CES 2026 is the year when “AI PC” stops being a buzzword and starts to show up in hardware decisions you can actually touch. Intel’s Core Ultra Series 3 chips and Copilot+ on Windows 11 are pushing laptop makers to rethink what a keyboard, touchpad, and display can do when there is a dedicated NPU and GPU ready to run local models, instead of just sending everything to a server somewhere and waiting for results to trickle back.
Acer’s answer is a two‑track strategy. The Aspire 14 AI and Aspire 16 AI bring Copilot+ and Acer’s own AI tools into mainstream machines that students and young professionals might actually buy, while the Swift AI family, Swift 16 AI, Swift Edge AI, and Swift Go AI, leans harder into thin‑and‑light design, OLED panels, and new interaction surfaces like a giant haptic touchpad for creators and on‑the‑go professionals who need more than a generic ultrabook can offer.
Designer: Acer

Acer Aspire 14 AI and Aspire 16 AI
The Aspire 14 AI and Aspire 16 AI are the kind of laptops that end up doing everything, from lecture notes and spreadsheets to light photo edits and streaming. Both are built around Intel Core Ultra Series 3 processors, up to a Core Ultra 9 386H with the new Intel Graphics, paired with up to 32 GB of LPDDR5X memory and up to 2 TB of PCIe Gen 4 SSD storage on the 16‑inch, or 1 TB on the 14‑inch. That headroom handles hybrid workflows where a dozen tabs, a video call, and a Copilot window are all open at once.
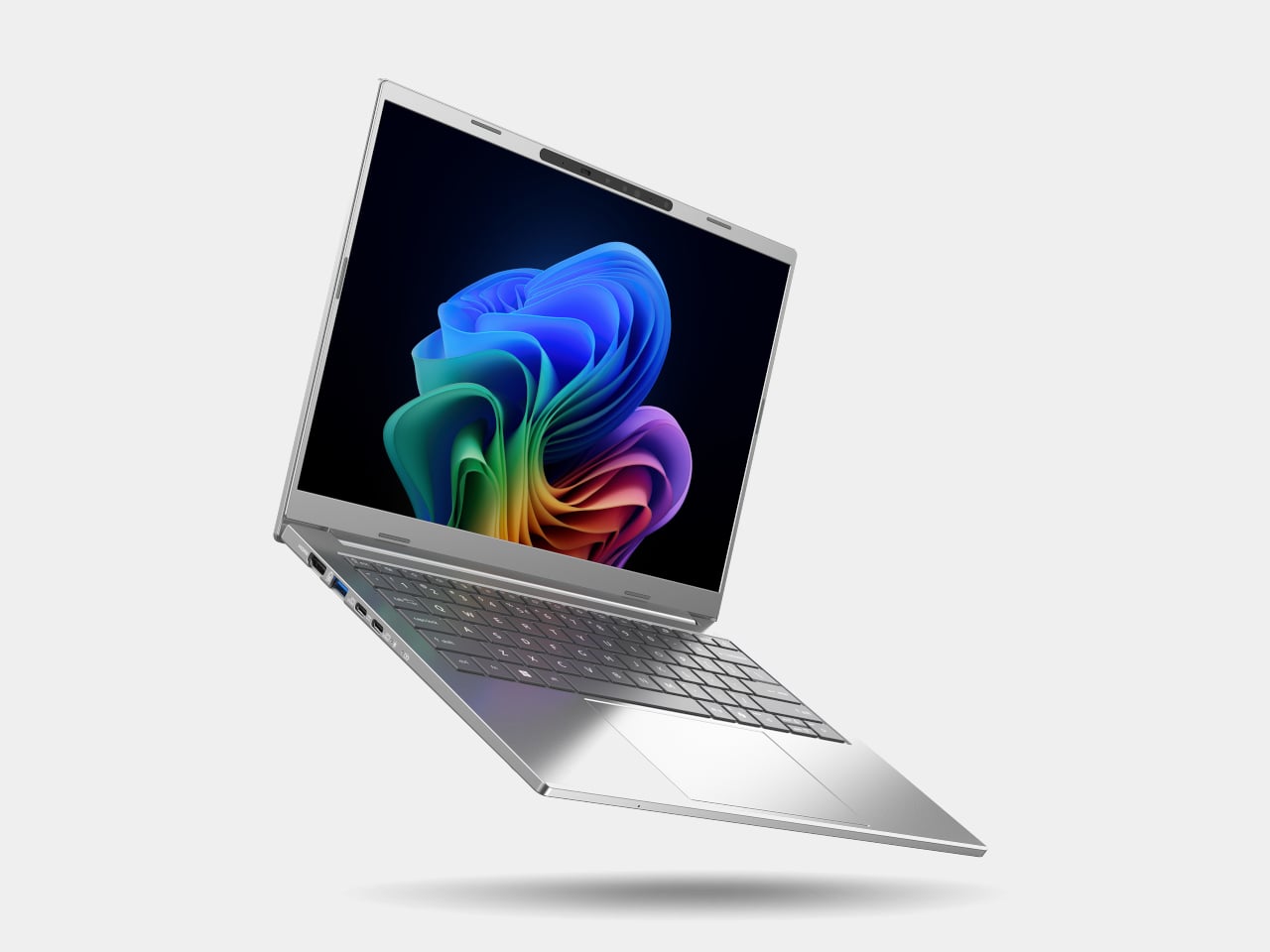
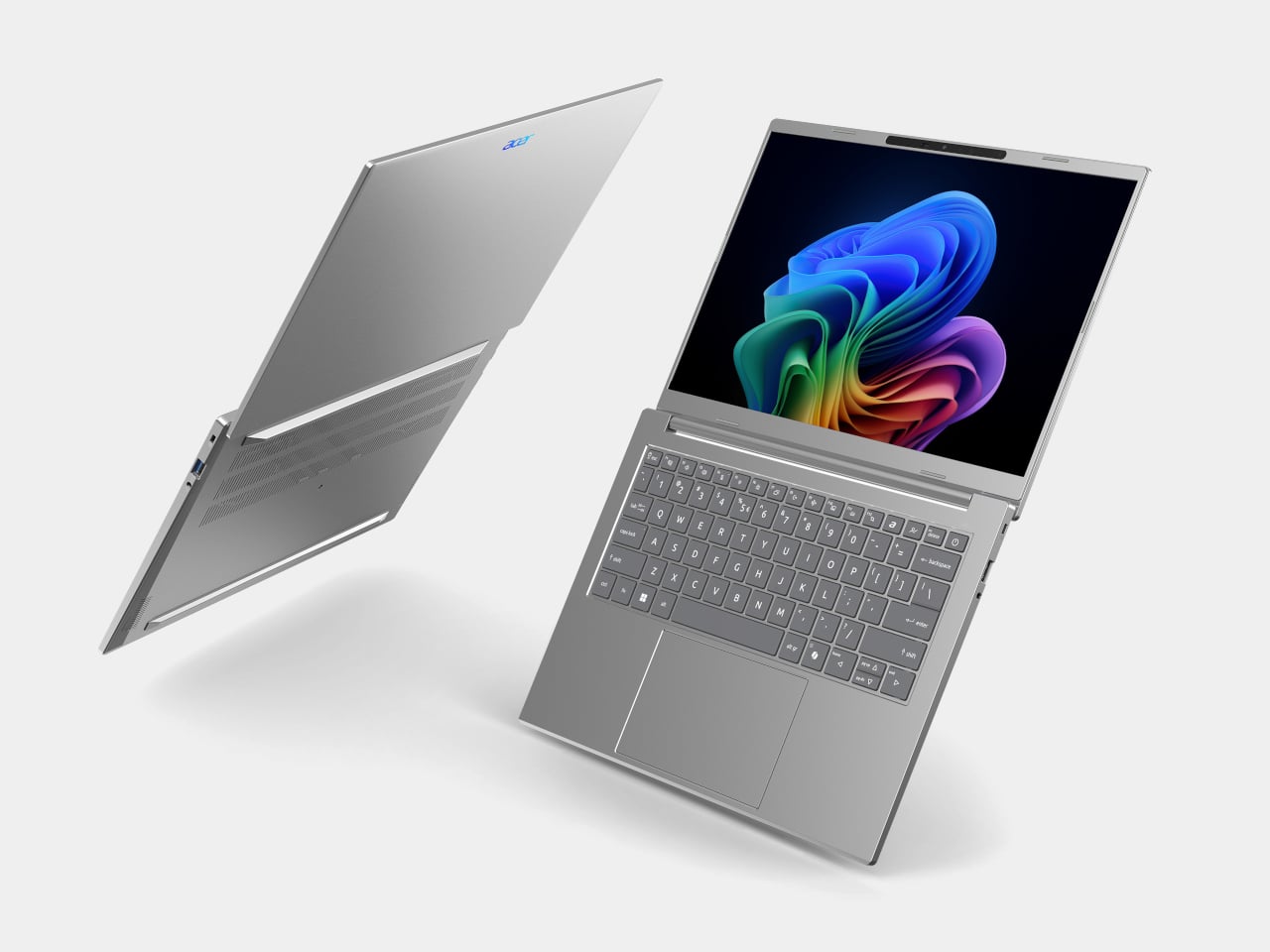


Acer Aspire 14 AI
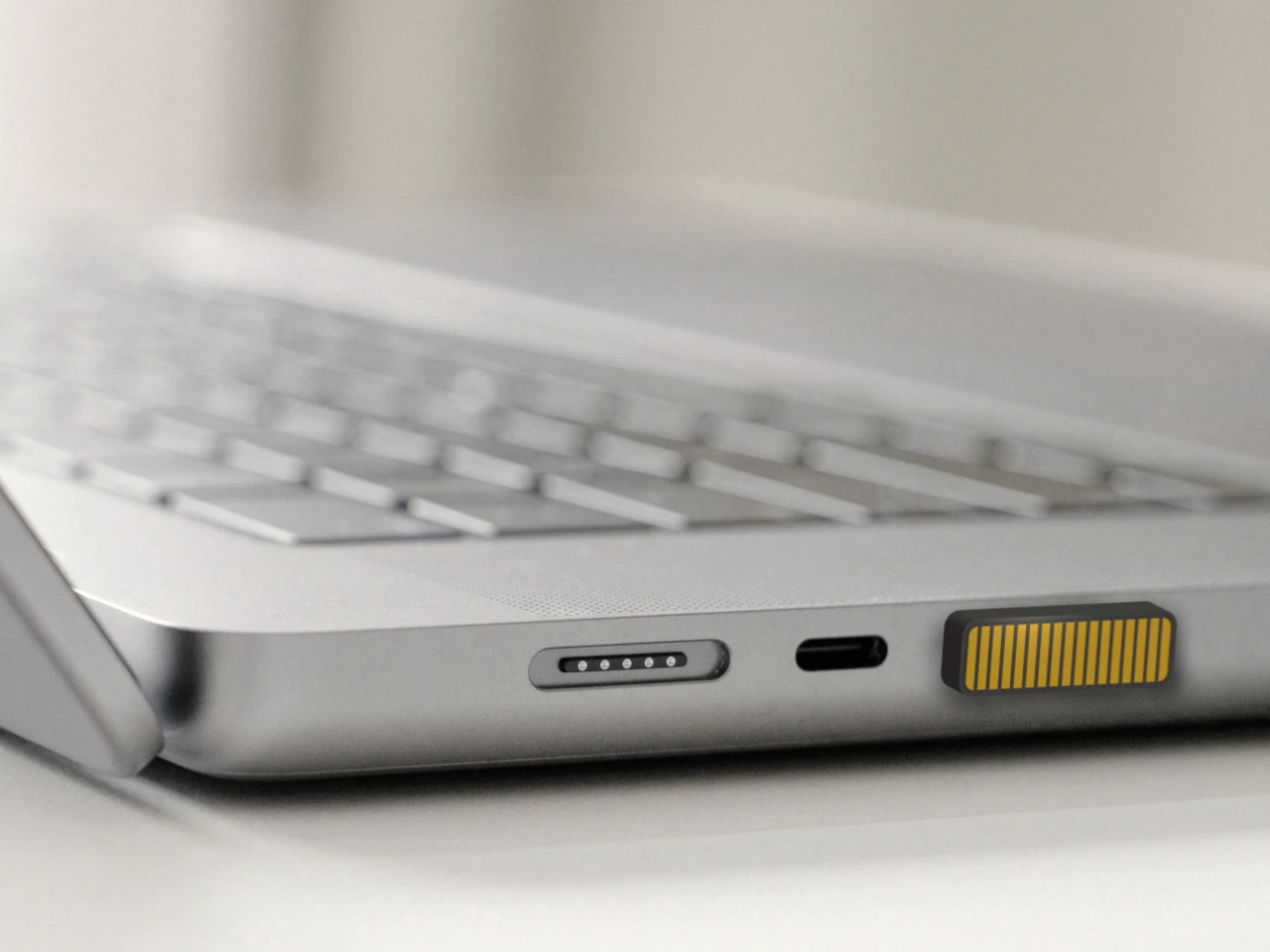
Both sizes use 16:10 WUXGA displays with refresh rates up to 120 Hz, with options for touch, non‑touch, and even OLED panels, which is unusual in the mainstream segment. The full‑flat 180‑degree hinge lets the screen lie completely flat on a table, useful when two people are huddled over a project or a group is reviewing a design. Large touchpads, thin‑and‑light chassis, and ports like Thunderbolt 4, HDMI 2.1, and USB‑A, with Wi‑Fi 6E and Bluetooth 5.3, keep them plugged into modern peripherals without needing dongle bags.
