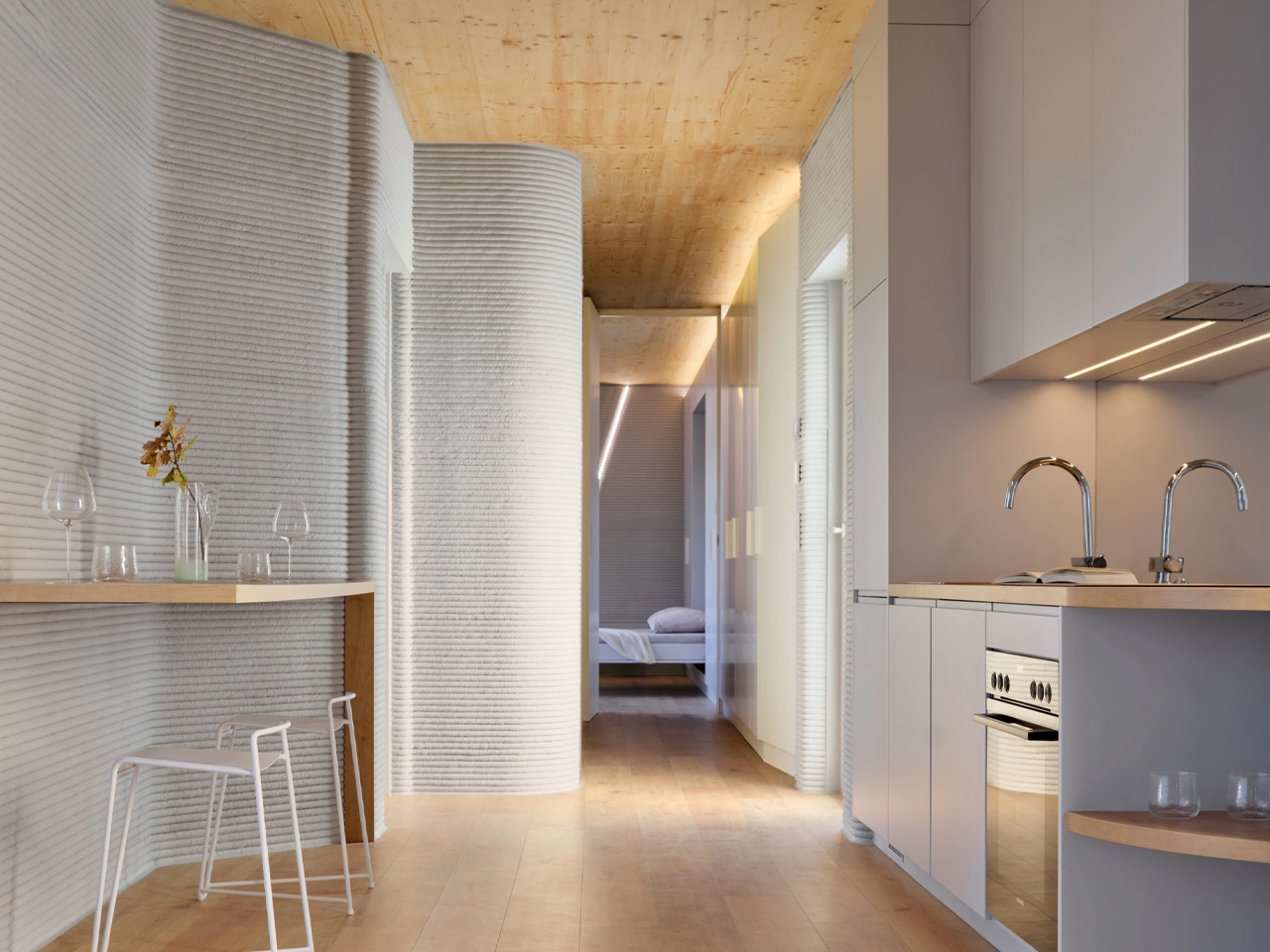
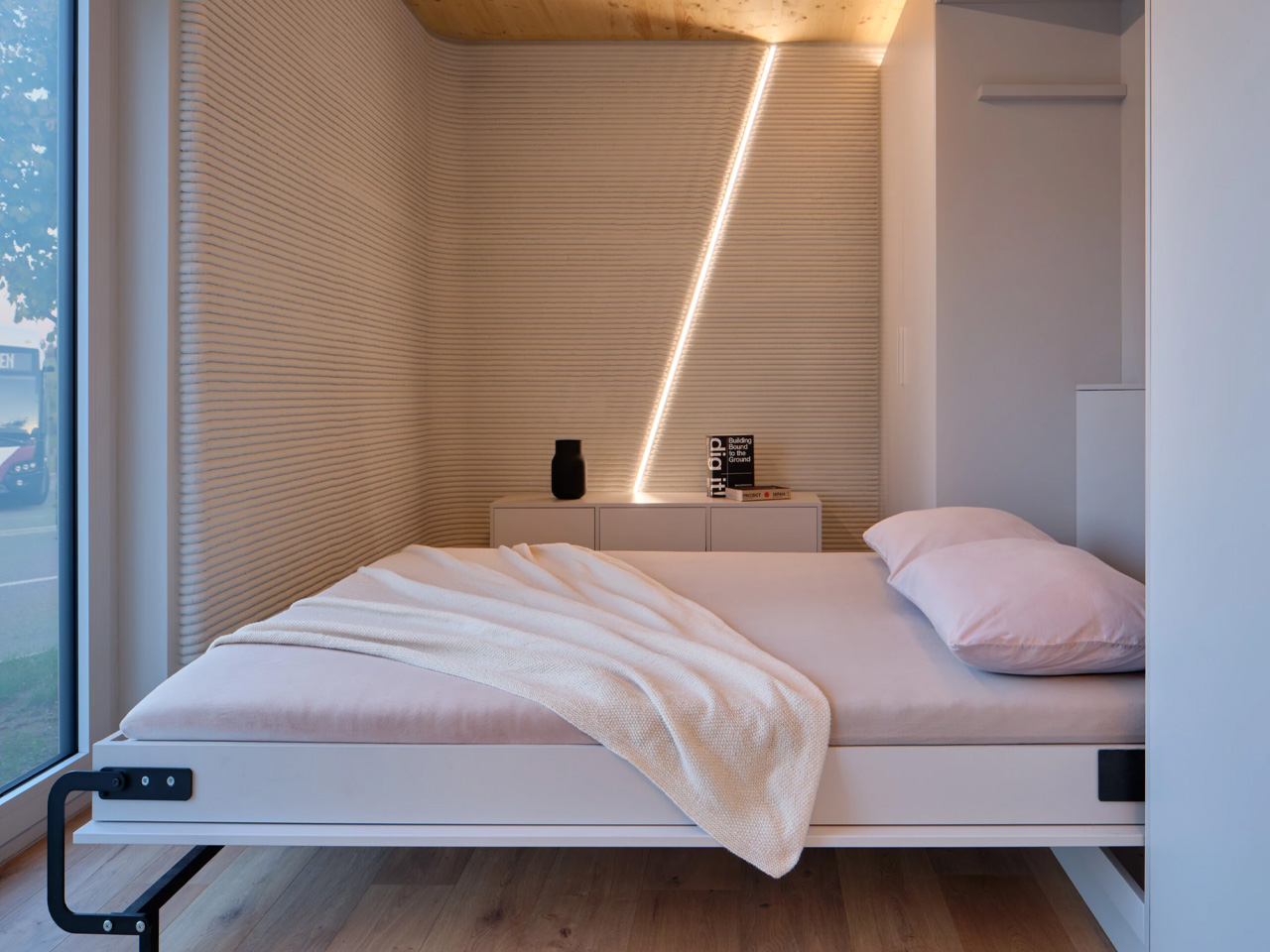
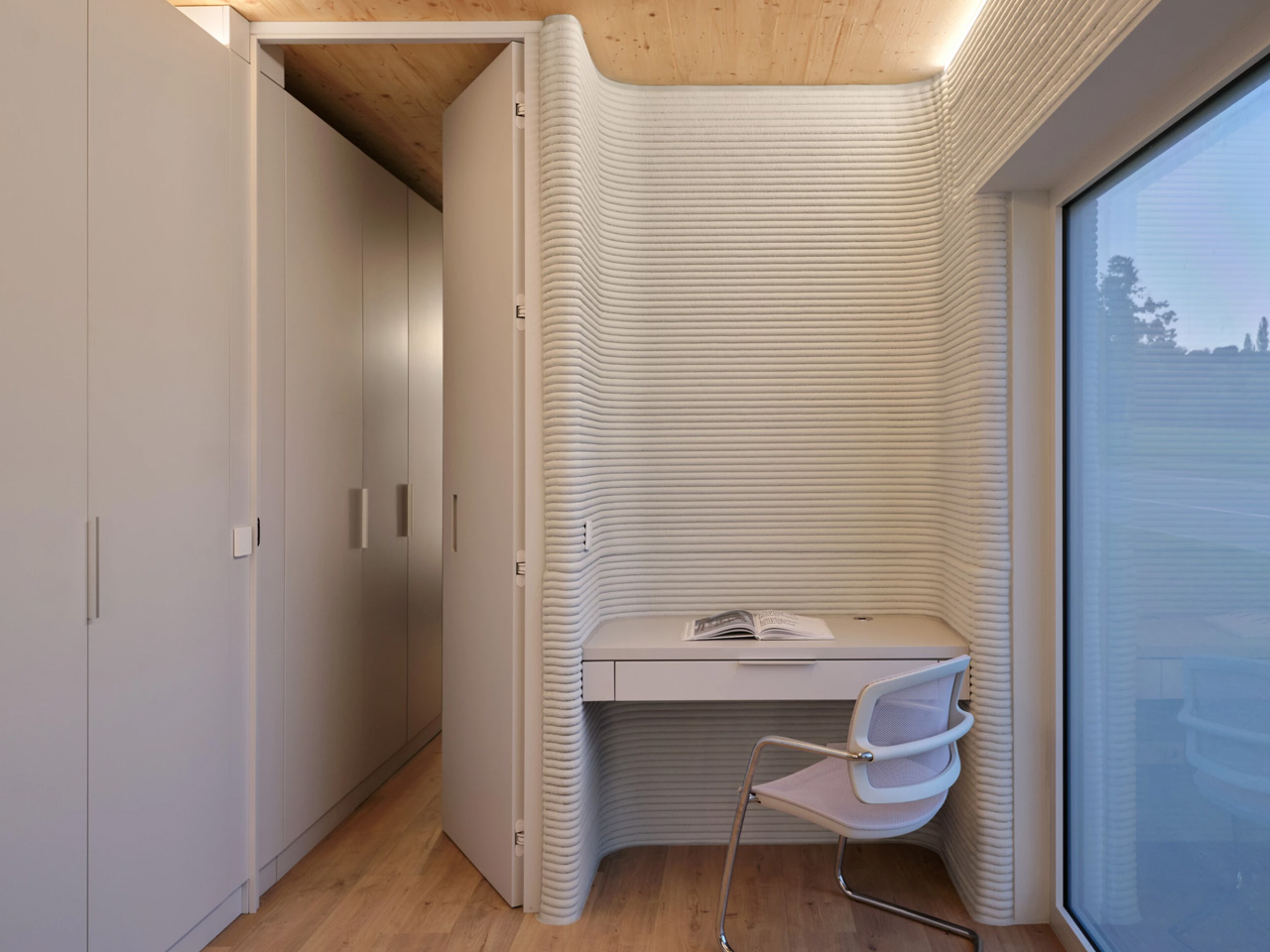
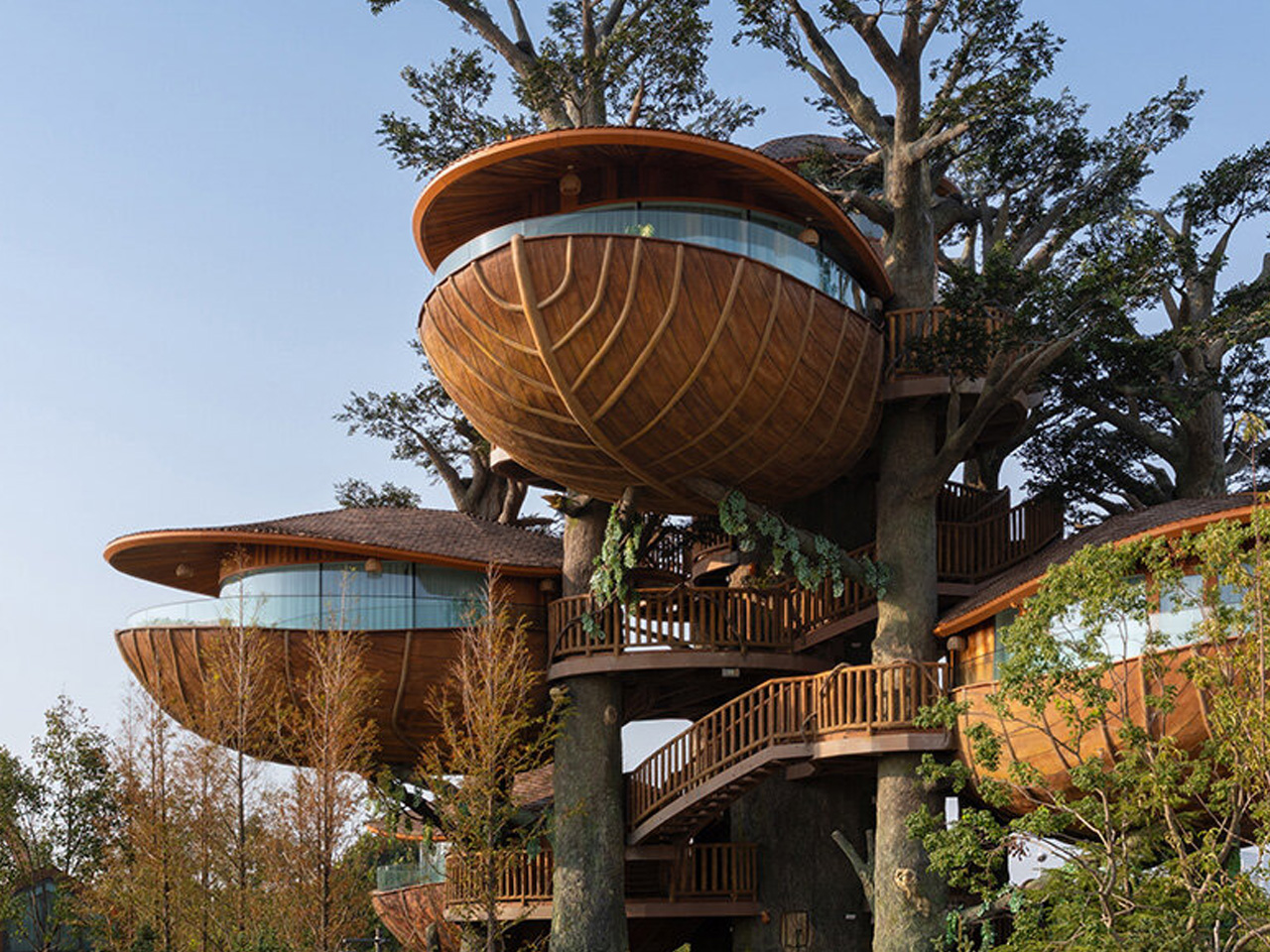
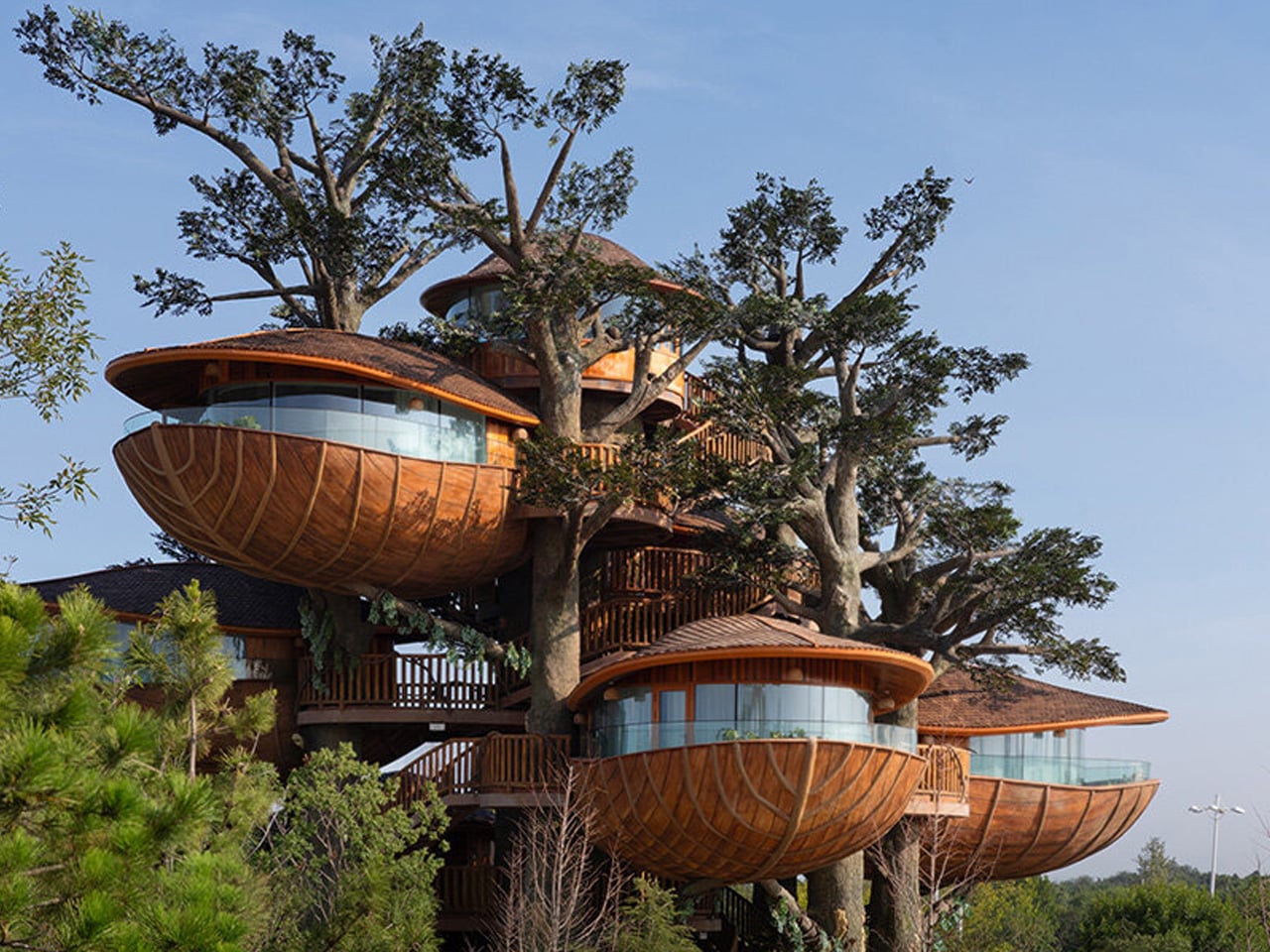
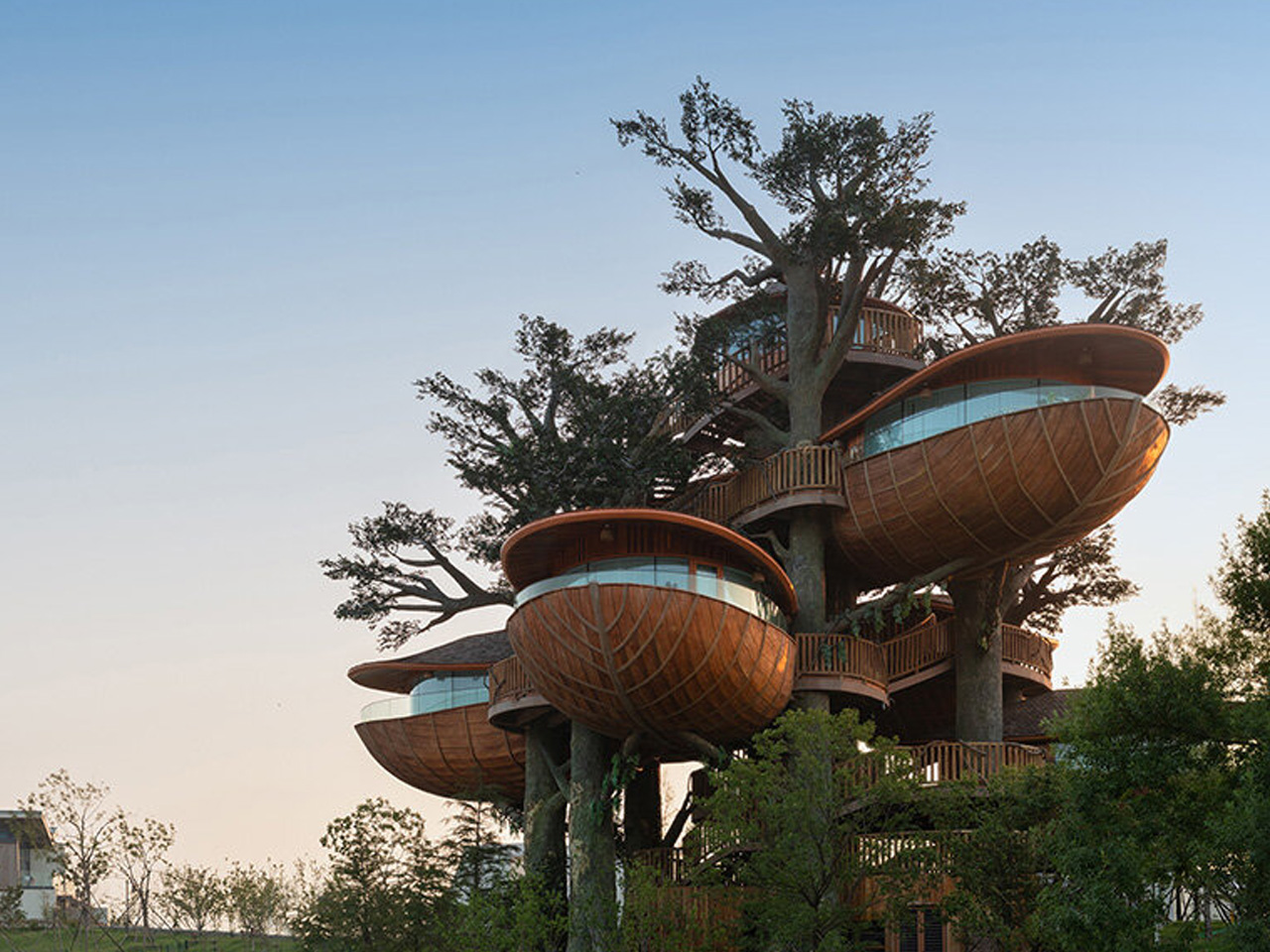
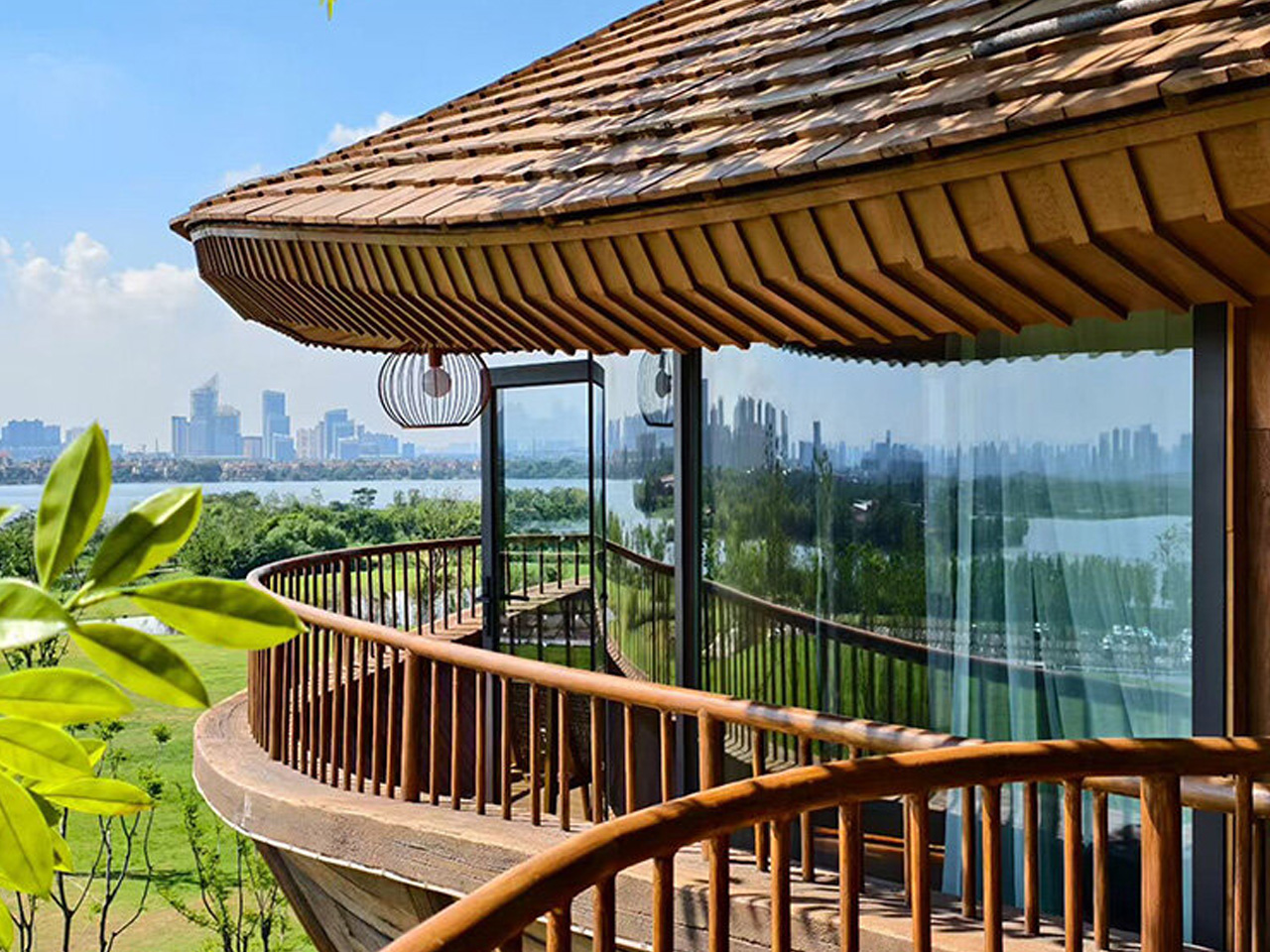
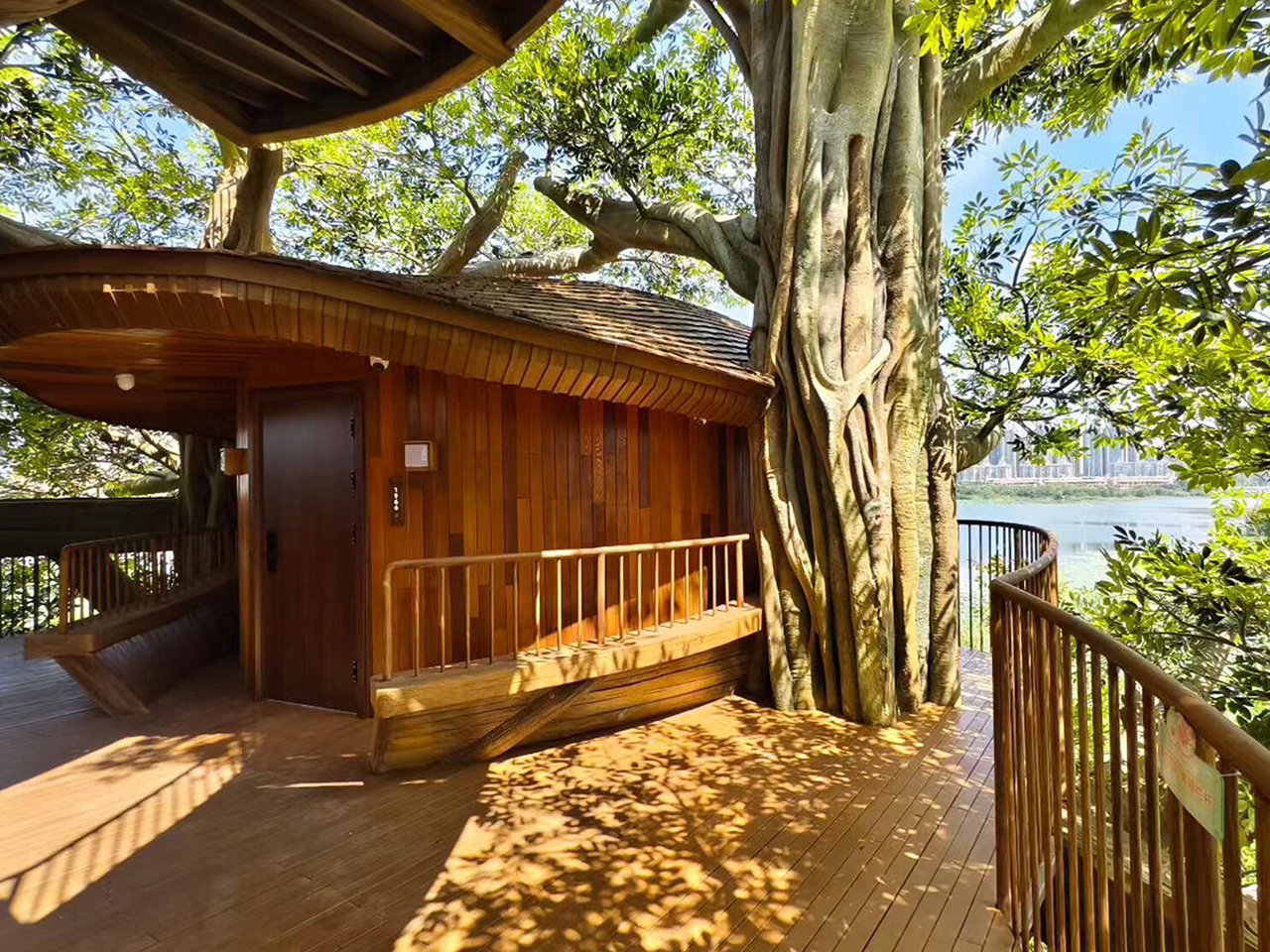
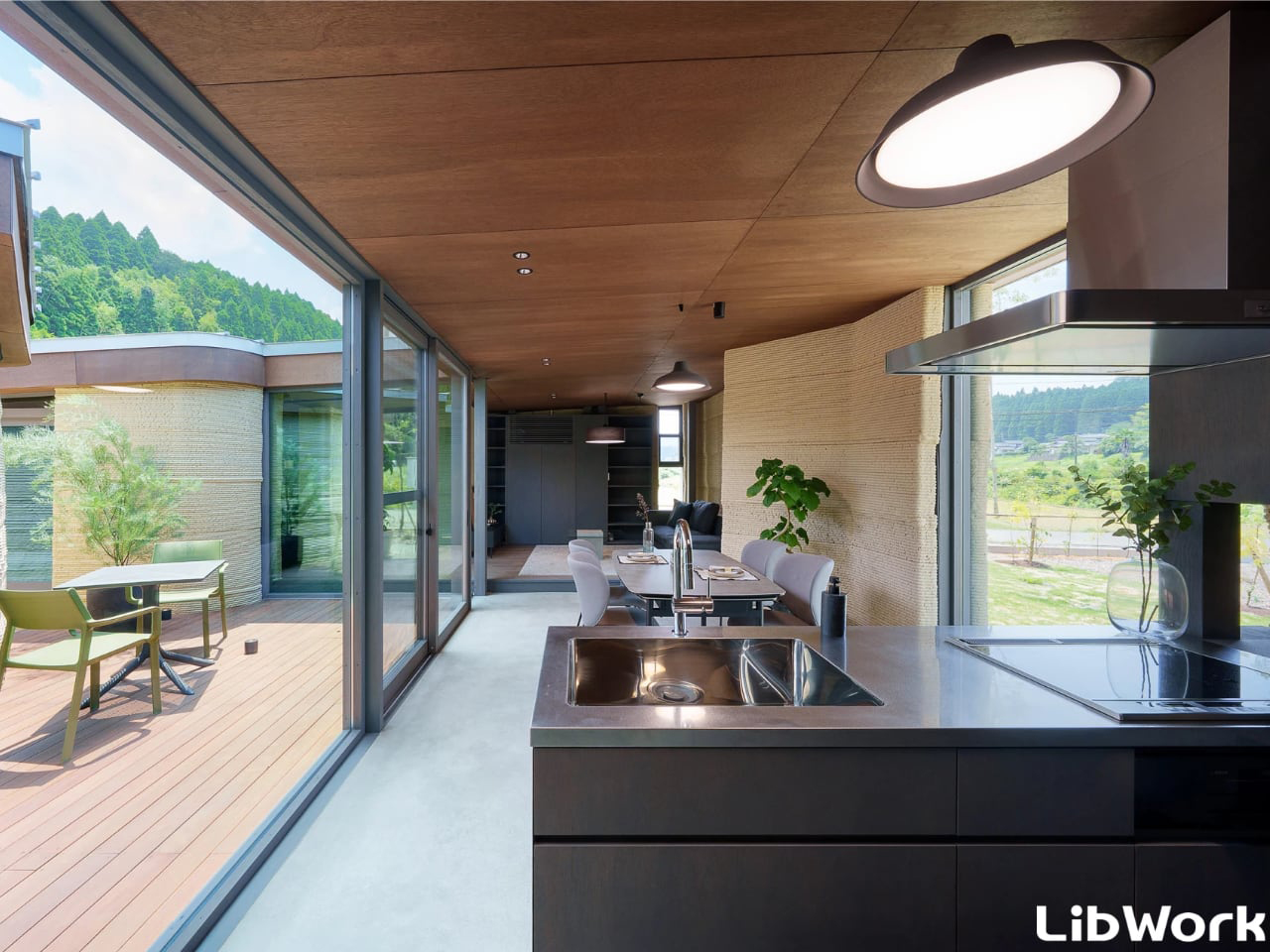
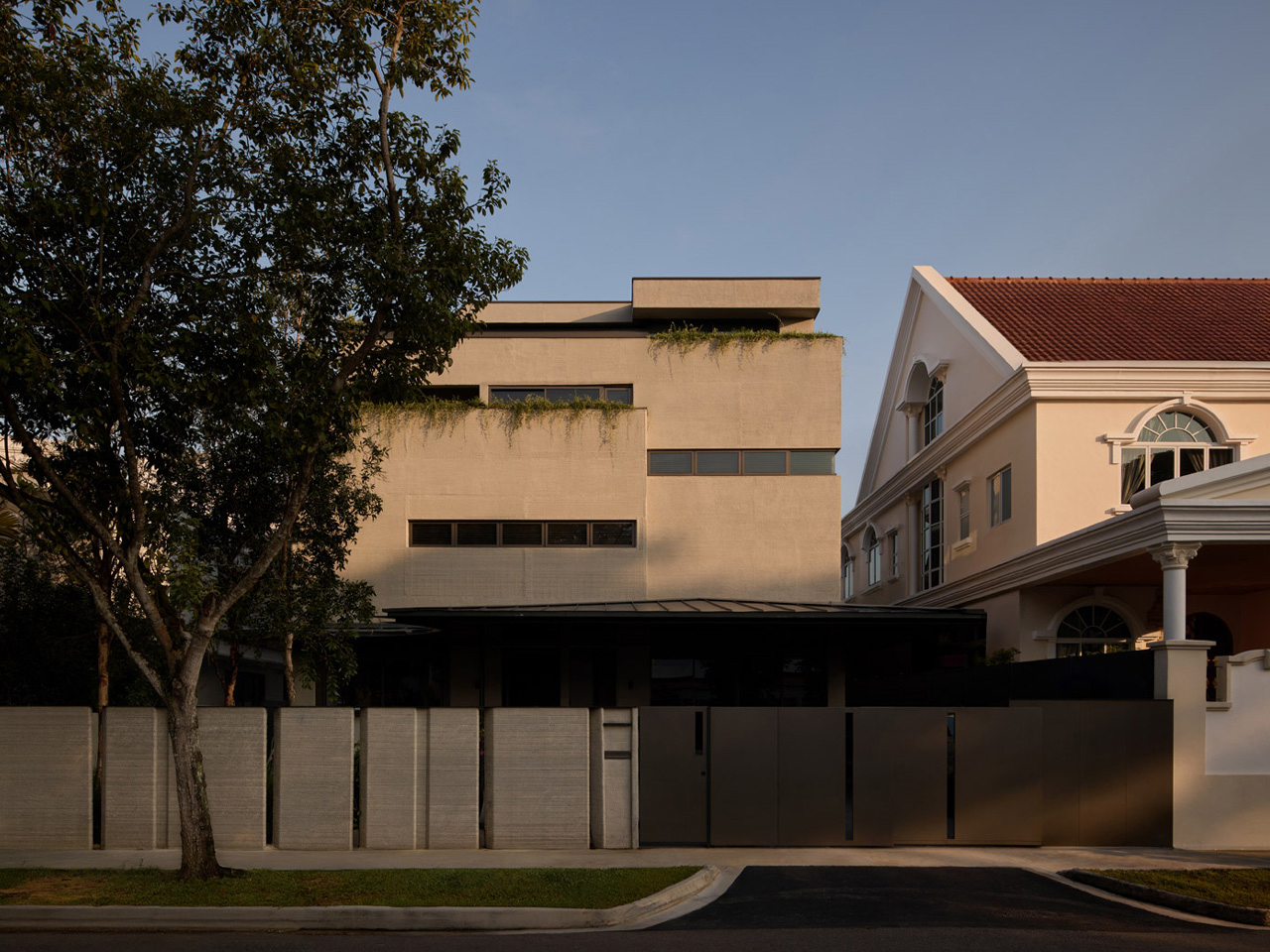
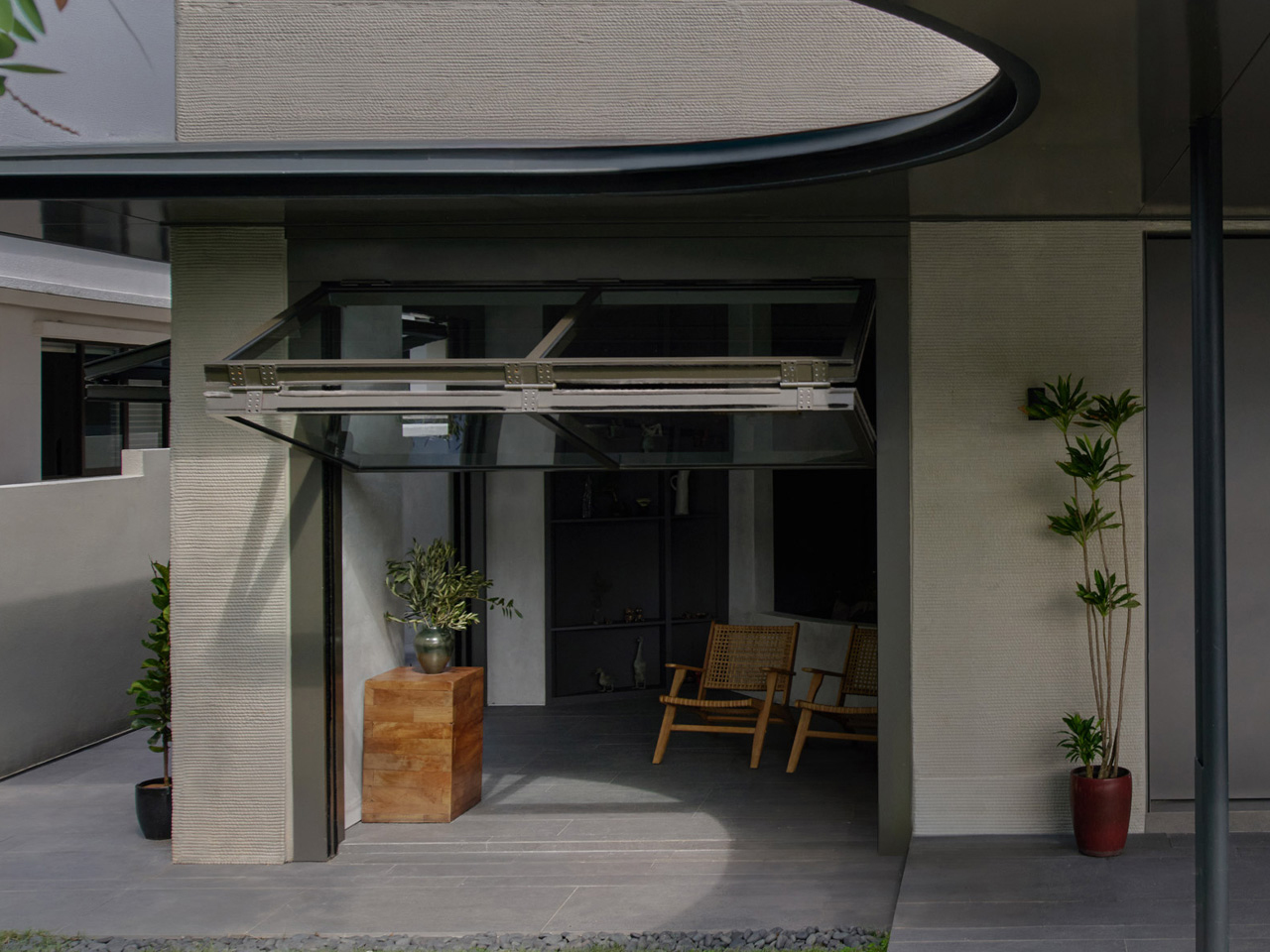
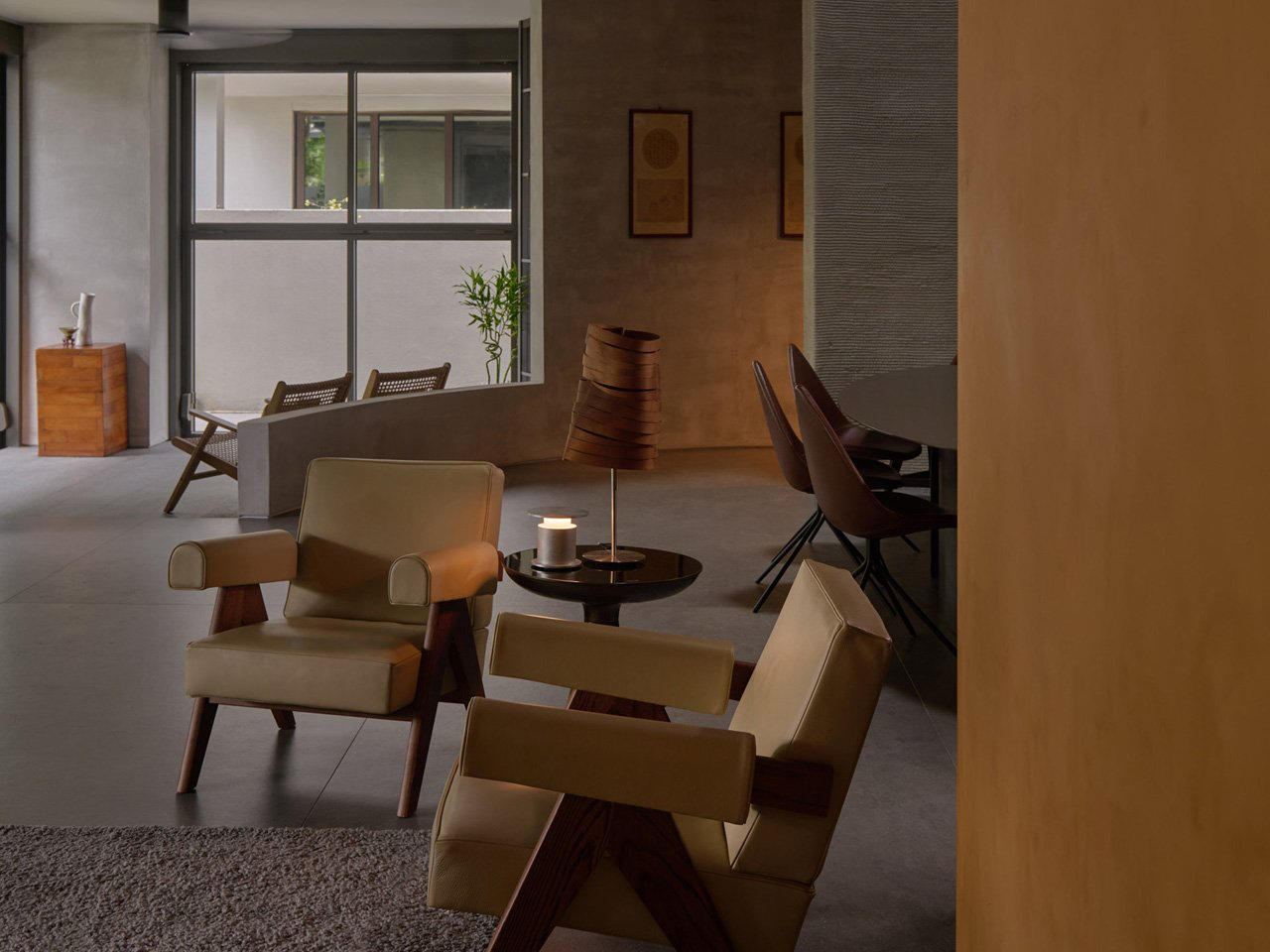
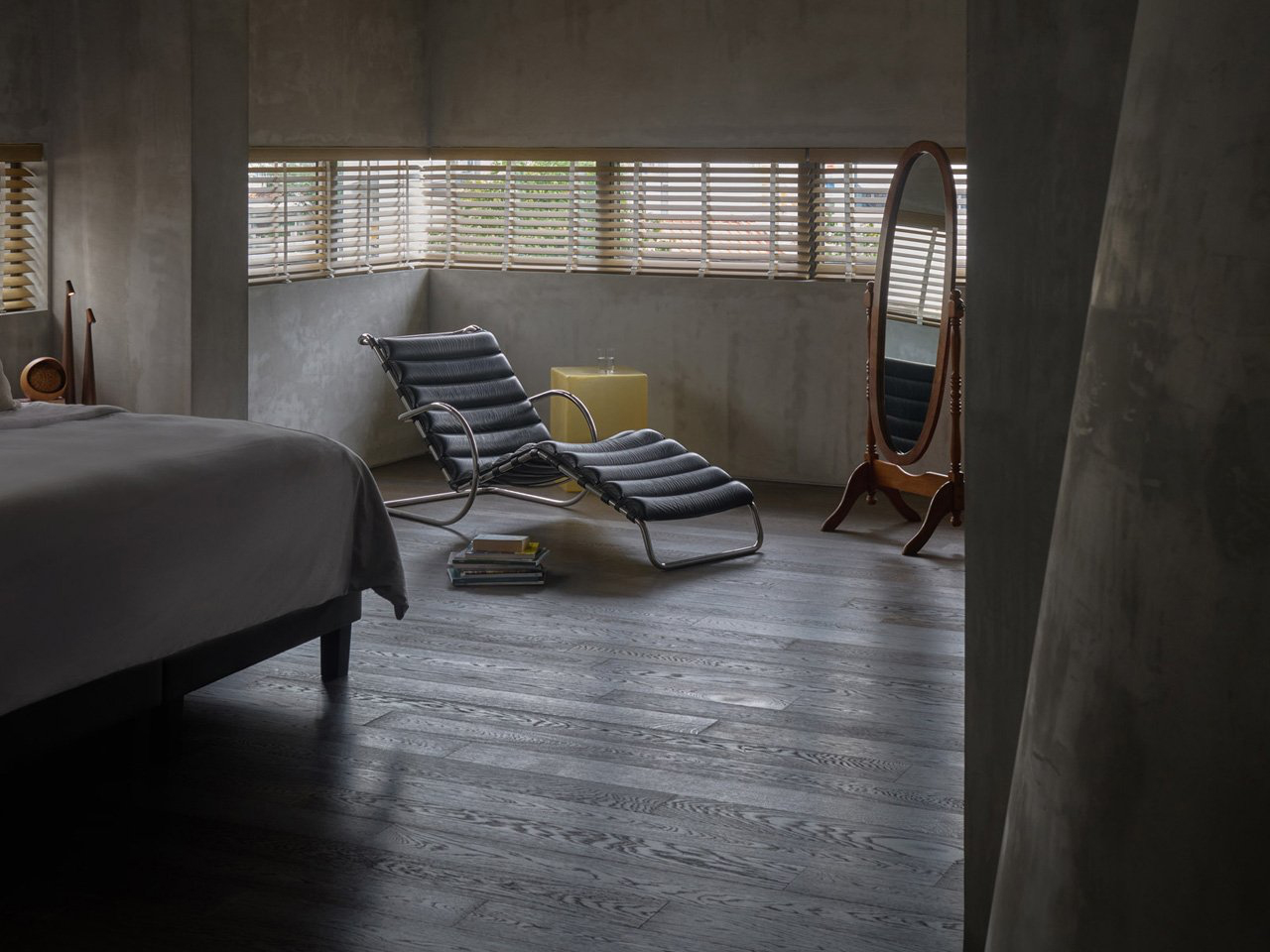
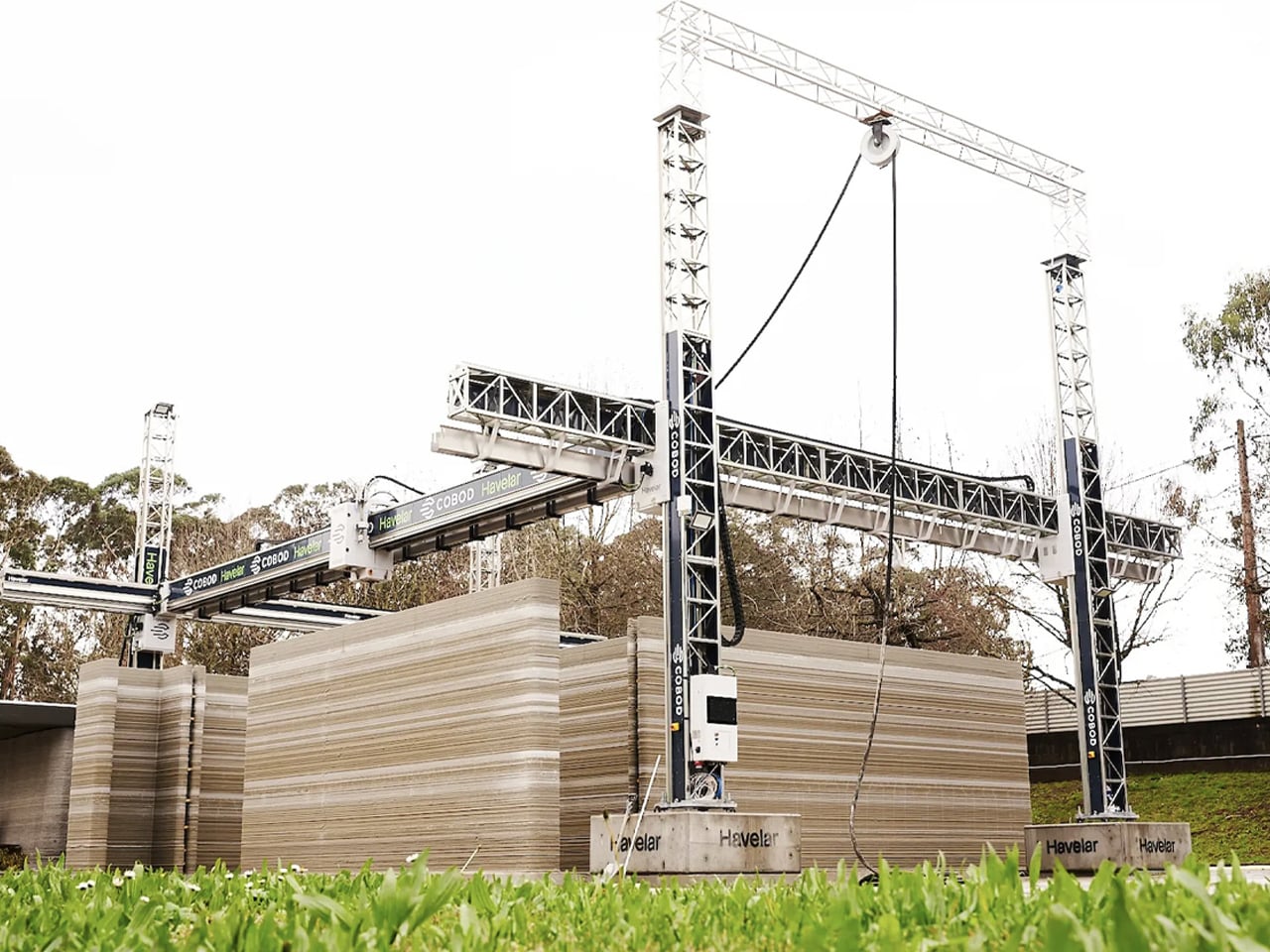
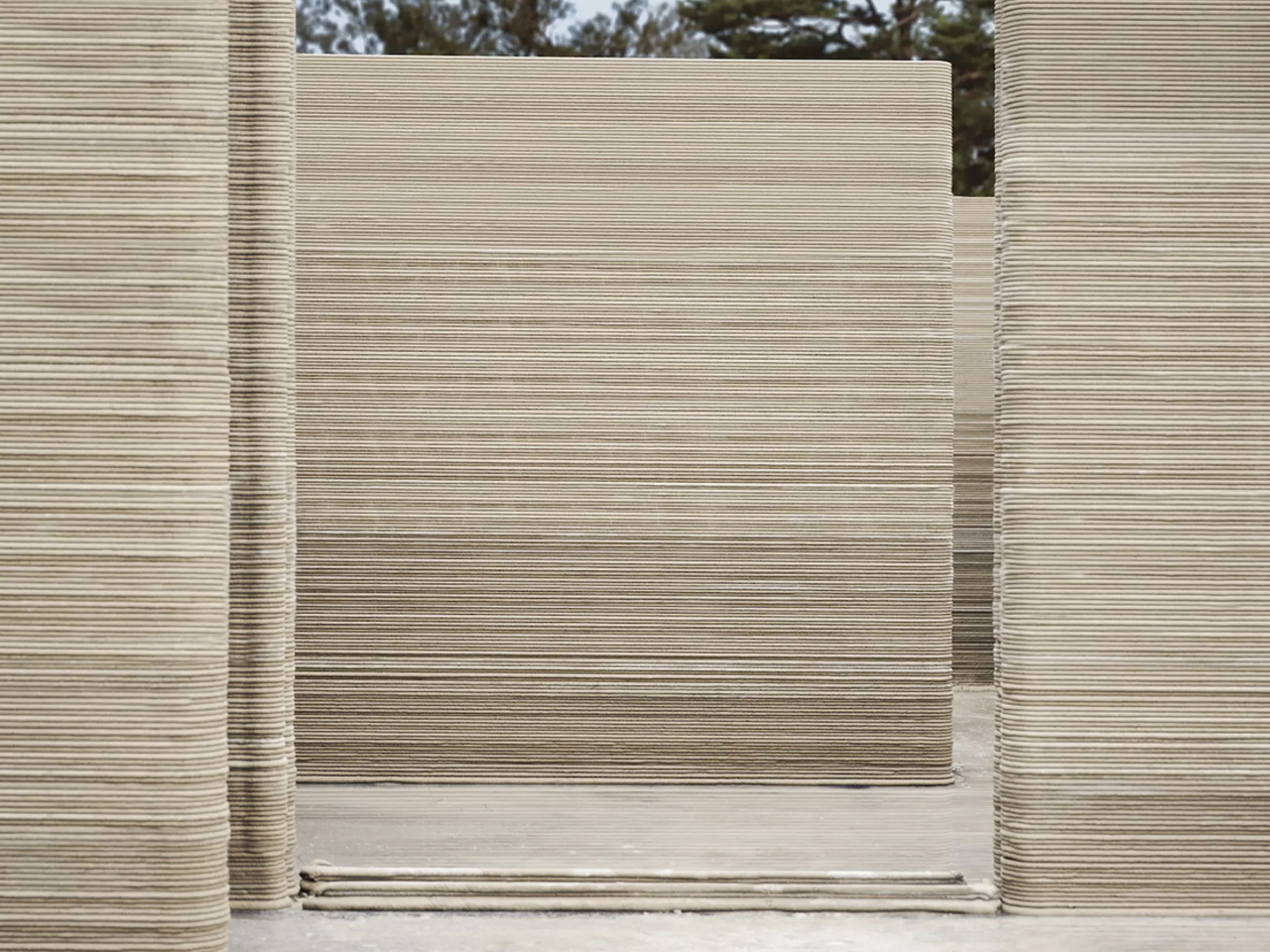
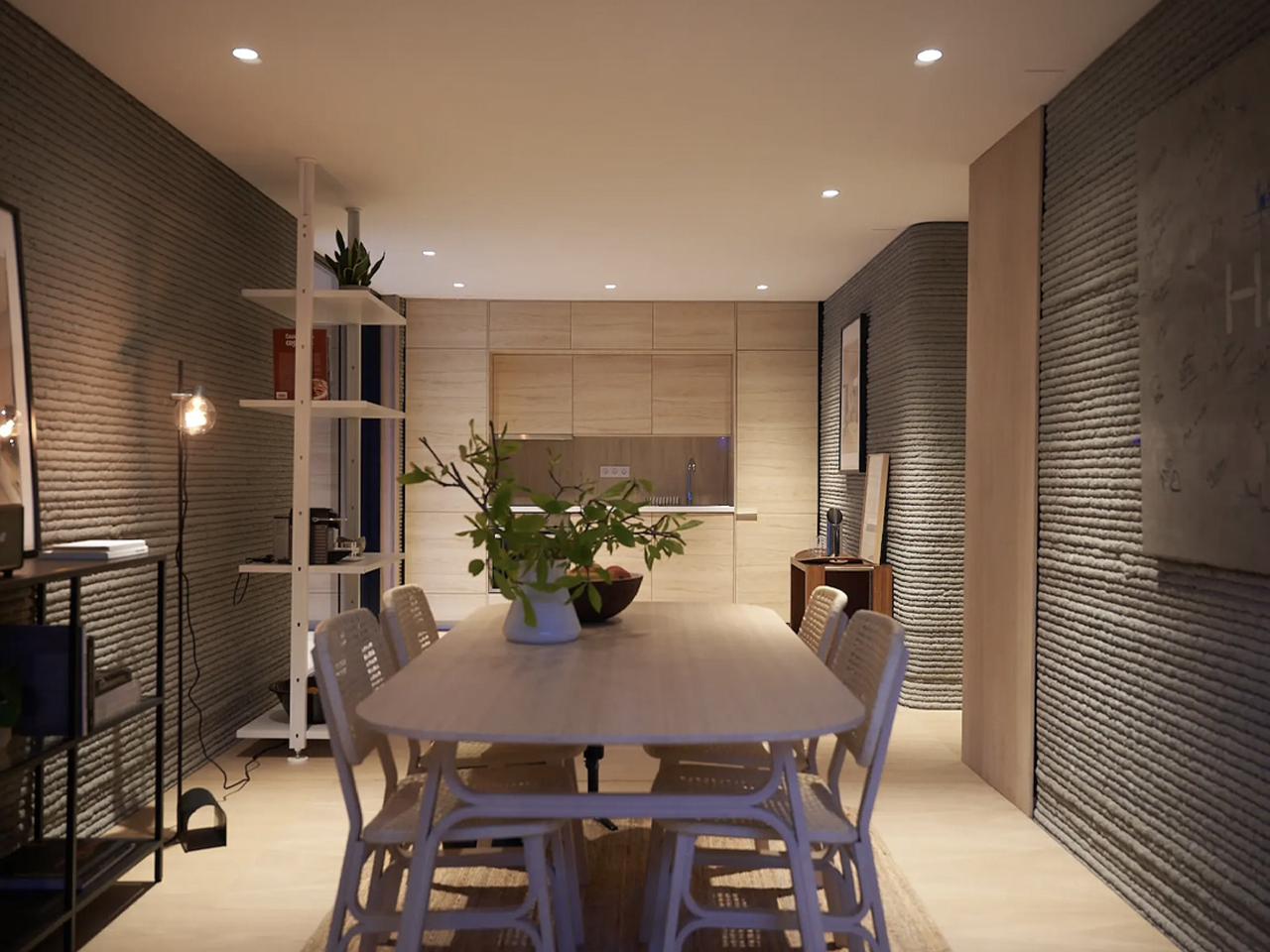
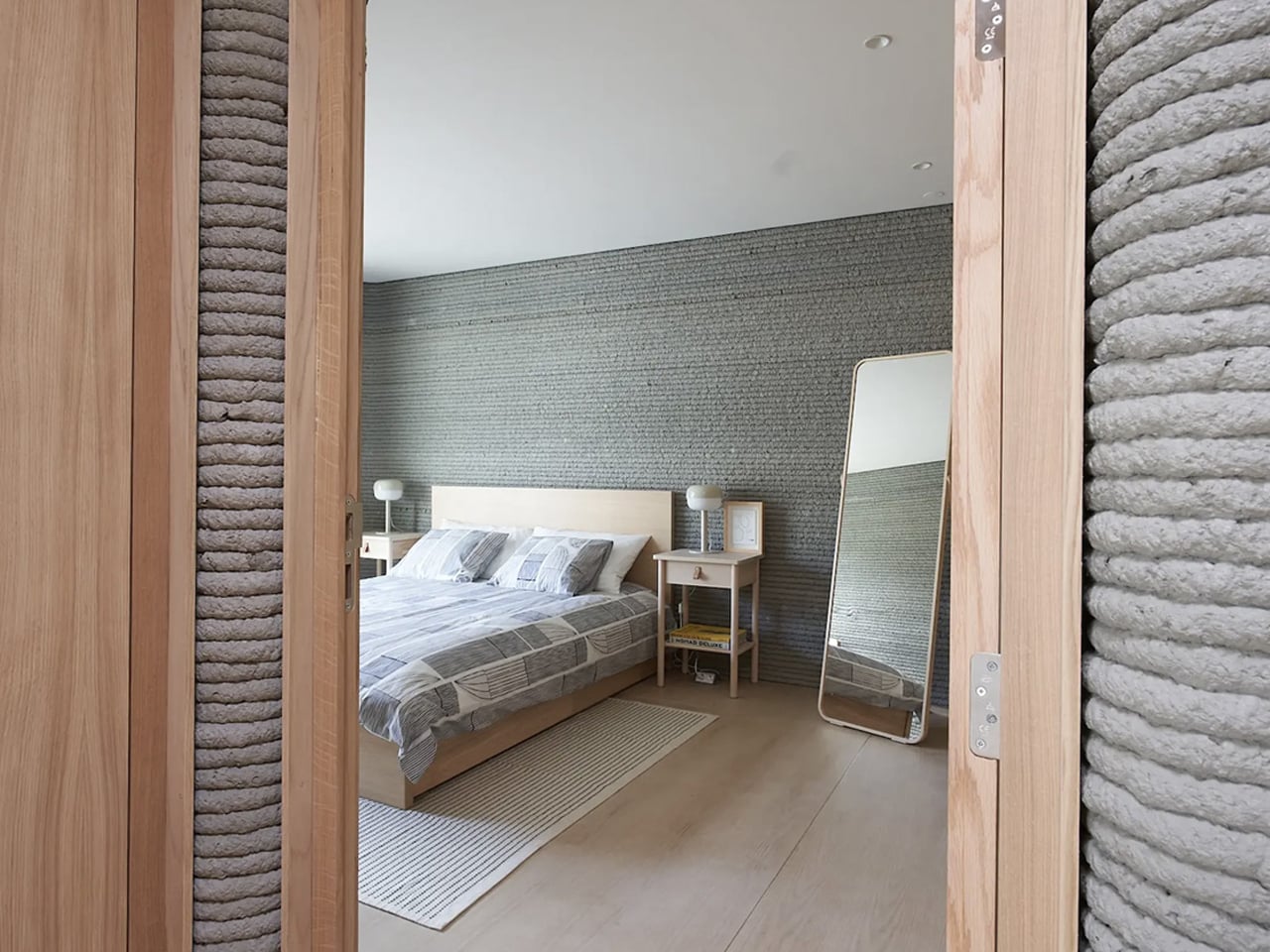
The concept of home is evolving, shifting from mere shelter to spaces that genuinely nurture our well-being. This means creating a harmonious connection with nature by designing homes that don’t just occupy land, but feel like an extension of it. Achieving this requires thoughtful choices in design and materials, starting with a deep understanding of the very ground on which the home will rise.
