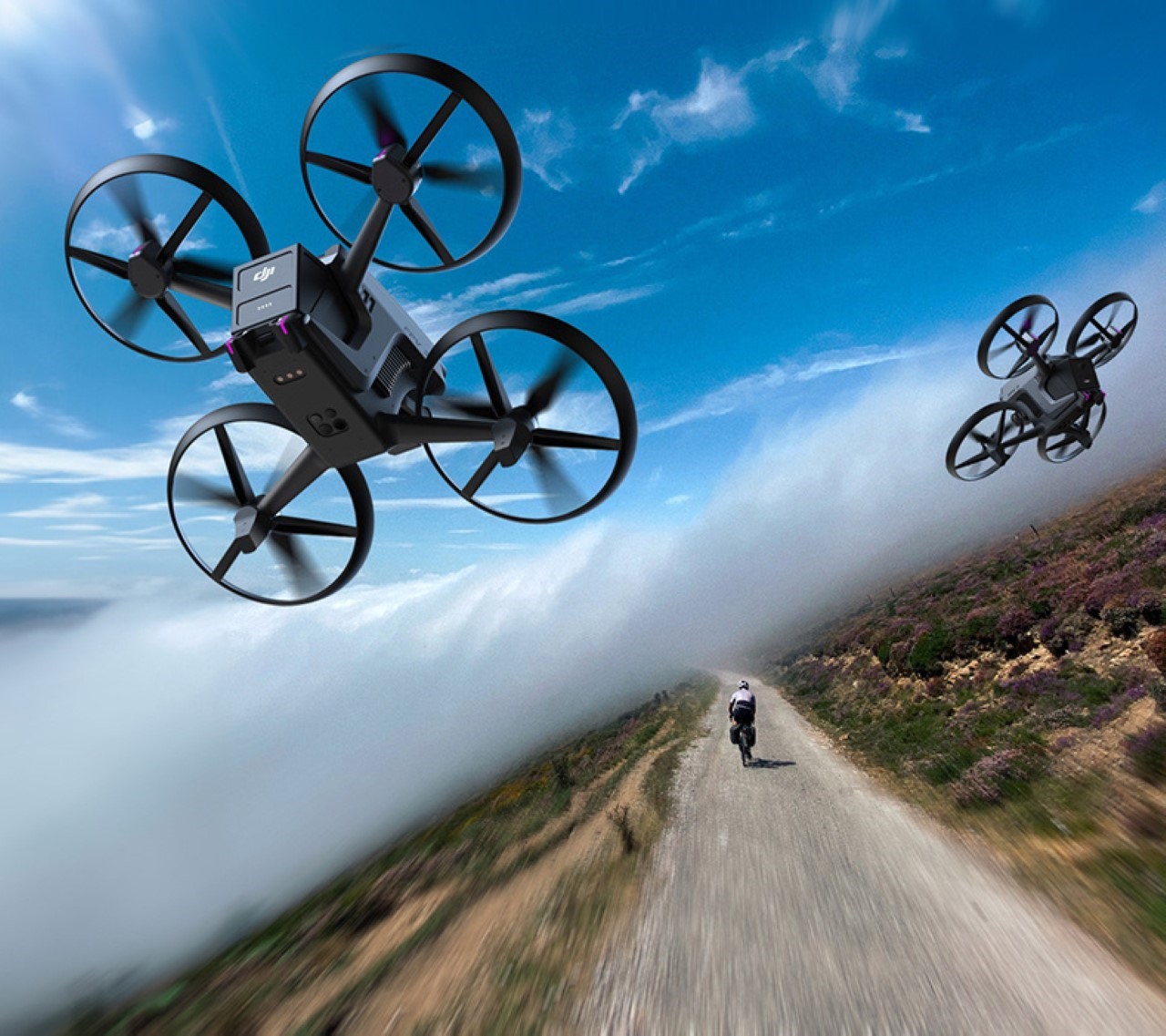
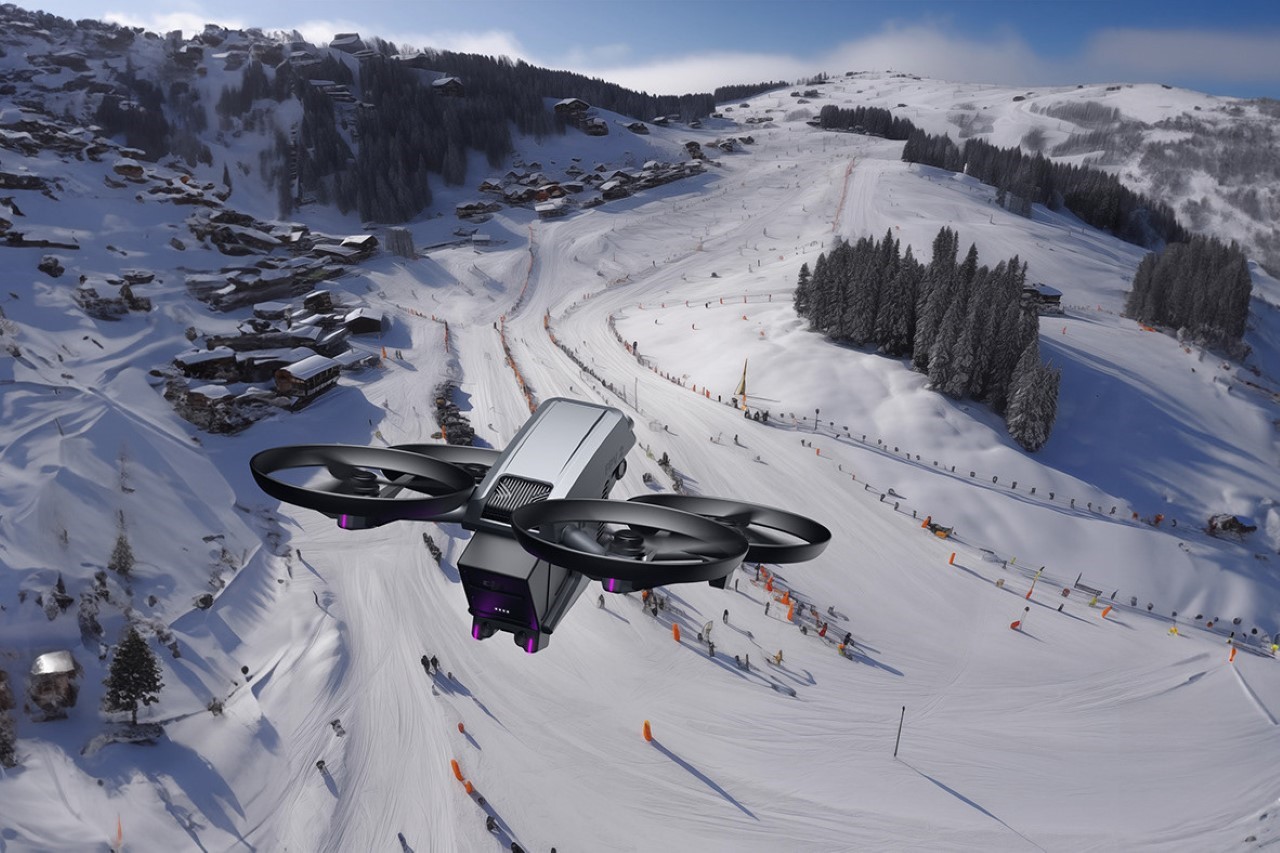
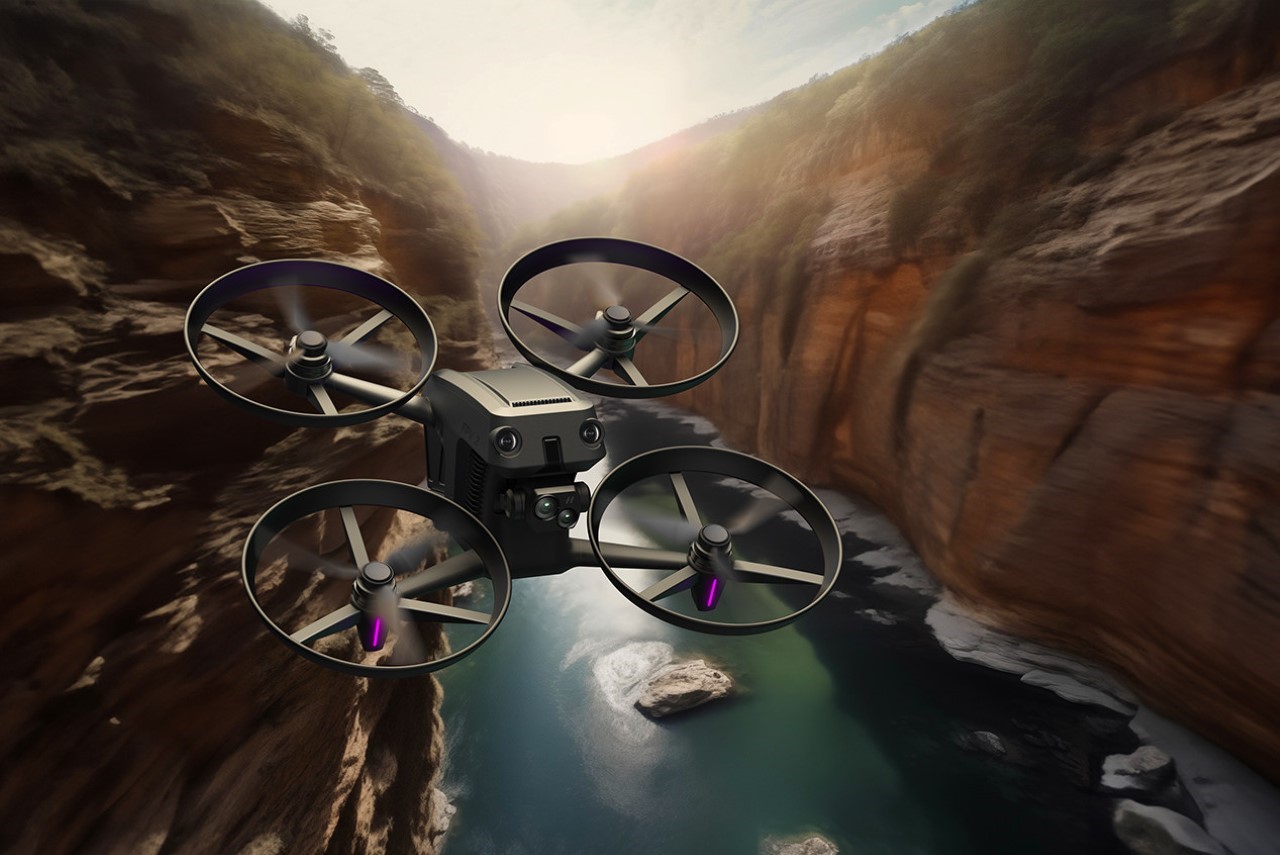
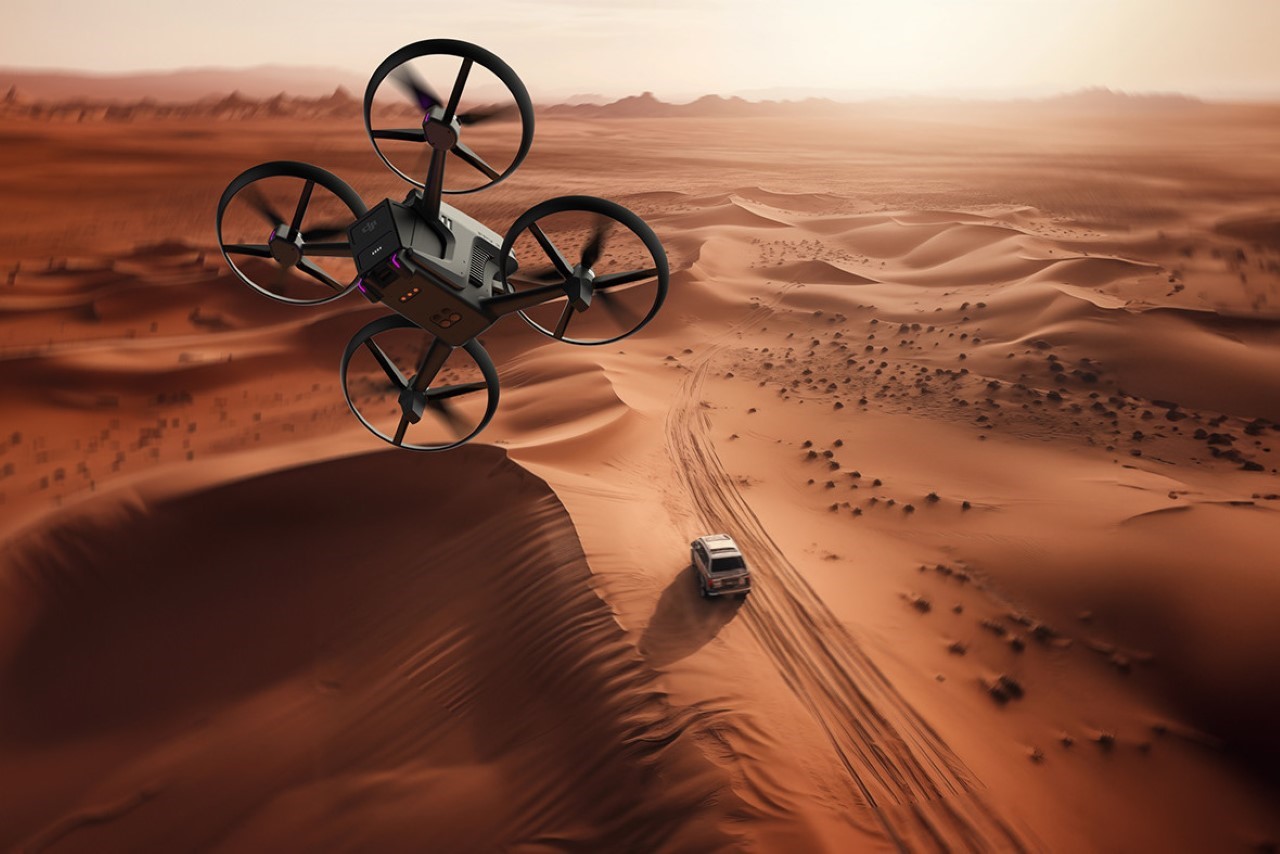
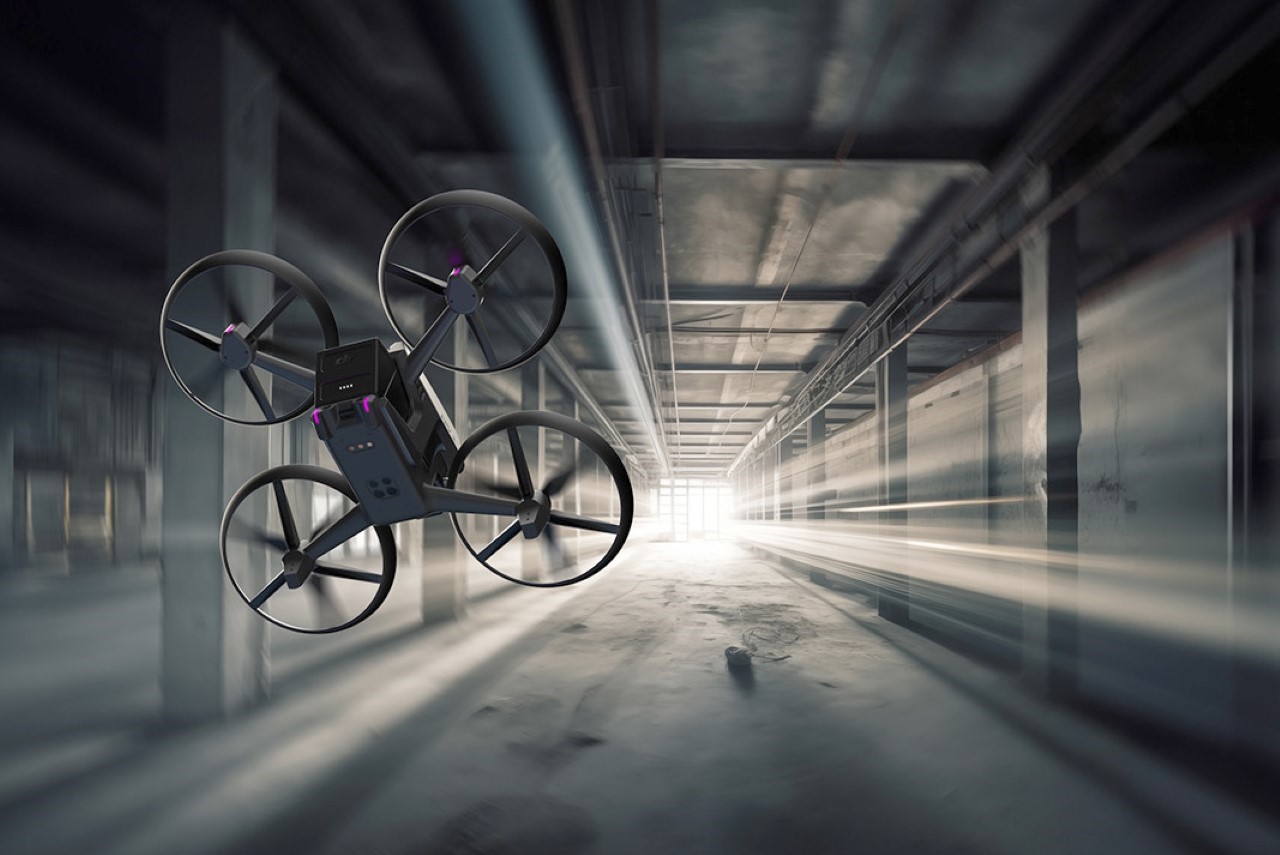
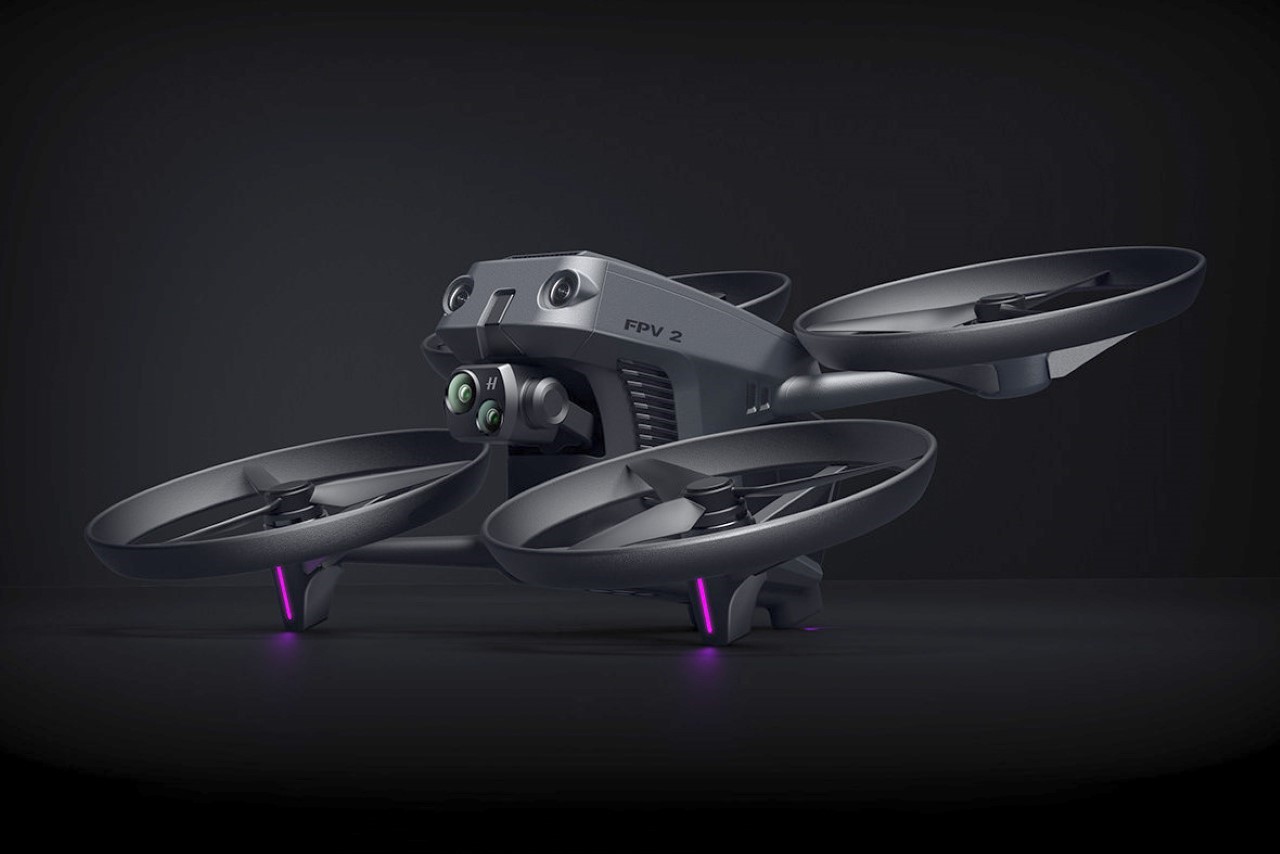
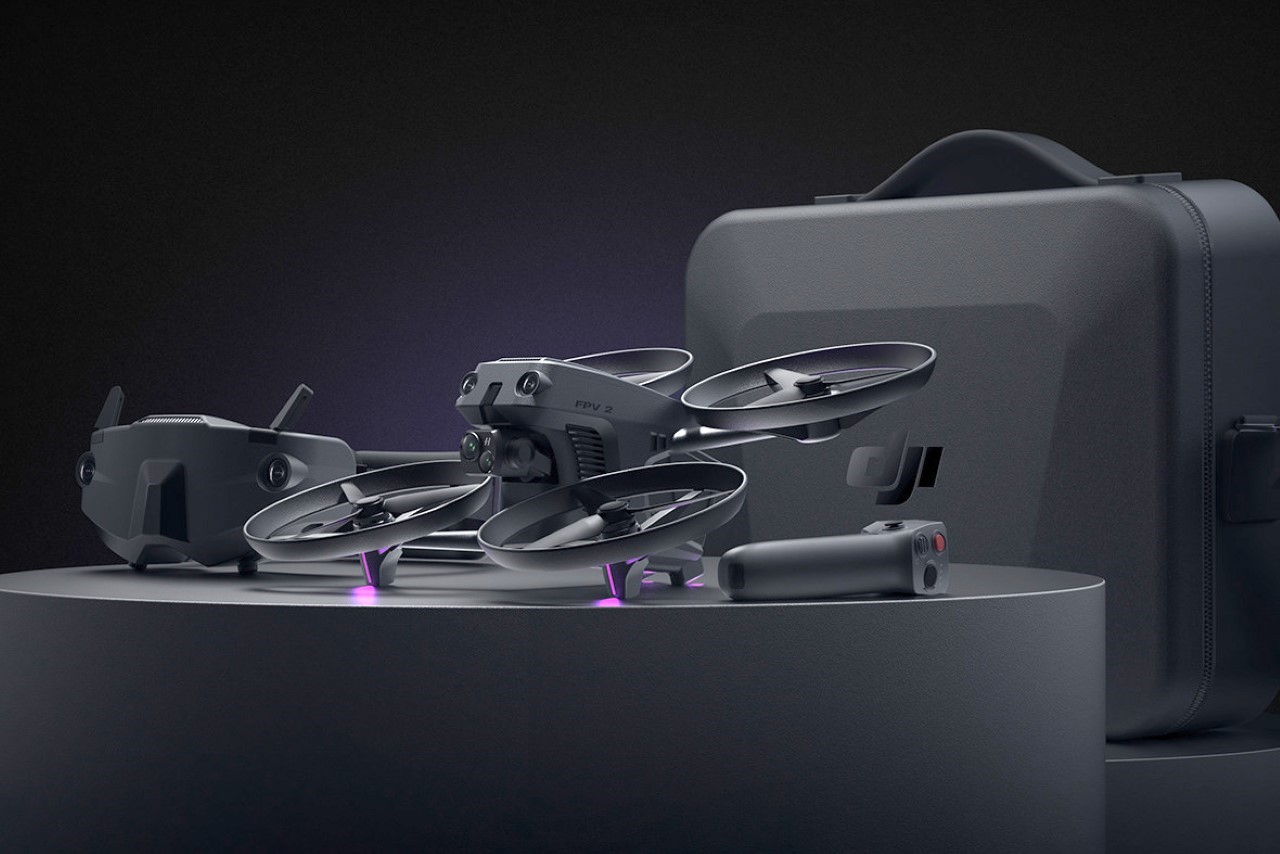
Polestar’s cool Nordic minimalism is not the first thing you expect to see in an FPV rig, yet this concept leans into that contrast and makes it feel inevitable. The drone lifts DJI’s “stacked” architecture of camera, flight controller, cooling, and battery, then wraps it in a crisp, automotive shell that would look just as natural parked beside an electric coupe as it would screaming through a canyon. Instead of the usual exposed carbon and repair-bench aesthetic, the body reads like a single sculpted volume, with the arms flowing out of a central spine and a long, glassy tech strip revealing the hardware beneath. Subtle light signatures, a clean white finish, and a battery module that wears the Polestar wordmark turn what is usually a niche racing tool into something that feels like a premium consumer product, without sanding off its performance edge.
