I’ll be honest. When I was first diagnosed with diabetes, one of my biggest fears wasn’t just managing my blood sugar or giving myself injections. It was the thought of walking around with devices that screamed “medical patient” everywhere I went. I wanted to feel like myself, not like someone who needed constant hospital-grade equipment just to get through lunch.
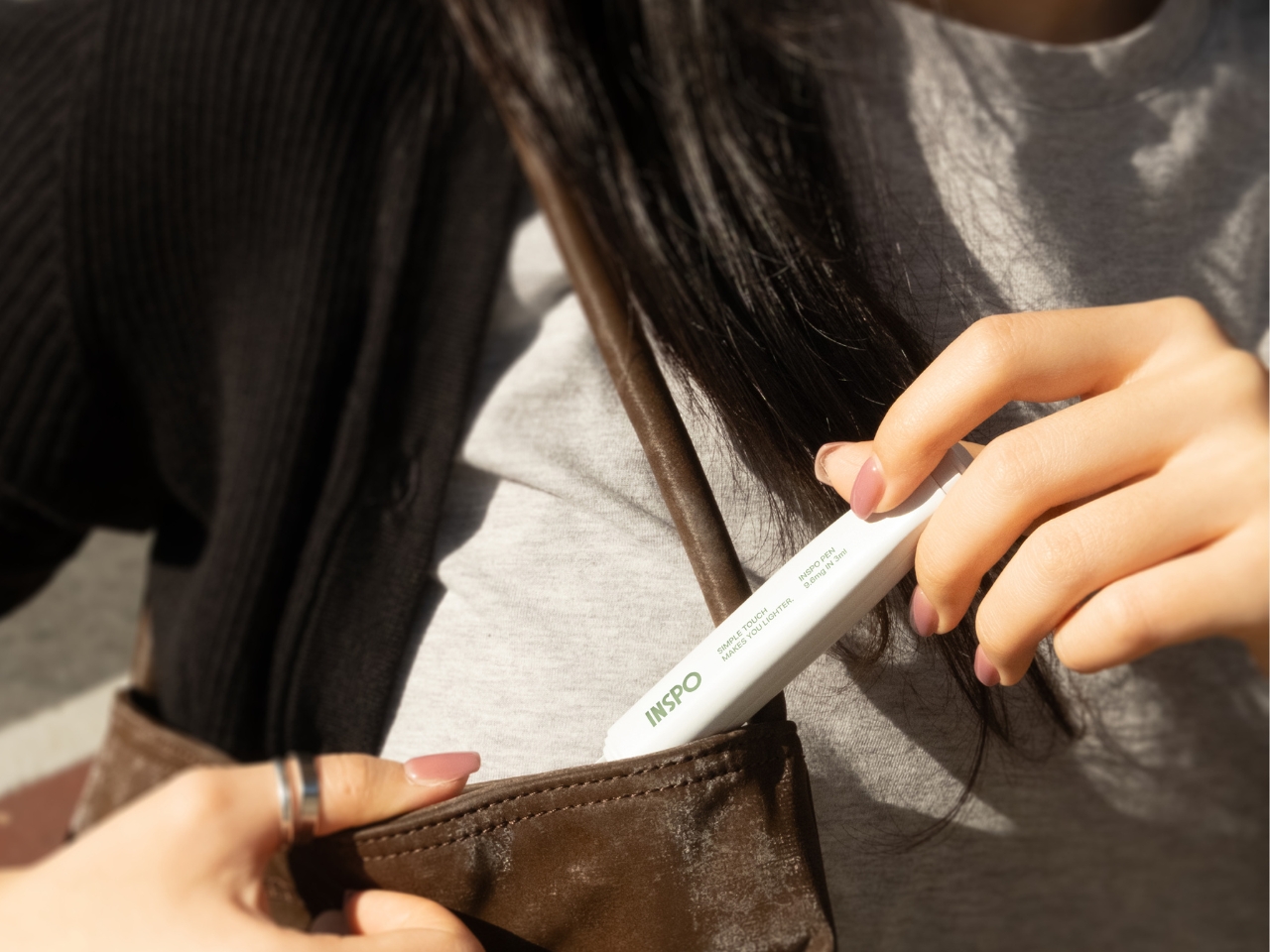
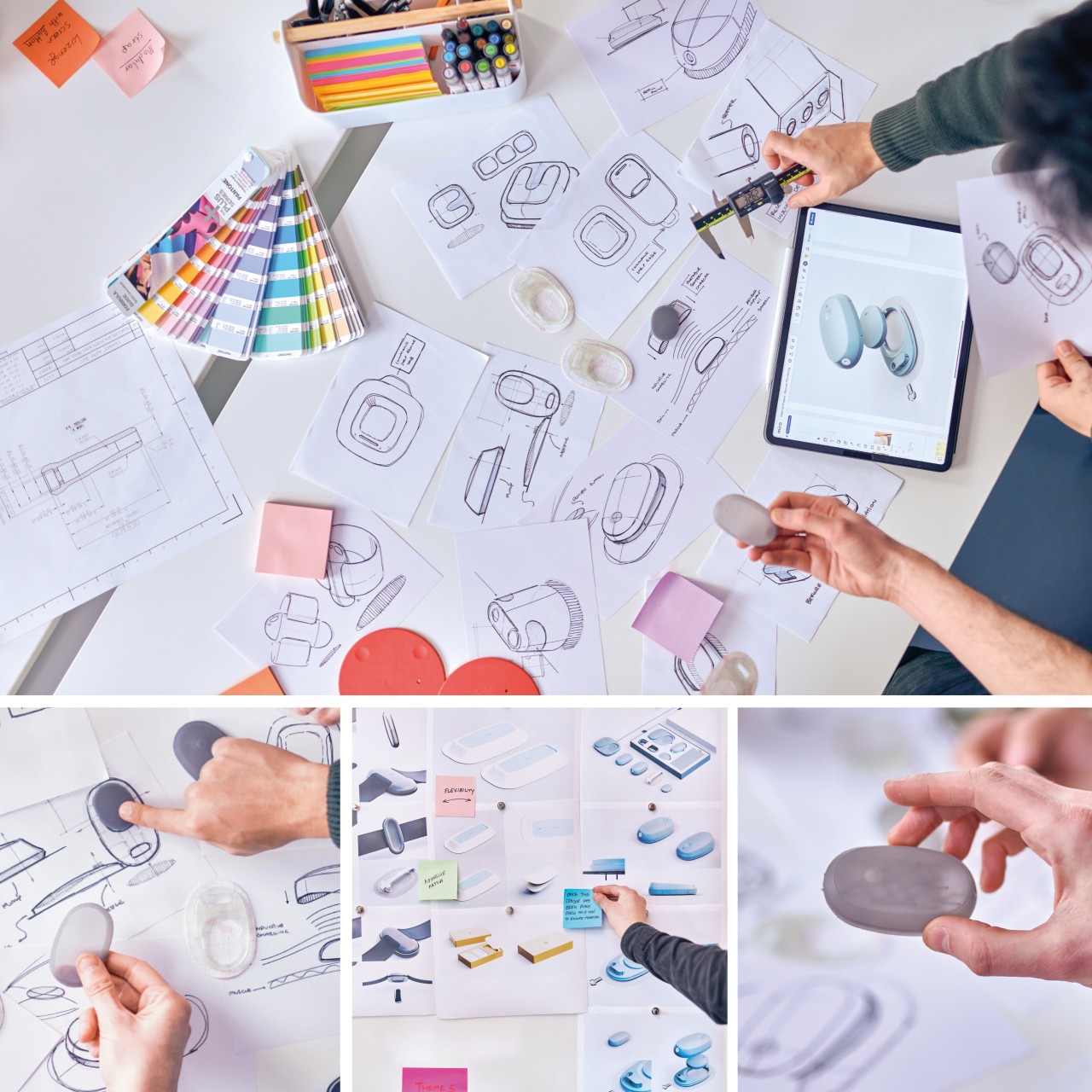
That’s why the INSPO smart insulin delivery system caught my attention. Designed by Minseo Lee and Haneul Kang, this isn’t just another glucose monitor or insulin pen. It’s a complete rethinking of what diabetes management could look like if someone actually considered how we want to live our lives.