This approach goes beyond mere aesthetics. Homes that integrate seamlessly with nature are naturally more energy-efficient, healthier, and more serene. By harnessing natural light, enhancing ventilation, and selecting materials with minimal environmental impact, we can create spaces that are visually captivating and also supportive of the planet and our personal well-being.
1. The Art of Site-Specific Design
Before a single line is drawn, one must first understand the site. The architect walks the land at different times of day, noting where the sun rises and sets and feeling the direction of evening breezes. They observe how rainwater flows, where mature trees stand, and the natural contours of the terrain. Each detail informs the design, ensuring the home responds to its surroundings rather than resists them.
A house created with this awareness naturally harmonizes with the environment. It reduces reliance on artificial heating and cooling while preserving the land’s inherent beauty, resulting in a dwelling that feels both enduring and alive.
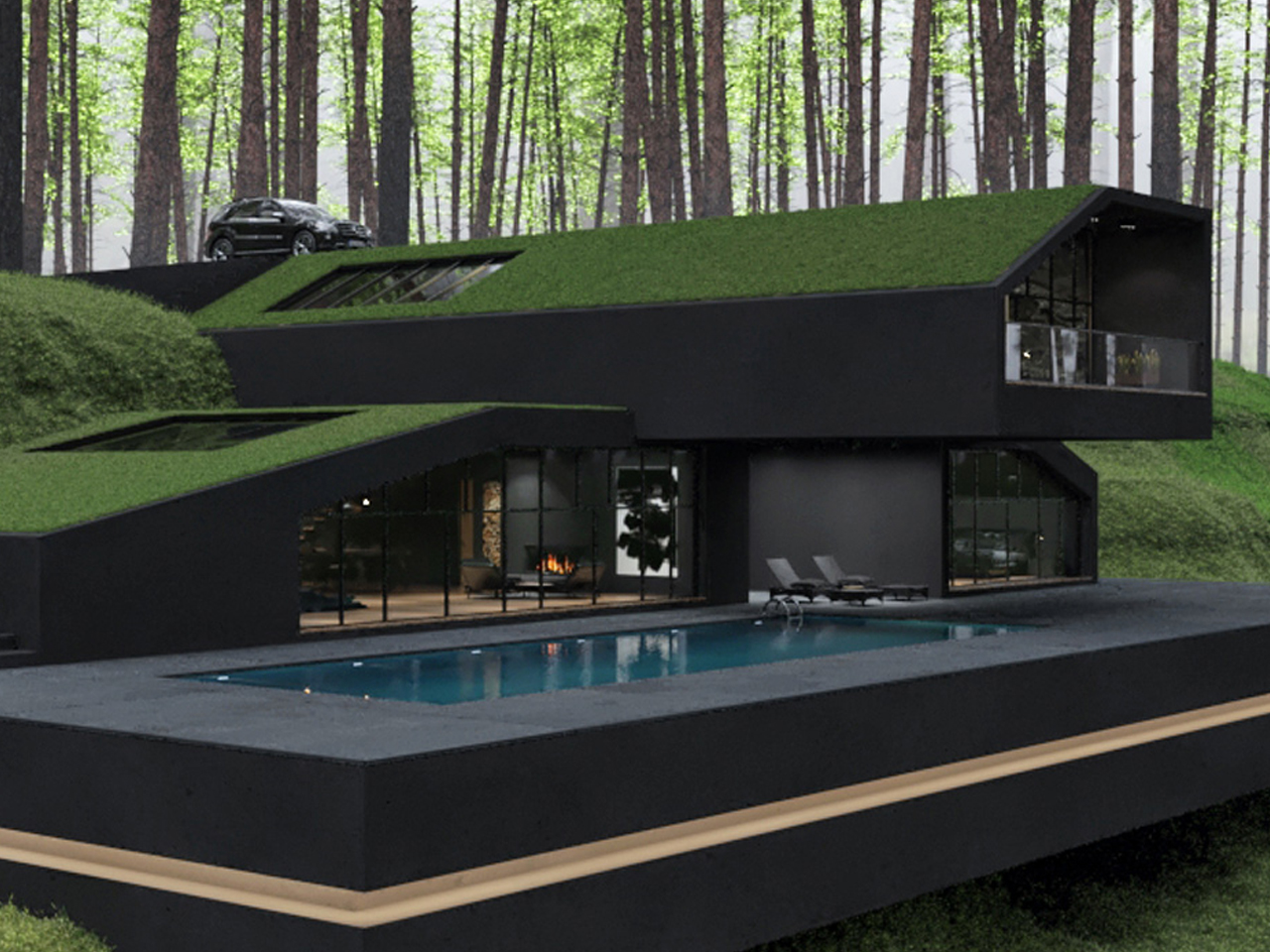
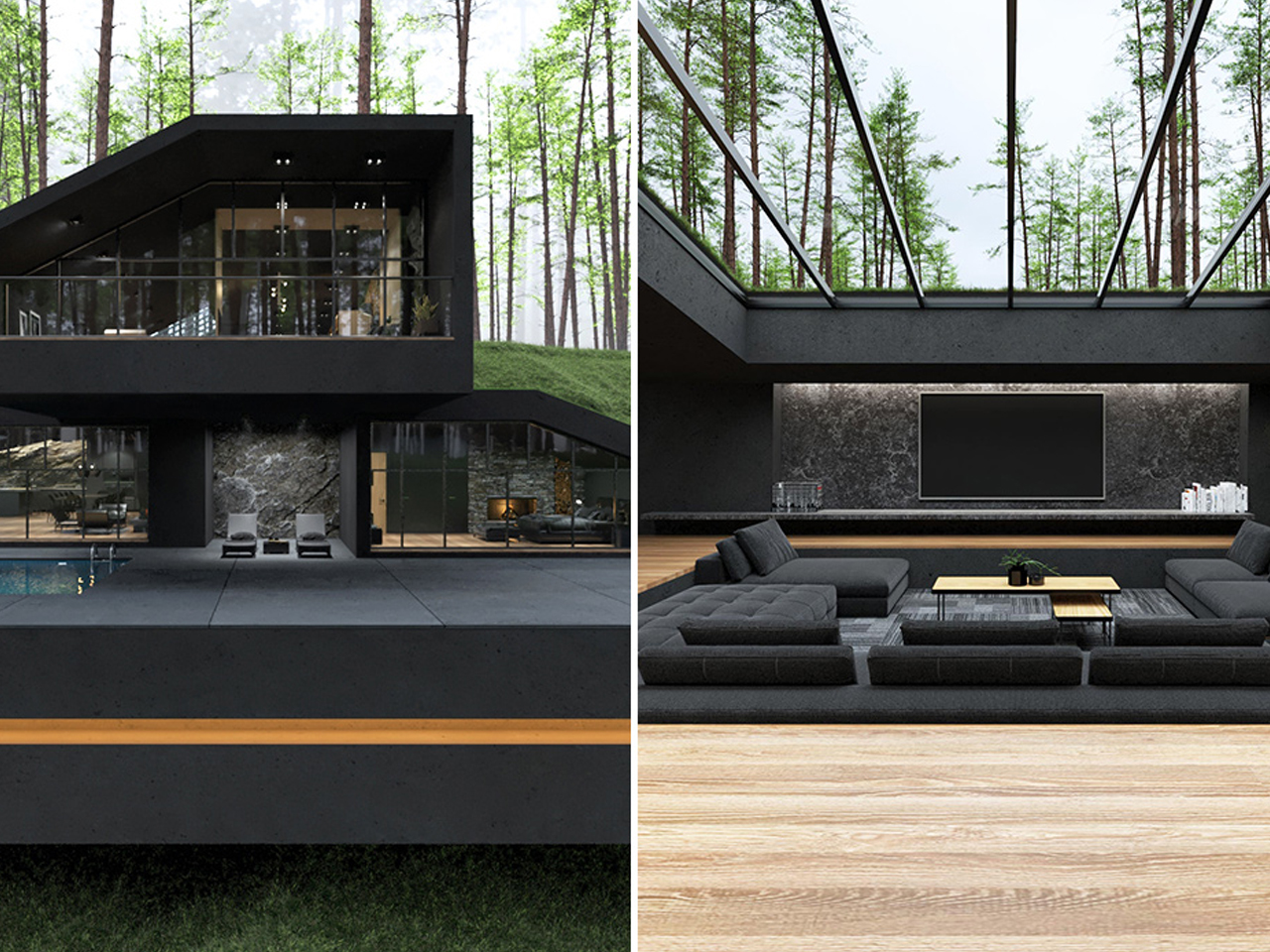


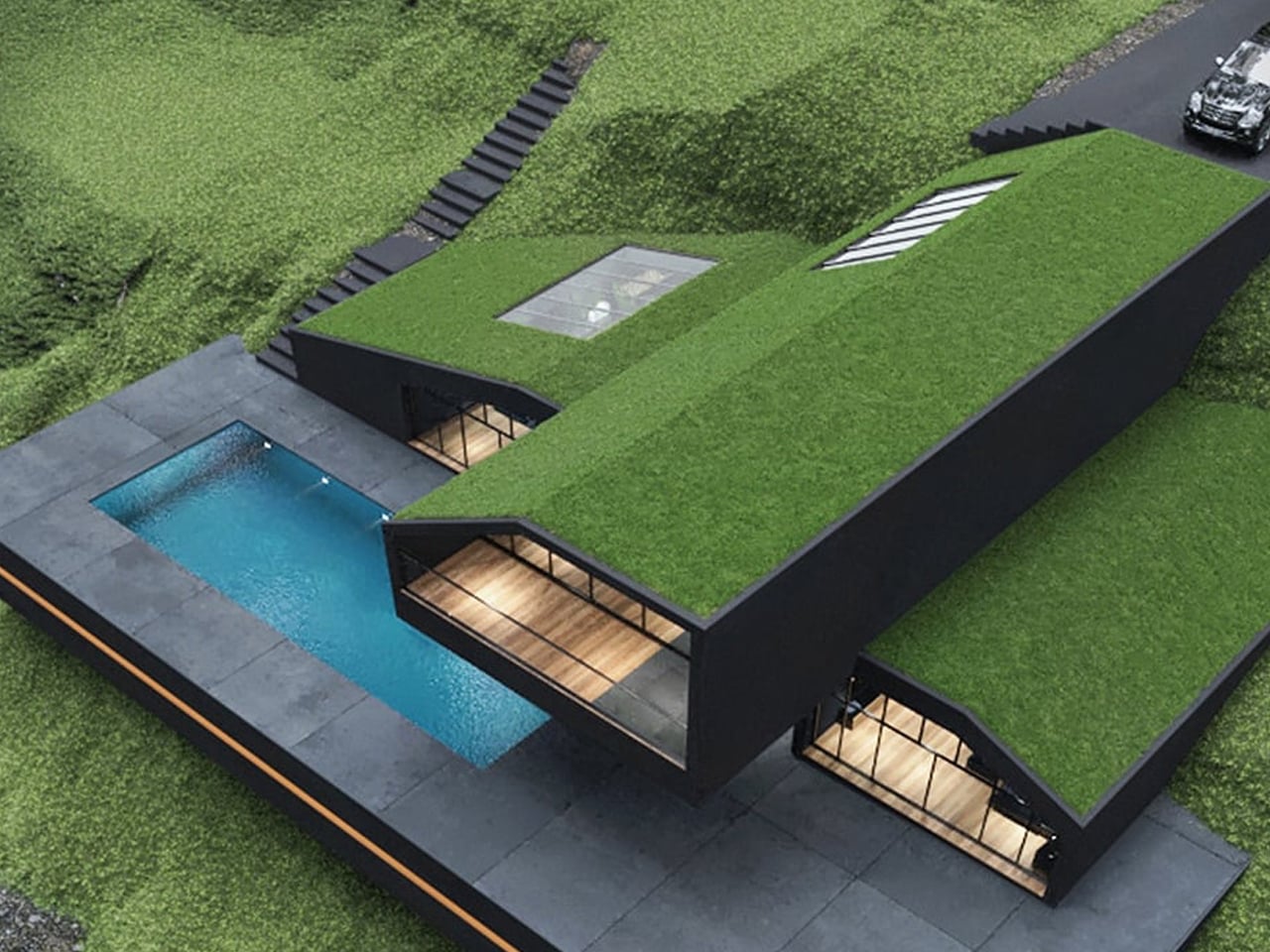
In the hills of Harriman State Park, New York, the Black Villa was designed as a striking, contemporary-style hobbit hole. Its most notable feature is a lush, grass-covered roof that integrates the home with its natural surroundings. Green roofs have steadily gained popularity over the past decade for their environmental and economic benefits. They provide natural insulation, reducing energy consumption and keeping rooftop temperatures 30–40°F cooler than conventional rooftops. The Black Villa further enhances efficiency through skylights and floor-to-ceiling windows, while also mitigating stormwater runoff, which is a feature especially useful in areas with poor drainage.