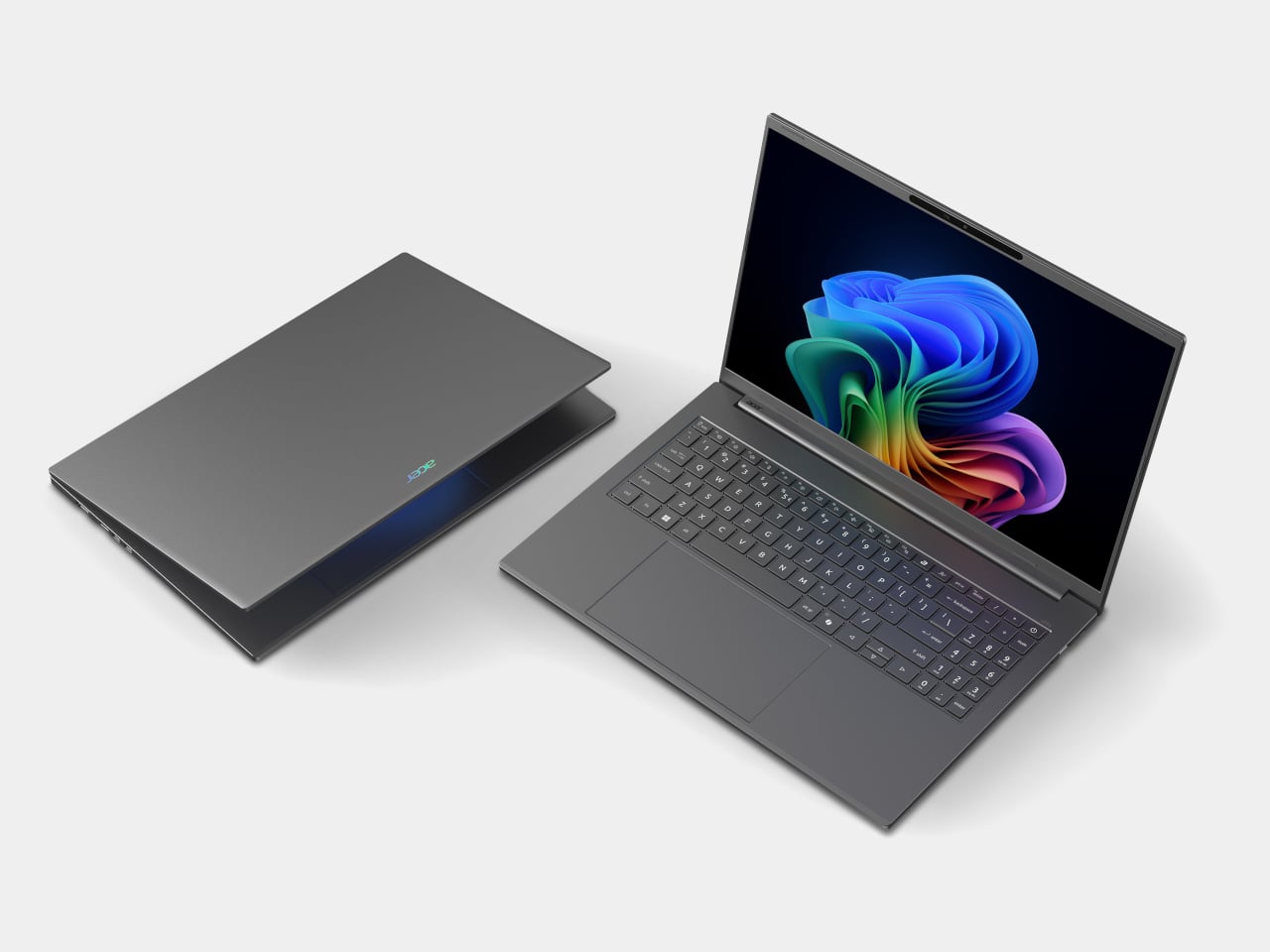


Acer Apsire 16 AI
Acer layers its own AI on top of Windows 11’s Copilot experiences. Intelligent Space acts as a hub for AI tools, AcerSense handles diagnostics and optimization, PurifiedView and PurifiedVoice clean up video and audio in calls, and My Key is a programmable hotkey that can trigger specific Copilot+ features like Live Captions with real‑time translation. For someone bouncing between languages and remote meetings, those small touches make the AI feel less like a gimmick and more like part of the daily routine.
Acer Swift 16 AI
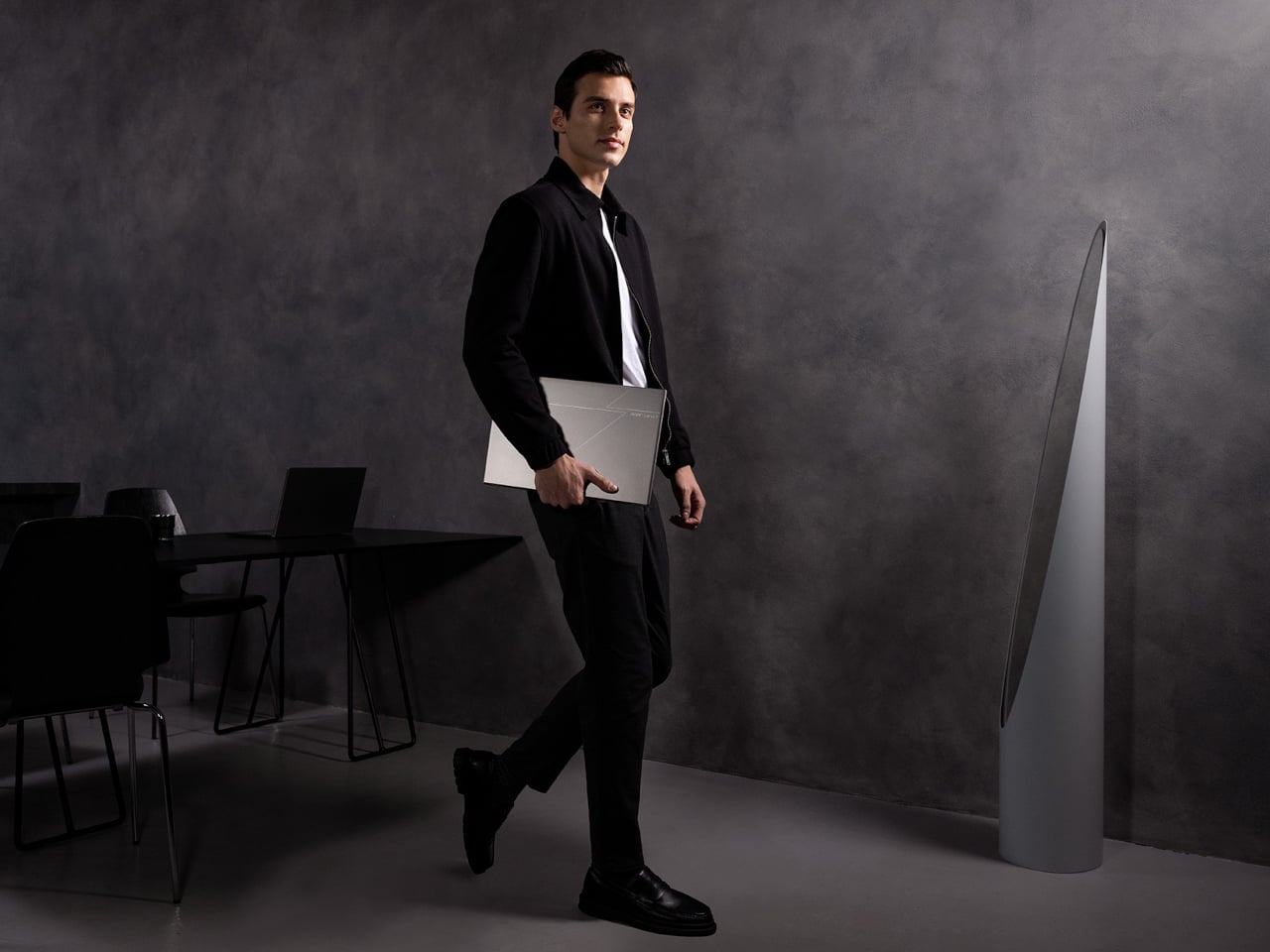
The Swift 16 AI is Acer’s CES flagship for people who live in creative apps. It runs up to an Intel Core Ultra X9 388H with Intel Arc B390 graphics, up to 32 GB of LPDDR5X, and up to 2 TB of SSD storage. The 16‑inch 3K OLED WQXGA+ display, with 120 Hz refresh, 100% DCI‑P3, and VESA DisplayHDR True Black 500, gives animators, video editors, and illustrators a bright, color‑accurate canvas that still fits in a 14.9 mm‑thin aluminum chassis.