Designers: Minseo Lee, Haneul Kang

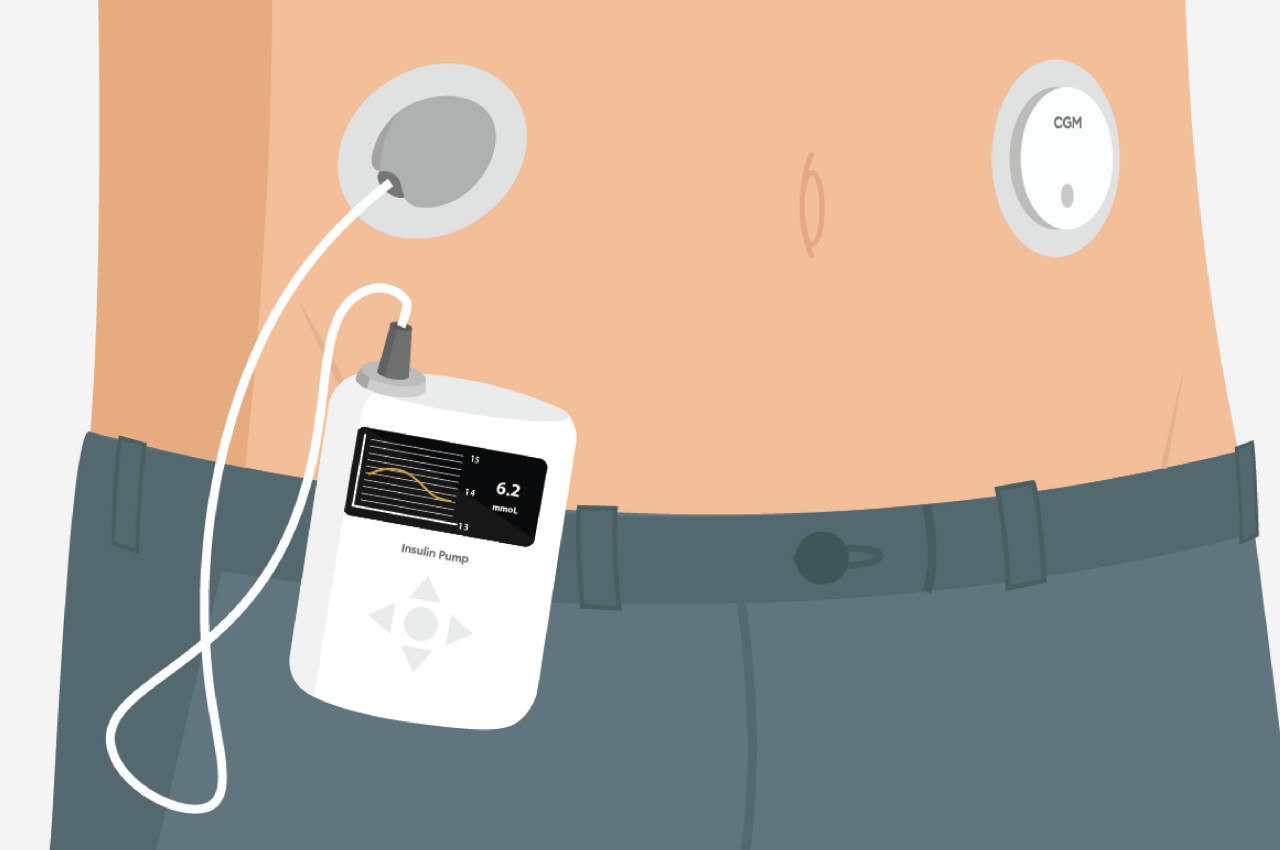
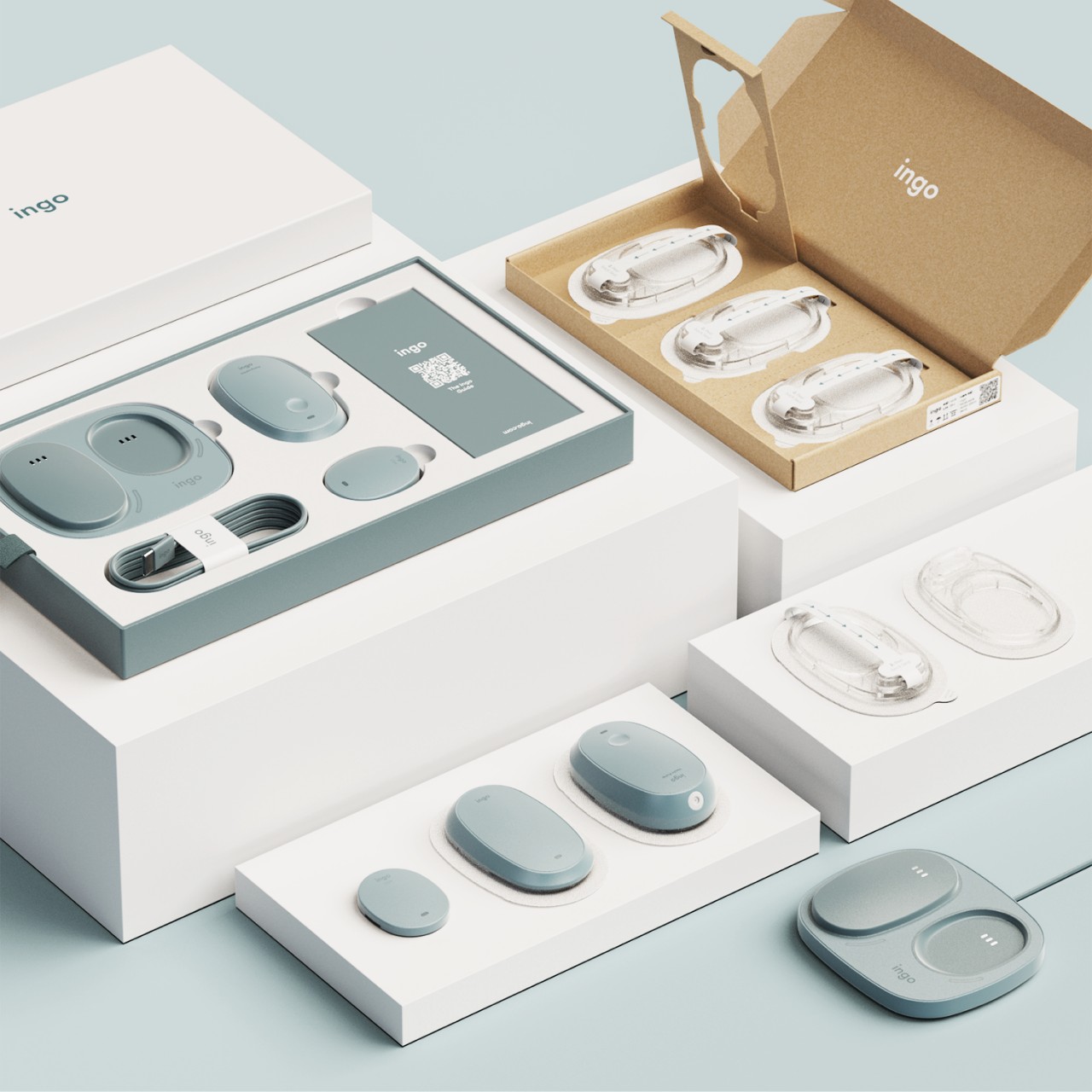
Current diabetes technology has made incredible strides, don’t get me wrong. Insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitors have genuinely saved lives. But they come with baggage that goes beyond their physical weight. The financial burden is real. High upfront costs, endless consumables, insurance companies that may or may not cover what you need. And then there’s the psychological weight of wearing something that looks like it belongs in a medical facility rather than at a coffee shop or the gym.
I’ve watched the design world transform emergency kits and fire extinguishers from eyesores into objects that blend beautifully into modern homes. INSPO applies that same philosophy to diabetes care. The message is simple but revolutionary: medical devices should expand their design language so we can use them naturally in daily life, not just in clinical settings.