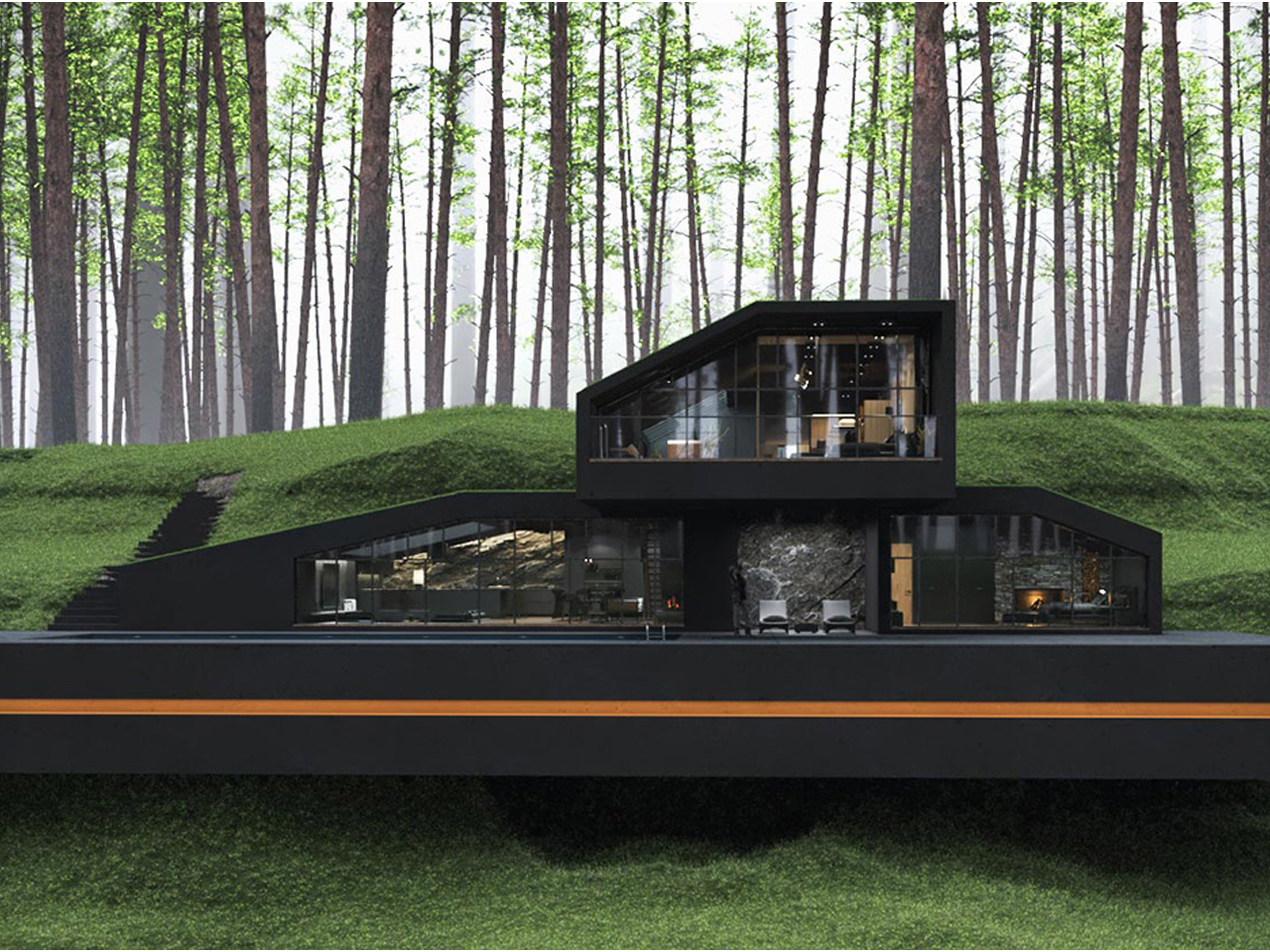
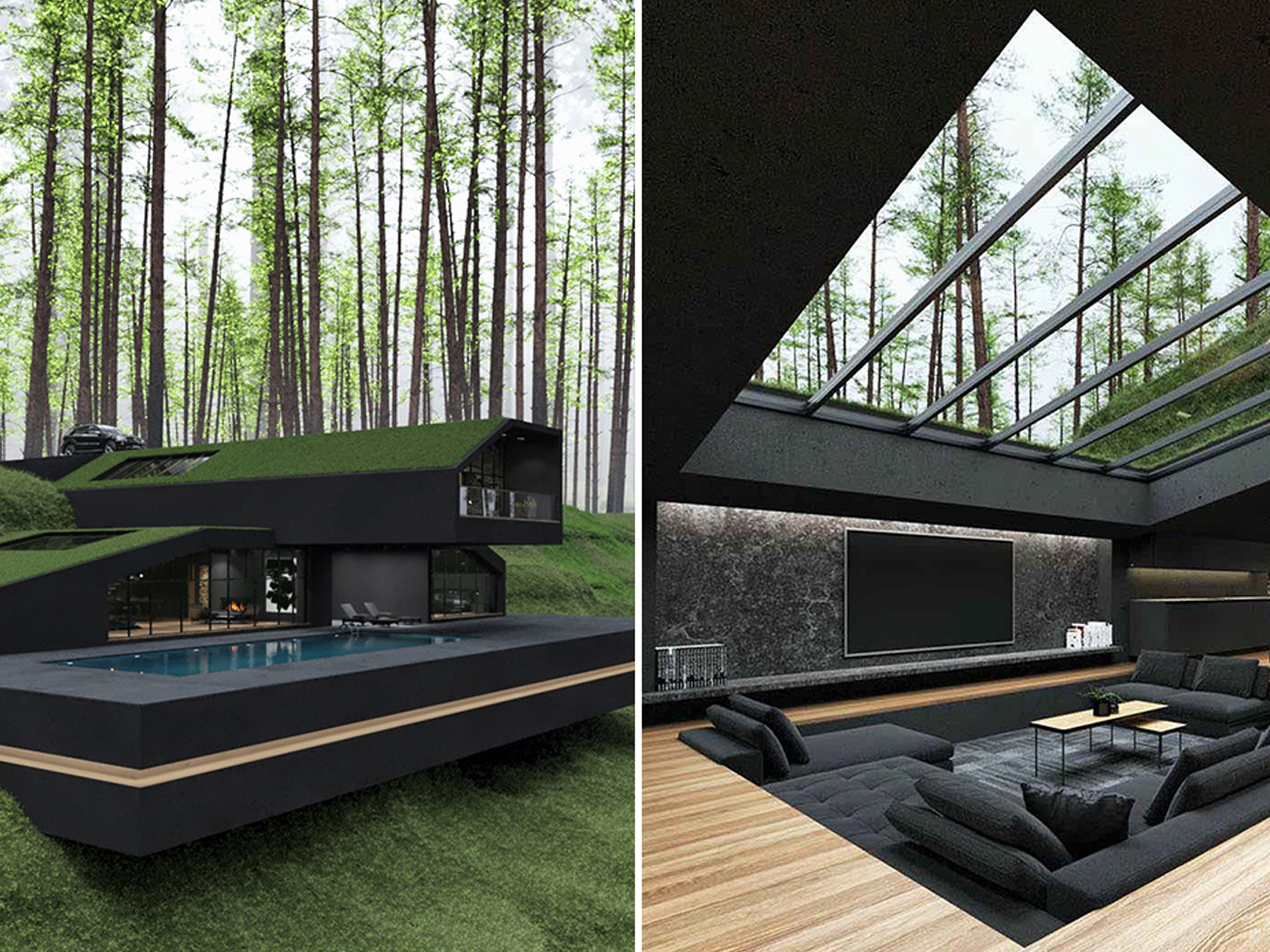


Despite its impressive design, situating the Black Villa within a national park raises questions about sustainability. Construction inevitably disrupts the existing landscape, making the eco-friendly elements feel partly aesthetic rather than fully functional. While the project may inspire interest in green roof architecture, its energy-efficient features appear more as part of the home’s visual appeal than as a model of practical environmental stewardship.
2. Rooted in Natural Materials
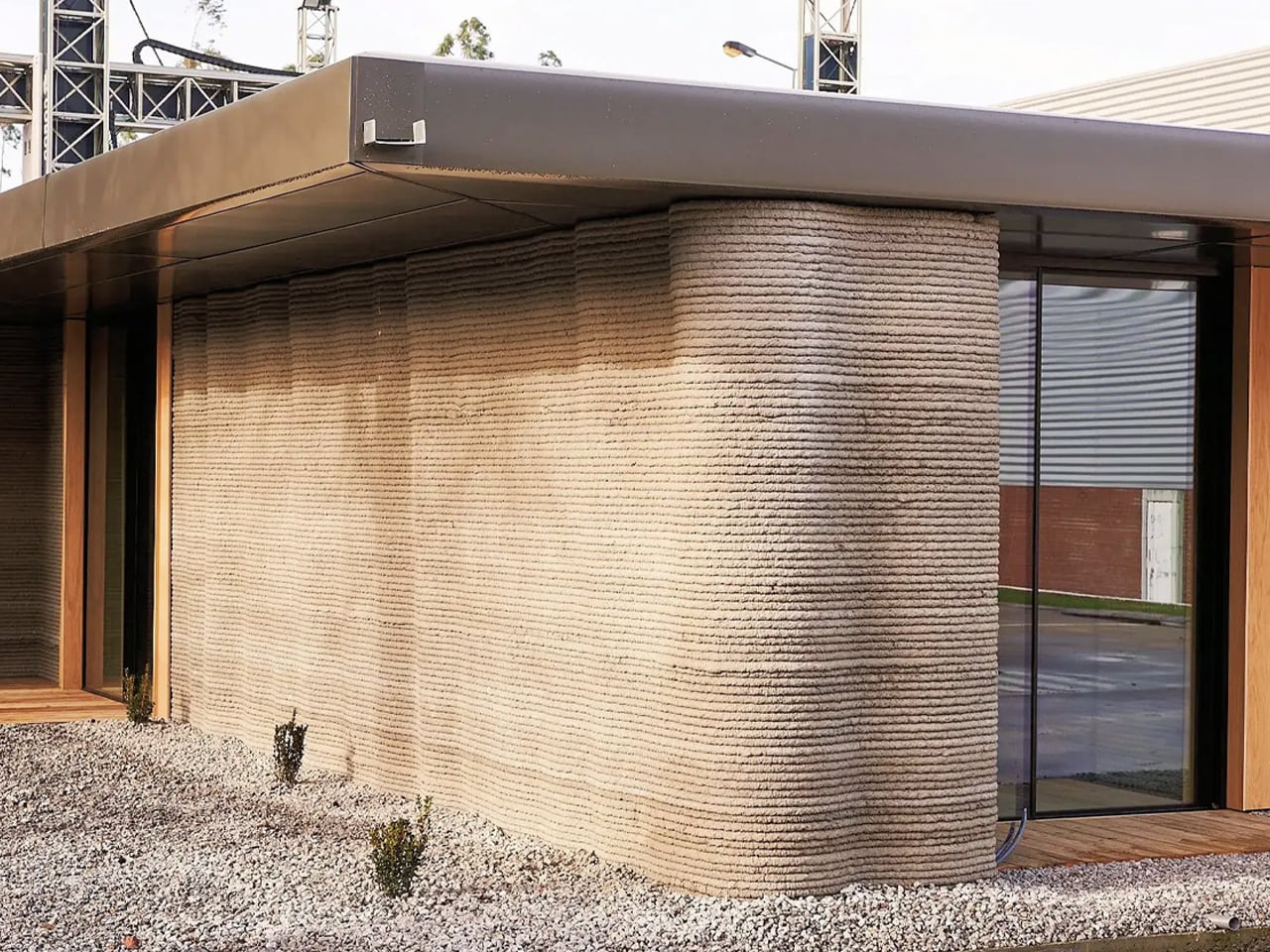
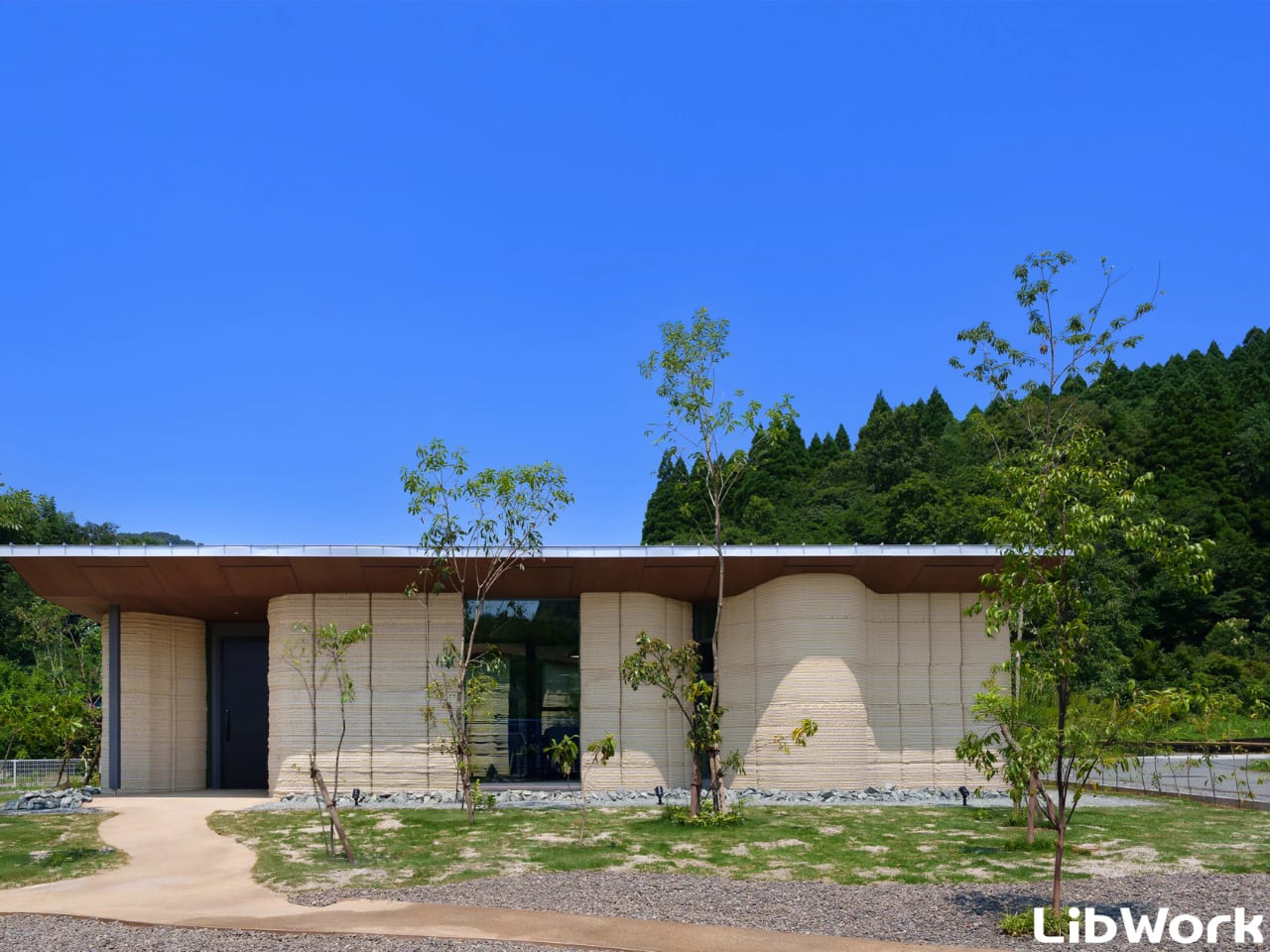
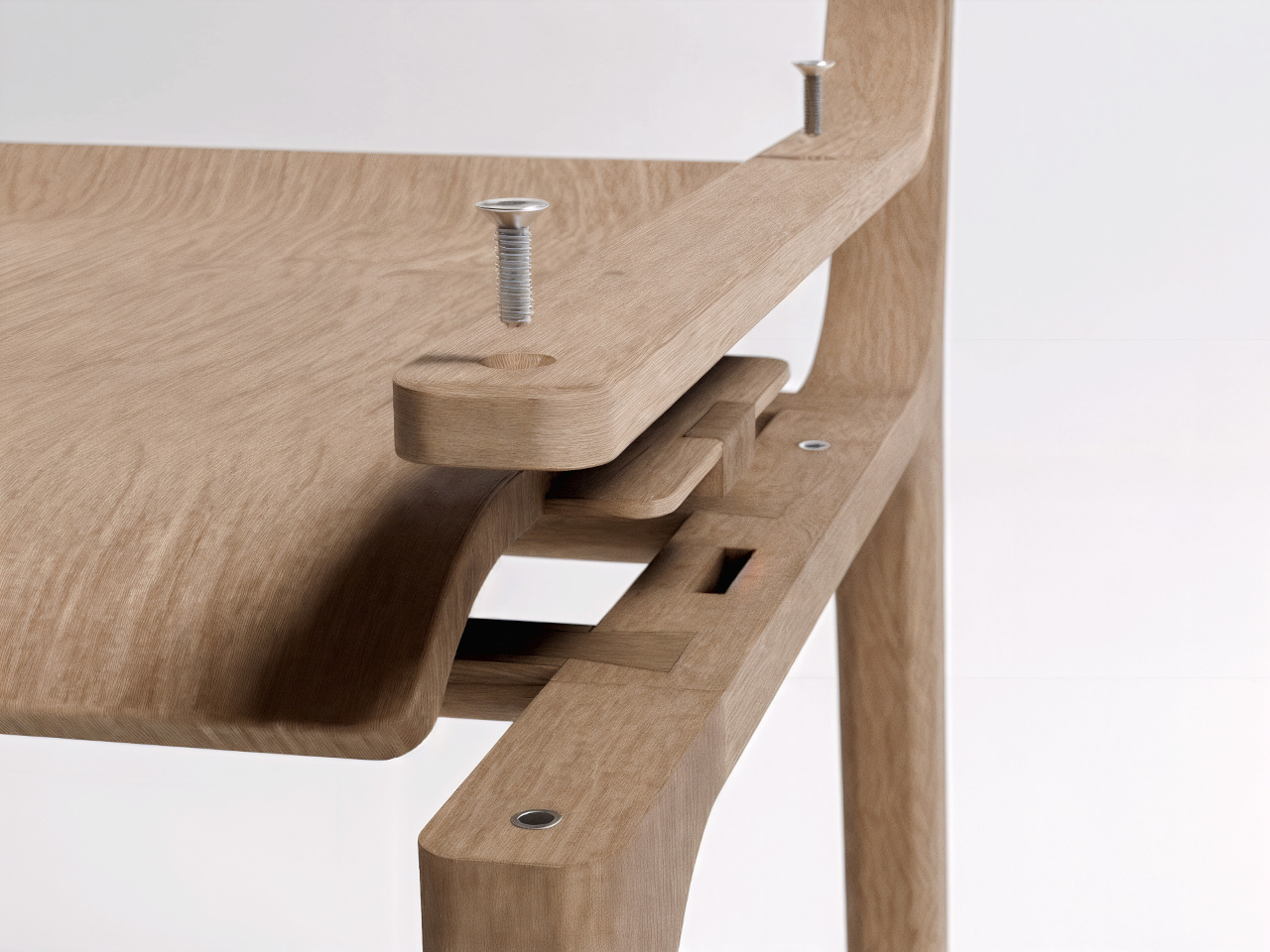
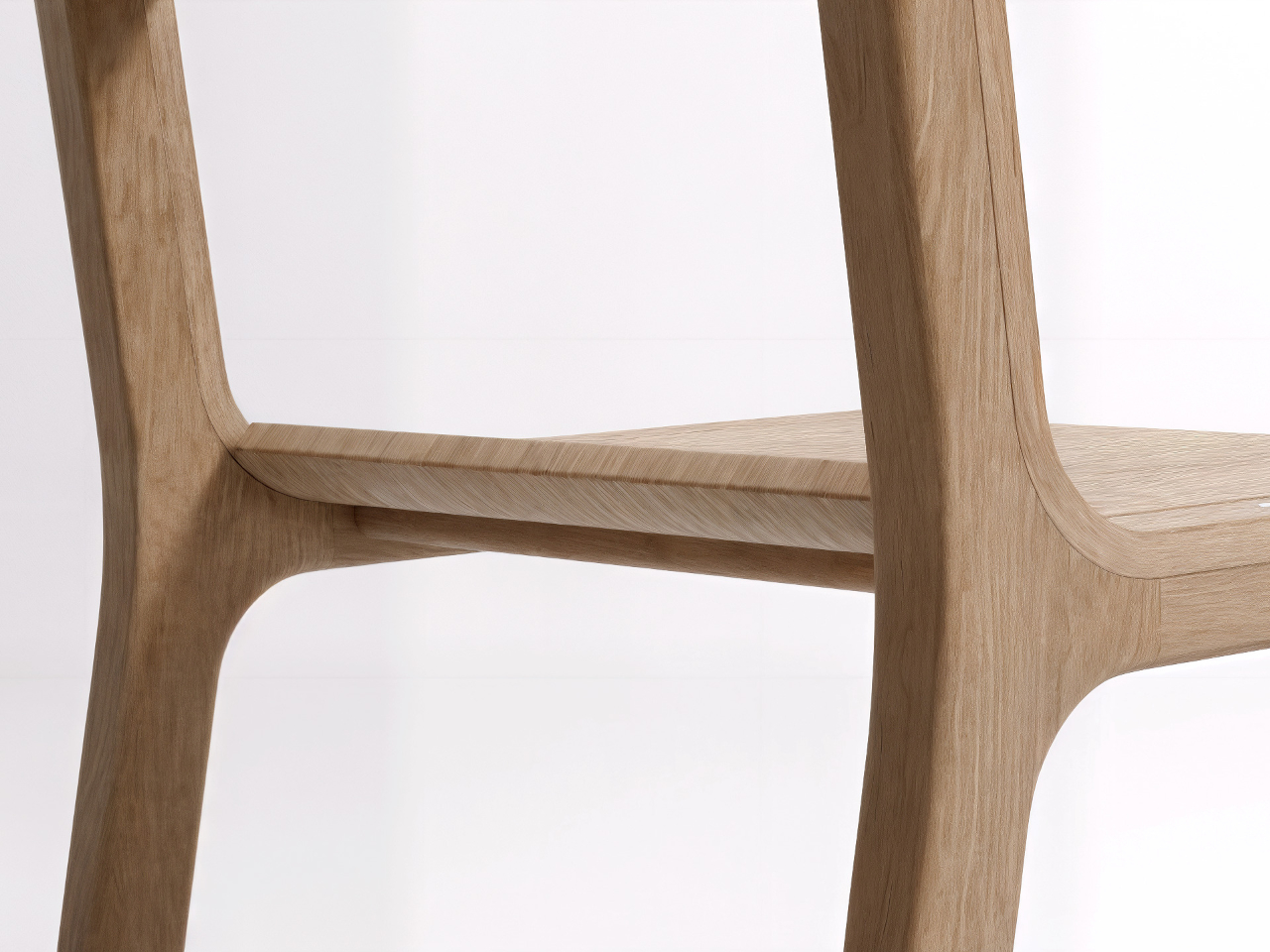
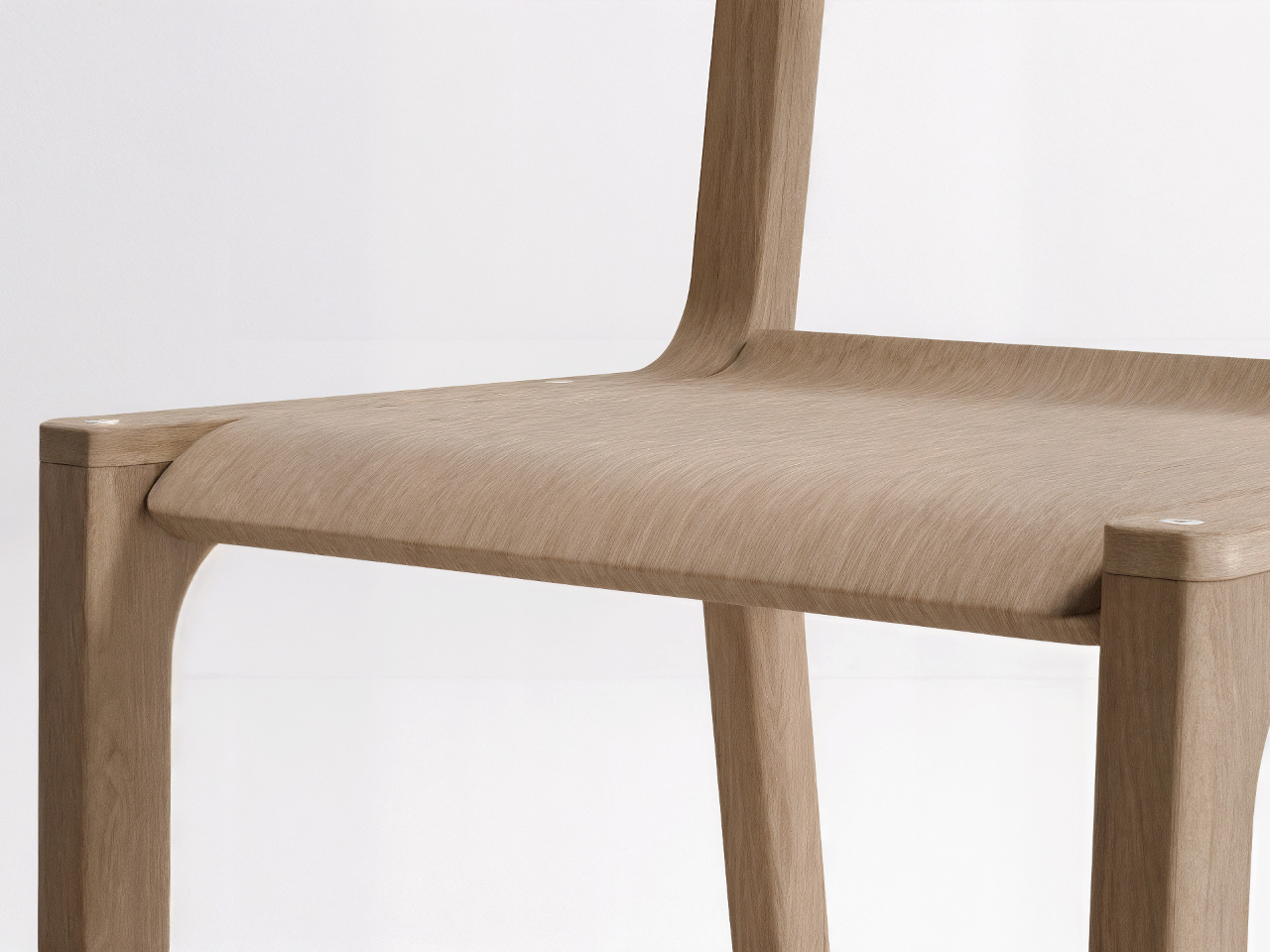
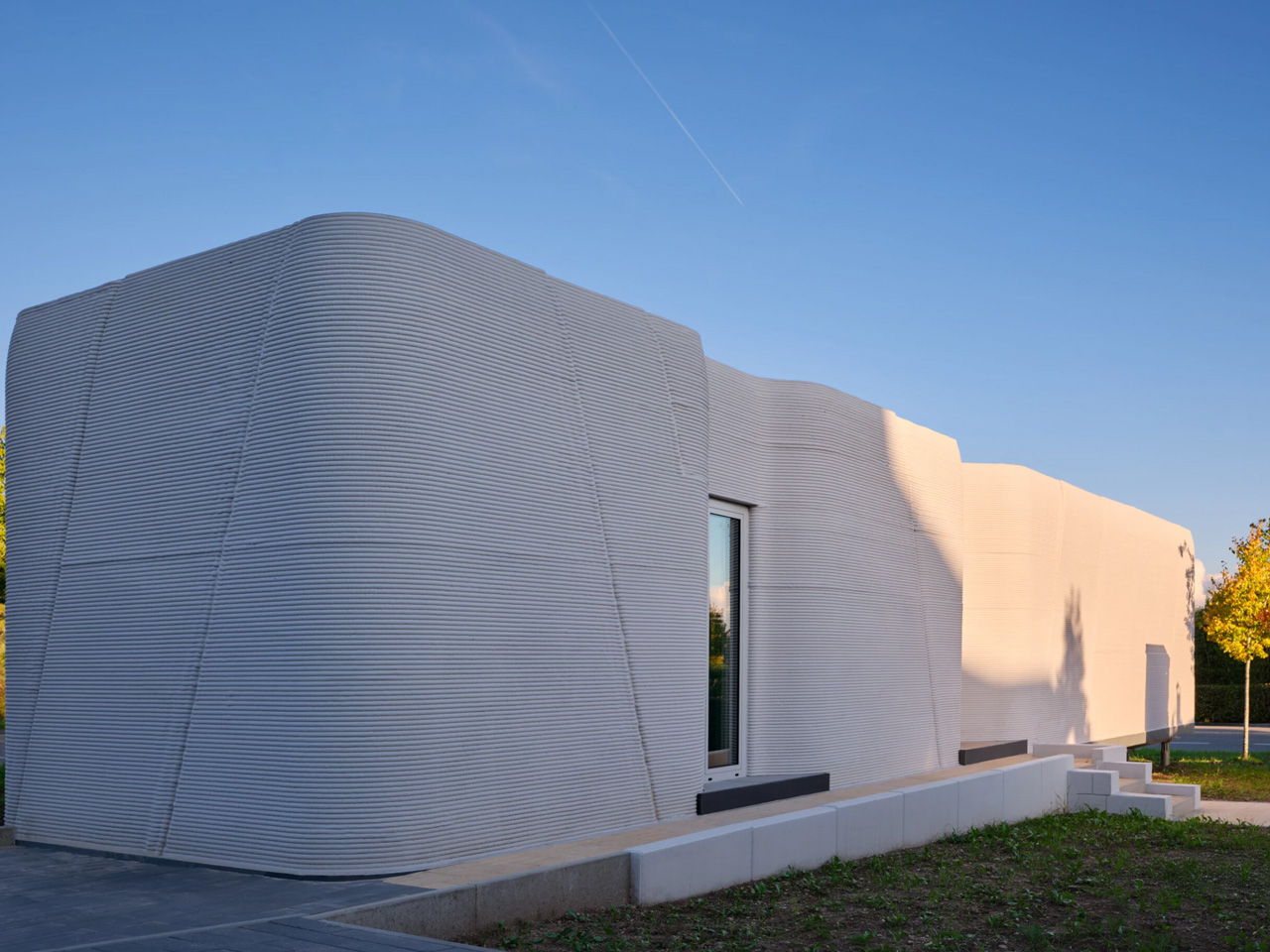
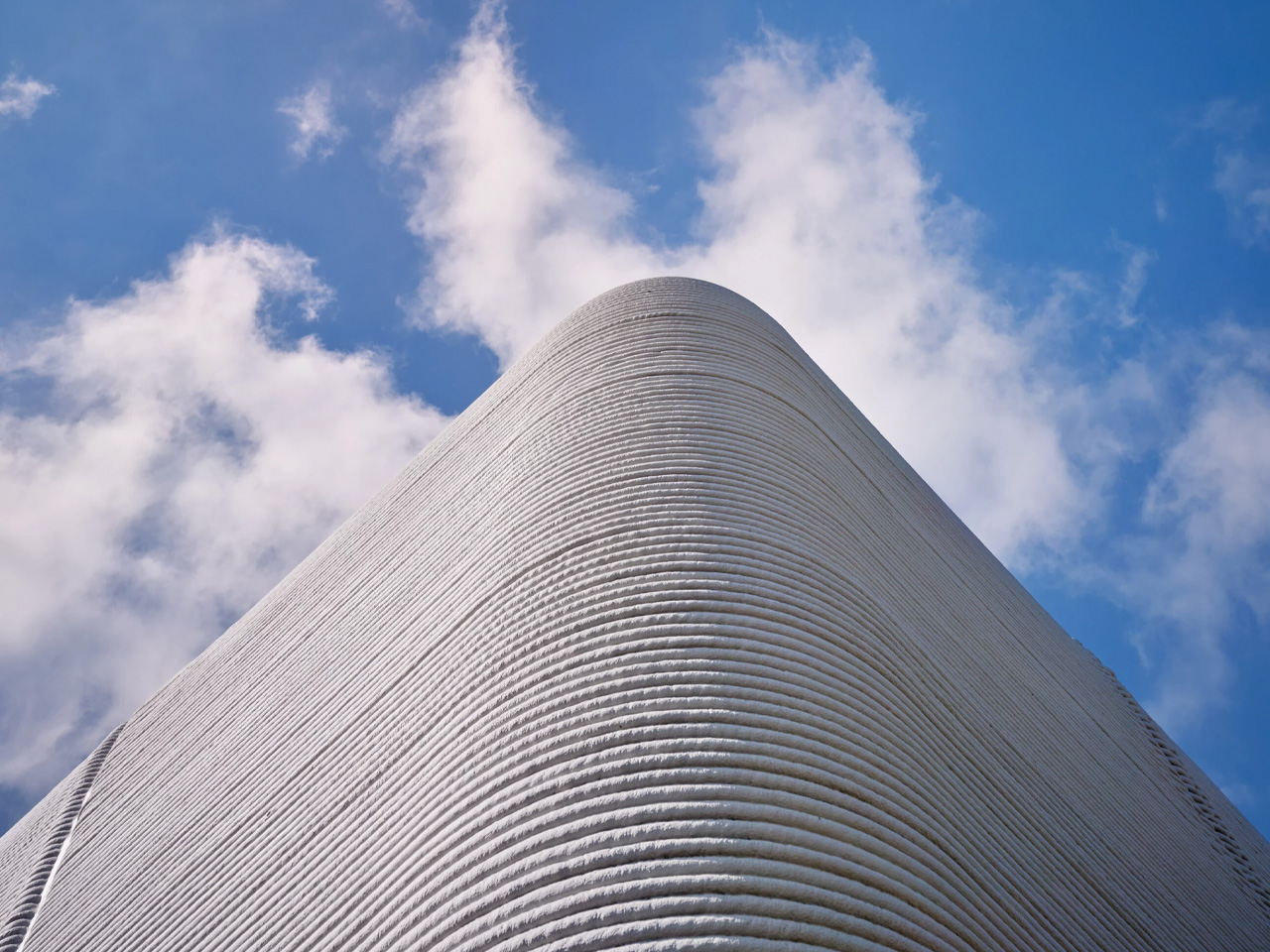
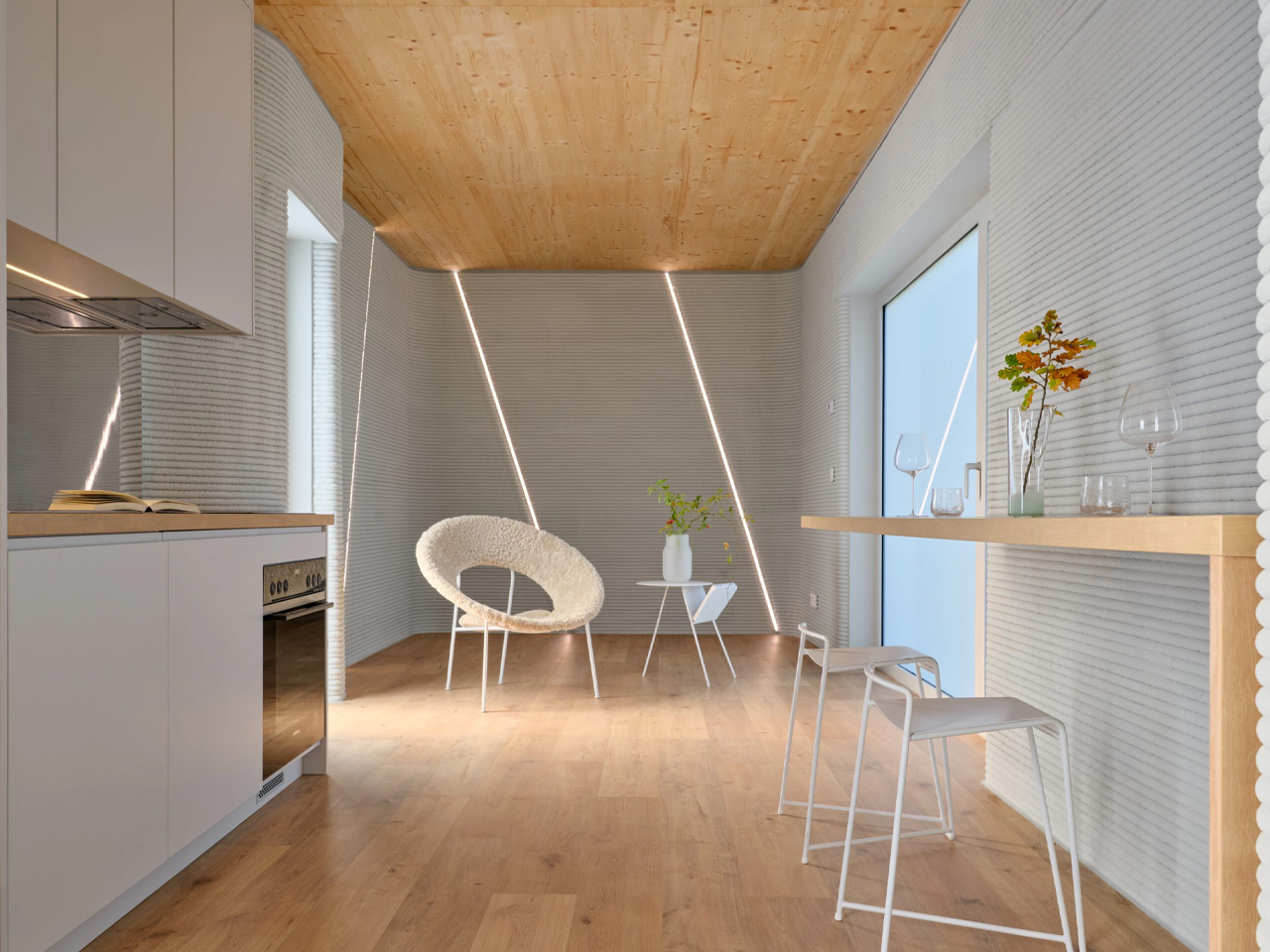
Material choice plays a pivotal role in shaping a home. Architects focus on what is locally available and has a low environmental impact. Wood, stone, and bamboo are not only beautiful but also often renewable and sustainably sourced. Traditional materials like rammed earth and clay plaster are experiencing a resurgence, valued for their natural insulation, breathability, and enduring appeal.
These materials do more than form walls as they give a home character, texture, and a unique story. By connecting the building to its environment, they create spaces that feel alive, timeless, and deeply rooted in the land they inhabit.