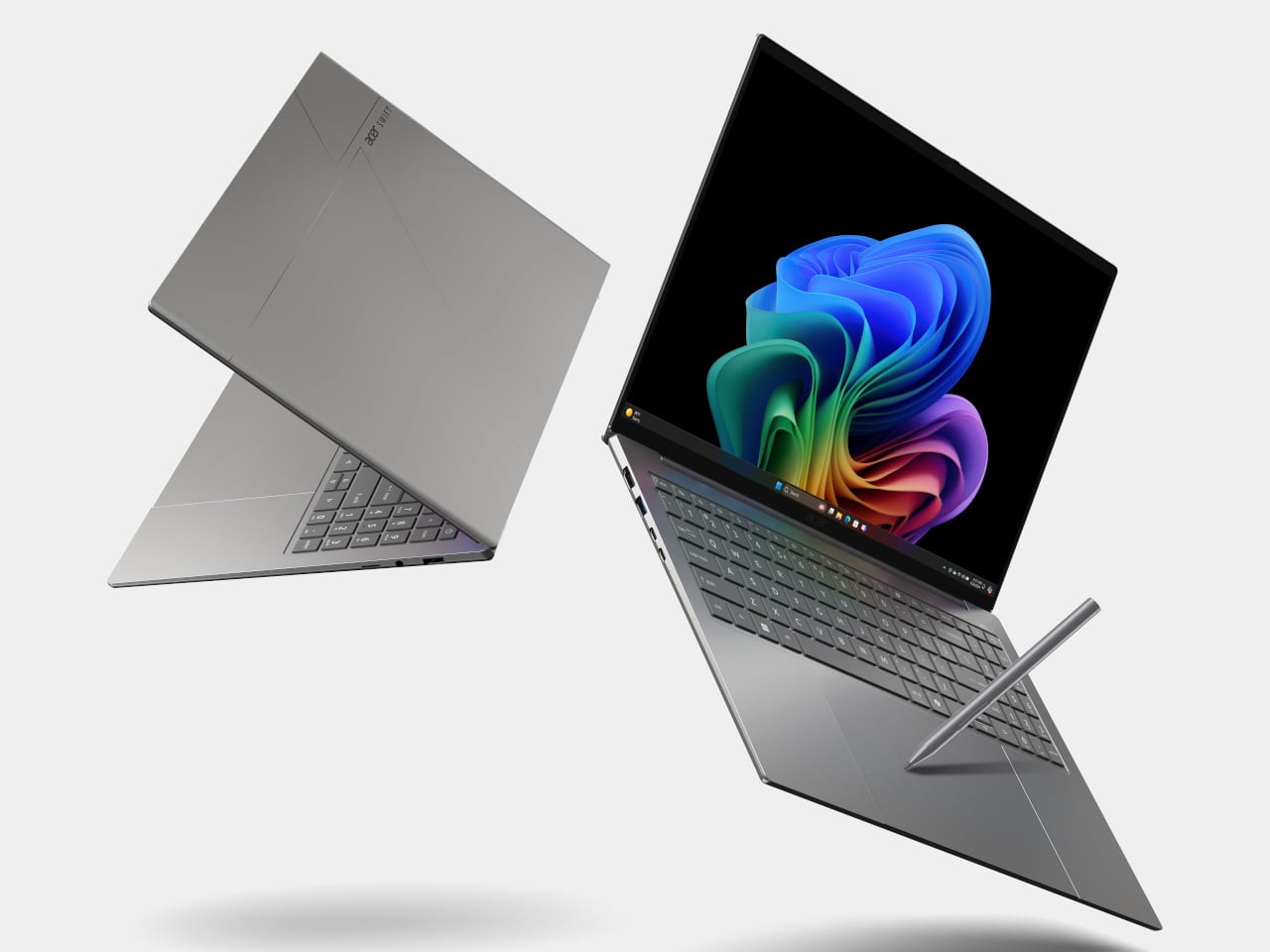

Acer Swift 16 AI
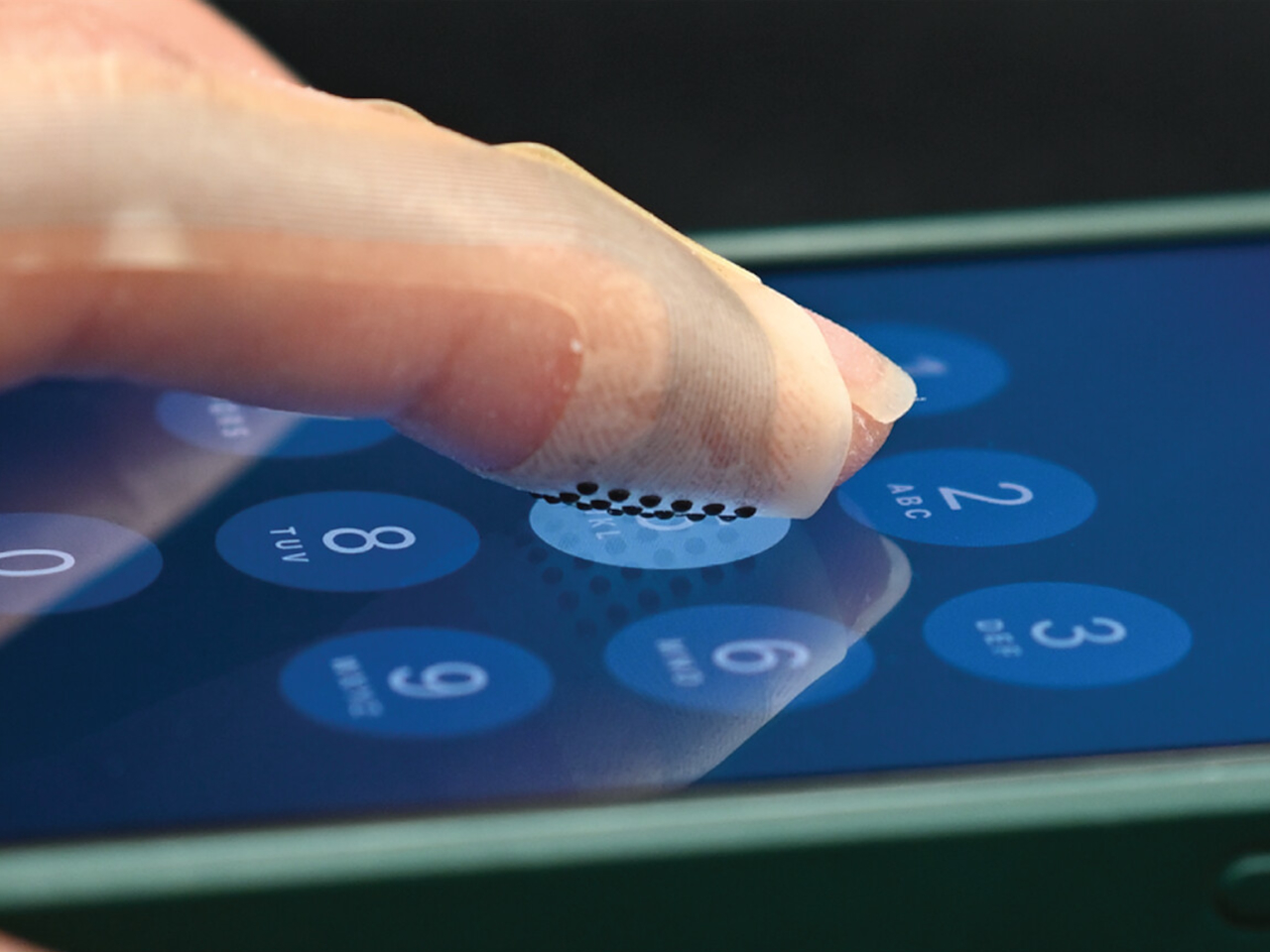
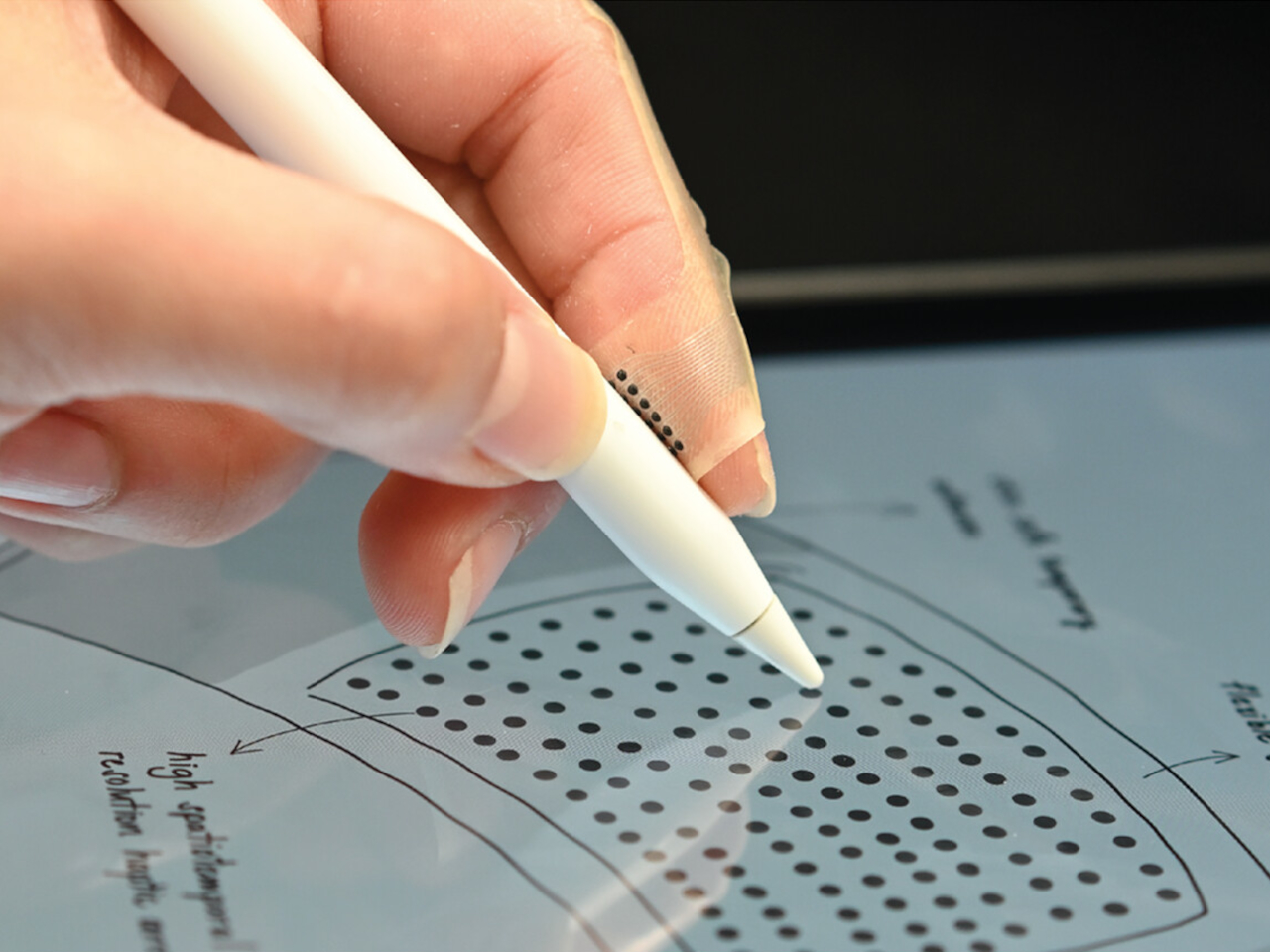
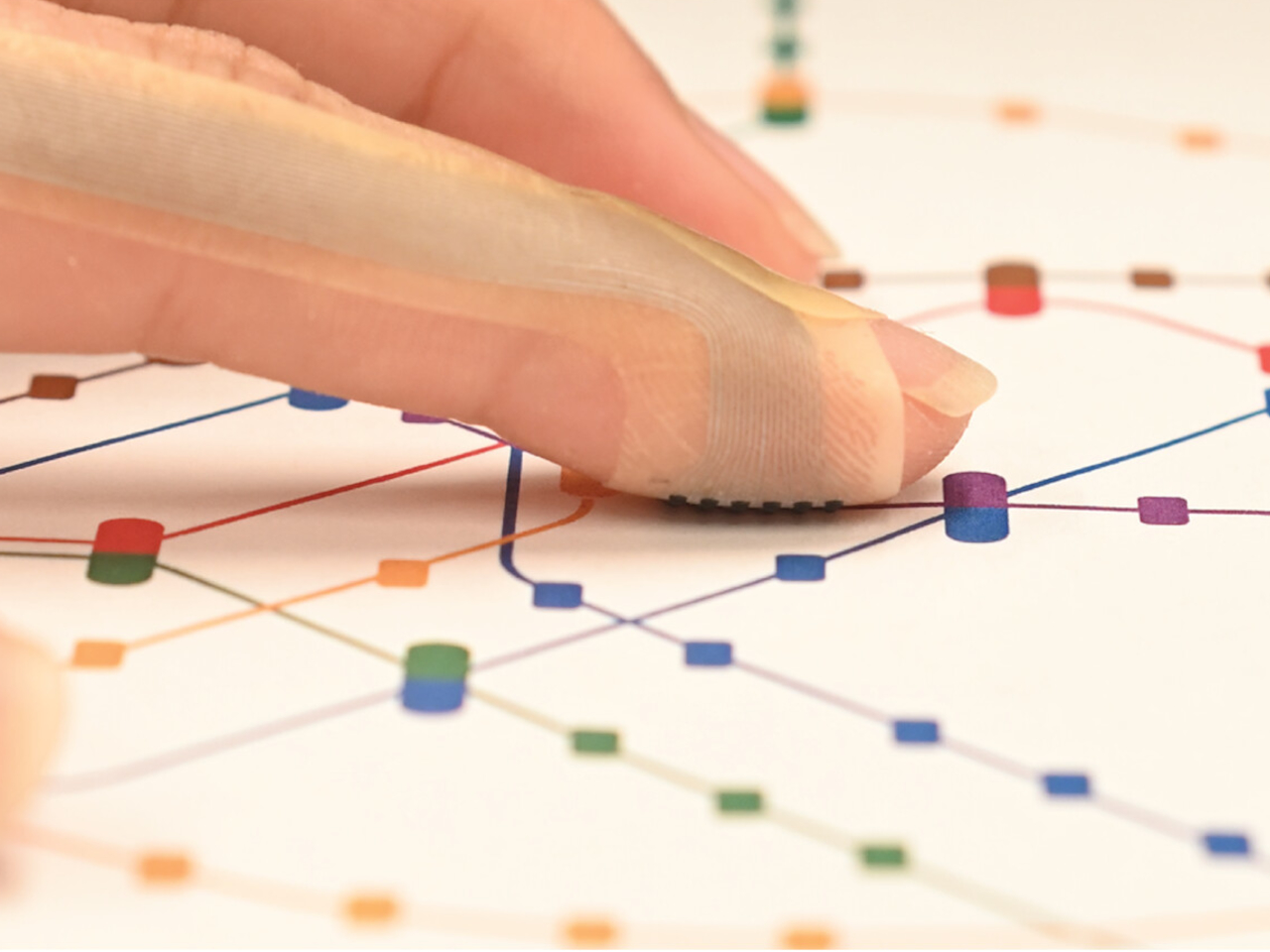
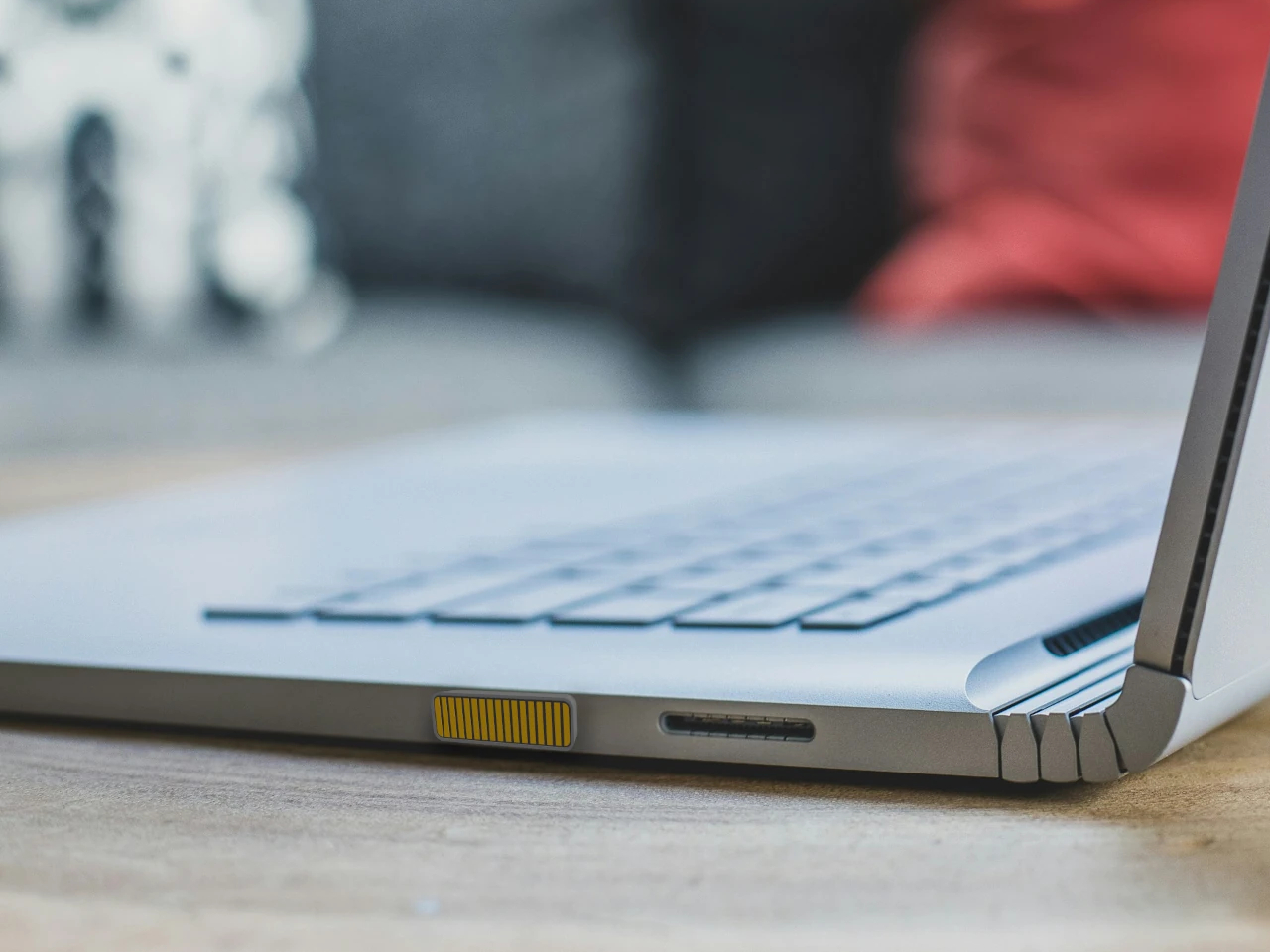
The headline feature is the world’s largest haptic touchpad, a 175.5 mm × 109.7 mm glass‑covered surface that supports MPP 2.5 stylus input. You can sketch, scrub