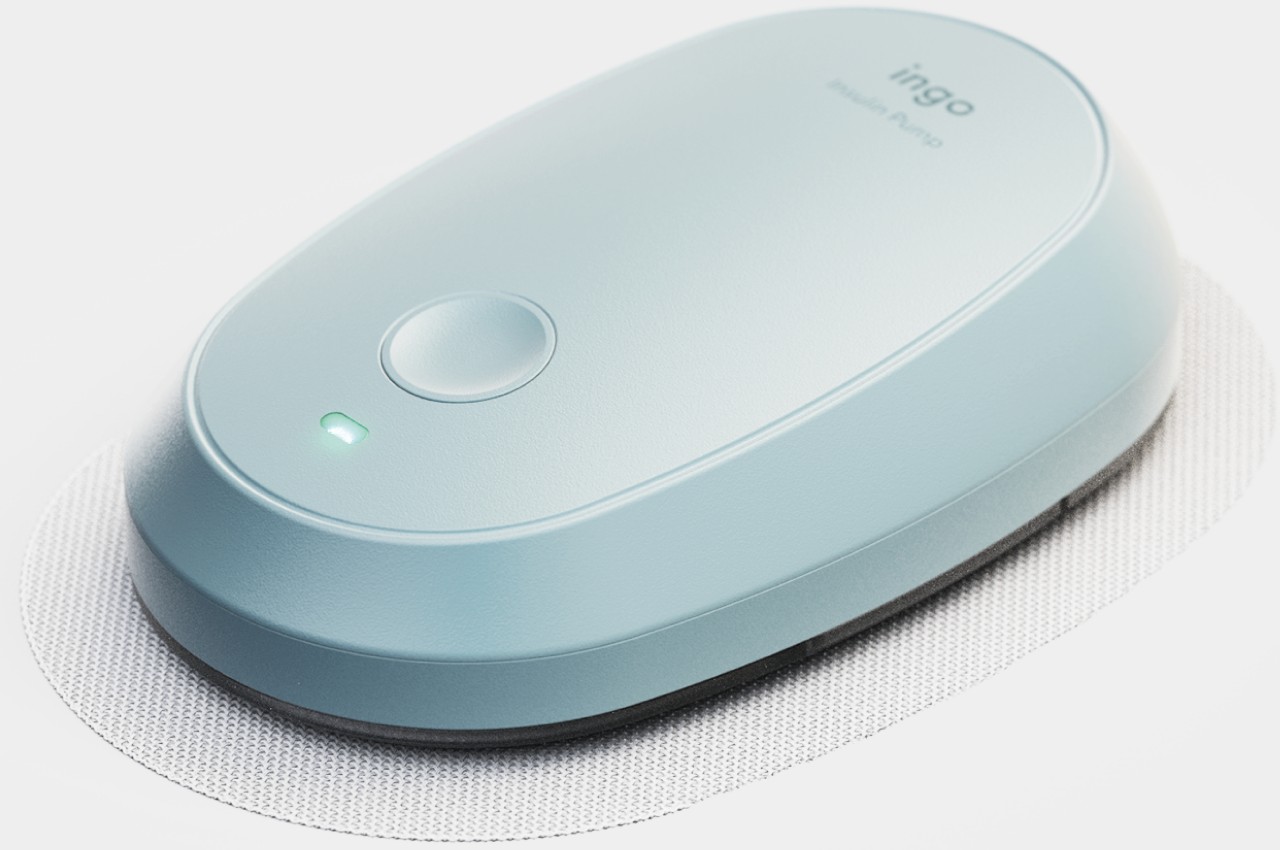
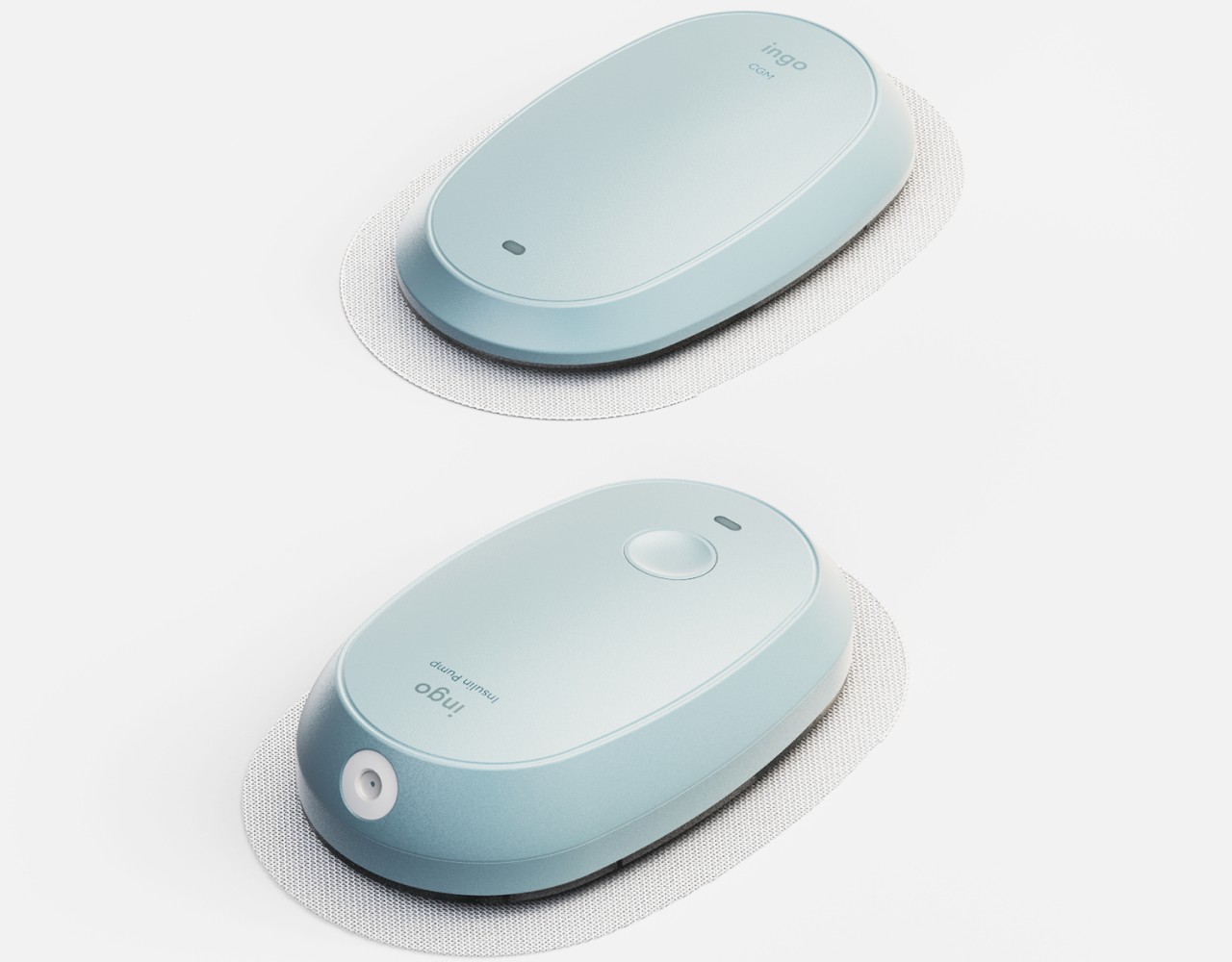
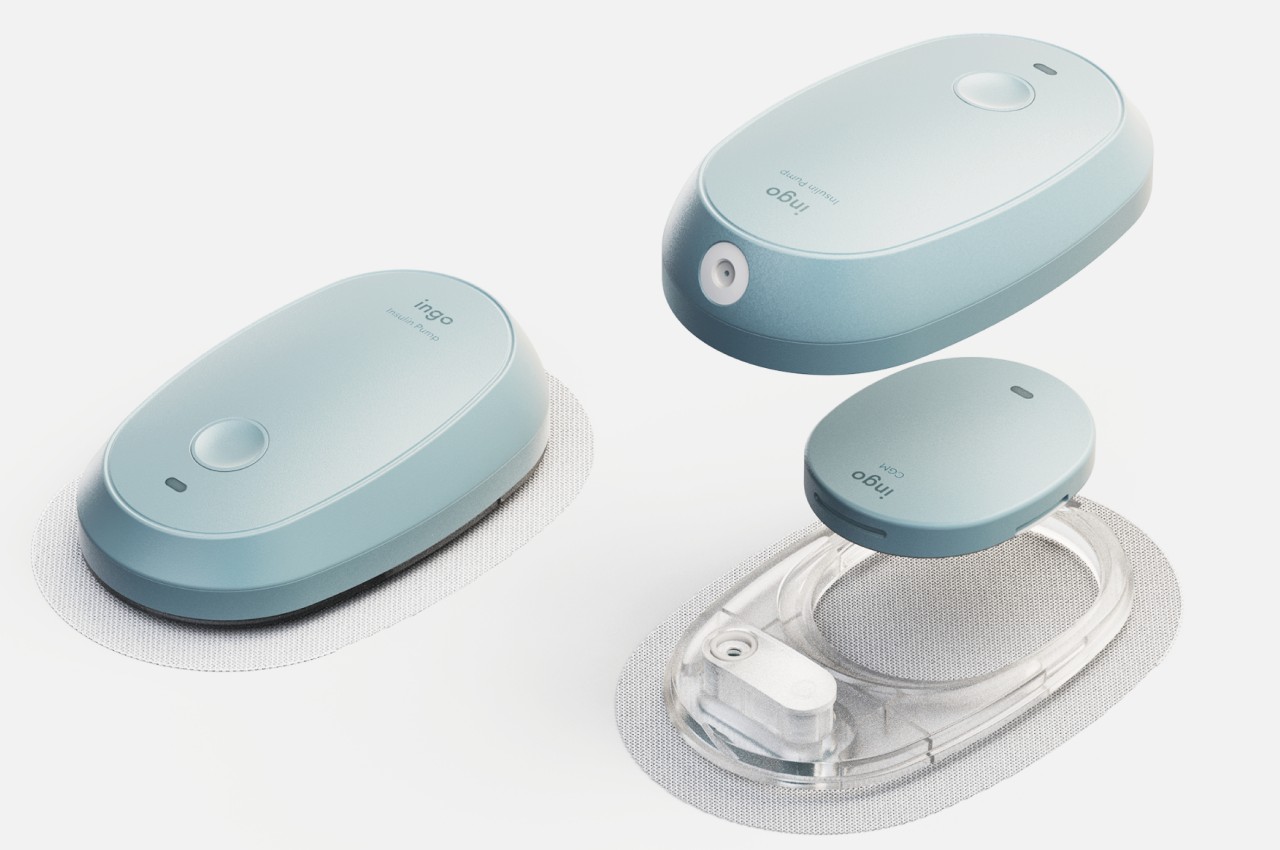
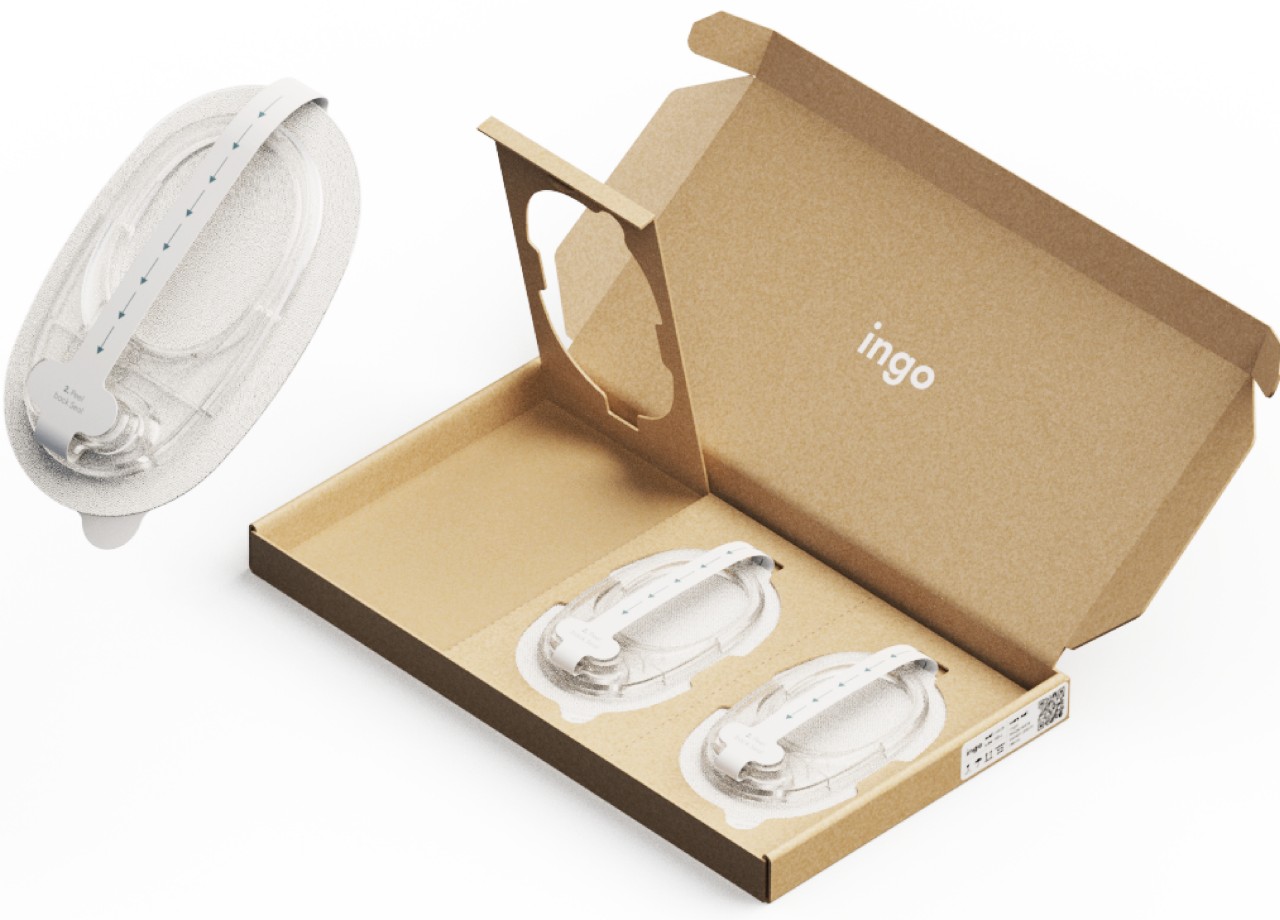
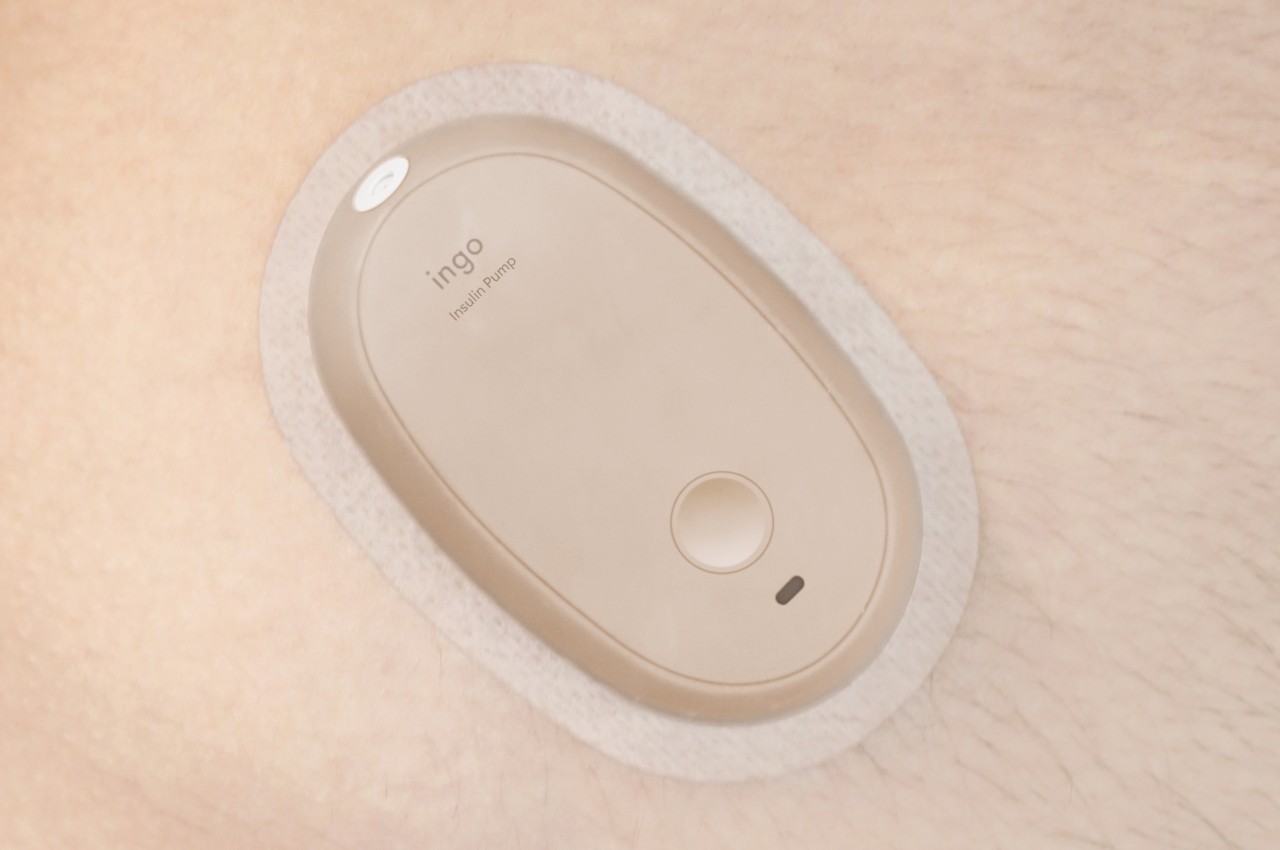
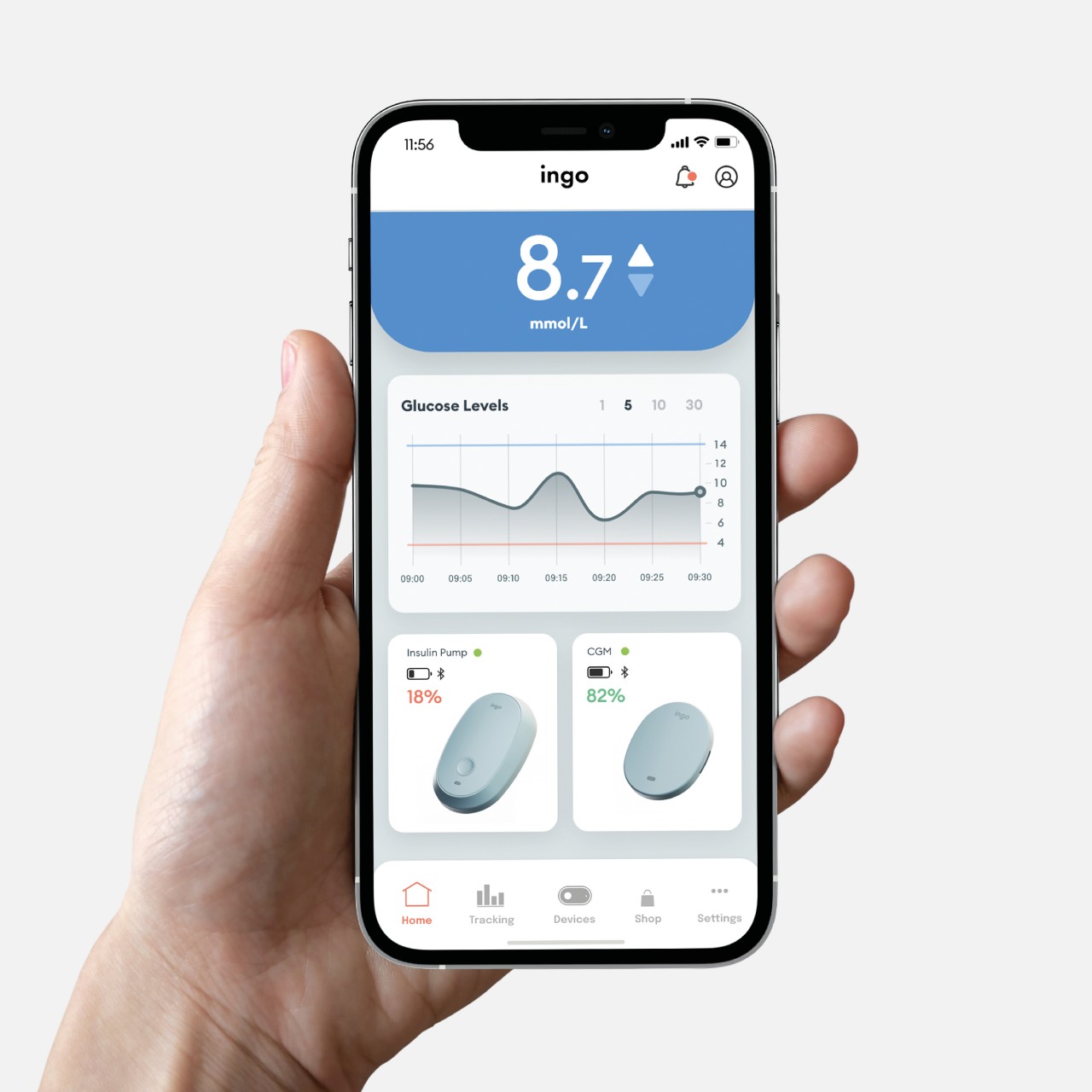
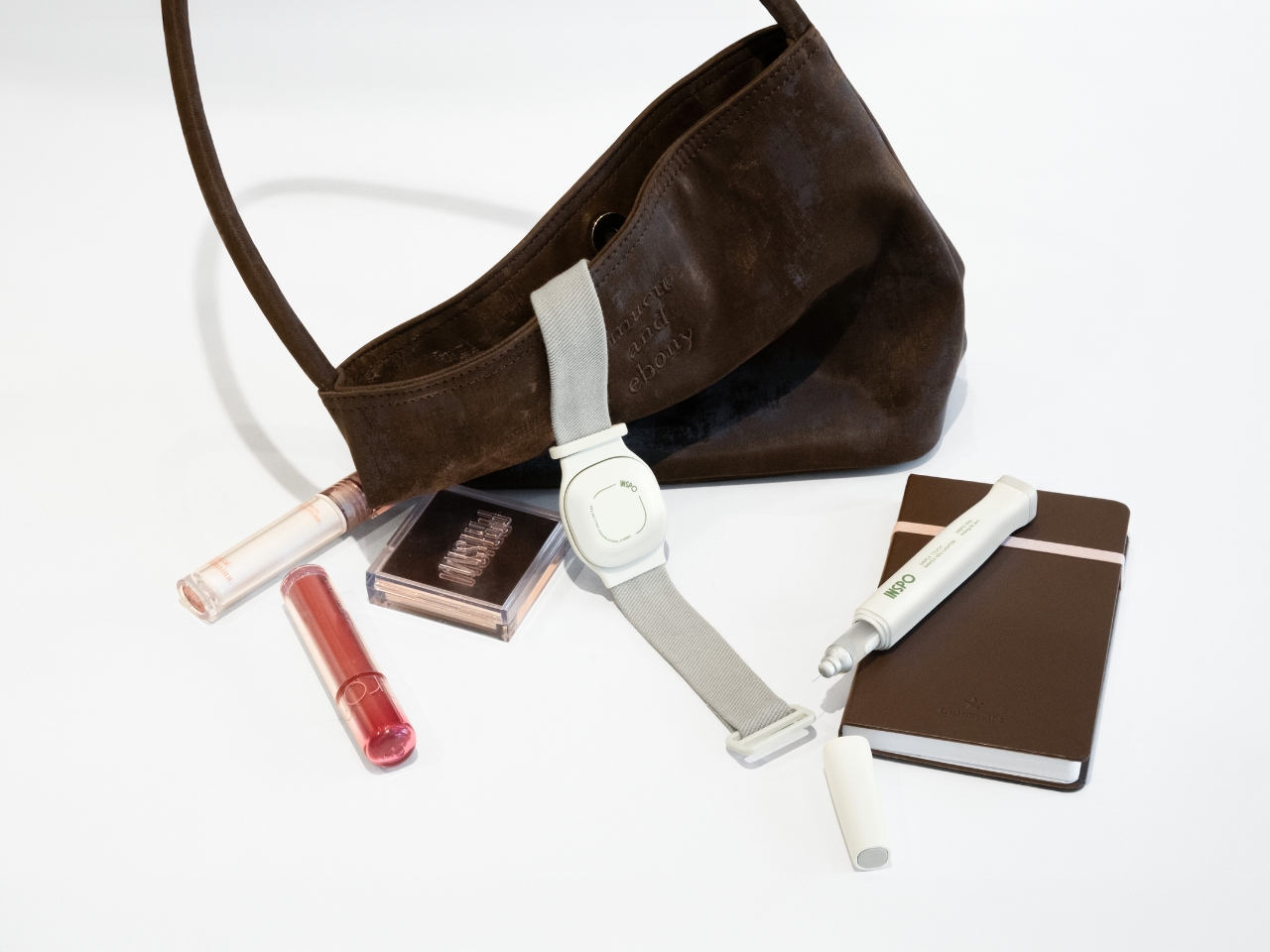
What makes INSPO different starts with its approach to glucose monitoring. The continuous glucose monitoring device