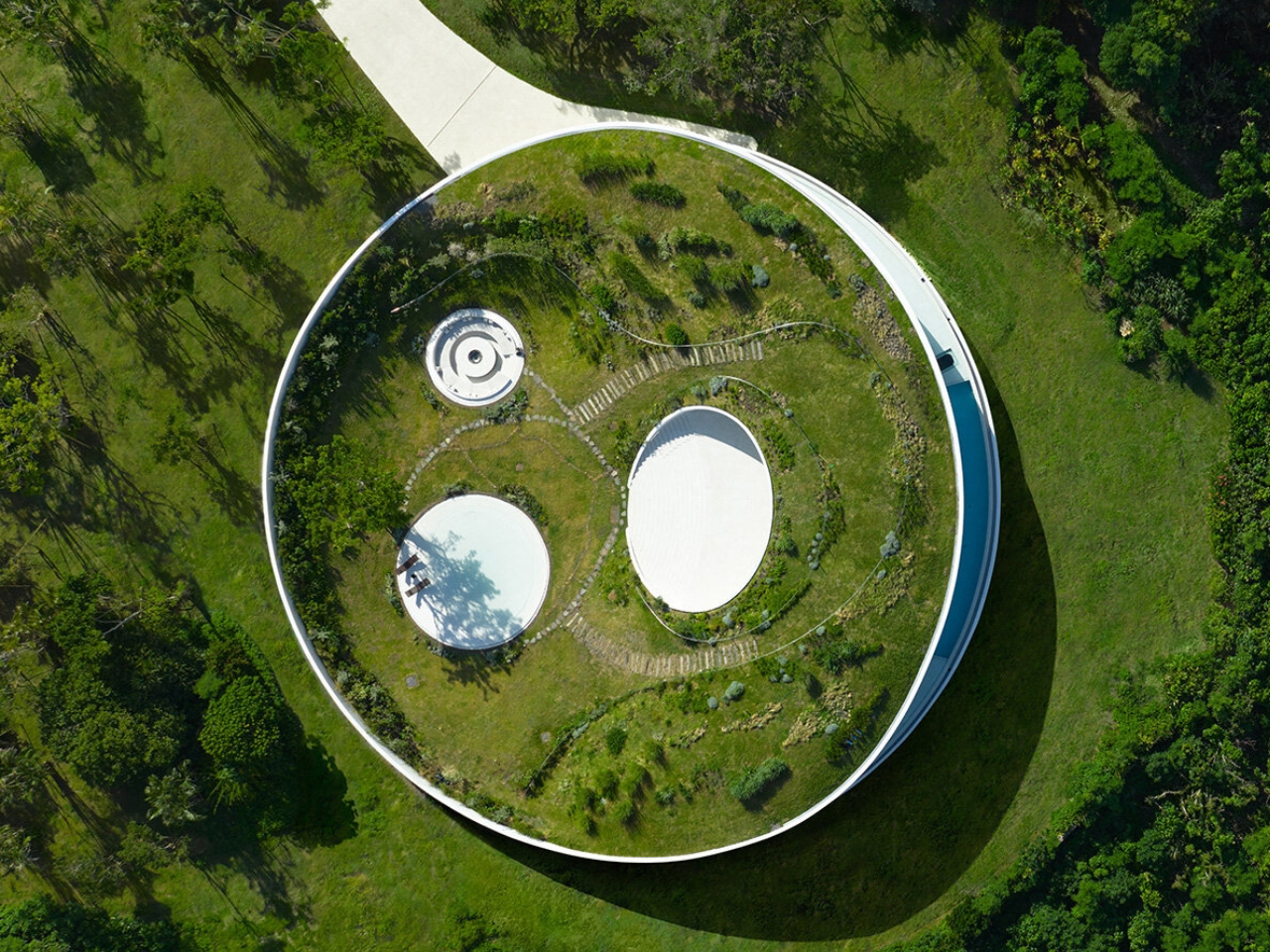
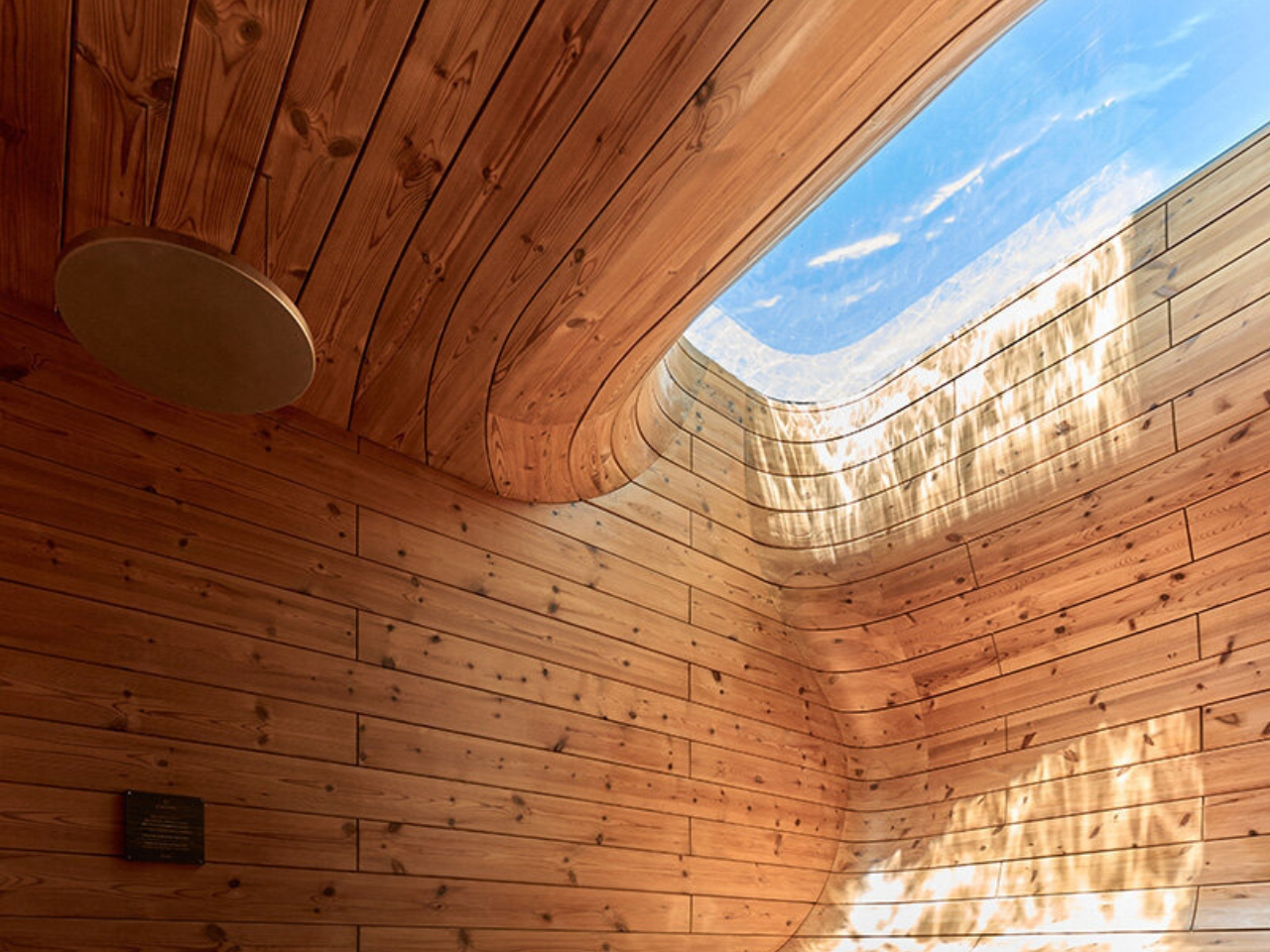


EARTH villa, designed by internationally acclaimed architect Sou Fujimoto for NOT A HOTEL, transforms the idea of a vacation home into a seamless blend of sustainability, futuristic design, and natural beauty. Located on Ishigaki Island in Okinawa Prefecture, Japan, the villa sits within a natural preserve, offering panoramic ocean views and lush greenery. Its bold circular layout encloses a private courtyard, while curved glass walls maximize natural light and sightlines, creating effortless indoor-outdoor transitions. The living green roof, covered with native grasses, provides insulation, reduces rainwater runoff, and supports local wildlife, making the villa eco-conscious and visually striking.
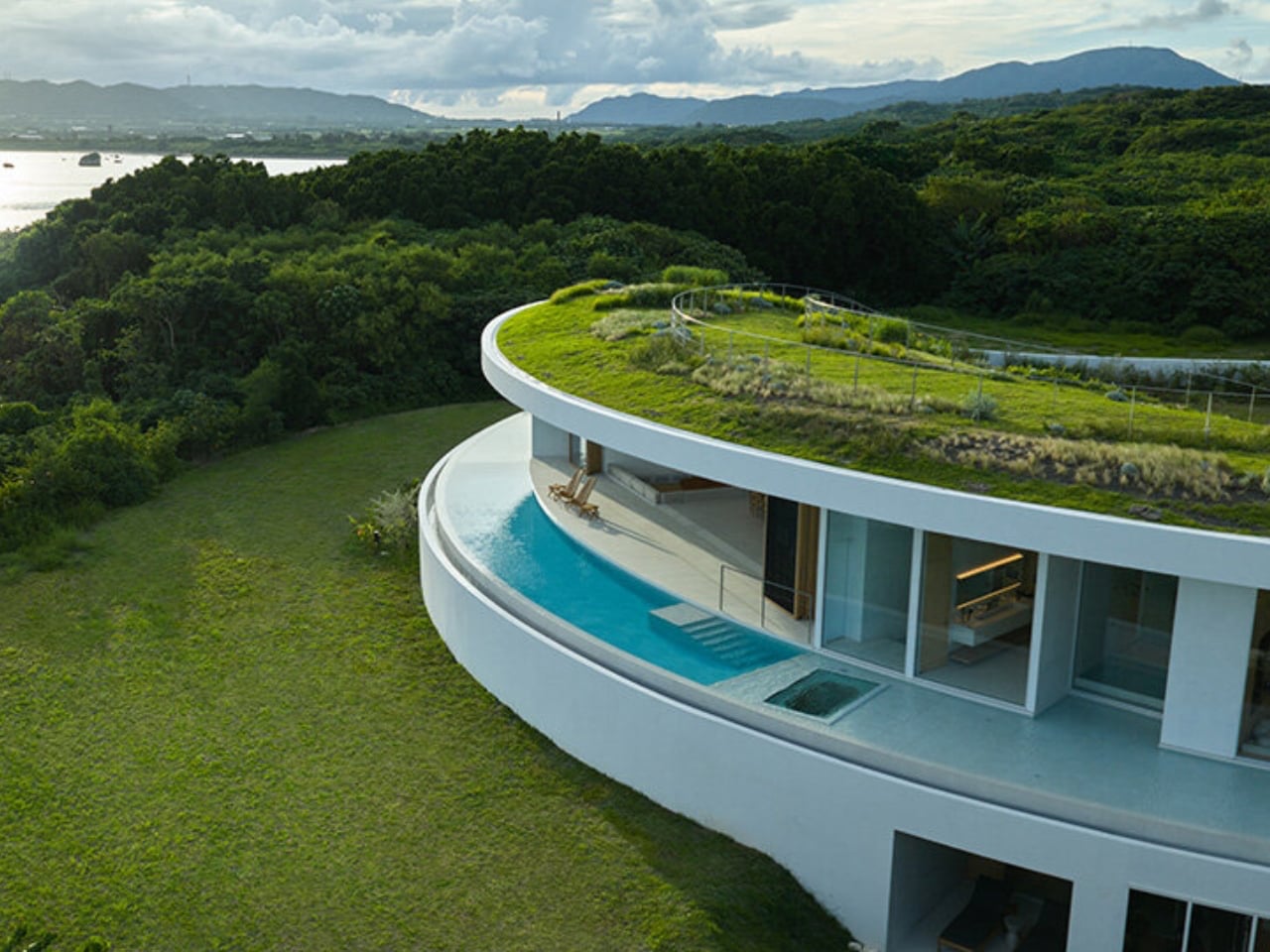
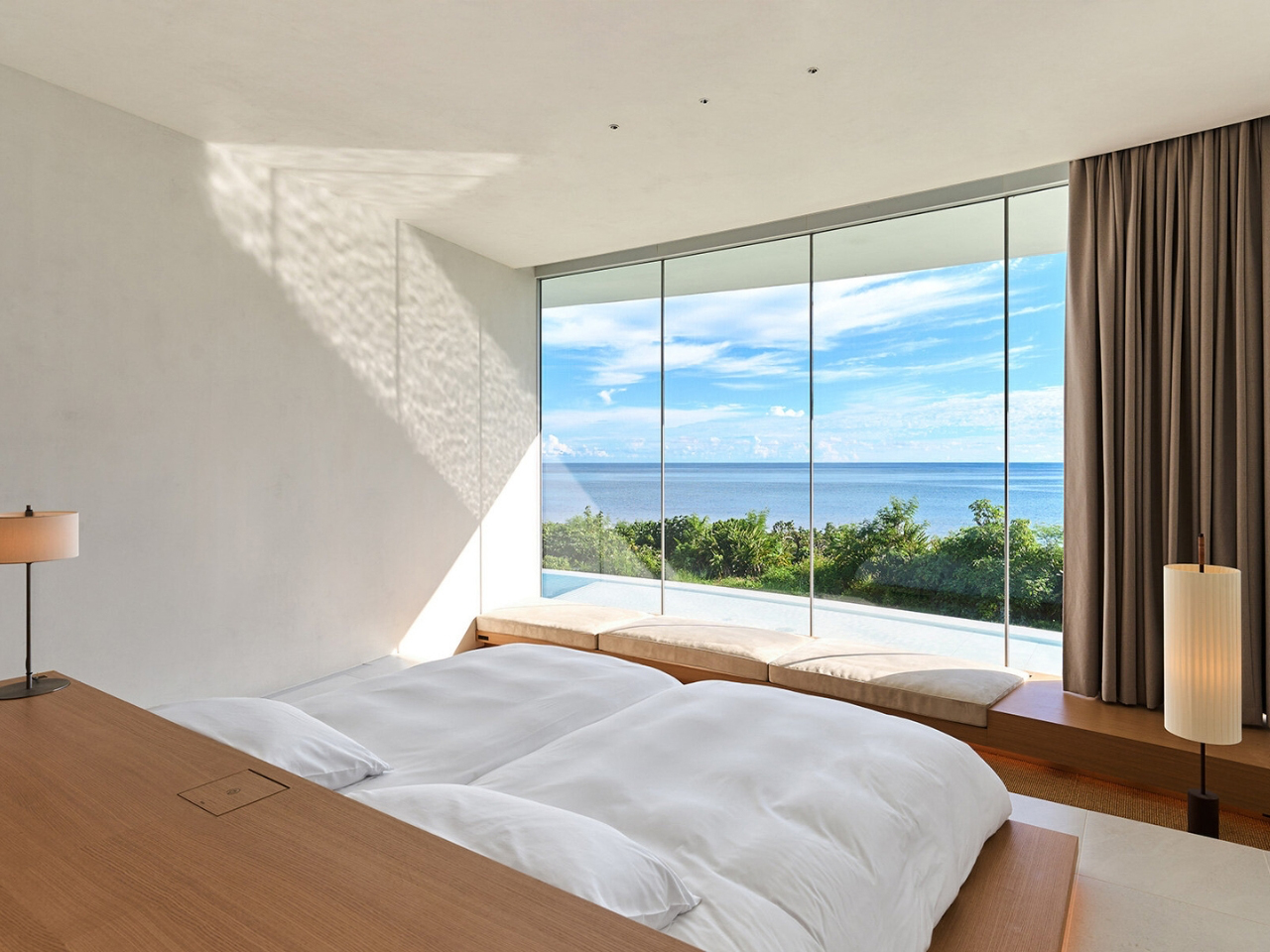
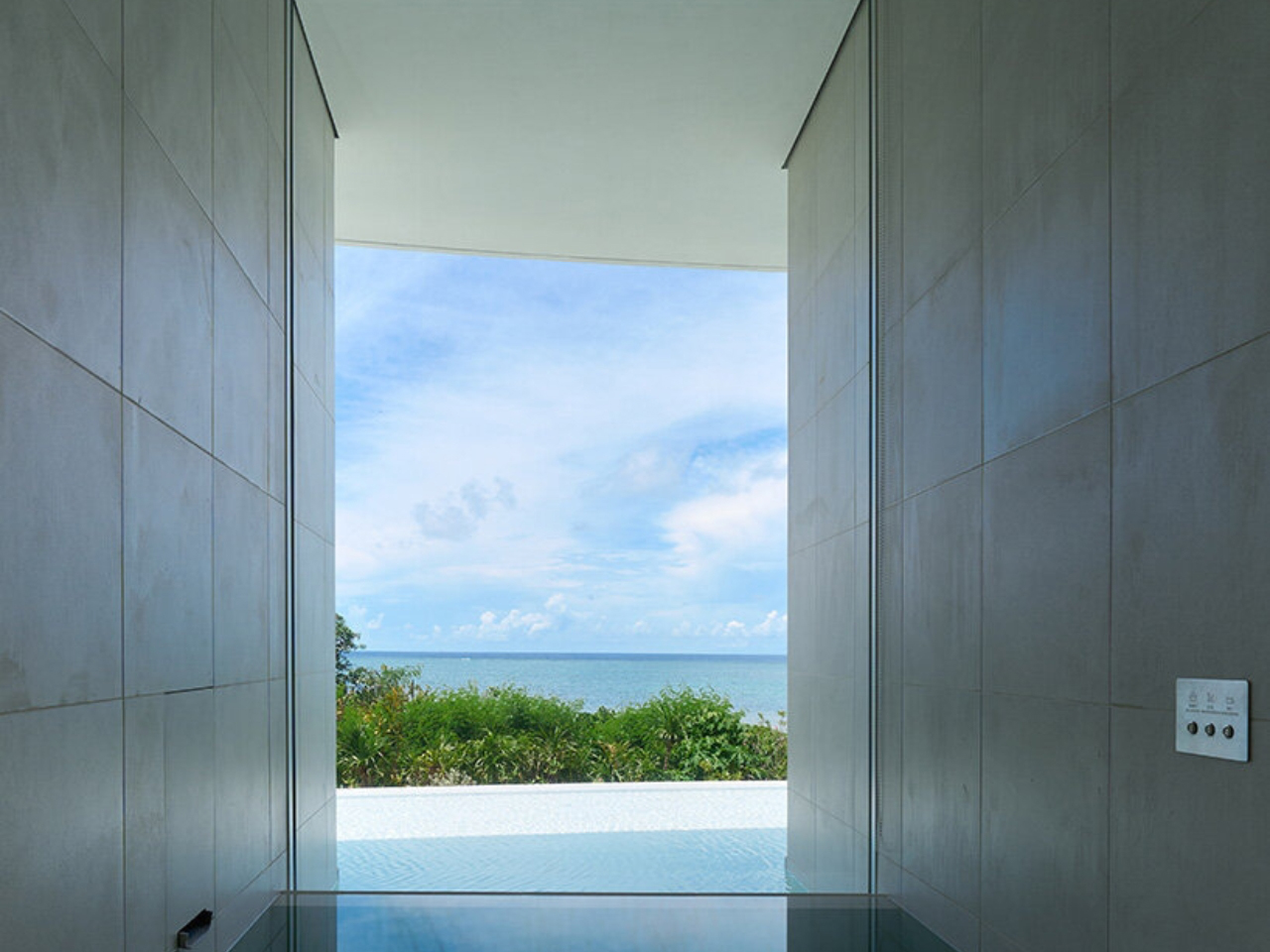



Inside, minimalist interiors with natural wood accents and earth tones create warmth and tranquility. Sustainable systems, including passive ventilation, solar panels, and rainwater harvesting, reduce environmental impact. EARTH offers luxury, flexibility, and hotel-level services, allowing guests to immerse themselves in nature while enjoying comfort and environmental stewardship at its finest.
