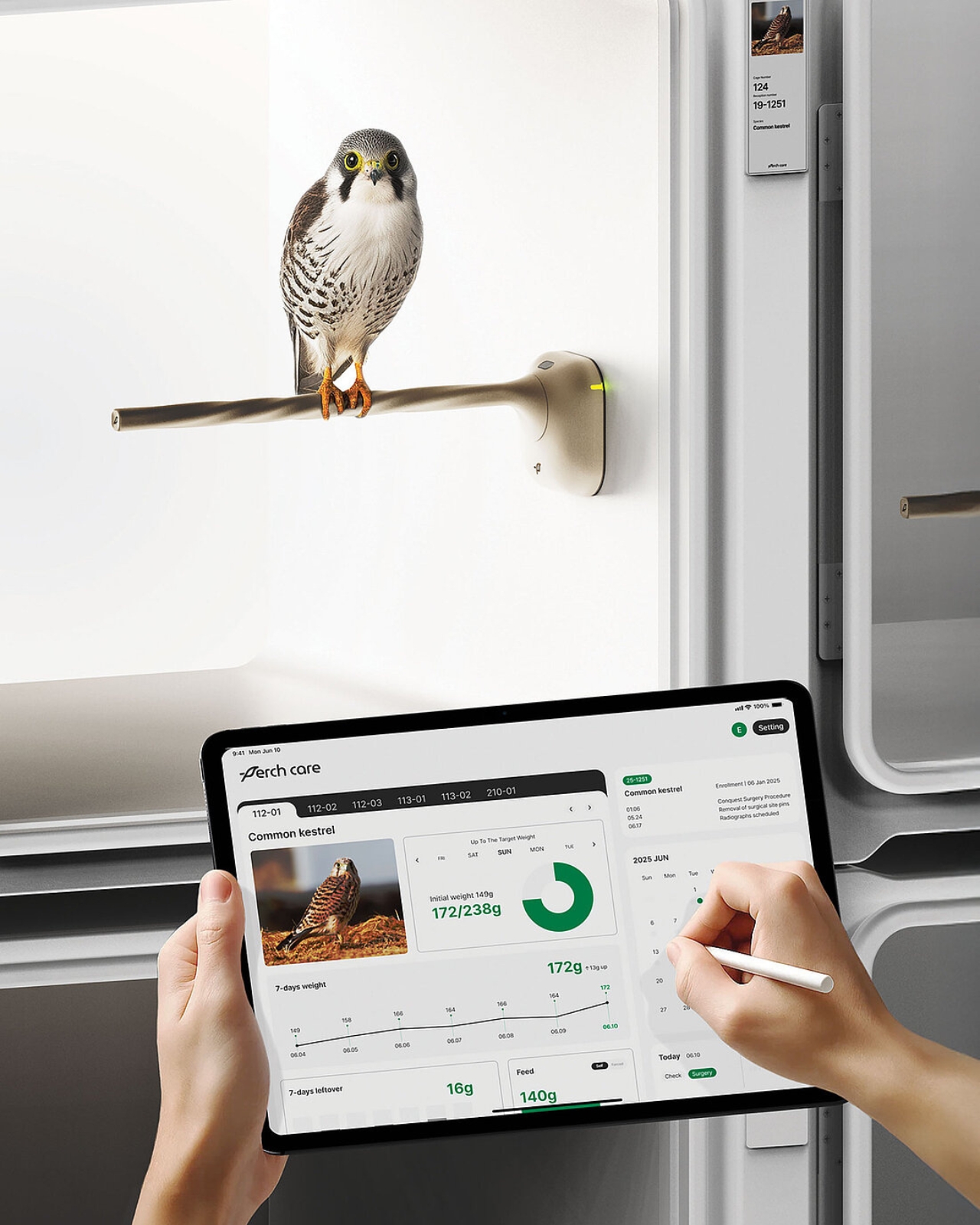
Picture this: you’re a wildlife rescuer trying to nurse an injured falcon back to health. Every few days, you need to catch the bird, restrain it, and place it on a scale. The bird panics, thrashing and screeching. Your heart races as you try not to get talons to the face. Sometimes, the stress alone can kill the very creature you’re trying to save. It’s a nightmare scenario that plays out in rescue centers worldwide, but a team of Korean designers just might have cracked the code on a better way.