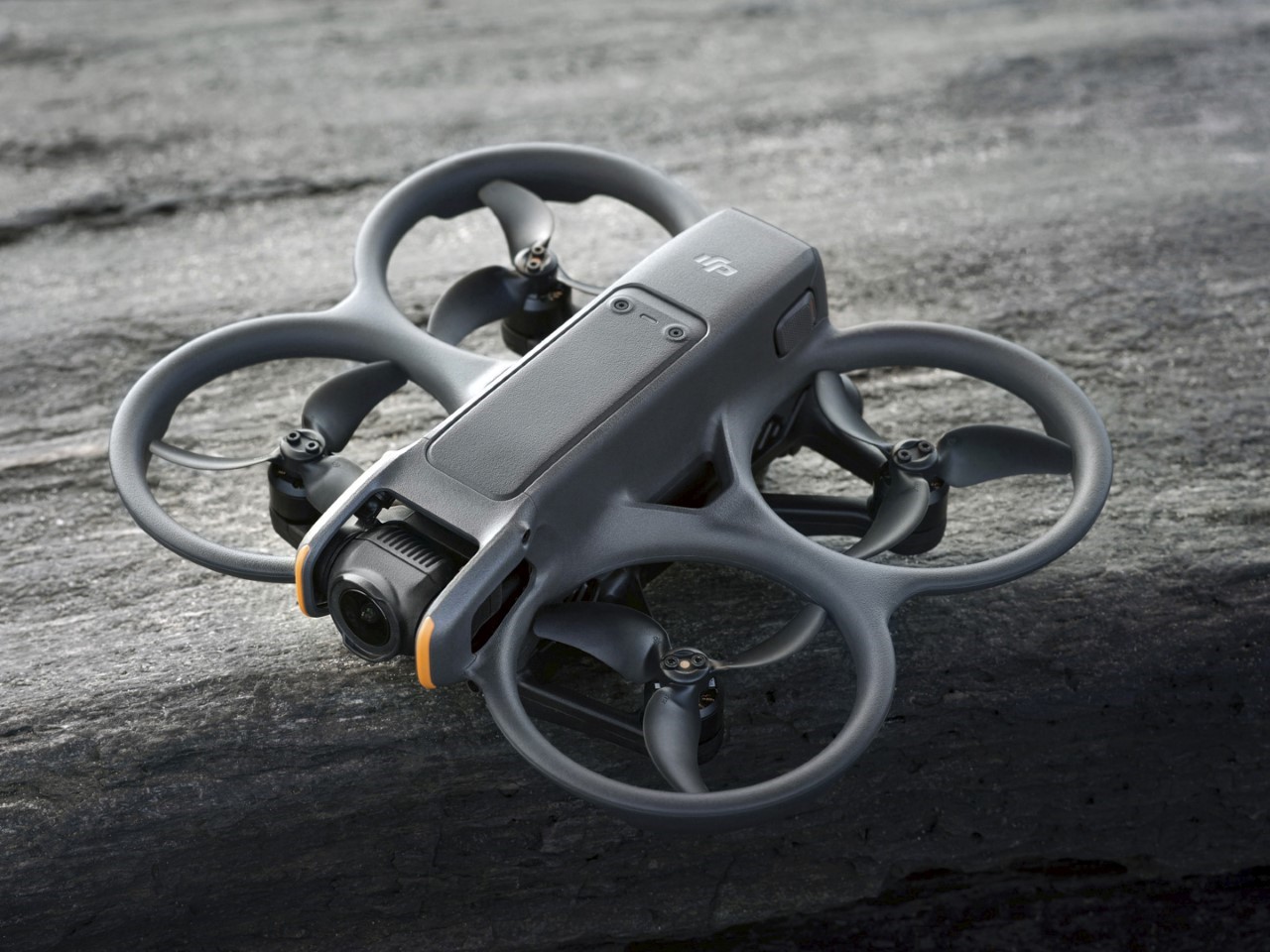
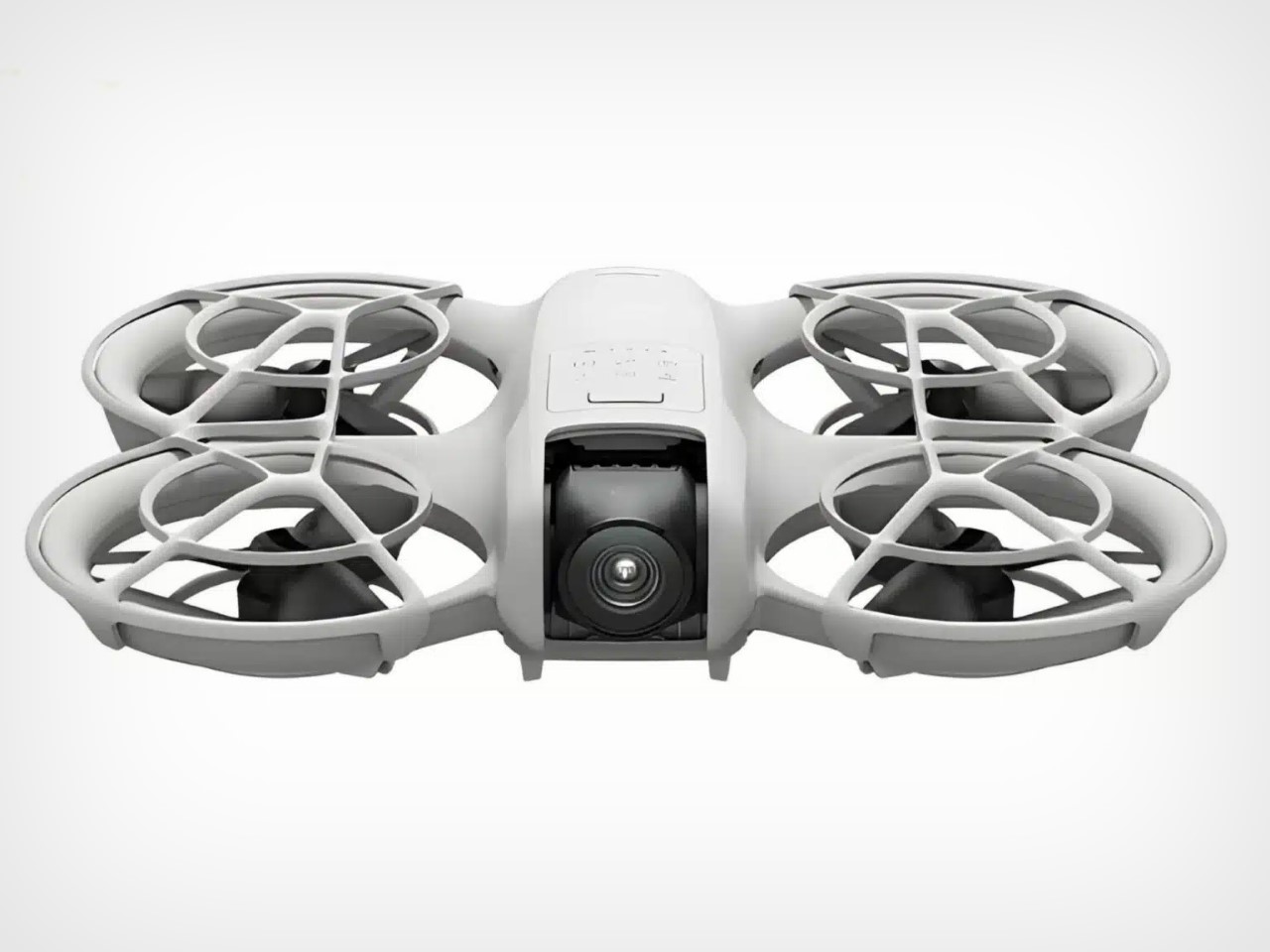
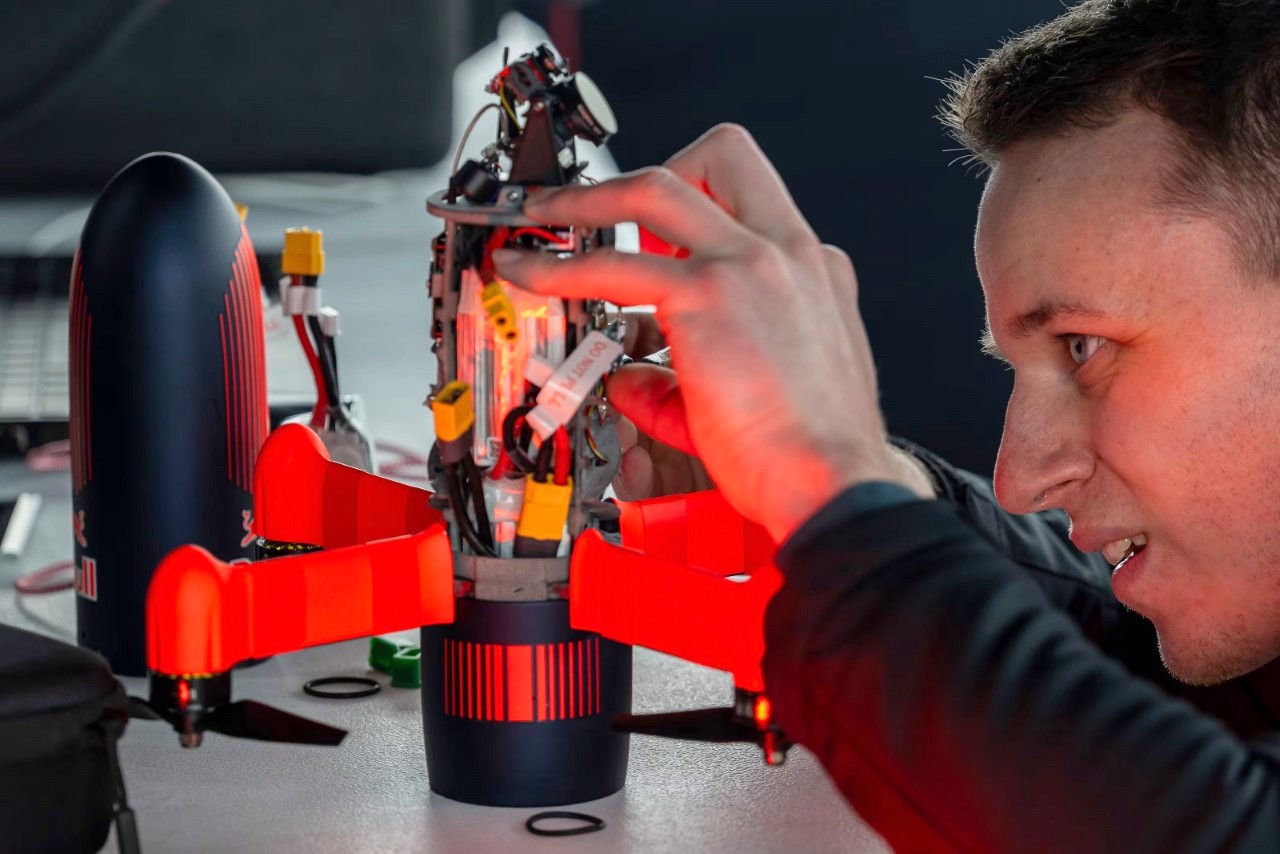
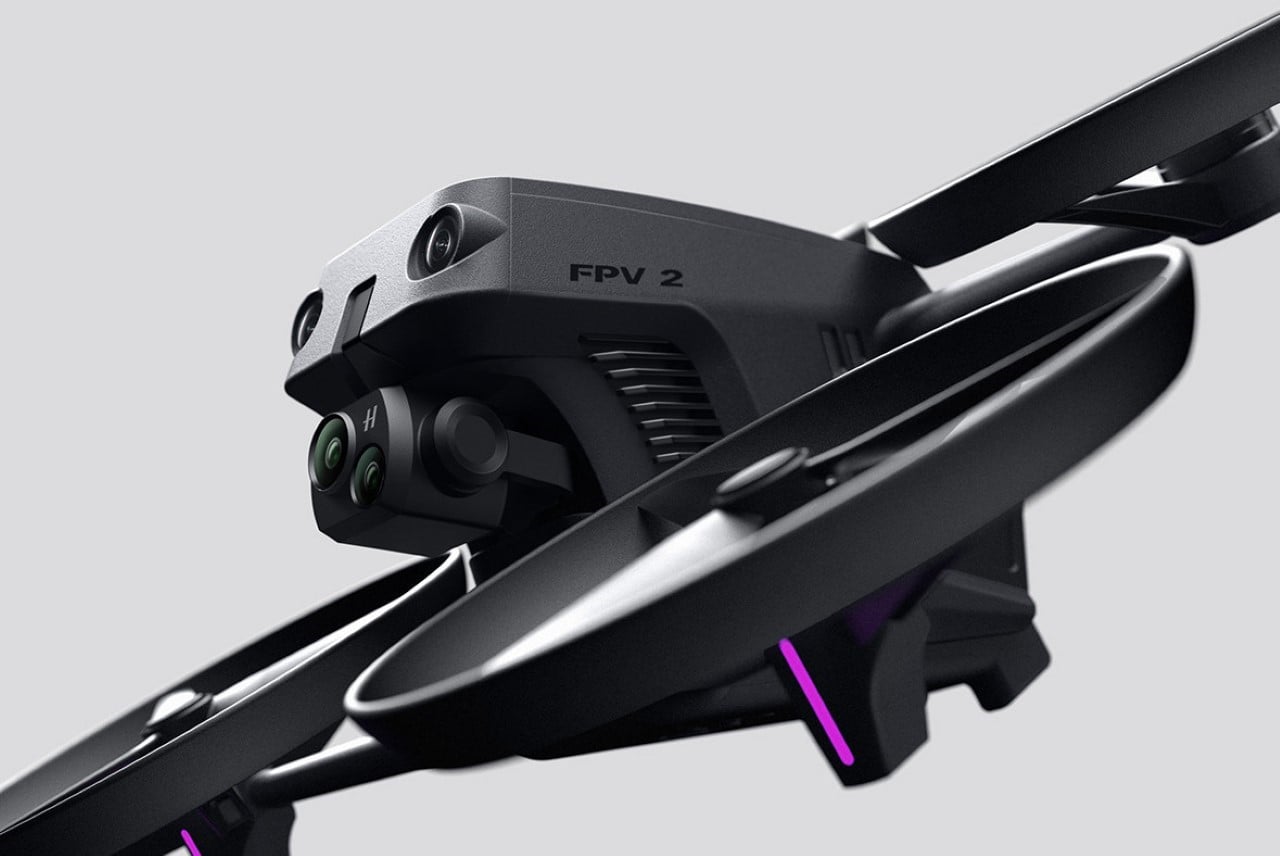
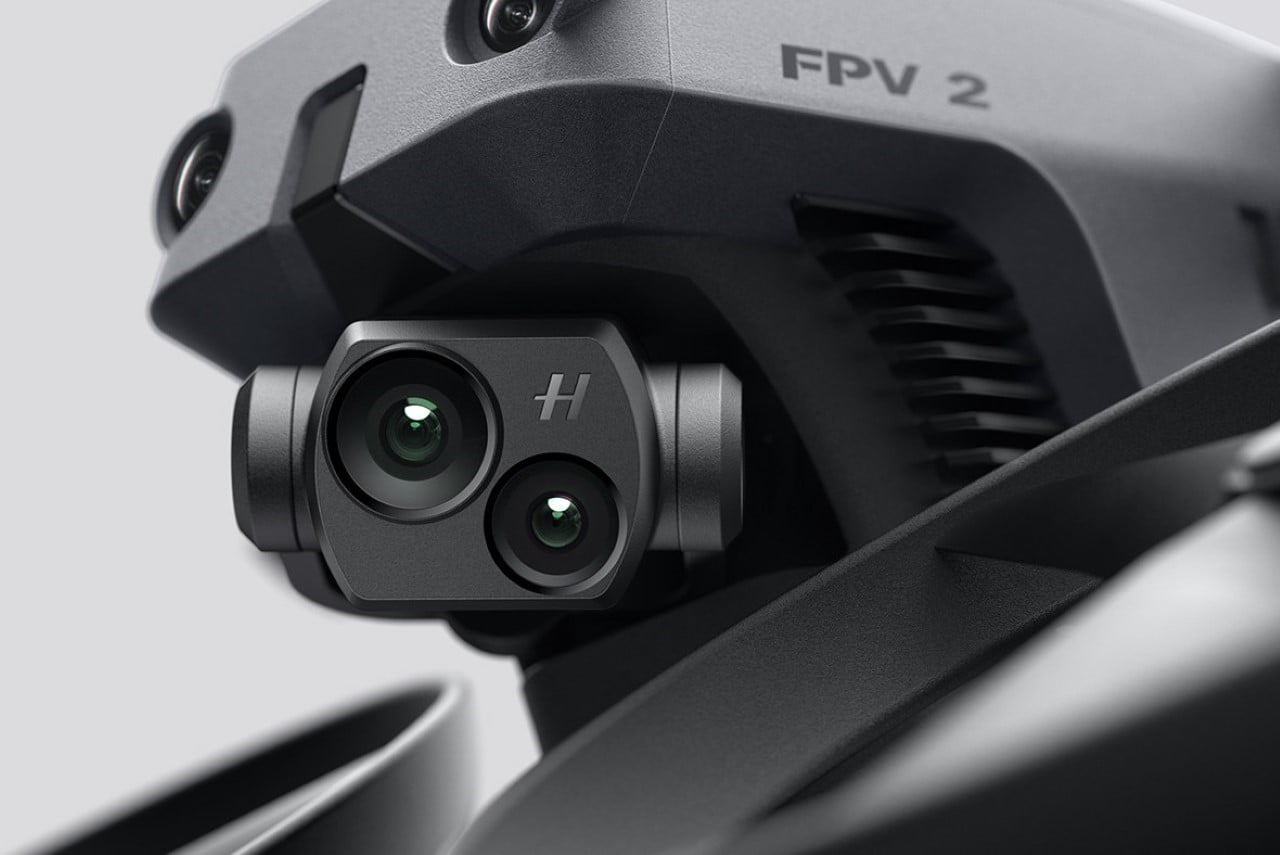
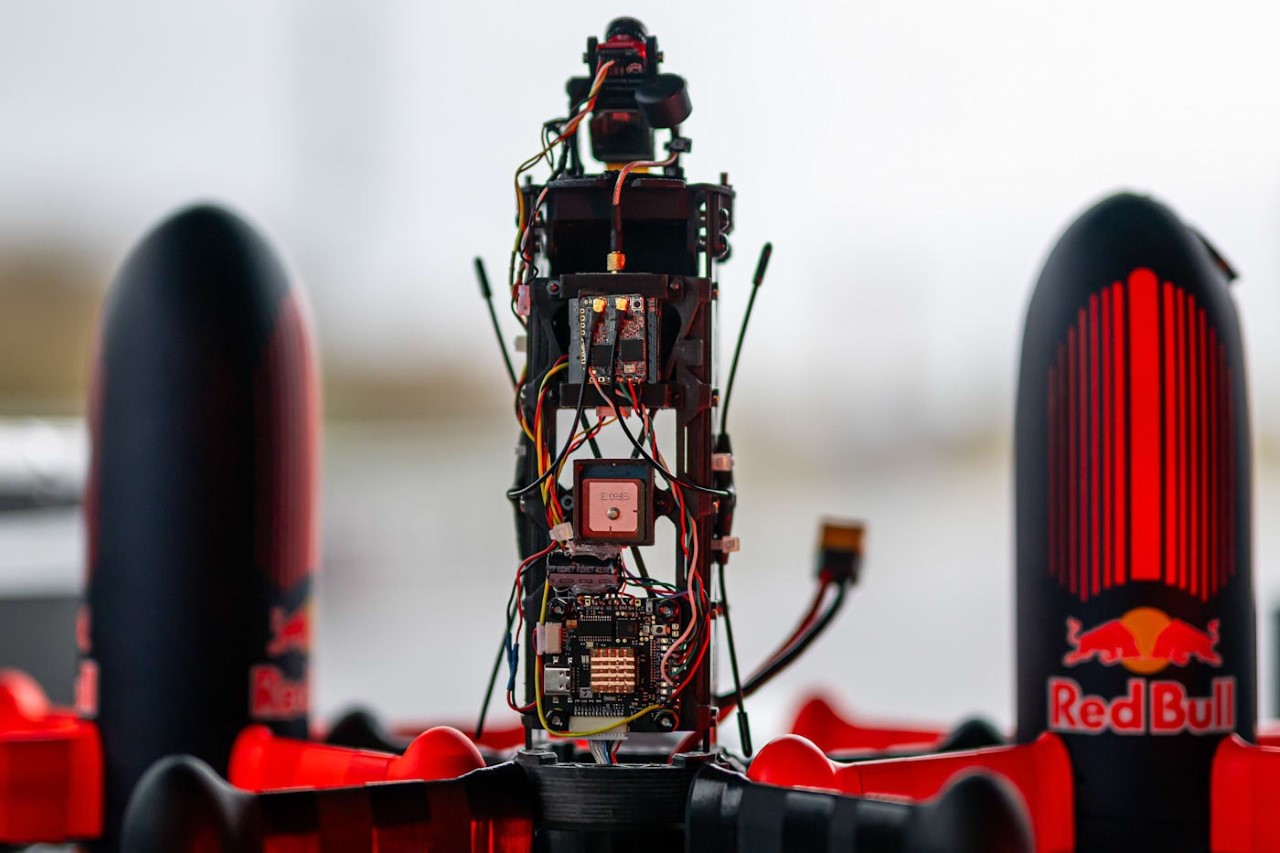
The design’s intelligence lies in how it translates DJI’s engineering logic into a clean visual language. The concept of “structural stacking” is central here, treating each primary component as a self-contained module arranged in a neat, vertical order. The camera and gimbal sit in a dedicated nose pod, followed by the flight control unit and heat dissipation systems under the long, dark canopy, with the battery locking in as a solid block at the rear. This layered approach brings an architectural order to the drone’s anatomy, making the technology feel organized and accessible. It moves away from the traditional FPV layout, where components are often fastened to an open frame, and instead presents a unified, product-like object that feels intentional from every angle.