straps onto your upper arm and measures blood sugar levels non-invasively. No more finger pricks throughout the day, no more finding discrete places to draw blood when you’re out. The CGM quietly does its job while you do yours, and the best part? It comes with customizable straps in various designs. Finally, someone understood that personal expression matters, even when we’re talking about medical devices.
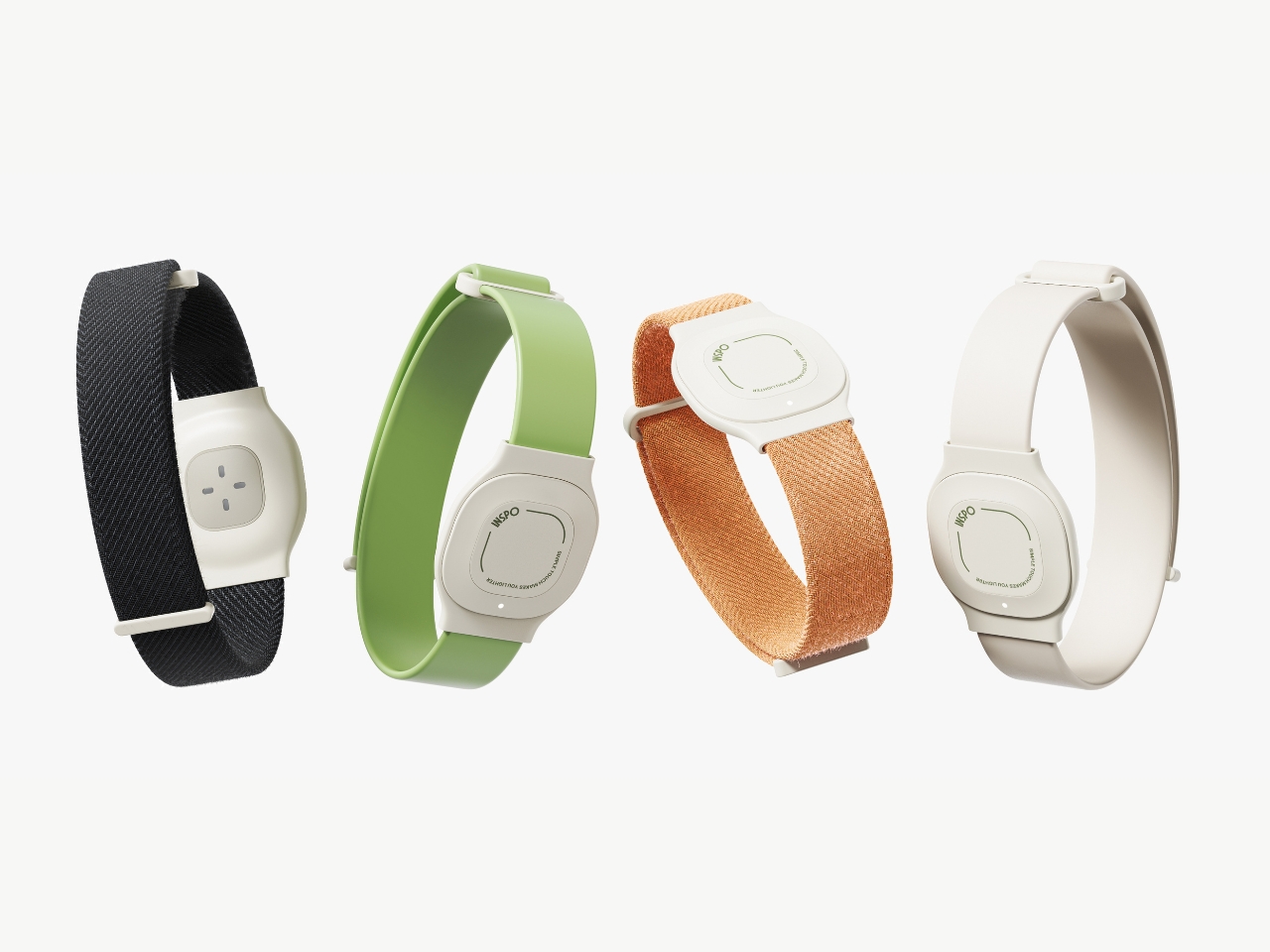

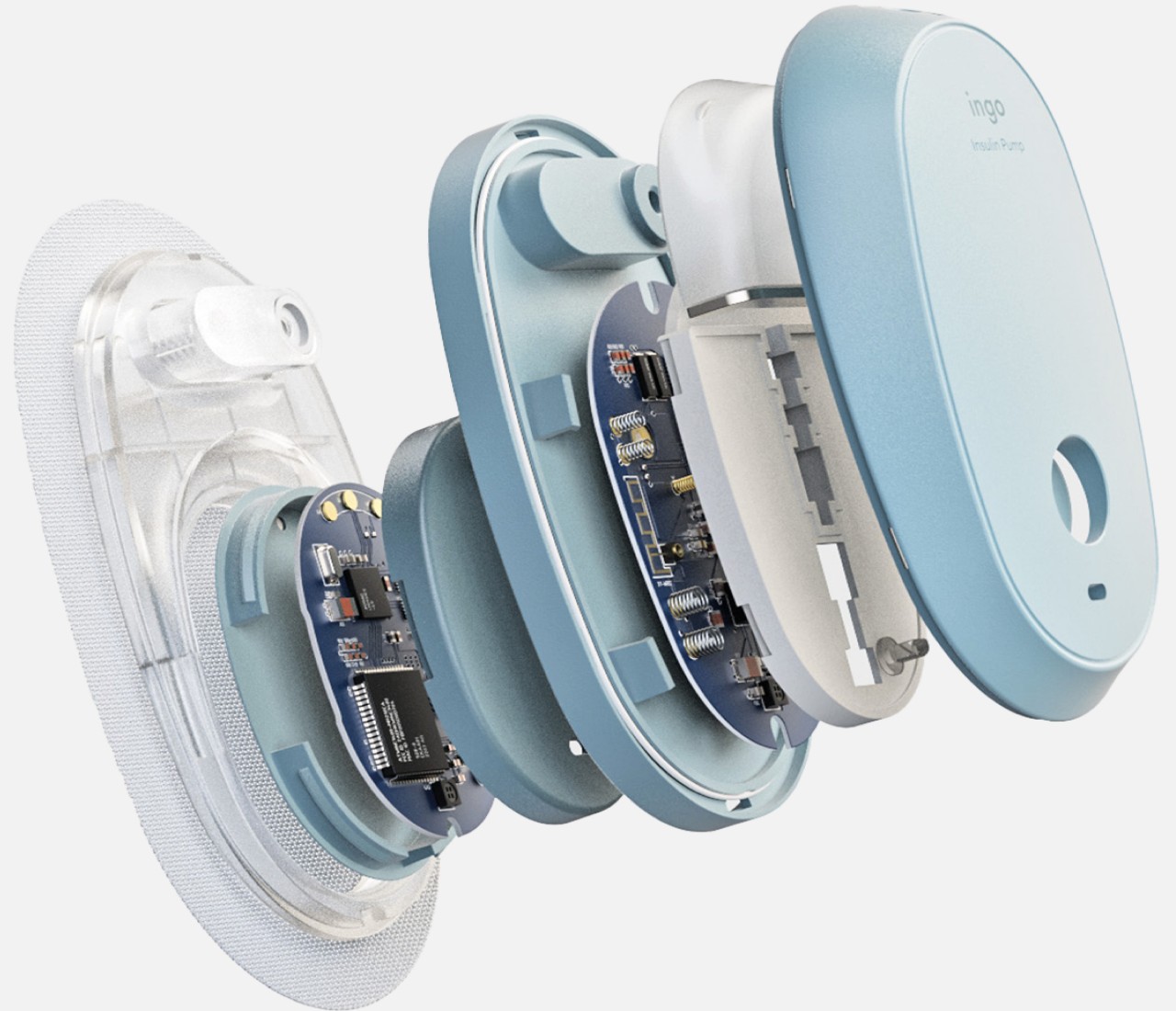
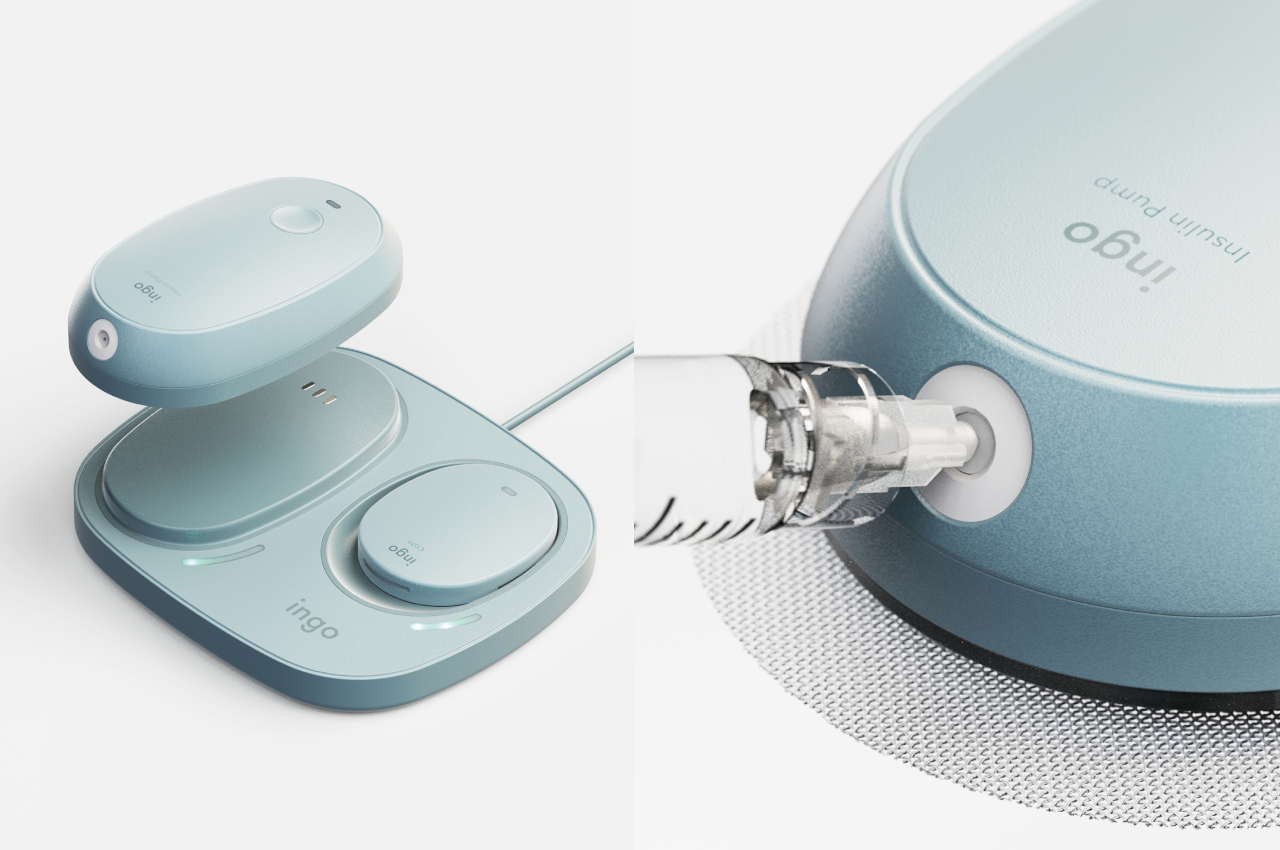
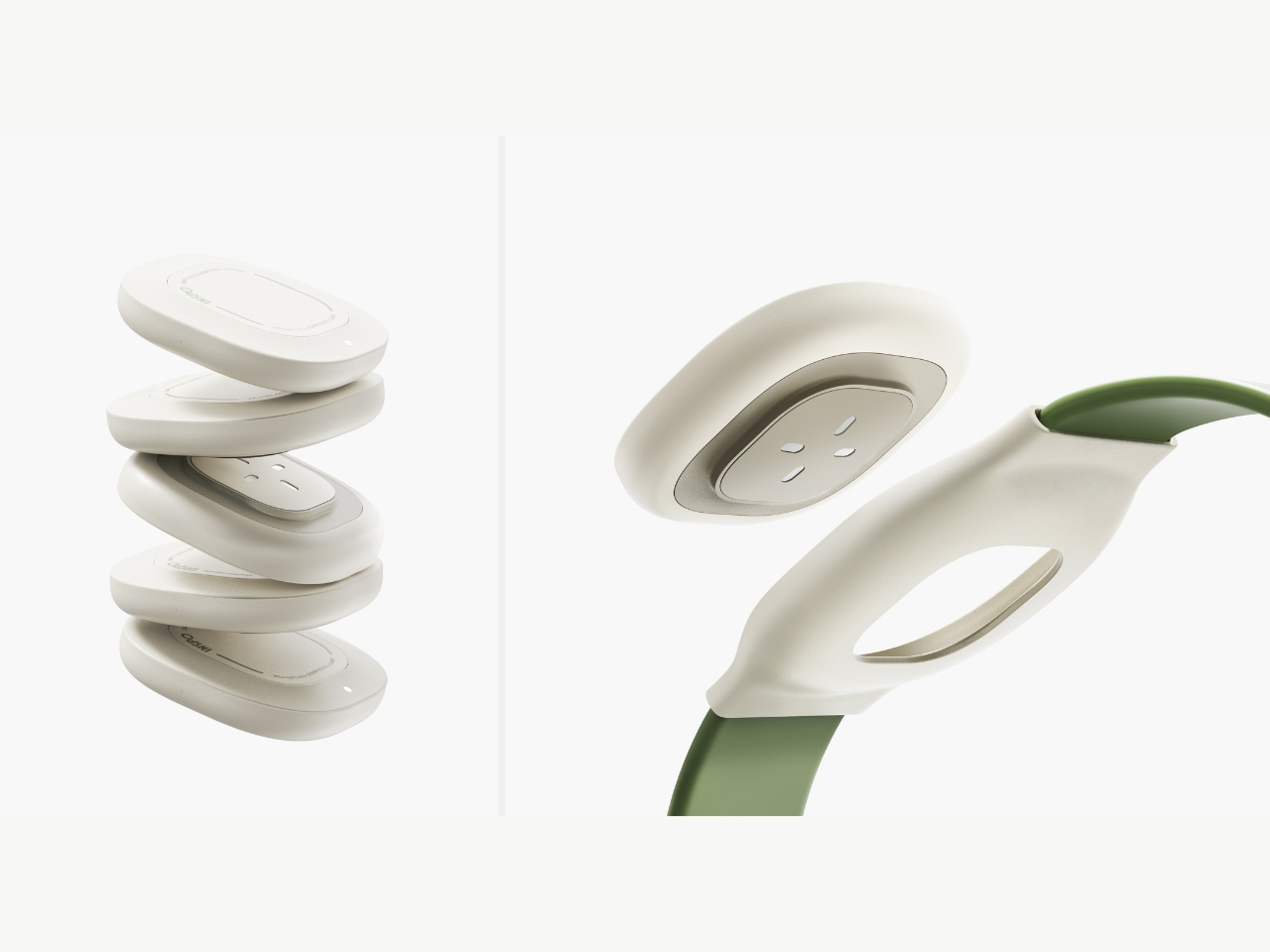
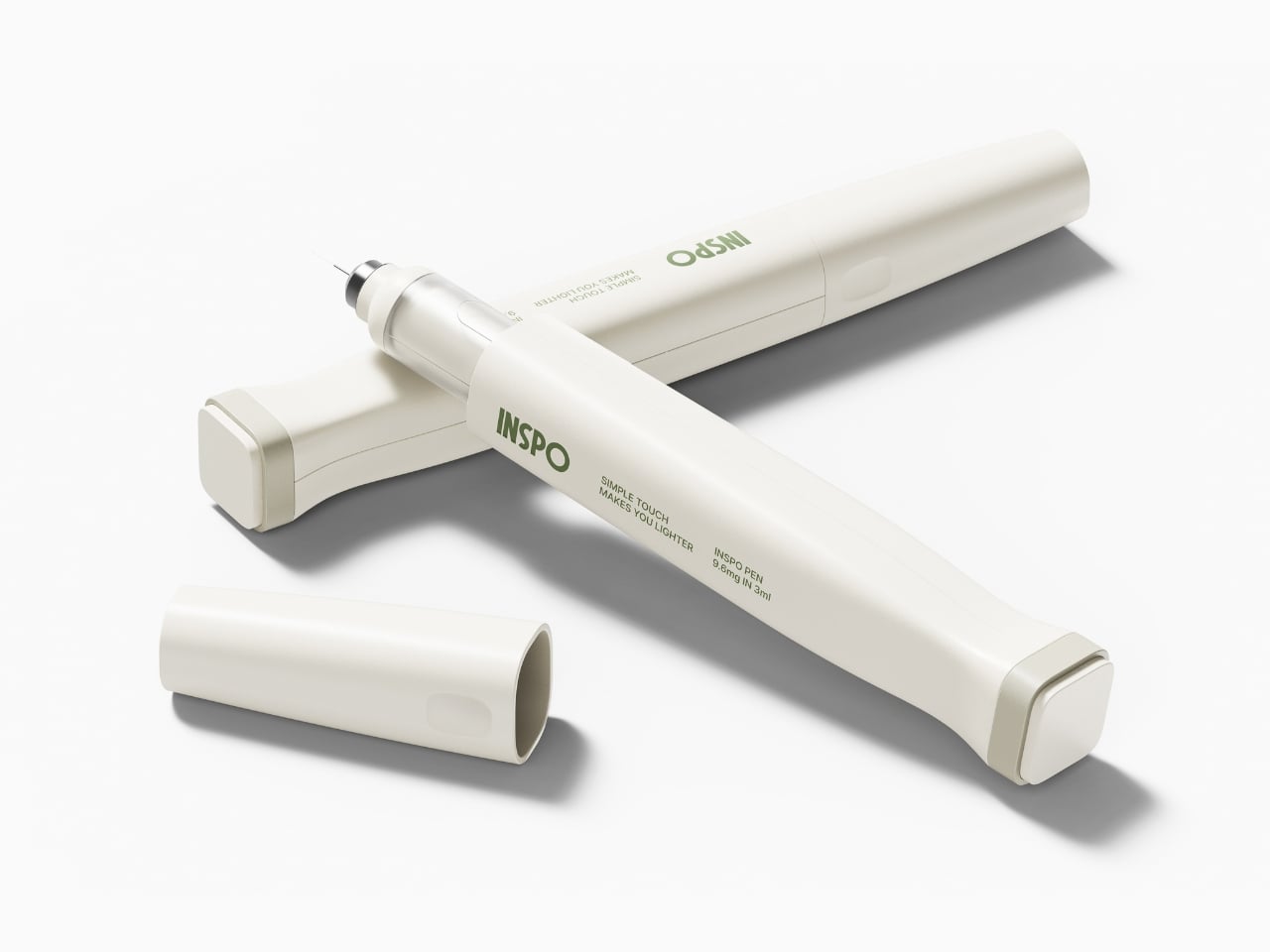
The insulin pen itself is where INSPO really shines. It works in real time with the CGM, automatically adjusting the dosage based on your current needs. When you need to inject, a hidden interface