timelines, or manipulate 3D models directly on the pad while the screen stays clear for reference or output. Haptics provide precise feedback with fewer moving parts, and Acer’s AI tools, accessed through the Intelligence Space hub, can tie into that surface for gesture‑driven creative workflows that feel more like using a tablet than a traditional laptop.
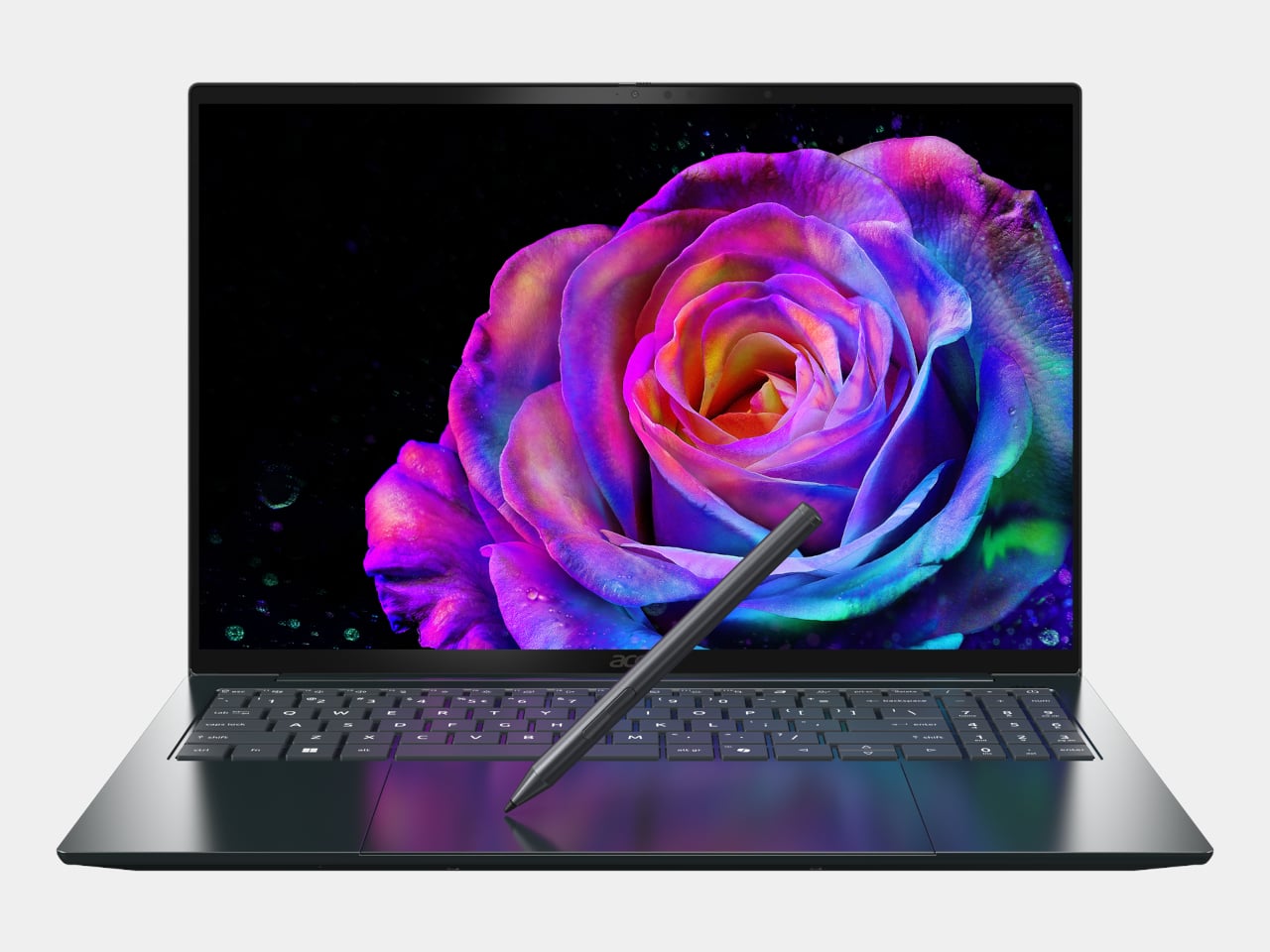

Acer Swift 16 AI (Best Buy Chassis)
Connectivity and audio round it out with Wi‑Fi 7, Bluetooth 5.4, dual Thunderbolt 4 USB‑C, USB‑A, HDMI 2.1, a MicroSD slot, DTS:X Ultra speakers, and an FHD IR camera. A 70 Wh battery with up to 24 hours of video playback on certain configs means the machine can survive long flights or a full day of on‑site shoots without hunting for an outlet.