Designer: Ocean
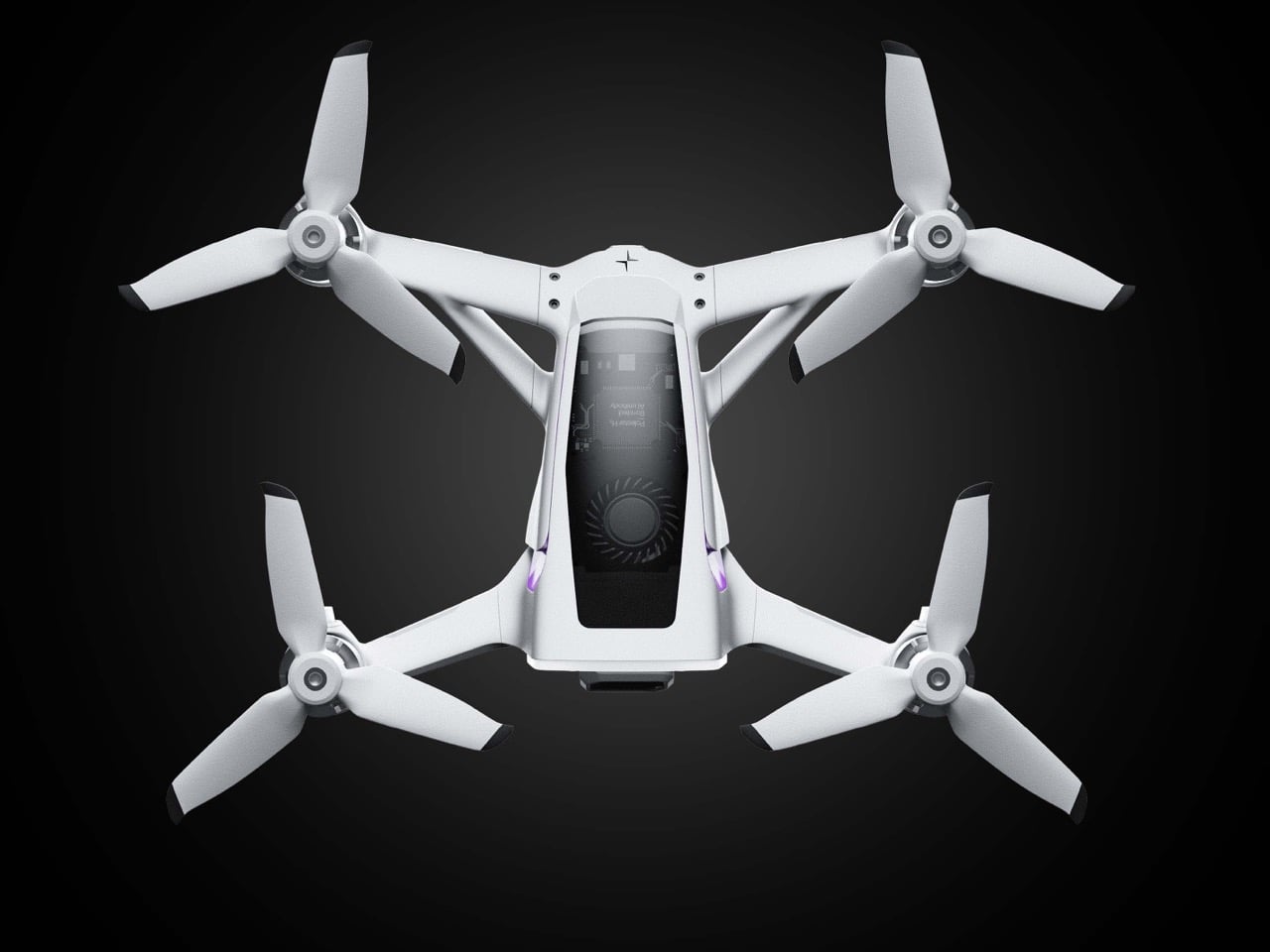
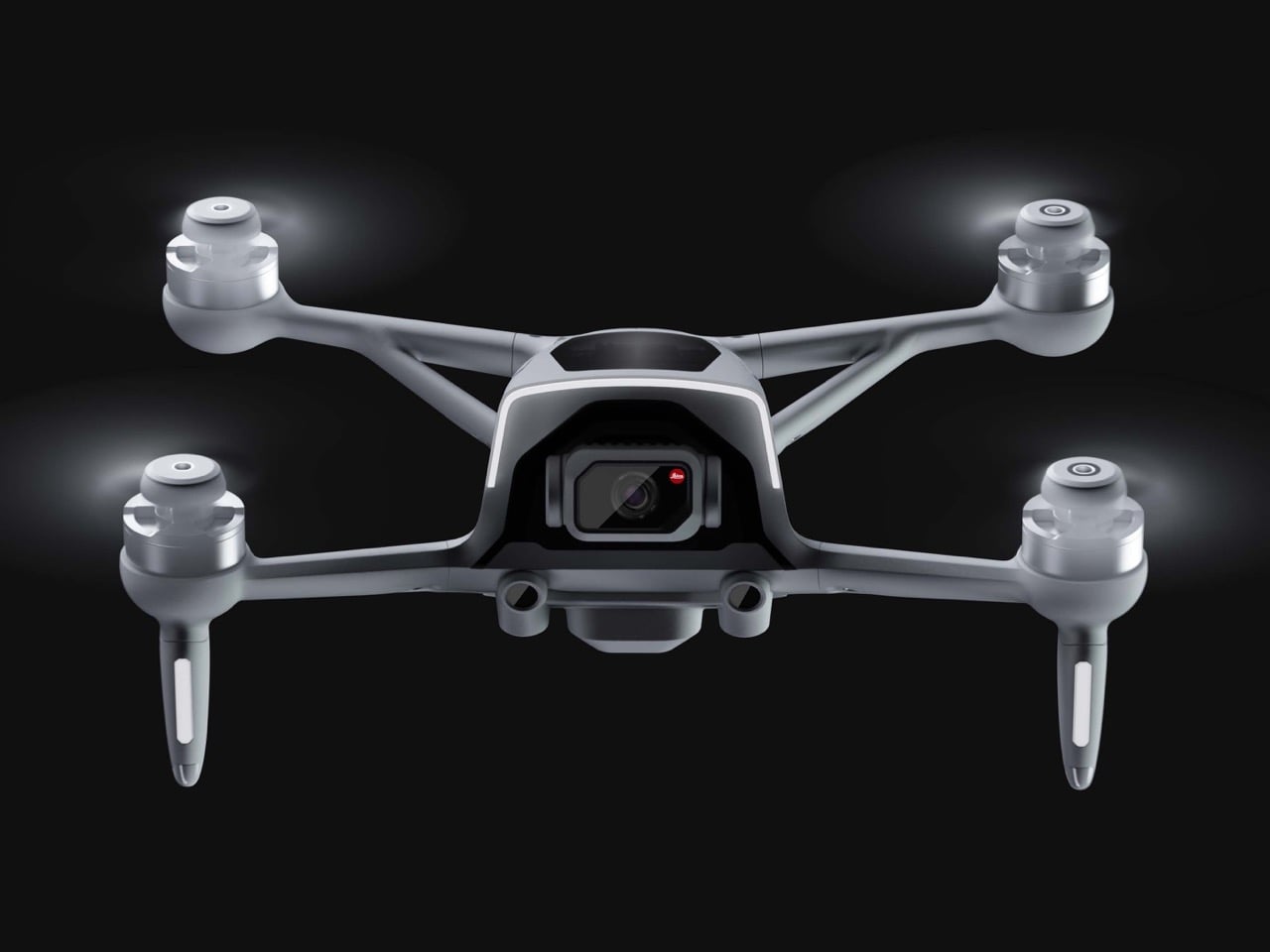


The drone’s body is finished in a matte, almost ceramic white, with surfaces that are both soft and incredibly precise, a hallmark of the EV brand’s surfacing strategy. The long, dark insert on top is more than just a cover; it’s a “tech window” that frames the internal hardware as a point of interest, much like Polestar does with its glass roofs and integrated sensor bars. Even the lighting is handled with automotive discipline. The thin purple accents feel like signature light blades, providing a controlled glow that suggests advanced technology rather than the often chaotic RGB strips found on custom FPV builds. The result is a machine that feels both high-tech and incredibly calm.