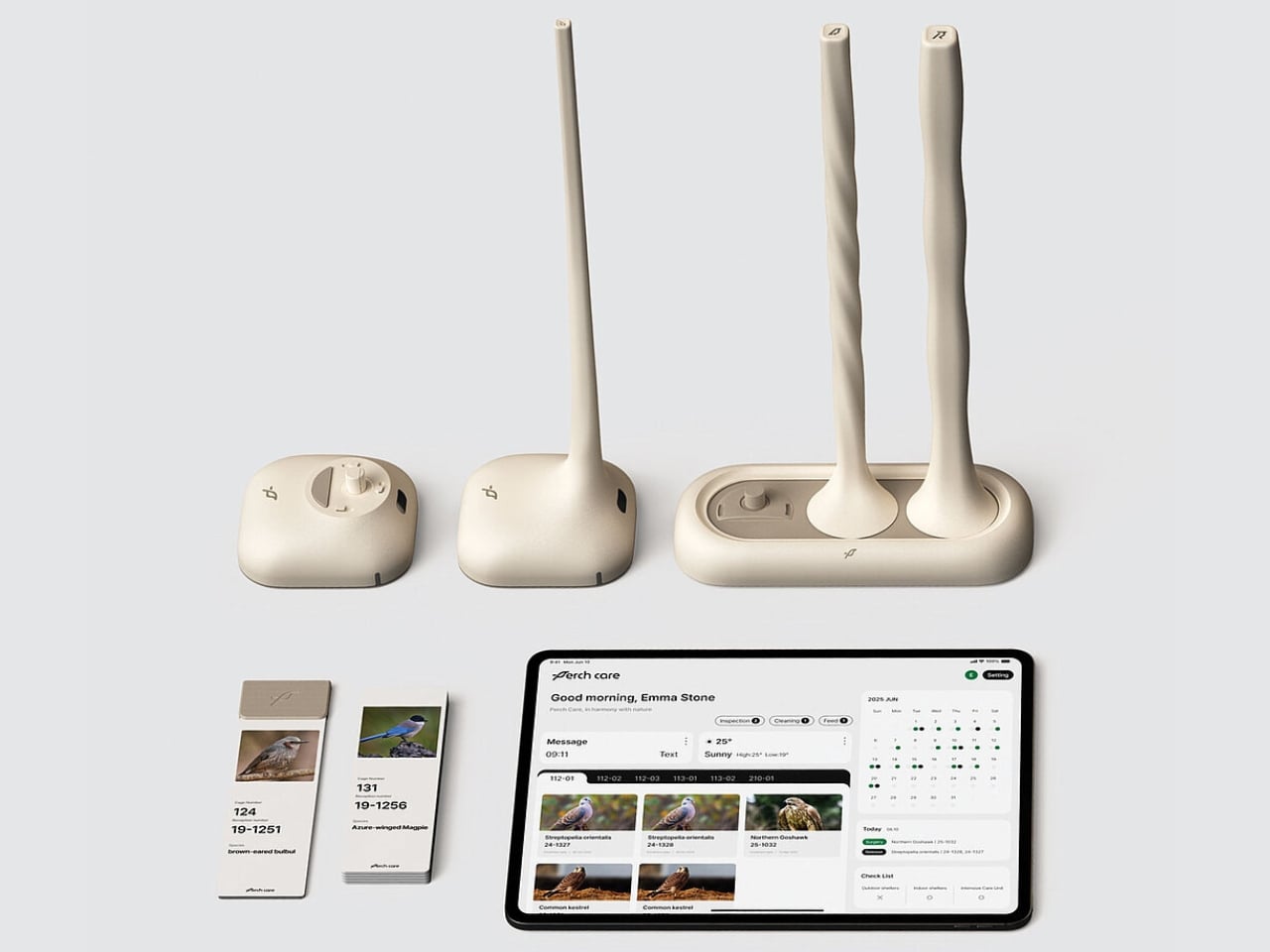
Enter PerchCare, a sleek smart perch that’s basically the Fitbit of the bird world, minus all the drama. Created by designers Lee Hanung, Kwon Hyeokwoo, Choi Yoonji, and Kim Minji, this Red Dot Award-winning design tackles a problem most of us never knew existed. But for wildlife rehabilitators, it’s been a persistent thorn in their side for decades.
Designers: Lee Hanung, Kwon Hyeokwoo, Choi Yoonji, Kim Minji

Here’s the thing about wild birds: they’re masters of disguise when it comes to illness. It’s a survival instinct hardwired into their DNA. In the wild, showing weakness makes you an easy target for predators, so birds will act perfectly fine even when they’re seriously unwell. That’s why tracking their weight becomes absolutely crucial. It’s often the only reliable indicator that something’s wrong before it’s too late. The design team didn’t just dream this up in a vacuum. They spent time interviewing rescuers at the Gyeonggi Northern Wildlife Rescue Center, getting their hands dirty with real-world insights. What they heard was consistent: the current method of weighing birds is dangerous for everyone involved. Birds get stressed to the point of harm, and caretakers risk injury every single time.