appears at the top of the pen, displaying your exact dosage. It’s discreet, elegant, and gives you the information you need without announcing your condition to everyone around you. The sensual, natural design means I wouldn’t think twice about using it at a restaurant or during a work meeting. It looks like something I chose to carry, not something I’m forced to manage.

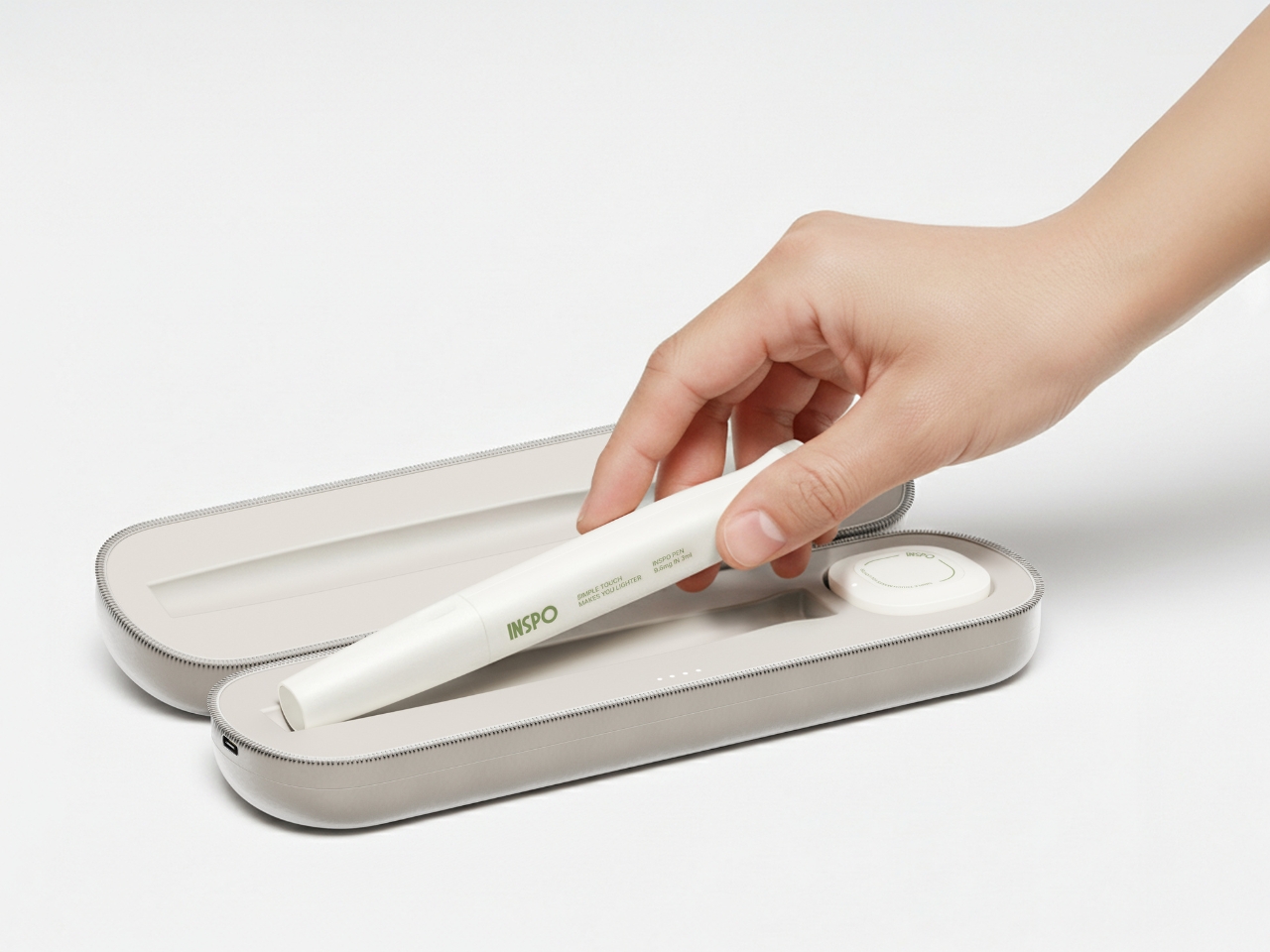
The system includes a sleek case that holds both the insulin pen and CGM, with built-in pogo-pin charging terminals. Everything stores and charges simultaneously, which means one less thing to remember, one less task in an already complicated daily routine. The case is designed to go anywhere, which matters when your life doesn’t revolve around being near an outlet or a safe storage spot.