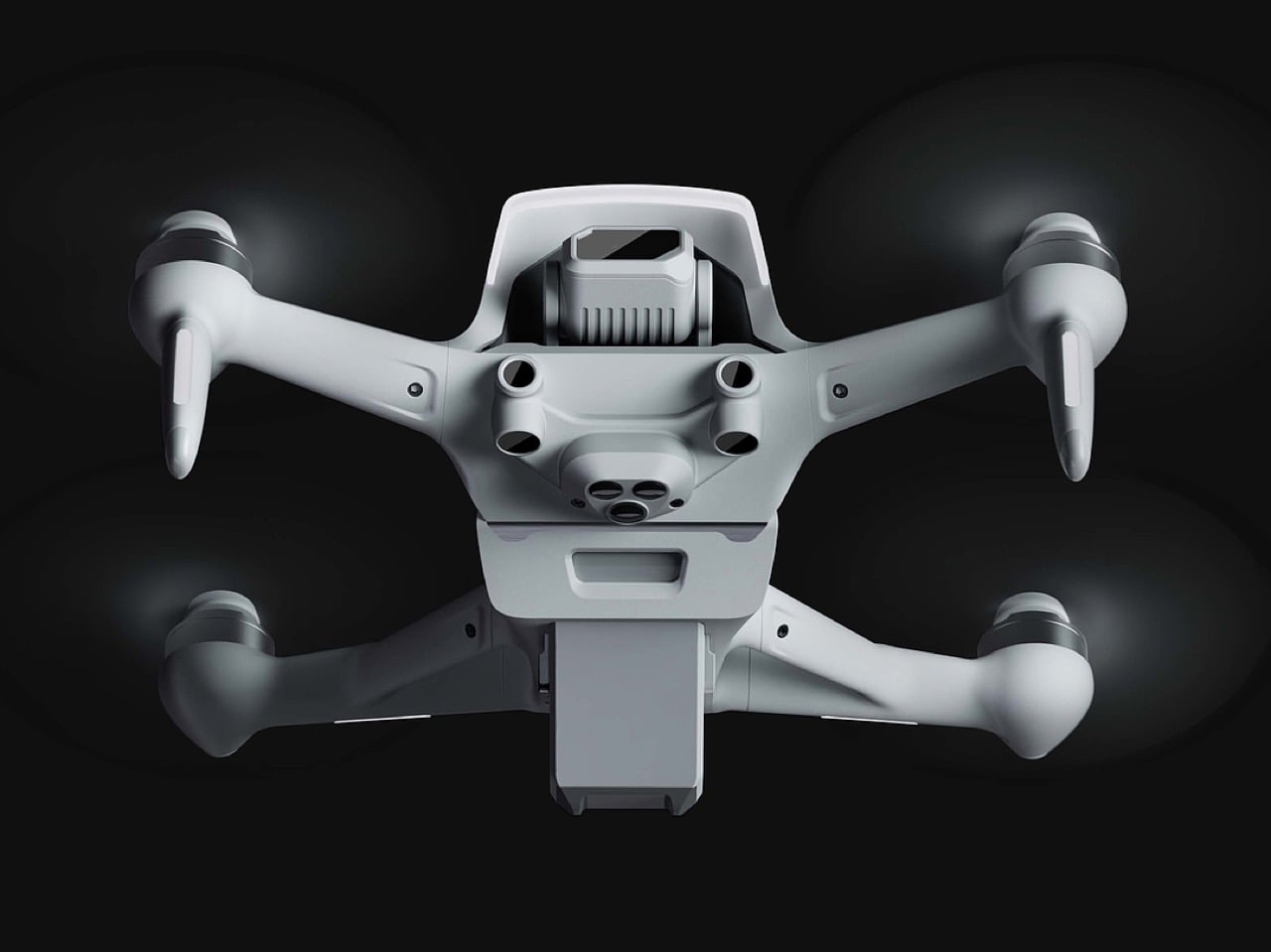

Still, this polished exterior does not compromise the drone’s aggressive spirit. The wide, planted stance and large, efficient-looking propellers signal that it is built for serious performance. A look at the underside reveals a dense cluster of sensors, cooling vents, and structural ribbing, confirming that this is a tool for demanding pilots, not a toy. The designer skillfully balances these hard-core elements with a consumer-friendly sensibility. The battery, for instance, is a perfect example. Branded with the Polestar logo and featuring clear, intuitive LED charge indicators, it feels like a piece of premium electronics, making a critical component feel safe and simple to handle for users who may not be seasoned hobbyists.
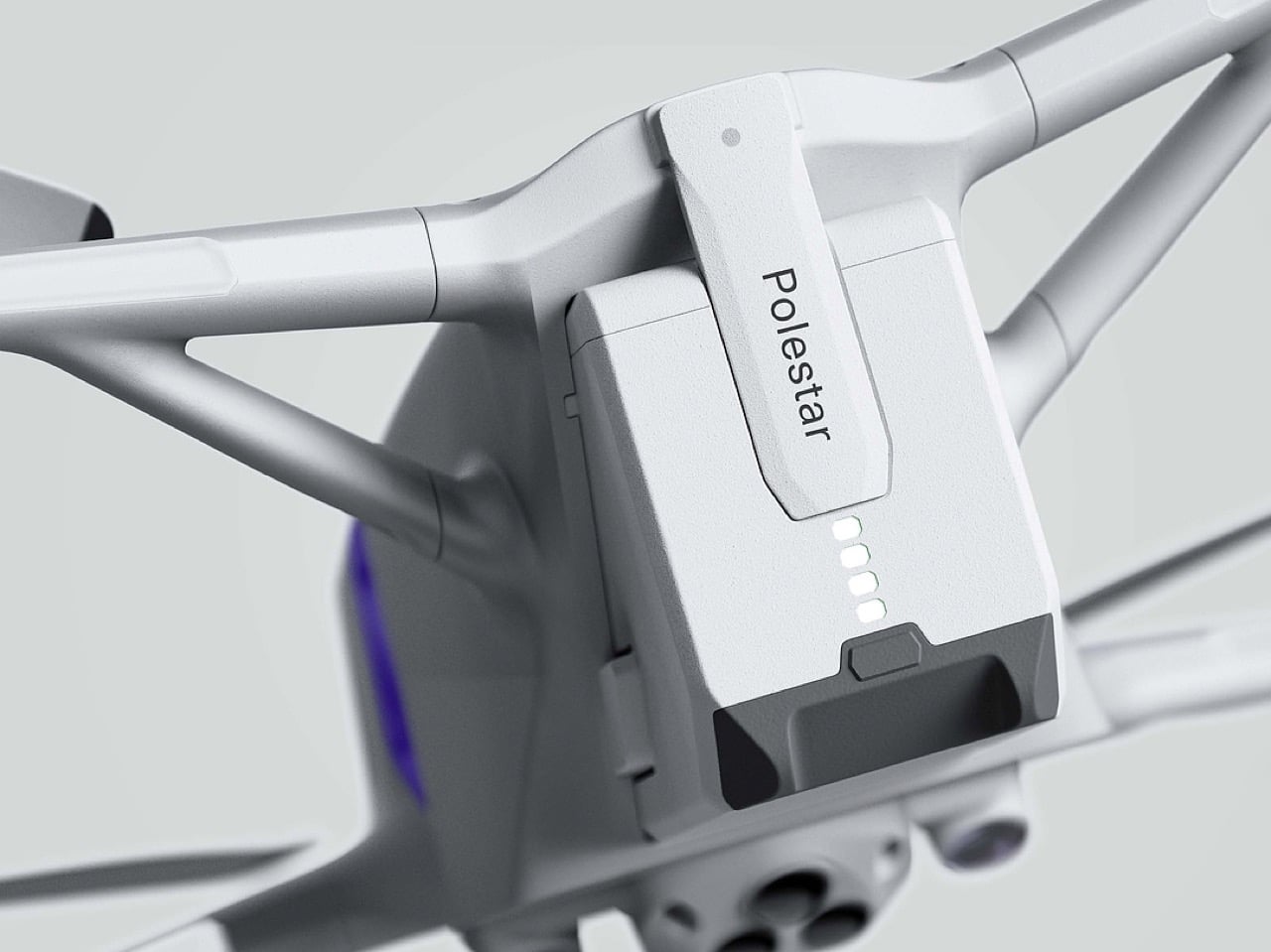