3. Harness Light and Air
Sunlight and fresh air are among the most sustainable and beautiful elements a home can embrace. Architects design spaces to maximize natural light, reducing reliance on artificial lighting while enhancing the interior ambiance. Large windows oriented toward the sun (south-facing in the Northern Hemisphere) capture winter warmth, creating naturally cozy spaces.
Thoughtful placement of windows and doors encourages cross-ventilation, allowing cool breezes to flow through the home. This reduces the need for mechanical cooling on many days. By prioritizing light and air, a house becomes more energy-efficient, comfortable, and in harmony with its environment.
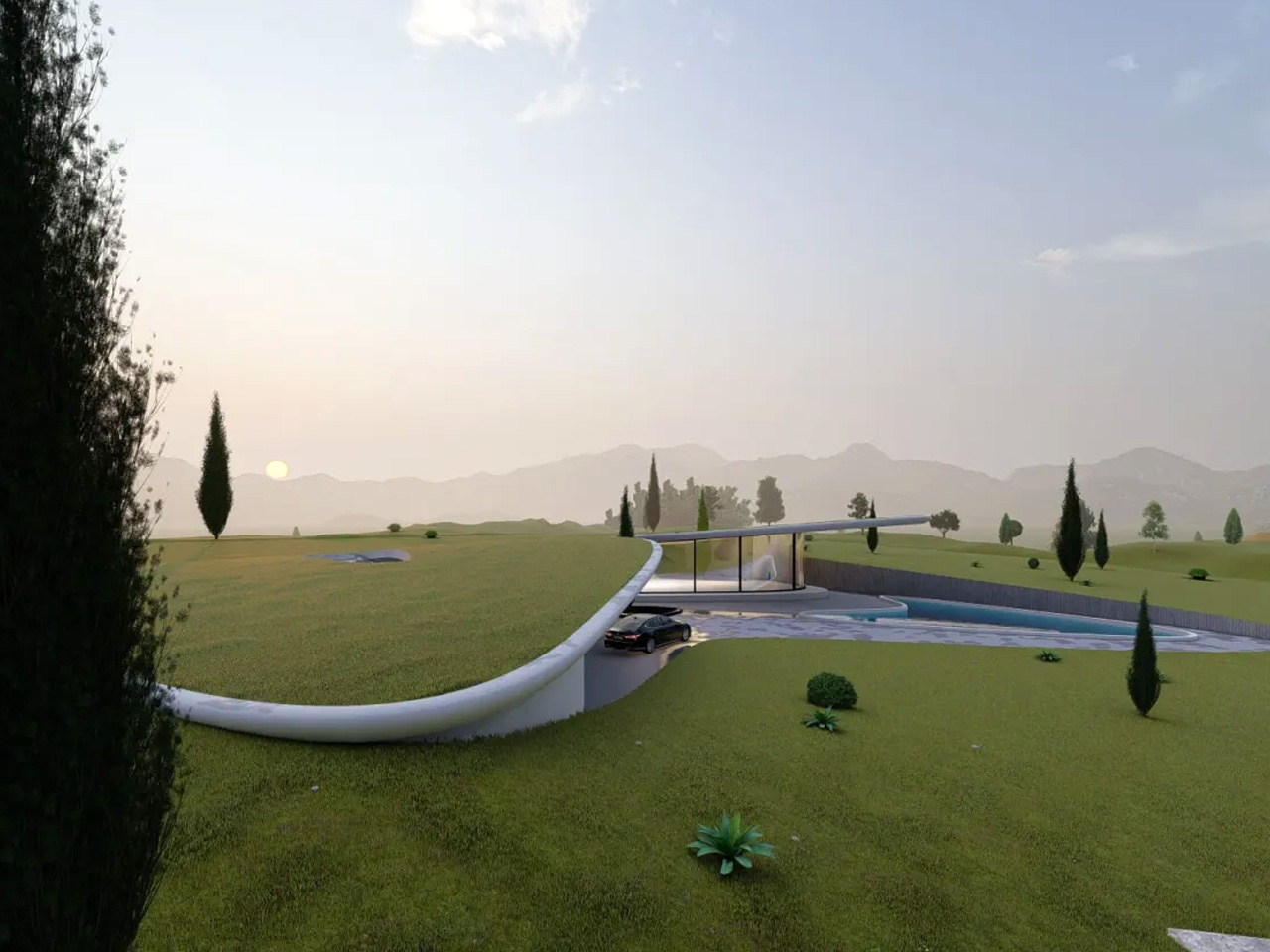
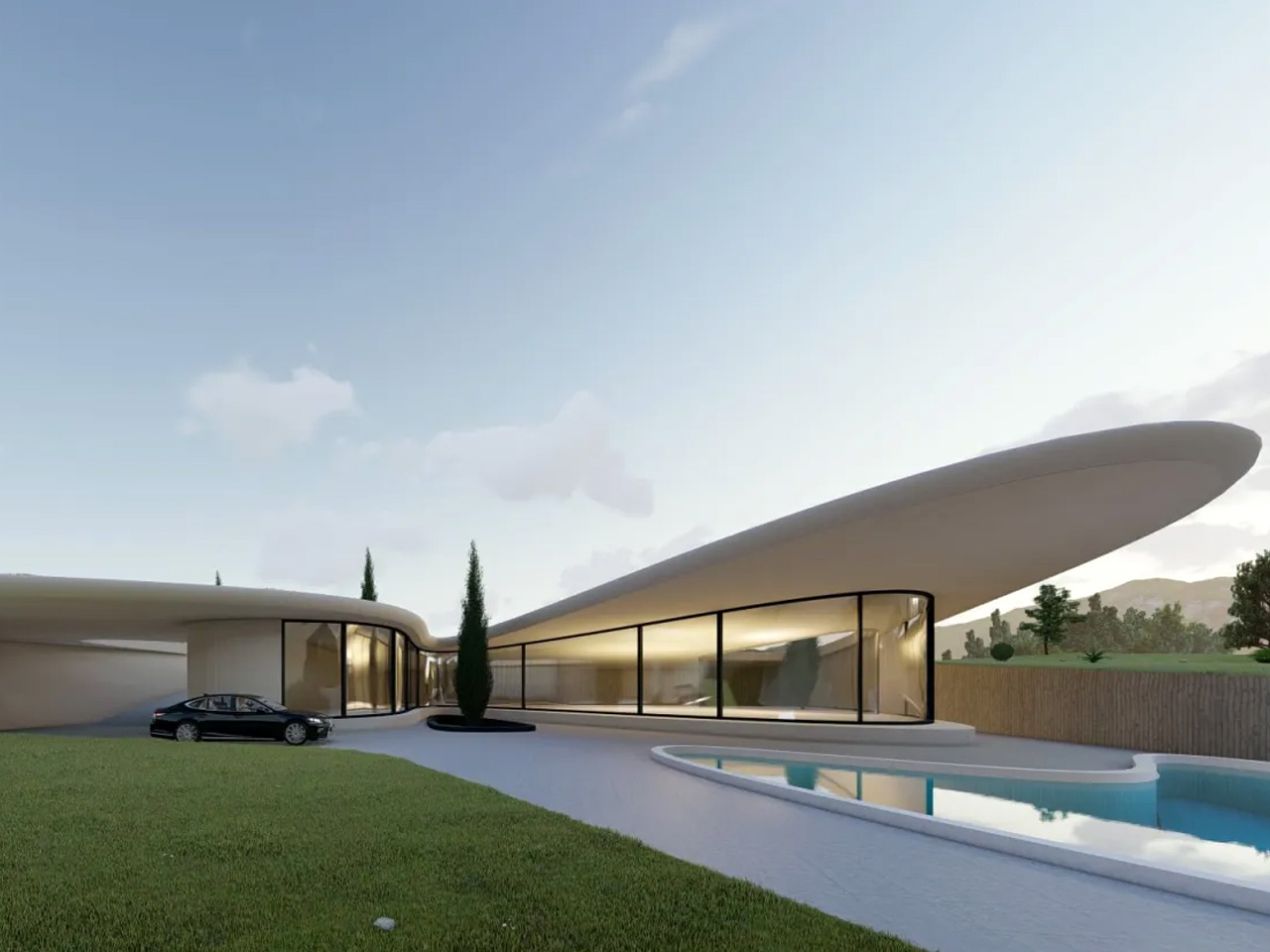


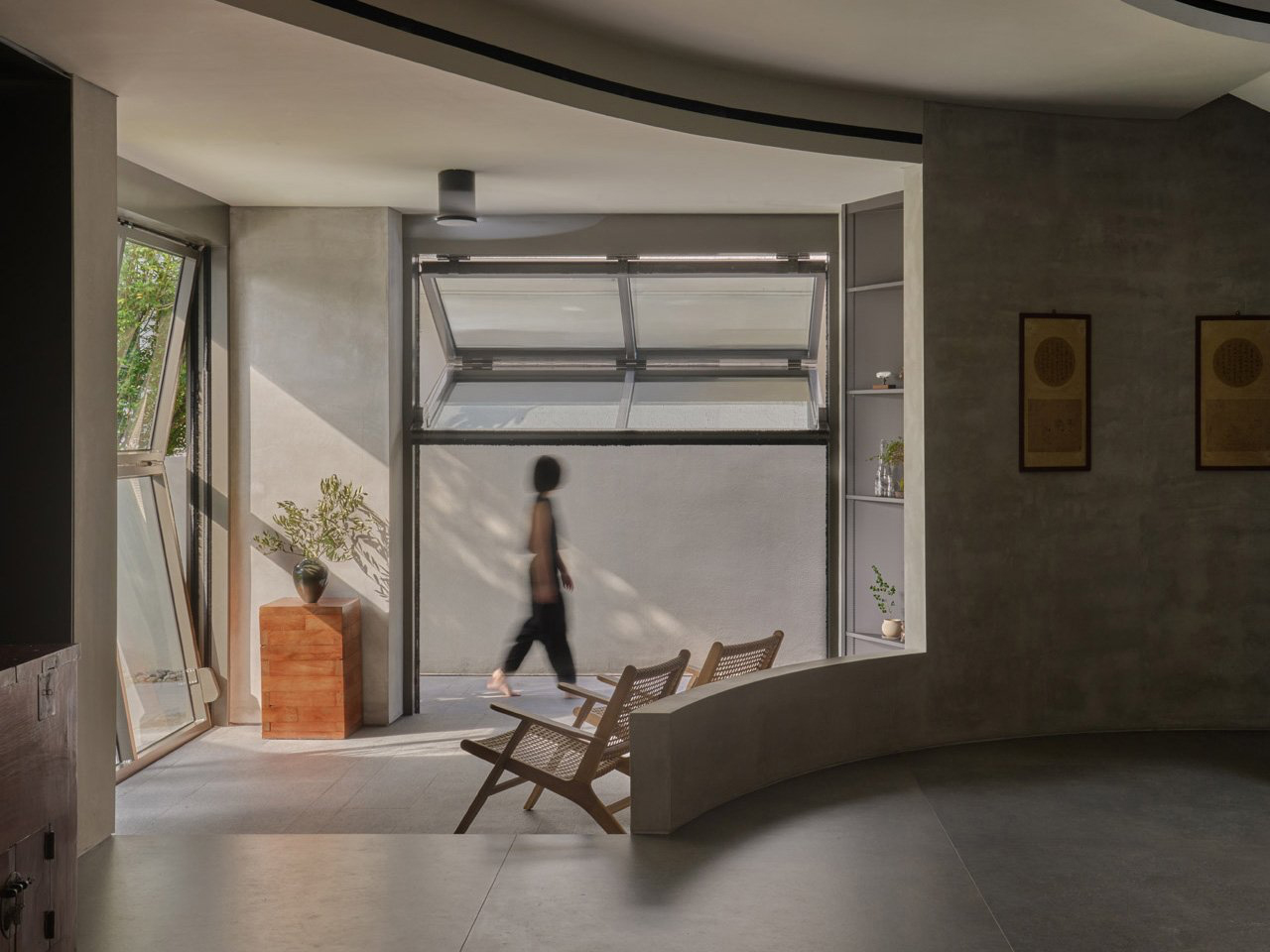
Nestled in the rolling hills of Nashtarood, House Under the Hill is an architectural marvel that blends seamlessly with its landscape. Much of the home is tucked beneath a living roof, echoing the surrounding terrain and allowing the structure to almost disappear into its site. Fluid forms, gentle curves, and careful play of light and shadow reveal the dwelling subtly, while broad glass panels frame views of the pool and greenery, merging interior and exterior. The palette of concrete, wood, and glass creates modern elegance, and open, flowing spaces connect the kitchen, dining, and lounge areas. Bedrooms and bathrooms are oriented for privacy, natural light, and tranquility, enhancing a sense of retreat.
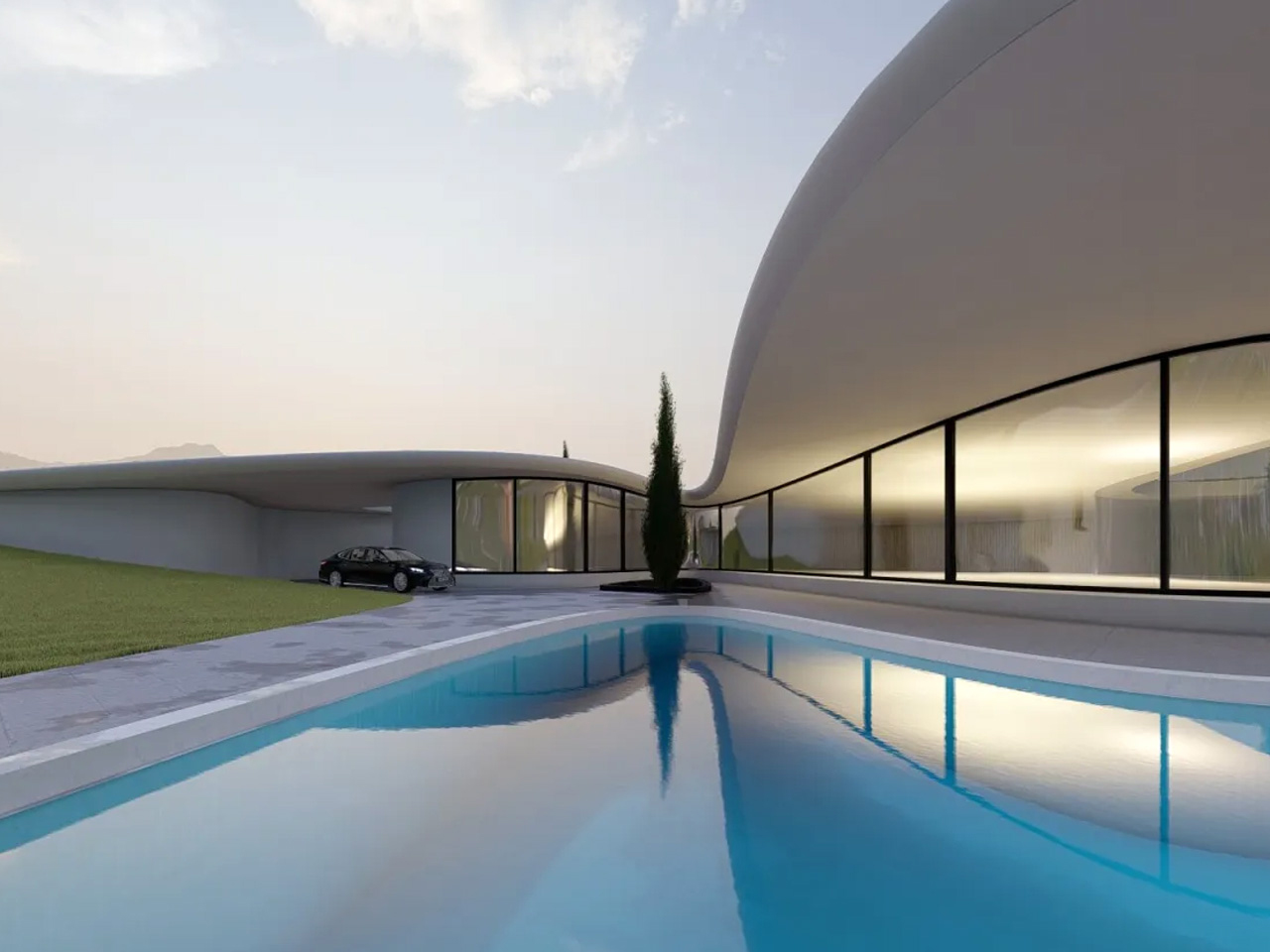
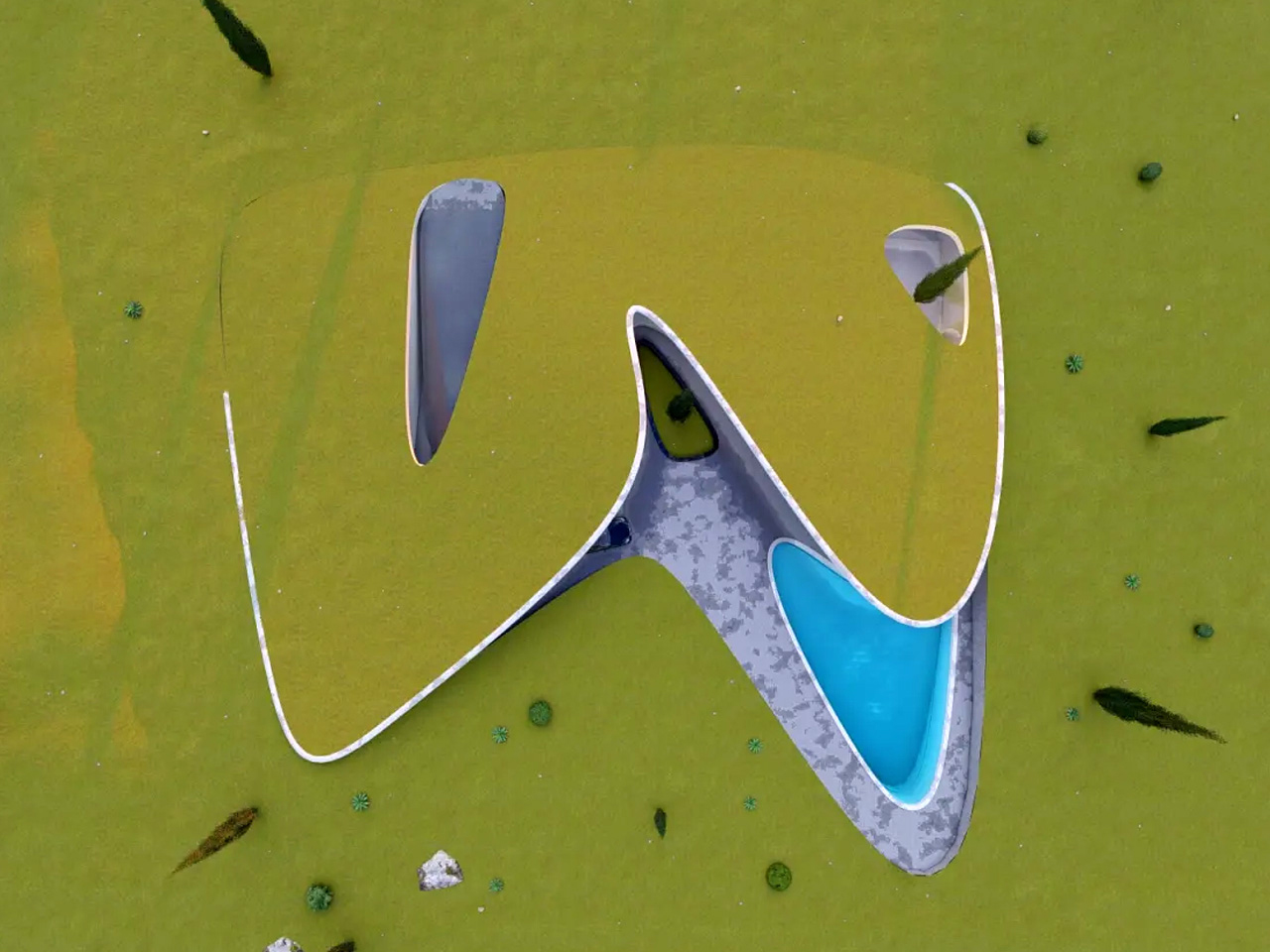


The green roof provides insulation, reduces environmental impact, and harmonizes the home with its surroundings. Outdoor terraces and pool areas offer year-round comfort, while integrated storage, durable materials, and soft, responsive lighting enhance functionality. House Under the Hill embodies a modern approach to living that belongs to the earth, offering a protective, nurturing, and adaptable sanctuary.