Acer Swift Edge 14 AI and Swift Edge 16 AI


Acer Swift Edge 14 AI
The Swift Edge 14 AI and 16 AI focus on portability for people who count grams in their backpacks. Built from a stainless steel‑magnesium alloy chassis, the 14‑inch model weighs under 1 kg and measures just under 14 mm thick, yet still meets MIL‑STD 810H durability standards. Both sizes run up to Intel Core Ultra 9 386H processors with Intel Graphics, up to 32 GB of LPDDR5X, and up to 1 TB of PCIe Gen 4 SSD storage, so they are not trading performance for weight.
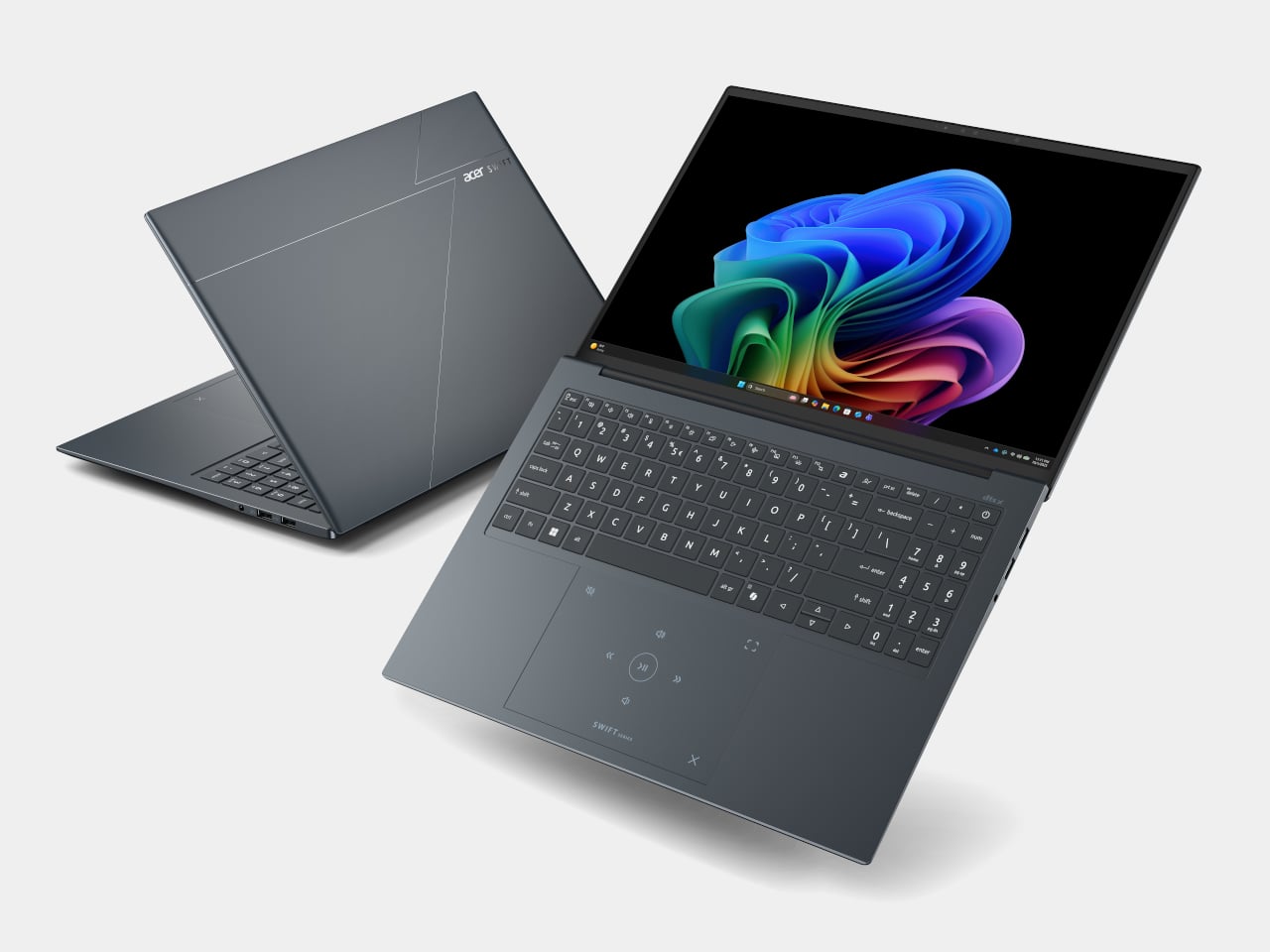


Acer Swift Edge 16 AI
Display options go up to 3K WQXGA+ OLED with 120 Hz refresh and 100% DCI‑P3, making them surprisingly capable for color‑sensitive work on the road. Acer’s multi‑control touchpads add gesture layers for media, presentations, and conferencing, letting you adjust volume, skip tracks, or manage calls without hunting for on‑screen controls. FHD IR cameras with Human Presence Detection, DTS:X Ultra speakers, Wi‑Fi 7, Bluetooth 6.0, and Thunderbolt 4 ports round out a package that feels tuned for frequent flyers who still need a proper workstation when they land.
Acer Swift Go 14 AI and Swift Go 16 AI
The Swift Go 14 AI and 16 AI sit as the “just right” machines in the Swift family, balancing performance, portability, and a slightly more accessible entry point. They use up to Intel Core Ultra X9 388H processors with Intel Arc B390 graphics, up to 32 GB of LPDDR5X memory, and up to 1 TB of SSD storage. The laser‑etched aluminum chassis opens a full 180 degrees, making them easy to use in cramped lecture halls or coffee shops.