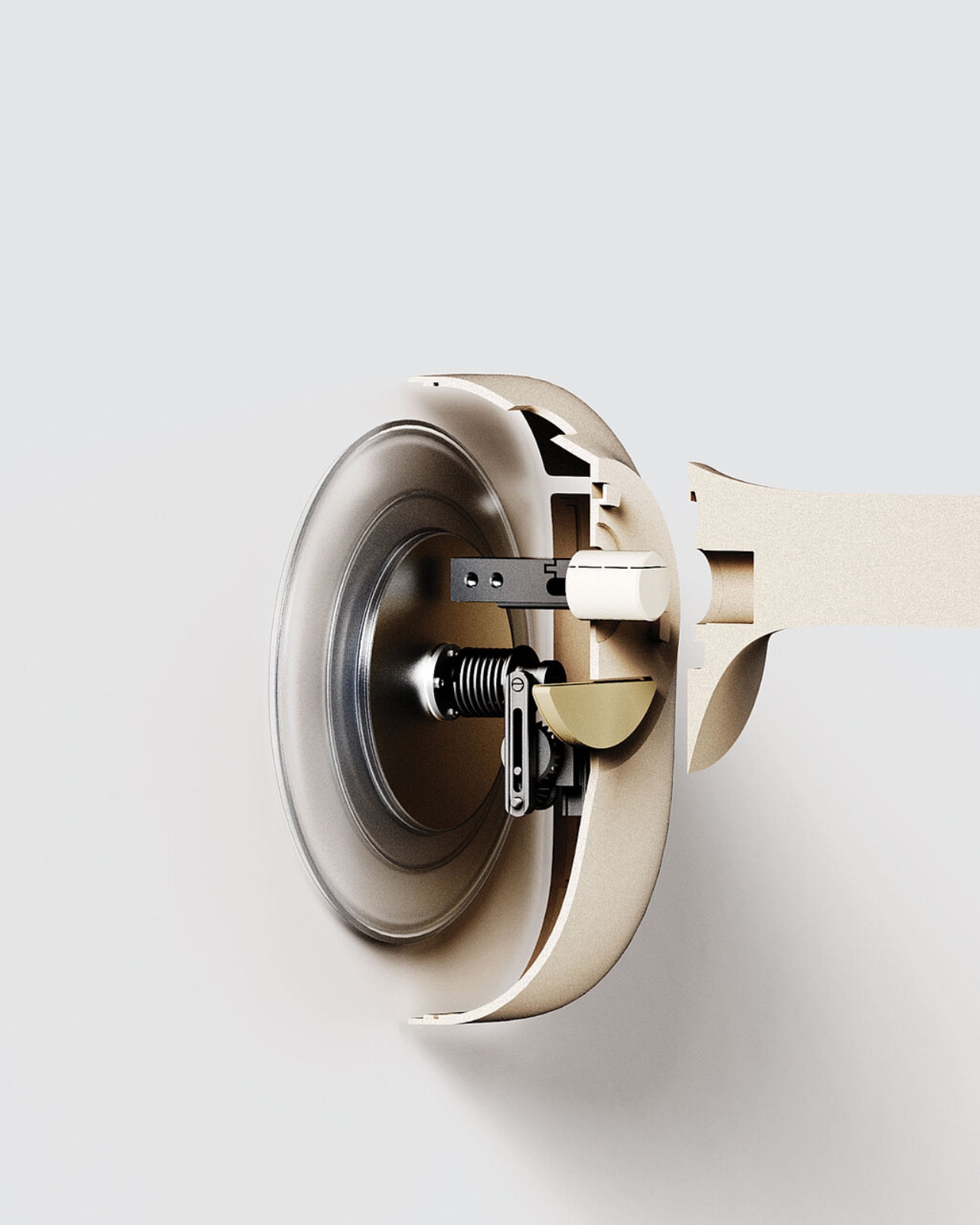
So how does PerchCare work its magic? The genius lies in its simplicity. Instead of forcing an unnatural interaction, it turns an everyday object into a monitoring device. Birds need to perch anyway, right? It’s what they do. By embedding weighing technology directly into something that mimics a natural branch, PerchCare lets birds just be birds while quietly collecting vital health data in the background.