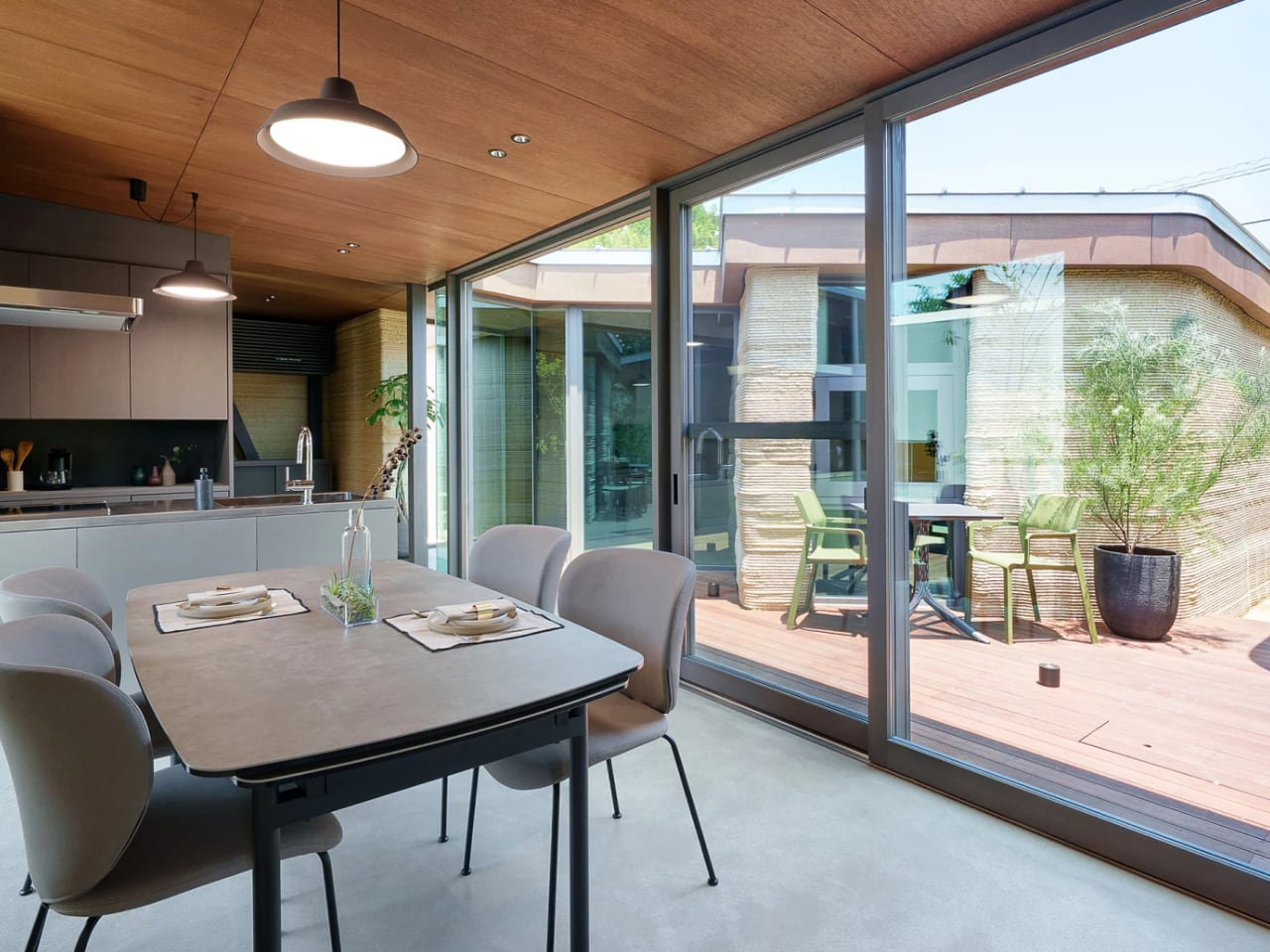
4. Integrate the Indoors and Outdoors
A home should feel connected to the natural world rather than isolated from it. Architects often use large glass sliding doors to merge indoor and outdoor spaces, allowing light and views to flow freely. Patios, decks, and other outdoor living areas are designed for easy access from main living zones, encouraging a fluid relationship with nature.
Thoughtful landscaping with native plants further blurs the boundary between house and environment. These spaces offer quiet retreats and areas for social gatherings, creating a home that celebrates the outdoors while remaining comfortable, functional, and deeply in tune with its surroundings.
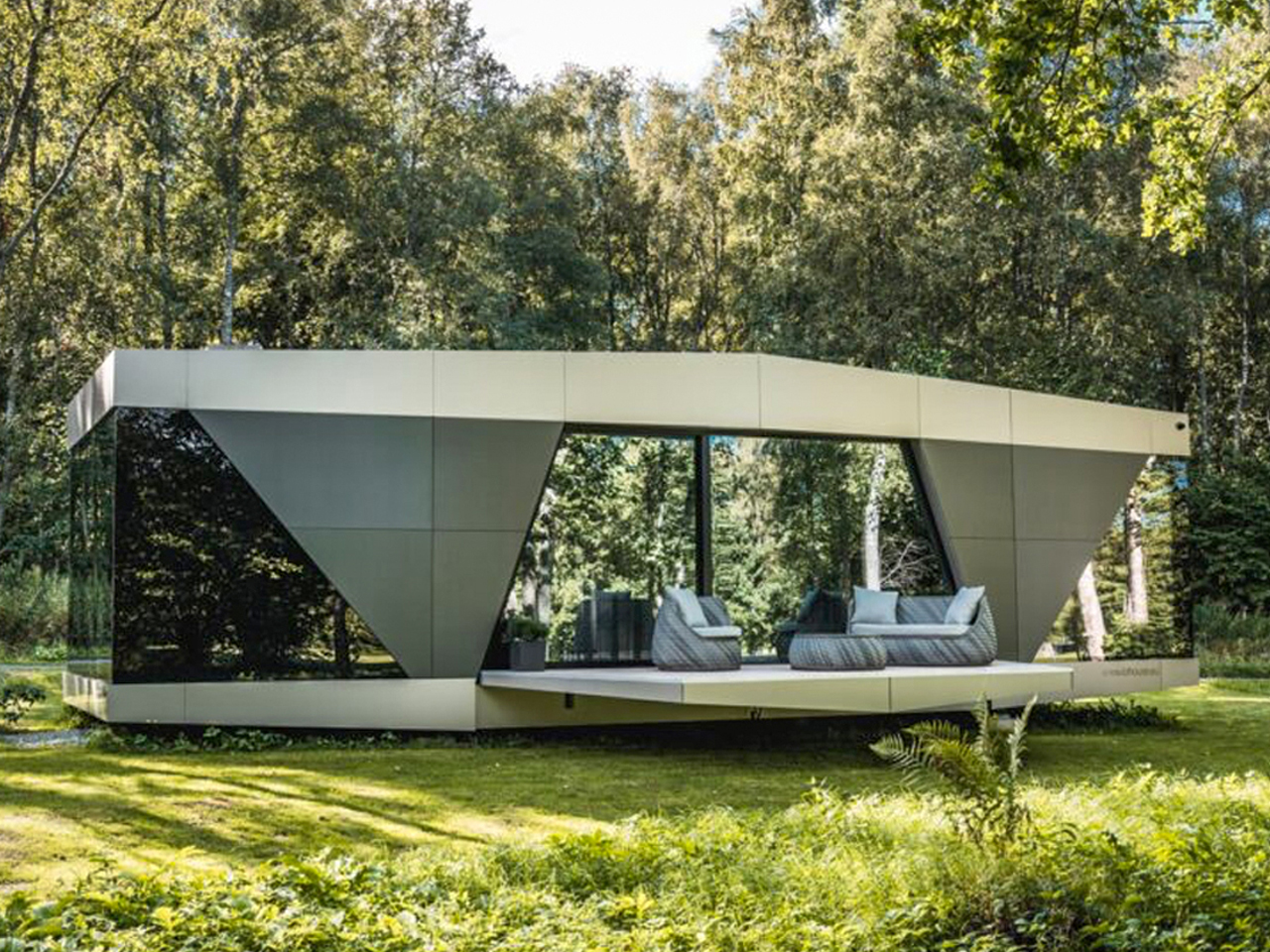
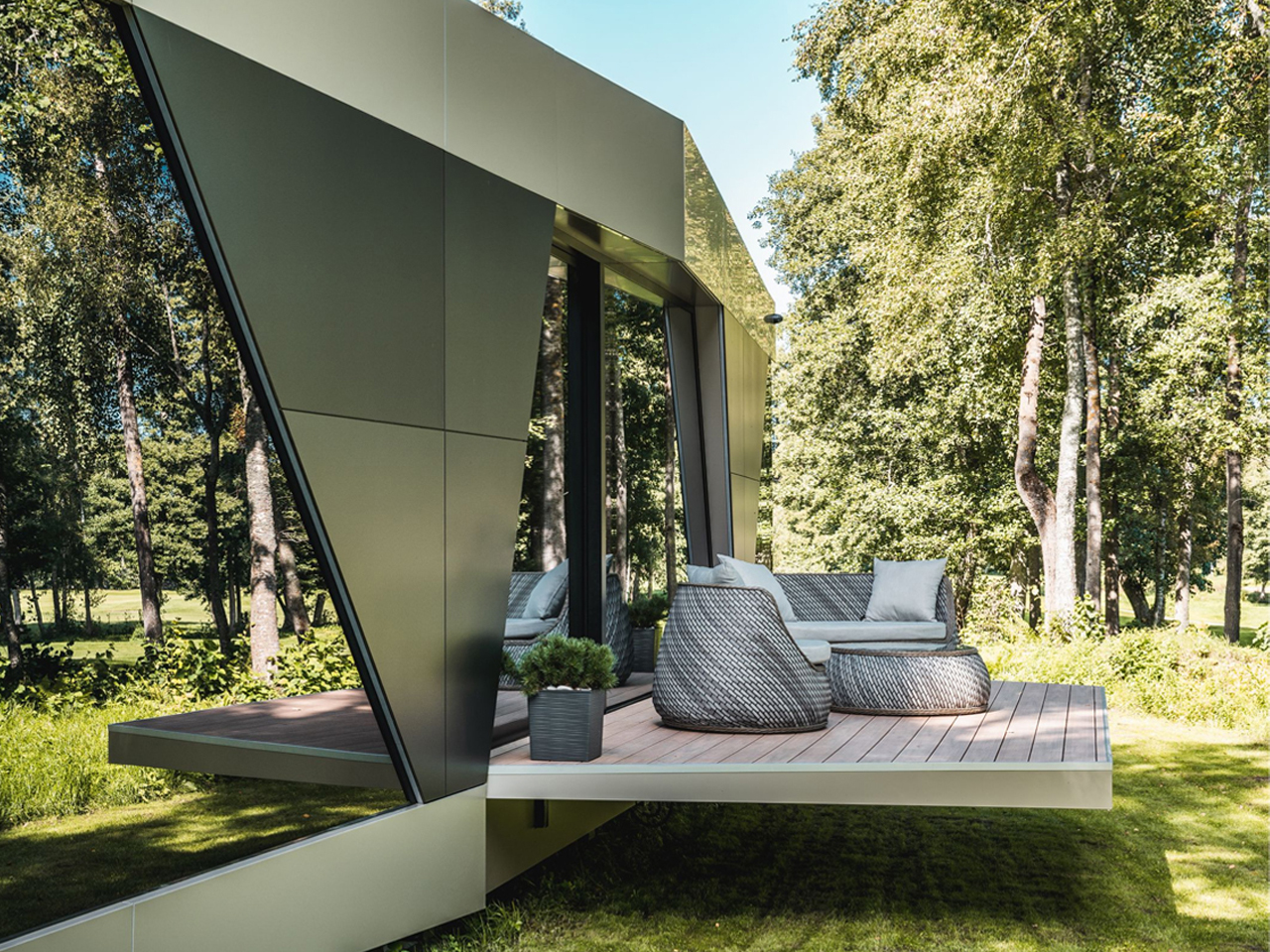


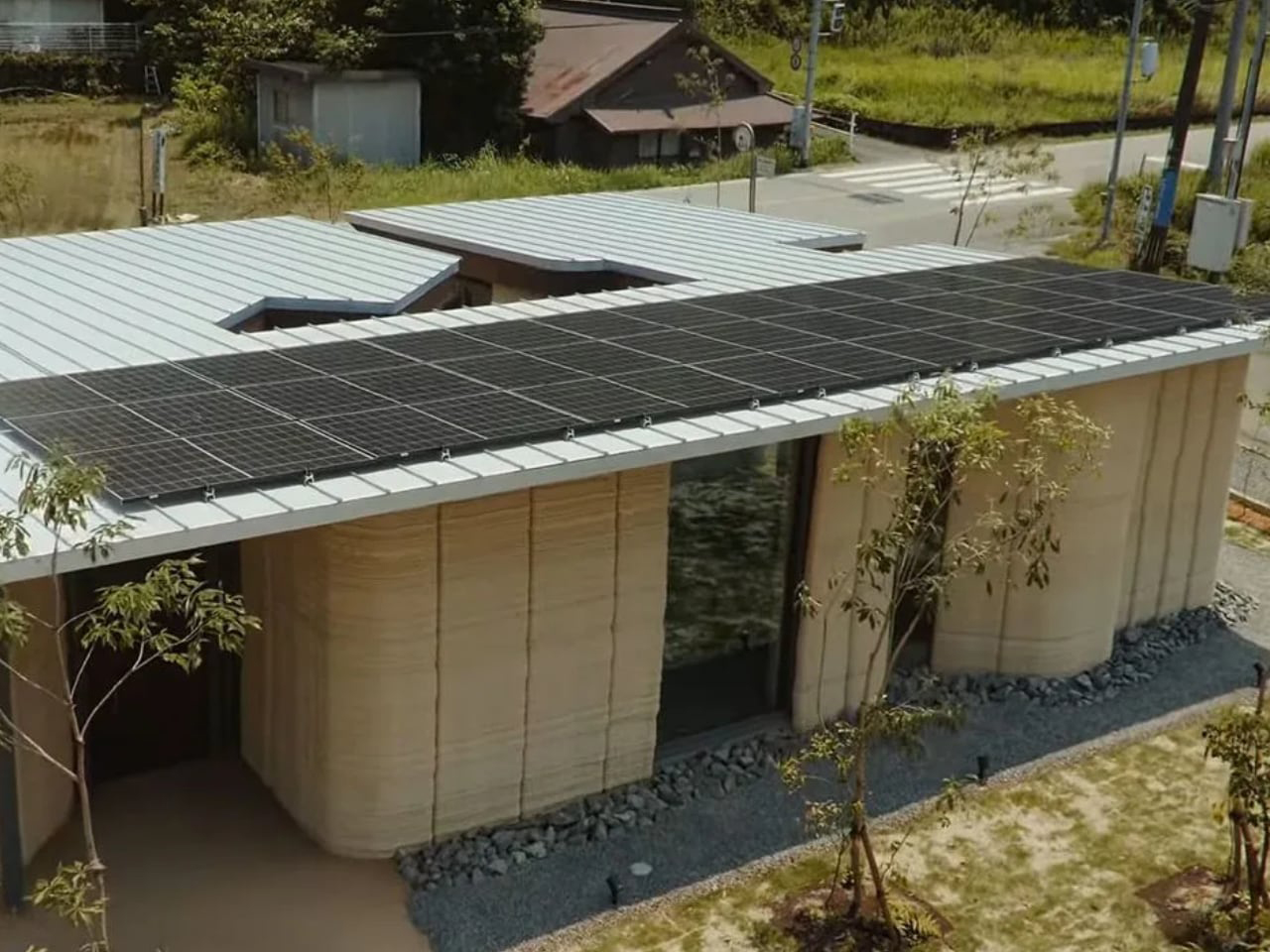
The Space is a sustainable smart home where fully autonomous utilities combine advanced technology with modern comfort. Developed by Stockholm-based iOhouse, it functions entirely off the grid, with water, electricity, heating, and Wi-Fi all controlled through a smartphone. Solar panels and a 220V generator supply power, while an air heat pump and integrated climate controls maintain year-round comfort. A built-in water and sewer system ensures clean water and plumbing wherever the home is placed. The exterior features a sleek, futuristic design with industrial-tech elements, complemented by floor-to-ceiling windows that connect the interior with nature.
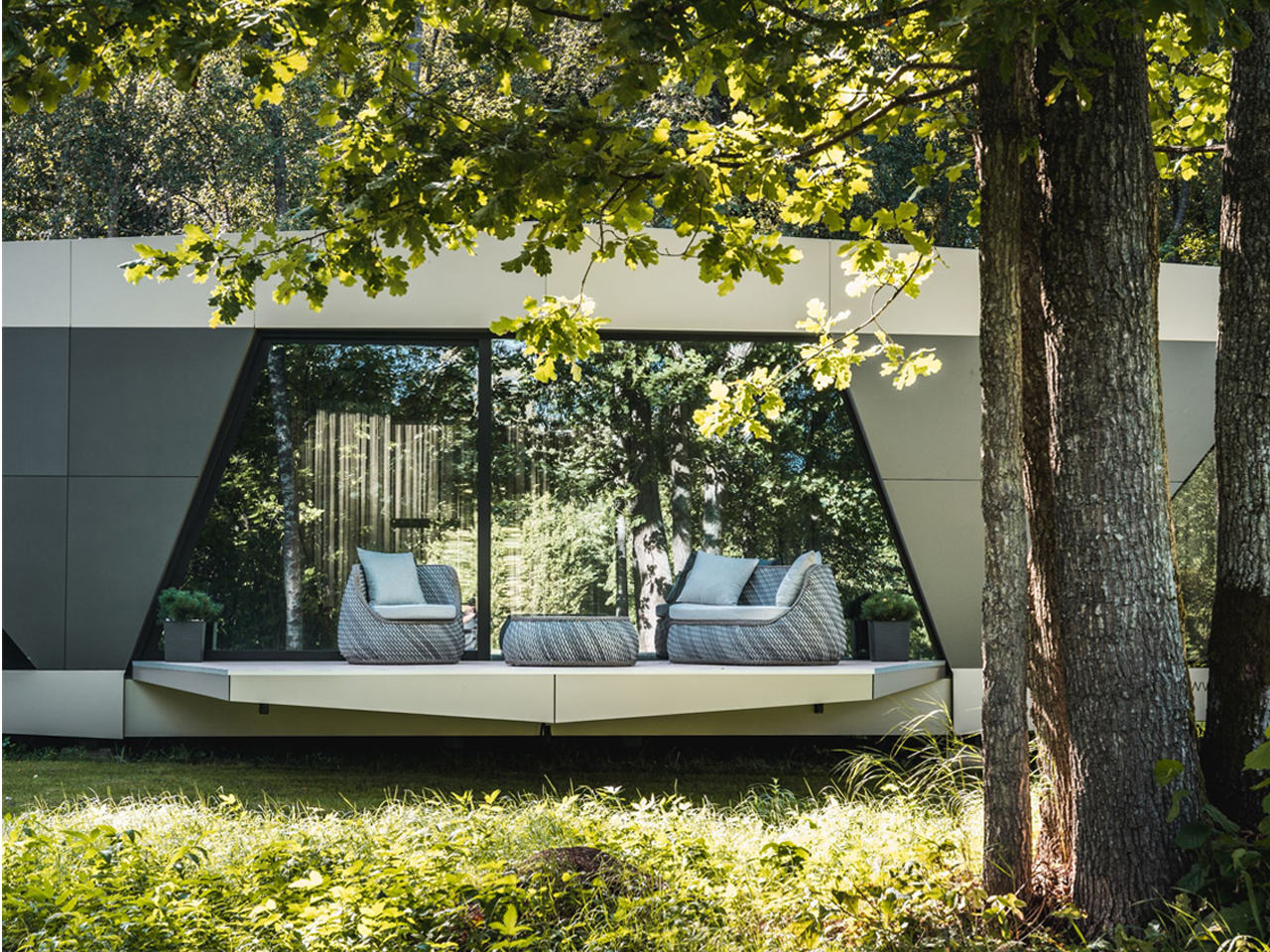
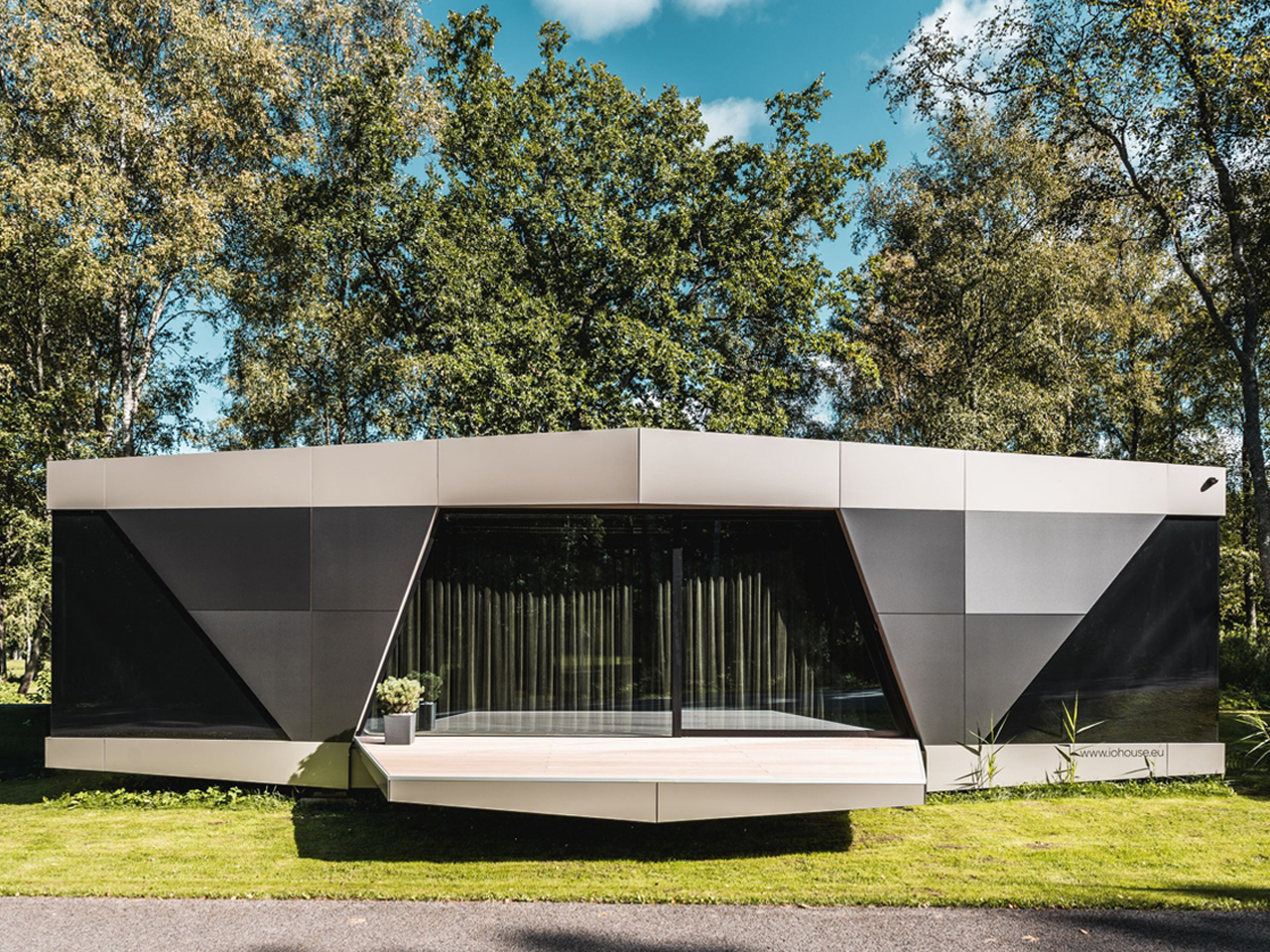
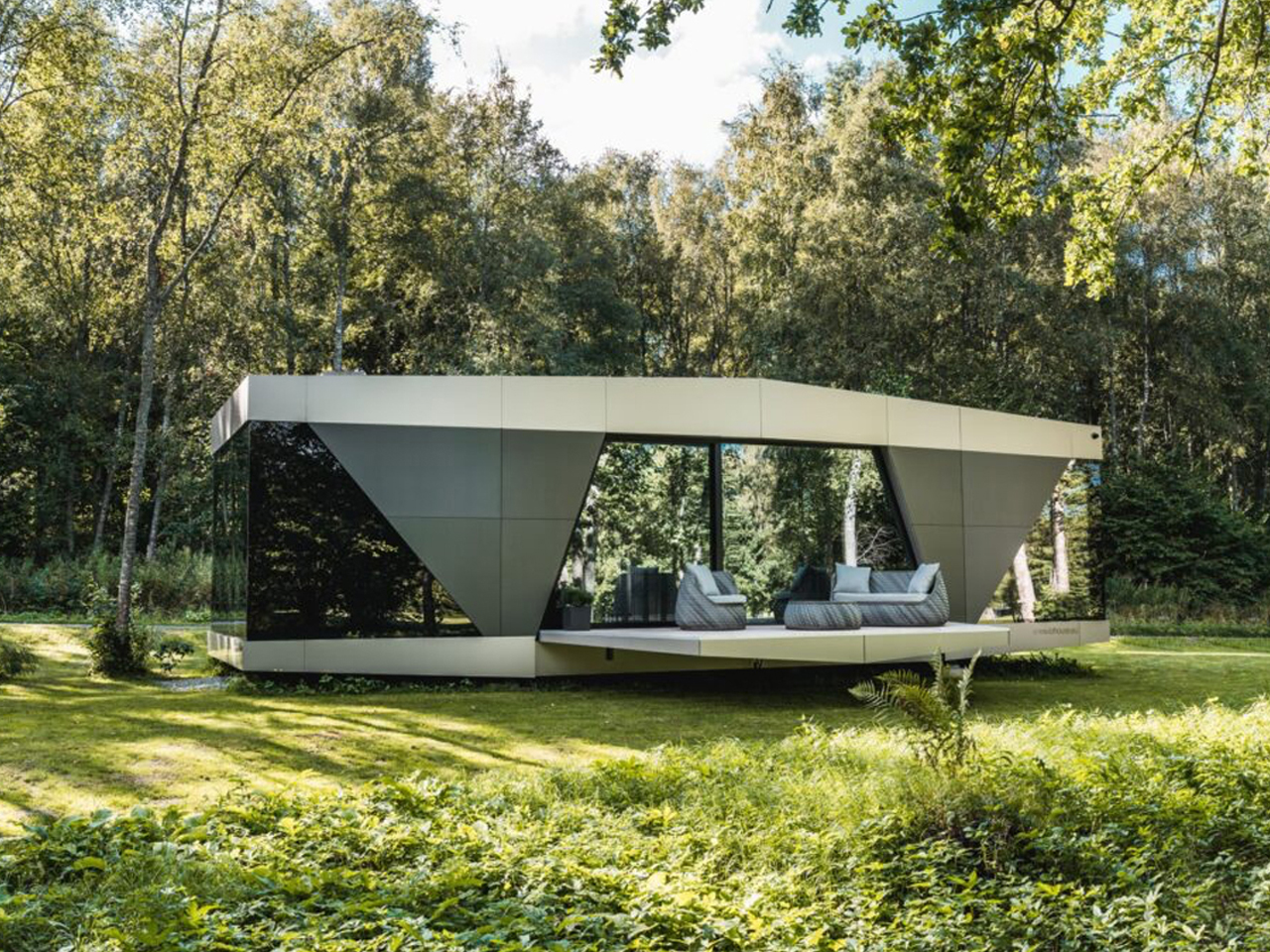



Inside, an open-floor layout with natural wood floors and muted gray tones creates a warm, inviting atmosphere. Every detail, right from fixtures and fittings to room shapes, has been carefully designed for comfort and aesthetics. With its smart systems and autonomous utilities, The Space allows residents to live freely, sustainably, and harmoniously with the environment.