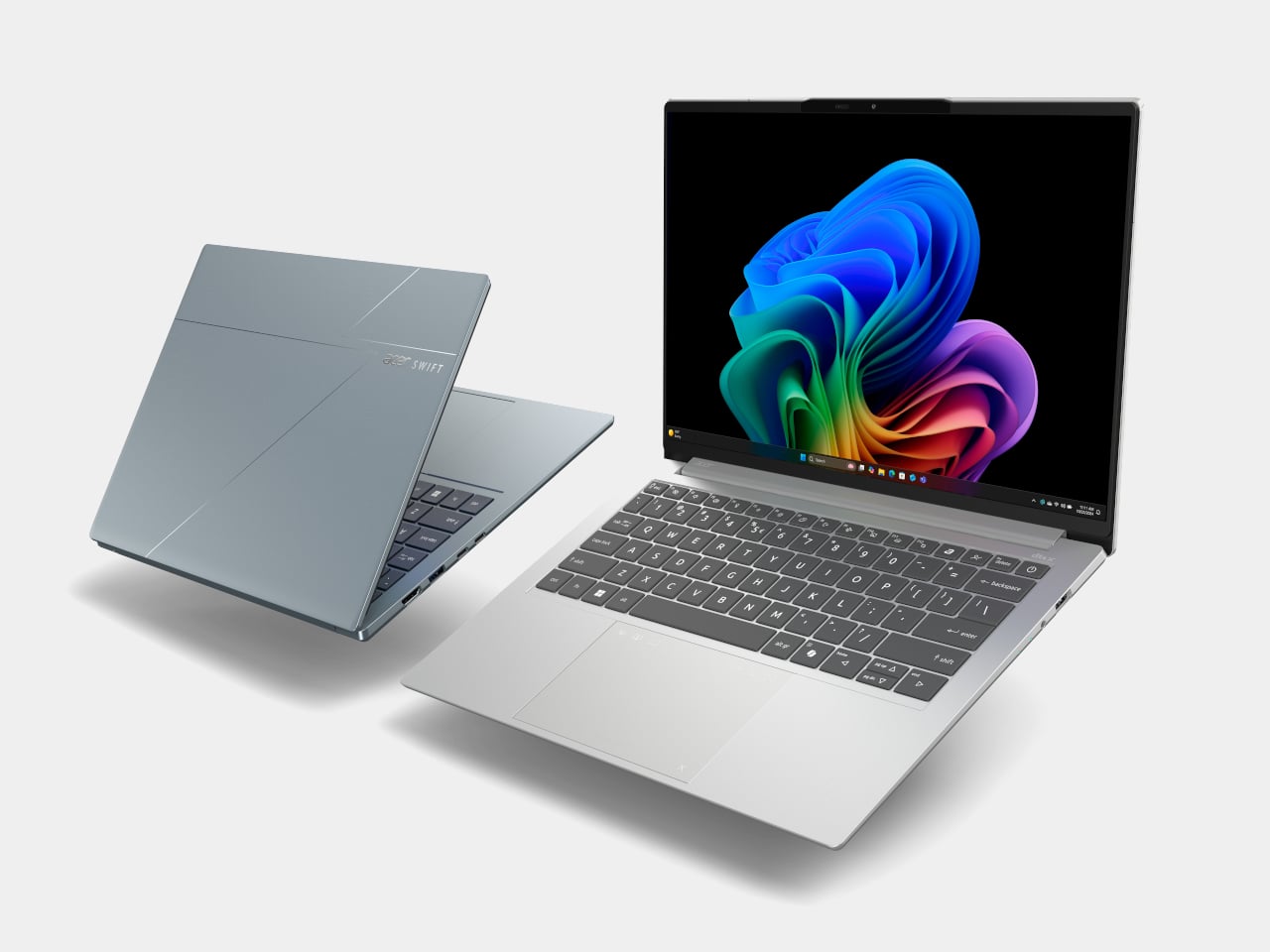

Acer Swift Go 14 AI
Display options include 2K WUXGA and 3K WQXGA+ OLED panels with wide color gamuts and smooth refresh rates, giving everyday productivity machines a surprisingly premium visual experience. The 5 MP IR cameras with HDR and Human Presence Detection improve video calls and privacy, while DTS:X Ultra speakers and multi‑control touchpads make them feel more like compact media centers than basic ultrabooks. Wi‑Fi 7, Bluetooth up to 6.0, and dual Thunderbolt 4 ports keep them ready for fast networks and external GPUs or docks.
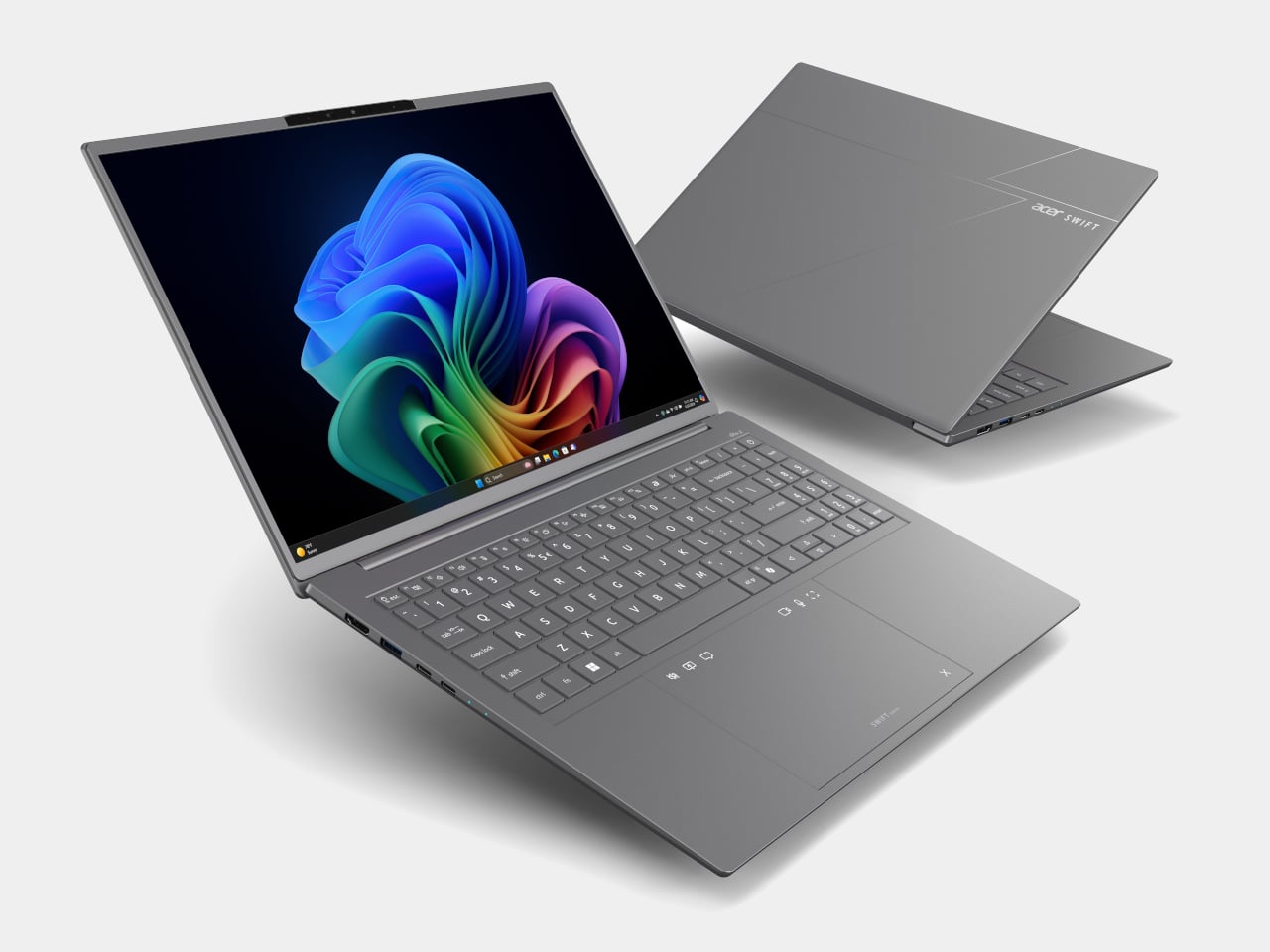

Acer Swift Go 14 AI
As Copilot+ PCs, the Swift Go models support features like Click to Do, Copilot Voice, and Copilot Vision, with Acer’s own Assist, VisionArt, User Sensing, PurifiedView, PurifiedVoice, and My Key layered on top. For someone who wants a thin‑and‑light that can handle both spreadsheets and AI‑assisted creative work, they are the approachable entry point into Acer’s more experimental Swift AI world, offering premium design without the flagship price or the haptic touchpad that some people might not know what to do with.
Acer at CES 2026: Laptops Designed for the AI Era
Aspire AI brings Copilot+ and Acer’s AI suite into familiar 14‑ and 16‑inch shells with optional OLED and 180‑degree hinges for collaboration, while Swift AI experiments with haptic touchpads, under‑1 kg magnesium shells, and OLED‑everywhere displays for creators and travelers. The CES 2026 message is that AI is no longer just a feature buried in software menus, it is starting to shape the hardware itself, from how you press on a touchpad to how light your laptop feels in a bag, which is exactly the kind of shift Yanko Design readers expect from the start of the year when everyone announces what laptops are supposed to look and feel like for the next twelve months.

The post Acer Swift 16 AI Has World’s Largest Haptic Touchpad With Stylus Support first appeared on Yanko Design.