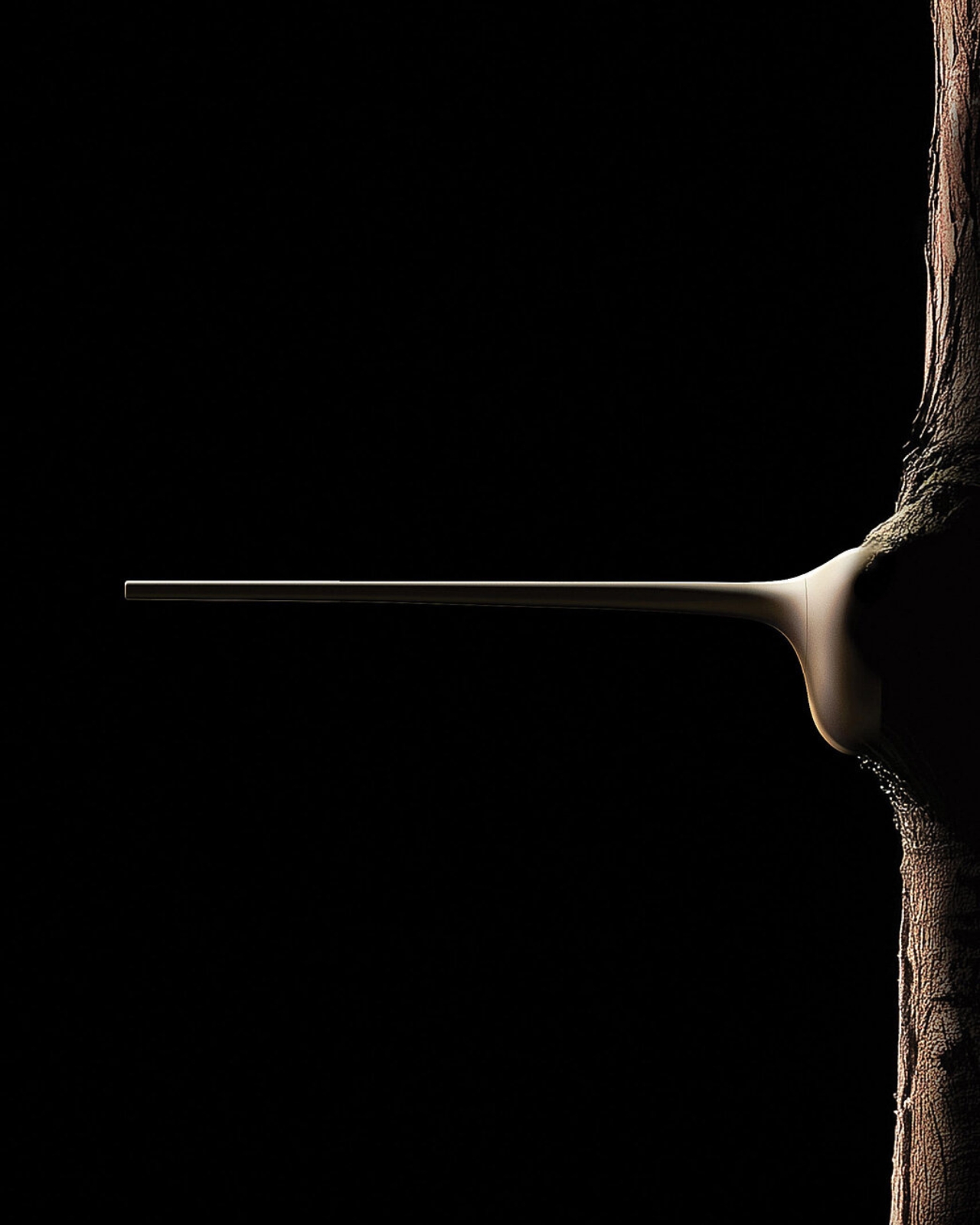
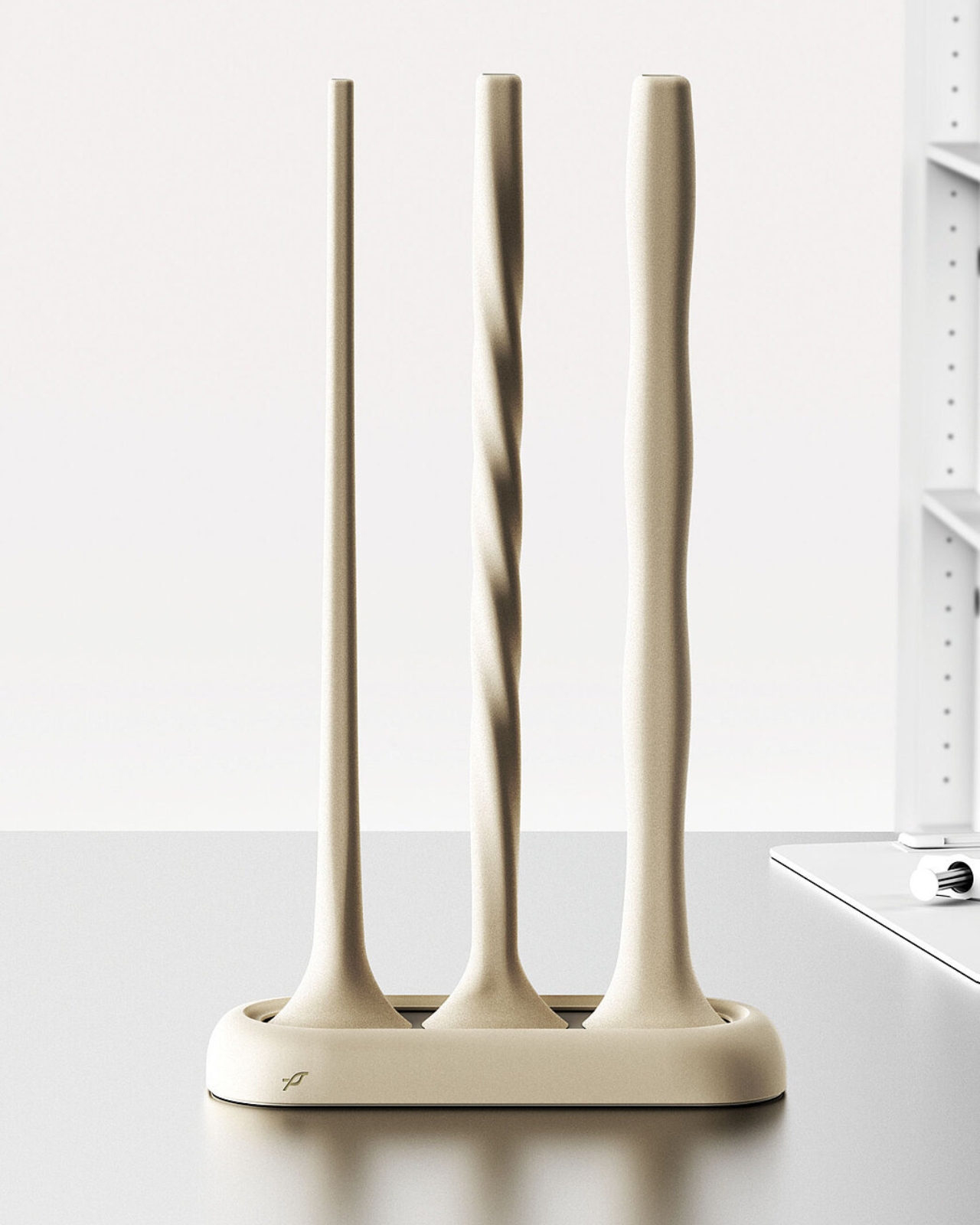
The perch itself looks refreshingly minimal, almost Apple-esque in its aesthetic. It comes in multiple sizes to accommodate different species, from tiny songbirds to larger raptors. The mounting system uses suction cups, which means installation is as easy as sticking it to the cage wall. No tools, no complicated setup, no engineering degree required. But the really cool part is how the system communicates. An integrated lighting system provides at-a-glance status updates, while a companion app delivers detailed charts and trends over time. Rescuers can spot concerning weight drops before they become critical, all without ever touching the bird. It’s like having a 24/7 health monitor that doesn’t require awkward vet visits.
The implications here go beyond just making life easier for rescuers (though that alone would be worth celebrating). When you reduce stress during rehabilitation, birds recover faster and more successfully. That means higher release rates back into the wild, which is ultimately the whole point of rescue work. Every bird that makes it back to its natural habitat is a win for biodiversity and ecosystem health.

There’s something beautifully poetic about technology that works by getting out of the way. In our world of constant notifications and flashy interfaces, PerchCare succeeds by being invisible to its primary users. The birds have no idea they’re being monitored. They just land on what feels like a normal perch and go about their business while the tech does its thing quietly in the background. This is design thinking at its finest: identifying a real problem, understanding the needs of all stakeholders (including the non-human ones), and creating a solution that’s both elegant and effective. It’s not about reinventing the wheel or adding unnecessary complexity. Sometimes the best innovations are the ones that feel obvious in hindsight.

The post This Smart Perch Weighs Birds Without Ever Touching Them first appeared on Yanko Design.