5. Water Management and Conservation
A sustainable home carefully considers how it manages water. Beyond conserving tap water, it works with the rain that falls on the property. Rainwater harvesting systems can collect and store water for irrigation and other non-potable uses, reducing reliance on municipal supply.
Landscaping with rain gardens and using permeable paving allows stormwater to be absorbed naturally, preventing soil erosion and replenishing groundwater. By thoughtfully managing water on-site, a home supports the local ecosystem, minimizes environmental impact, and demonstrates how small, intentional steps can create meaningful, lasting benefits for both the property and the surrounding landscape.
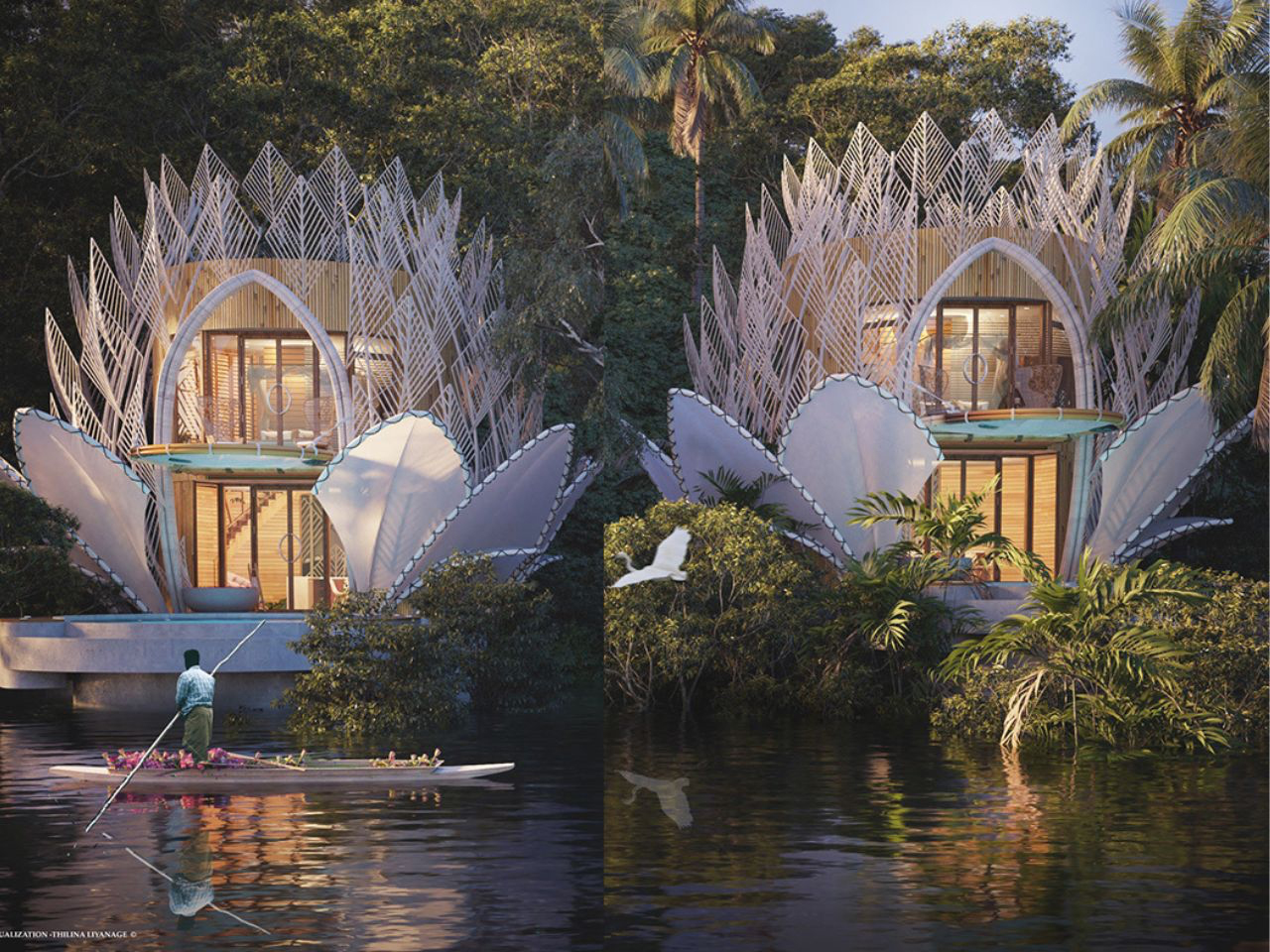
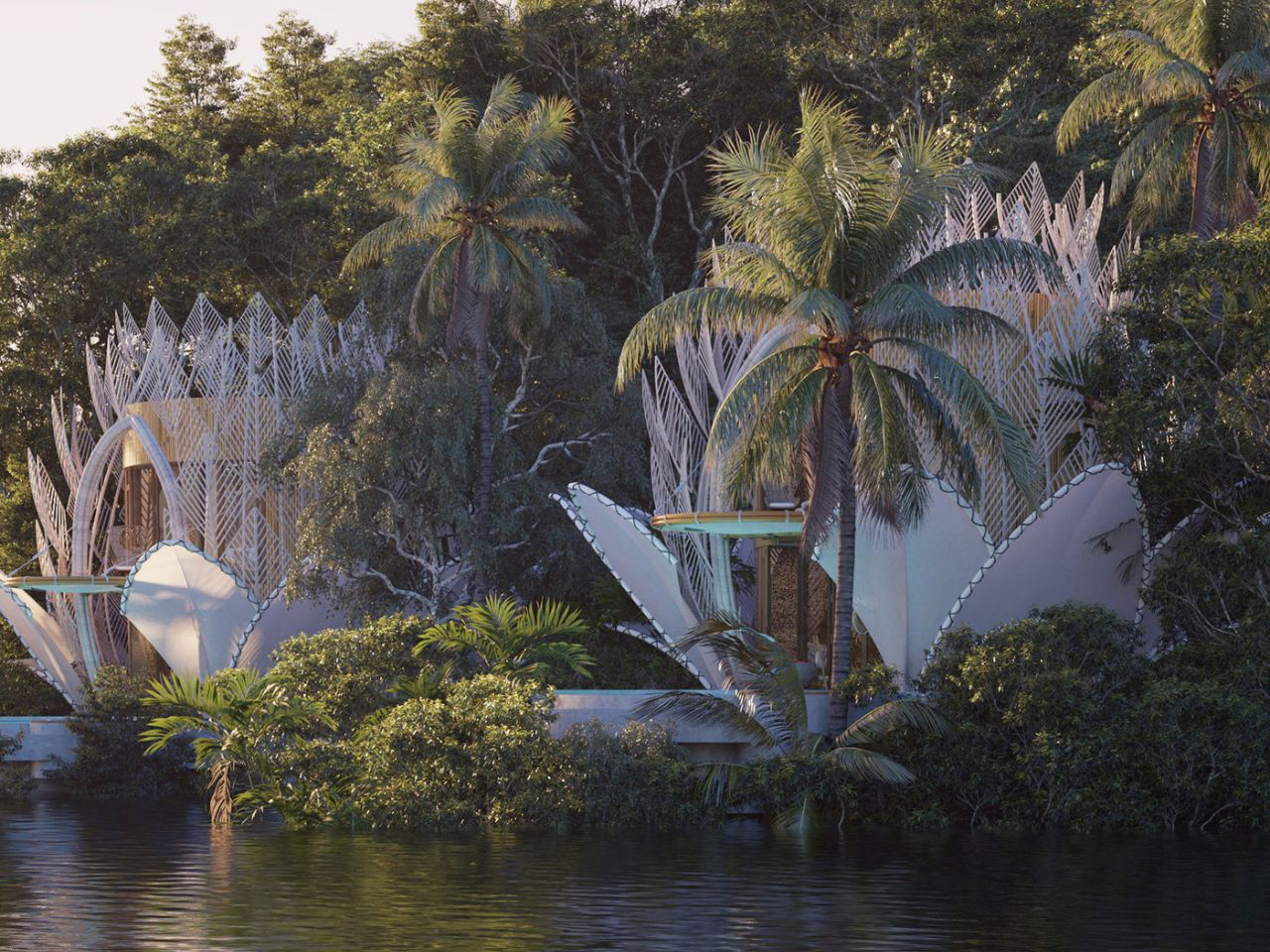


Nestled in the tropics where lush forest meets a serene lake, the Blue Water Lily Villa is a fairytale-like architectural masterpiece. Inspired by biomimicry, its design mirrors the delicate elegance of a water lily while remaining practical and sustainable. Comprising two two-story structures with direct lake access, the villas appear to float on the water’s edge. Petal-like forms rise gracefully from the landscape, creating layers that unfold like a blooming lily. The lower level features an open-plan living and dining area that flows seamlessly toward a small pool, framed by the lake and surrounding greenery.
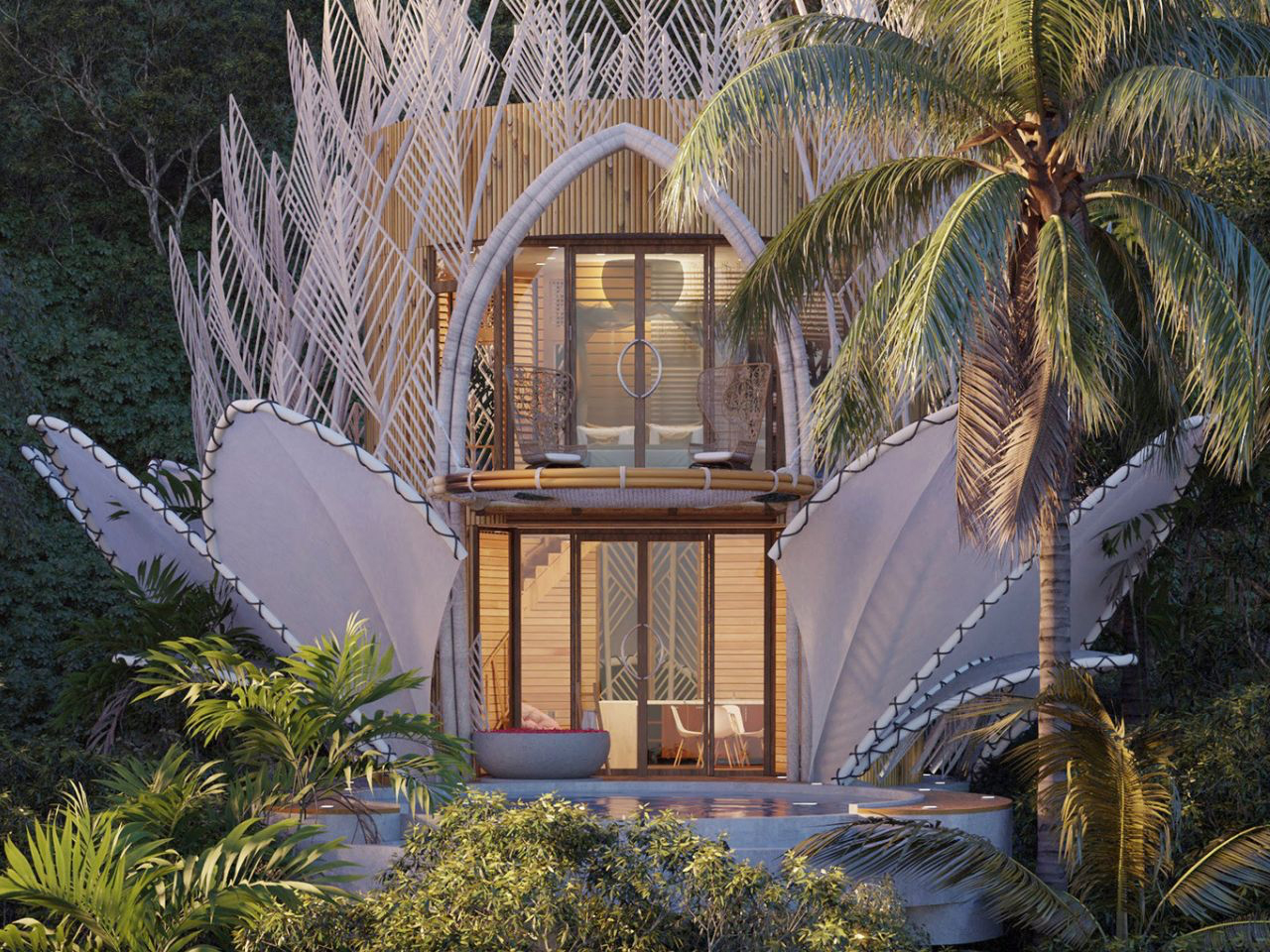
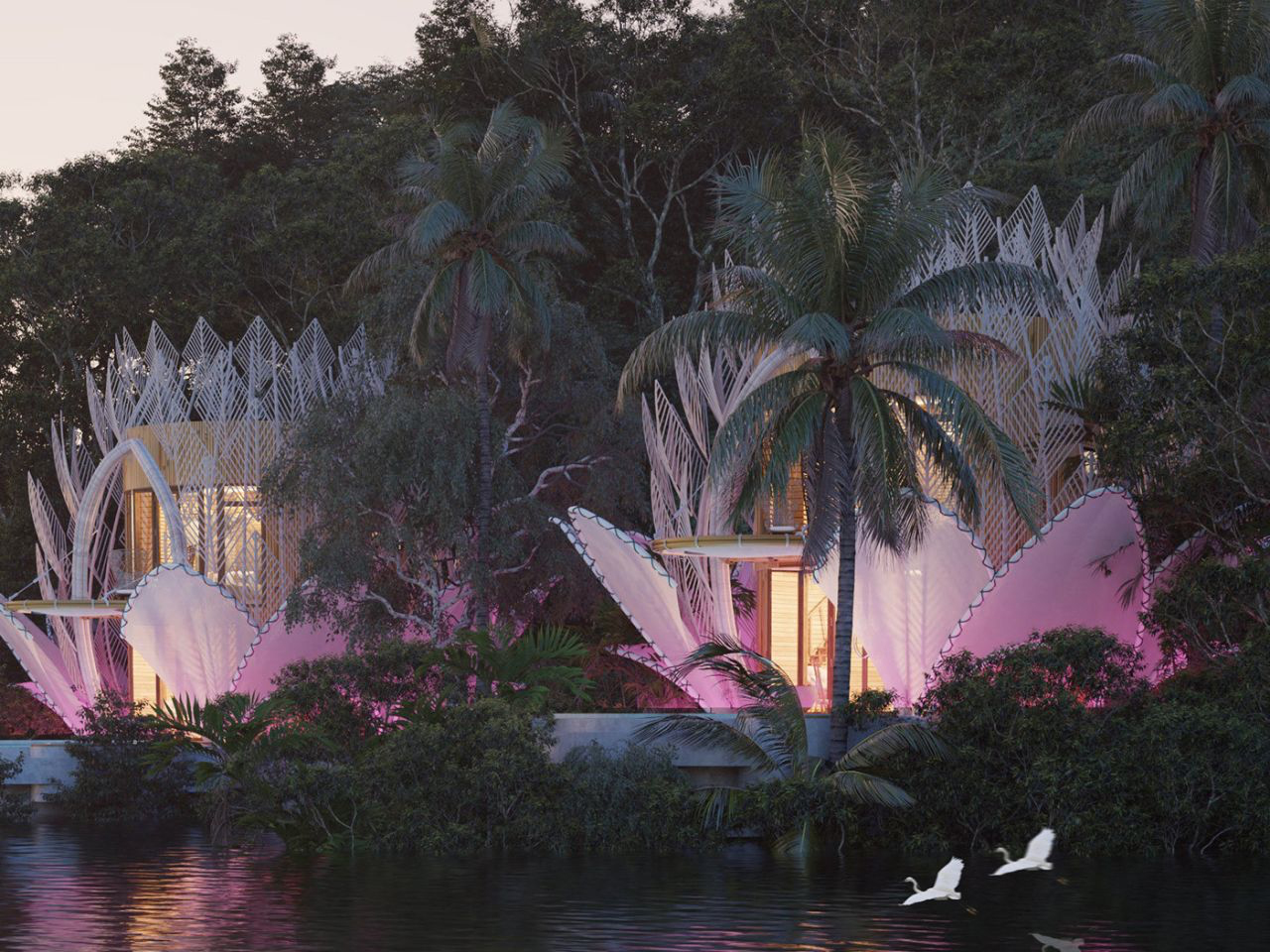


Upstairs, cozy bedrooms open onto cantilevered seating, offering elevated views of the natural surroundings. Prefabricated metal elements and locally sourced bamboo form delicate, translucent “petals,” blending aesthetics with sustainability. At night, soft pink uplights illuminate the fabric-covered petals, transforming the villa into a glowing, magical water lily, harmonizing architecture, nature, and modern comfort.
Creating a home in harmony with nature is a journey of intention and care. It moves beyond shelter to craft a sanctuary that nurtures its inhabitants and the environment. By thoughtfully choosing materials and design, the home listens to the land, embraces its rhythms, and stands as a lasting testament to mindful and sustainable living.
The post 5 Architect-Designed Homes That Disappear Into the Landscape first appeared on Yanko Design.


















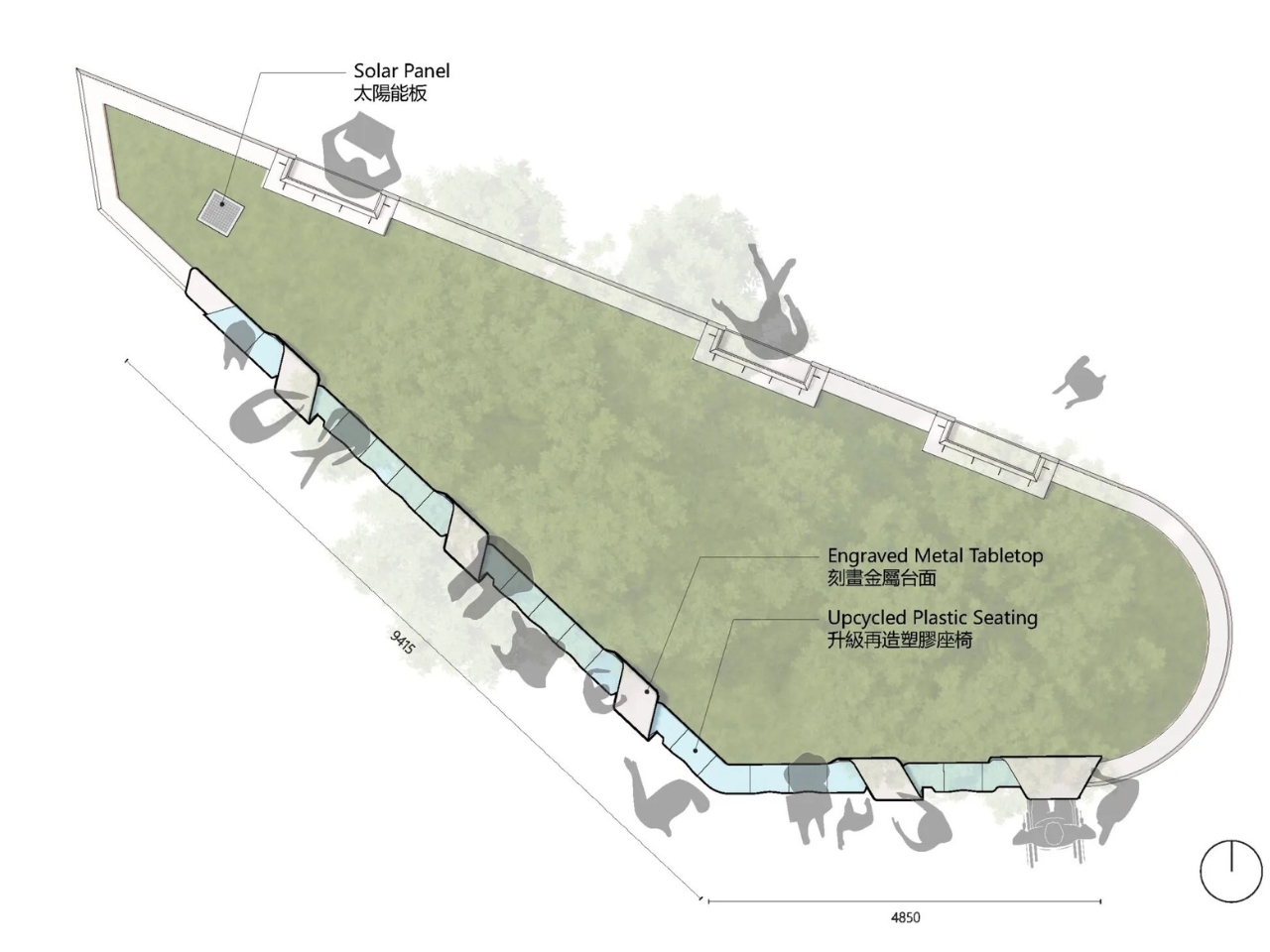

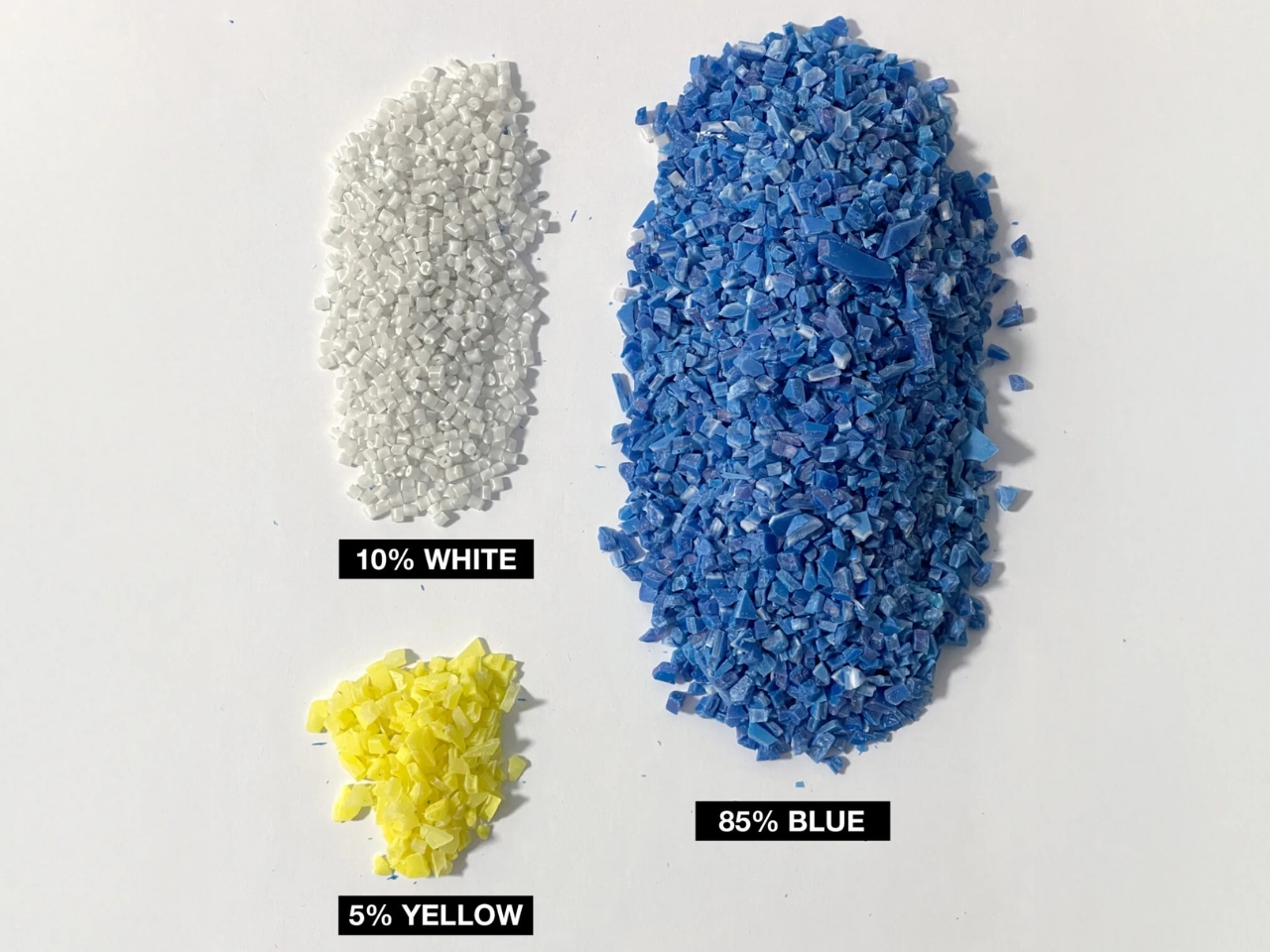






















 ‘
‘