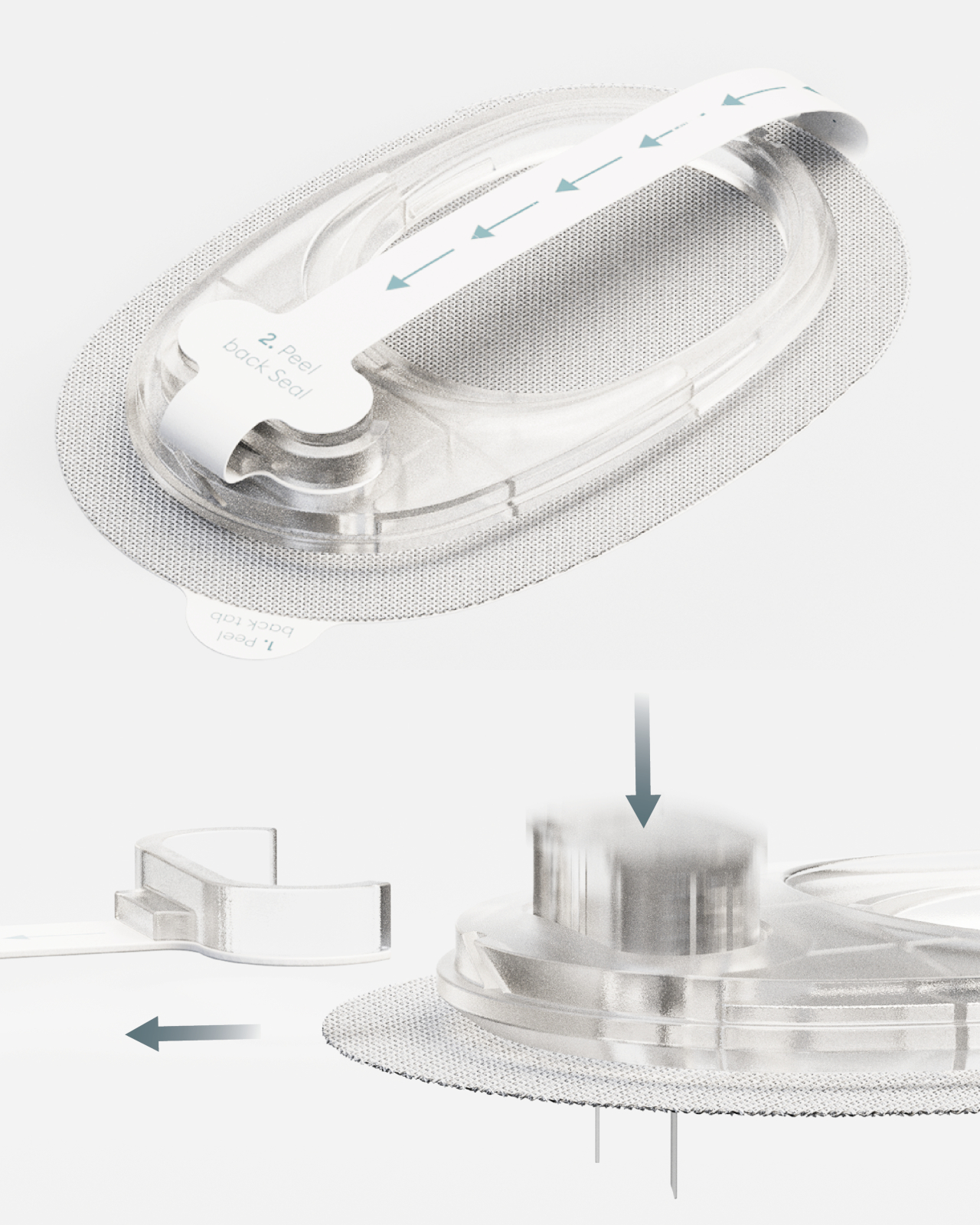
Using INSPO is refreshingly simple. You wear the CGM on your upper arm. It measures your glucose continuously and transmits that data to the insulin pen. When you need insulin, you check the hidden interface for your precise dose, then inject with a single touch. That’s it. No complex calculations, no second-guessing, no mental gymnastics while you’re trying to enjoy your meal or focus on your day.
The designers talk about transforming diabetes devices “from something you once hid, to a lifestyle device you’re proud to reveal.” That resonates deeply with me. I’m tired of feeling like I need to apologize for my condition or hide the tools that keep me healthy. INSPO represents a shift in thinking where managing diabetes doesn’t mean sacrificing style, confidence, or the simple pleasure of blending in when you want to.
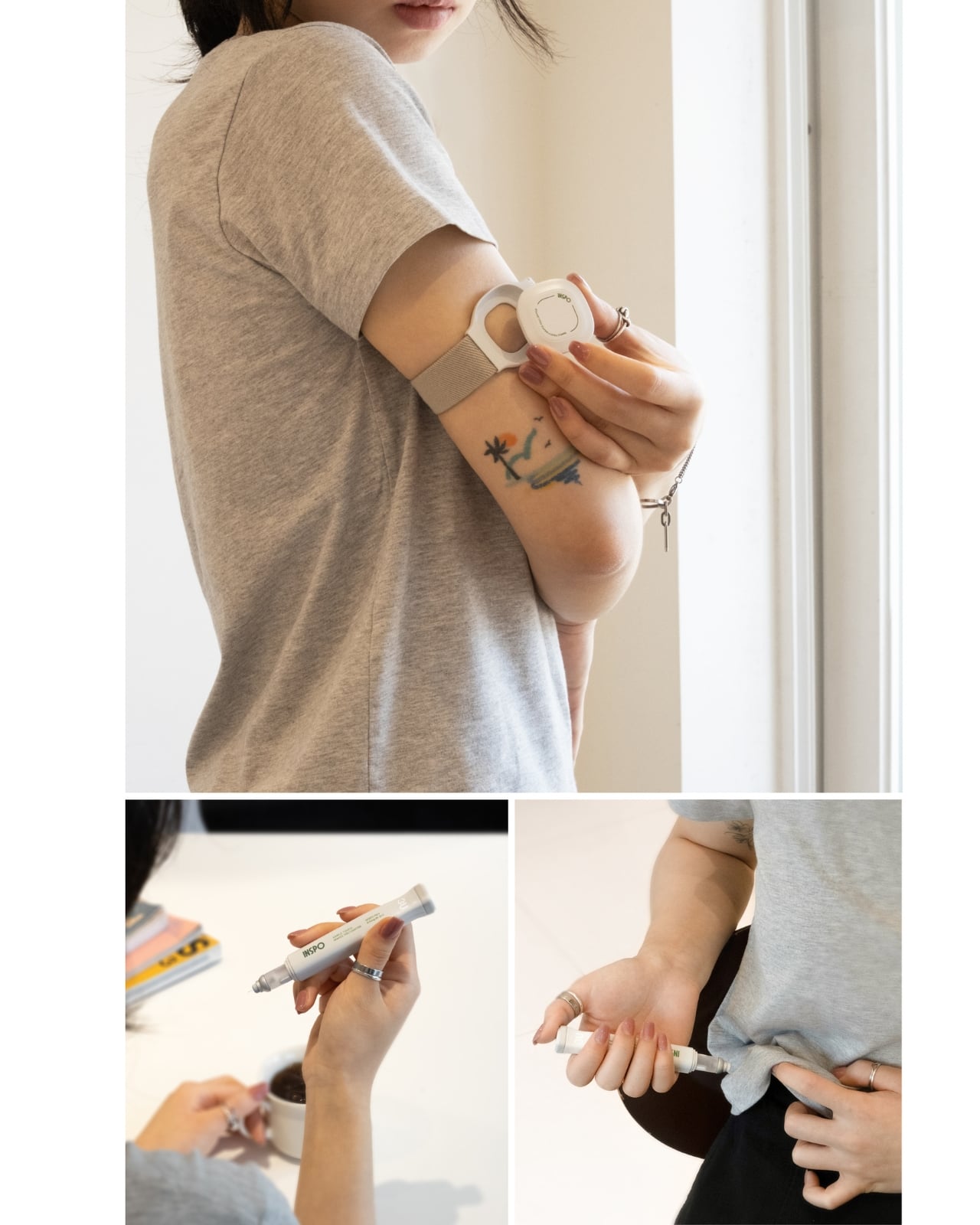

This is what the future of diabetes care should look like. Not just smarter technology, but thoughtful design that acknowledges we’re whole people with lives we want to live fully. INSPO doesn’t just help manage diabetes, it helps us reclaim the parts of ourselves we shouldn’t have to give up in the first place.

The post A Diabetes Device You’d Actually Want to Carry Every Day first appeared on Yanko Design.