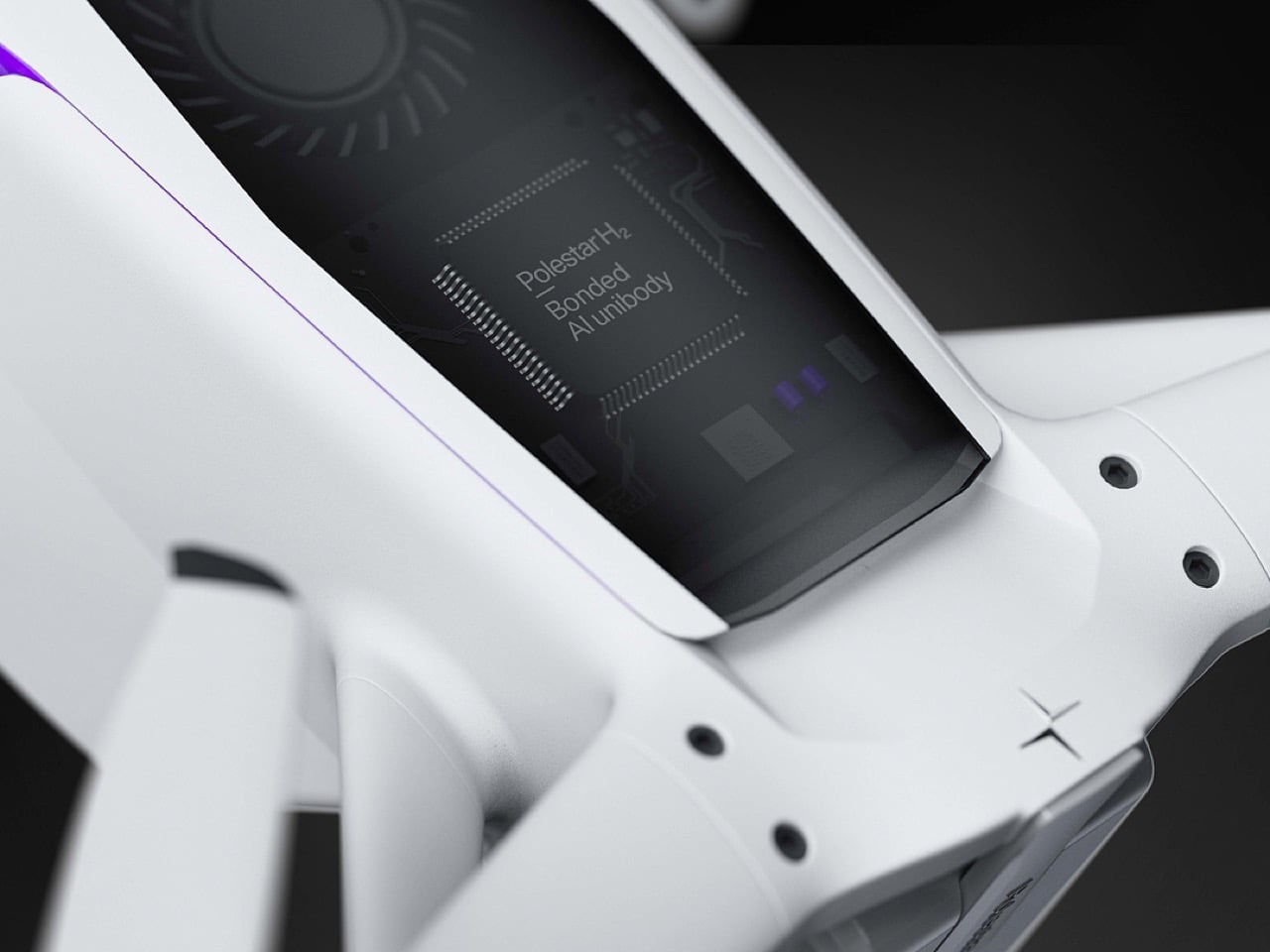


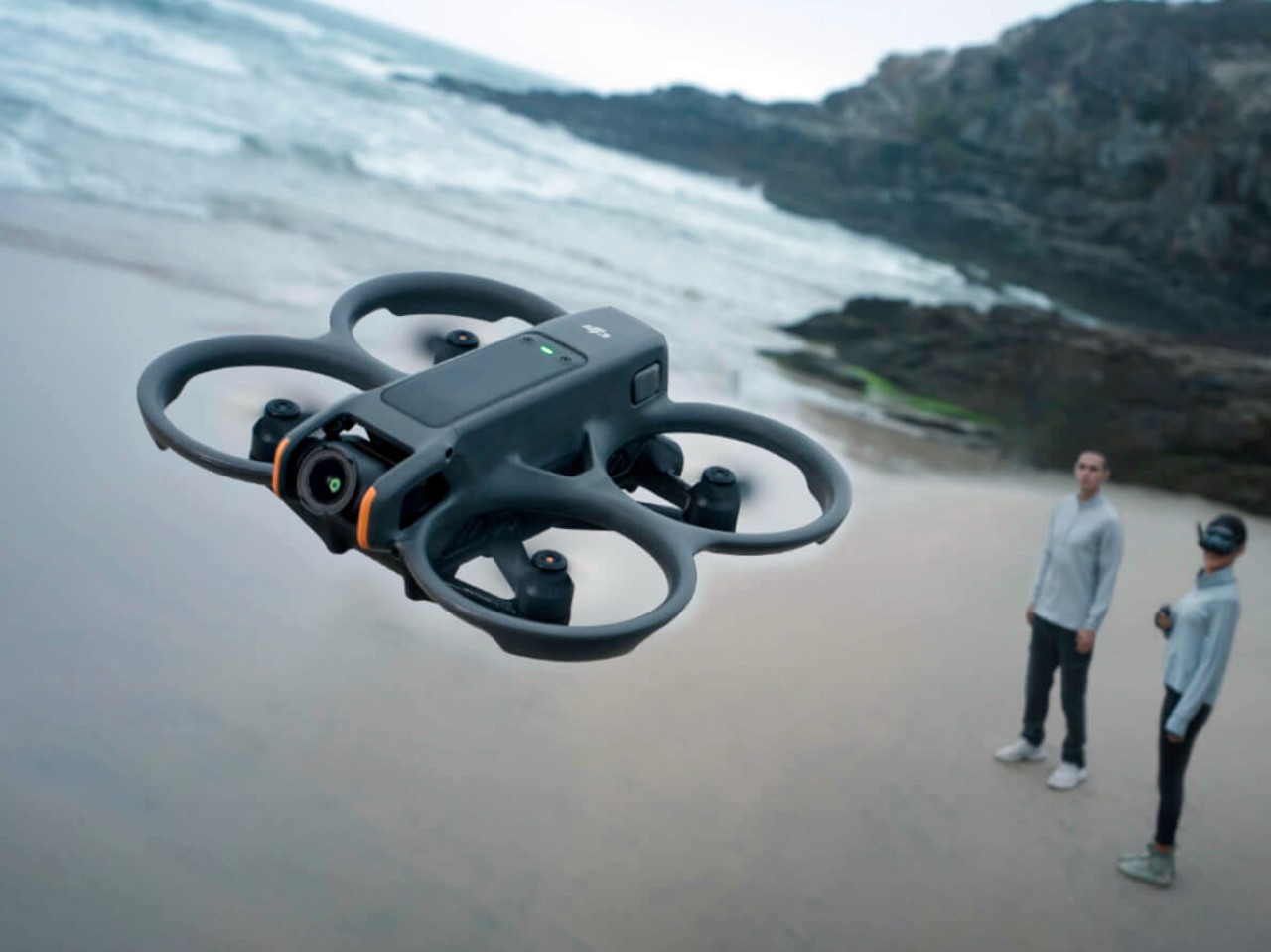
Ultimately, this concept imagines an FPV experience for the tech enthusiast who appreciates sophisticated design as much as raw performance. It is a drone for the person who owns a Polestar, not just because it is electric, but because of its commitment to a clean, forward-looking aesthetic. By merging the robust, modular architecture of a DJI product with the refined, human-centric design of a modern EV, this concept suggests that the future of high-performance drones might be less about exposed wires and carbon fiber, and more about the seamless integration of power and polish.
The post DJI Meets Polestar in This Sleek White FPV Drone Concept That Rejects the Racing Aesthetic first appeared on Yanko Design.