PROS:
- Unique immersive experience with vision goggles
- 8K 360 capture with post-flight reframing
- Intuitive one-hand grip controller and automated modes lower the skill barrier
CONS:
- Several pieces to carry and manage: drone, goggles, and controller
- First-time setup and learning curve can feel overwhelming
- Visual observer requirements in places like the U.S. limit solo flying
Antigravity is Insta360’s bold experiment in what happens when a 360‑camera company stops thinking only about the camera and starts redesigning the entire act of flying. It is an independent drone brand, incubated by Insta360, built on the same obsession with immersive imaging and playful storytelling, but free to rethink the aircraft, the controls, and the viewing experience as one coherent object. Instead of asking how to strap a 360 camera onto a drone, Antigravity asks how to make the whole system feel like a natural extension of your point of view.
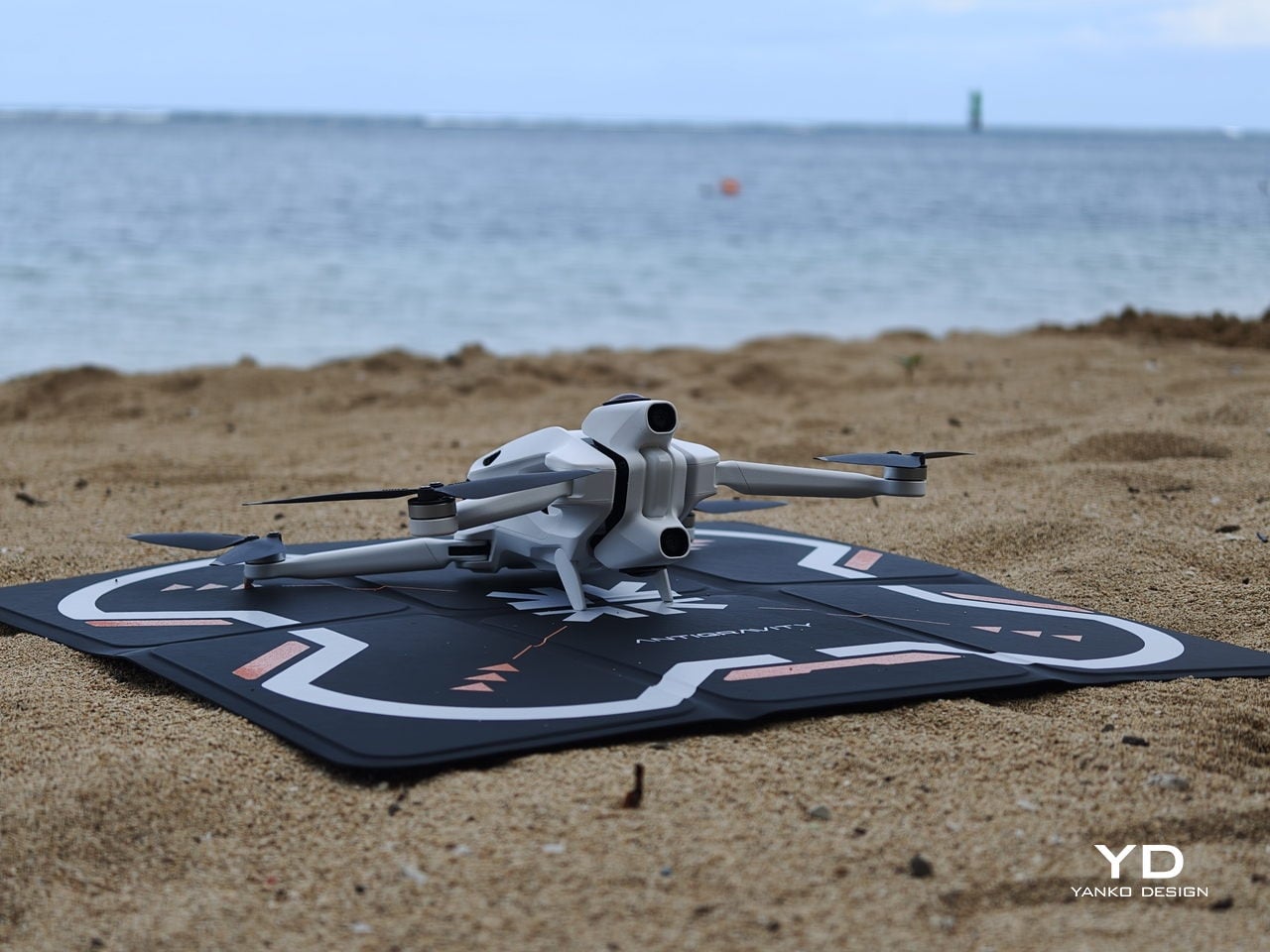
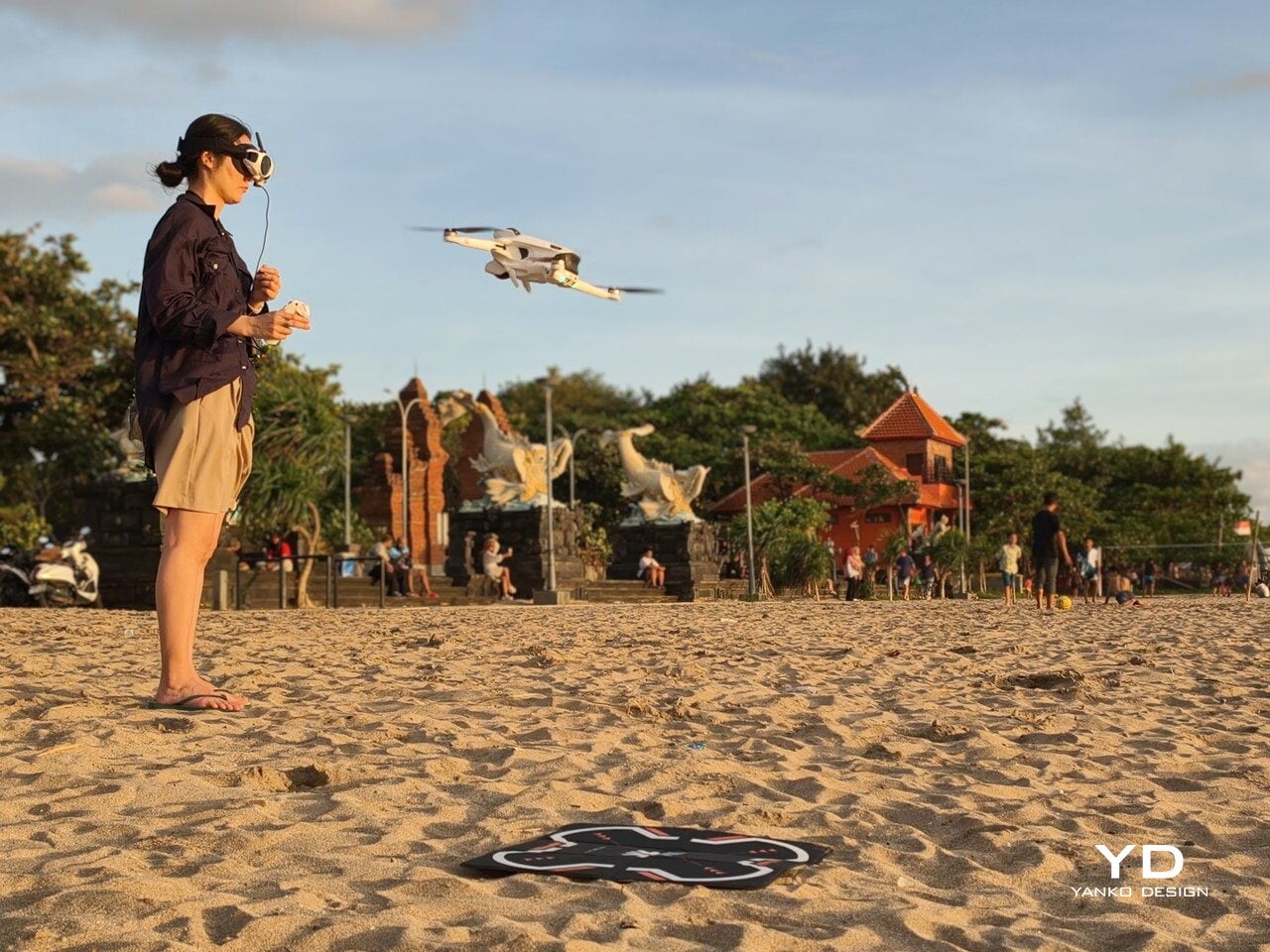
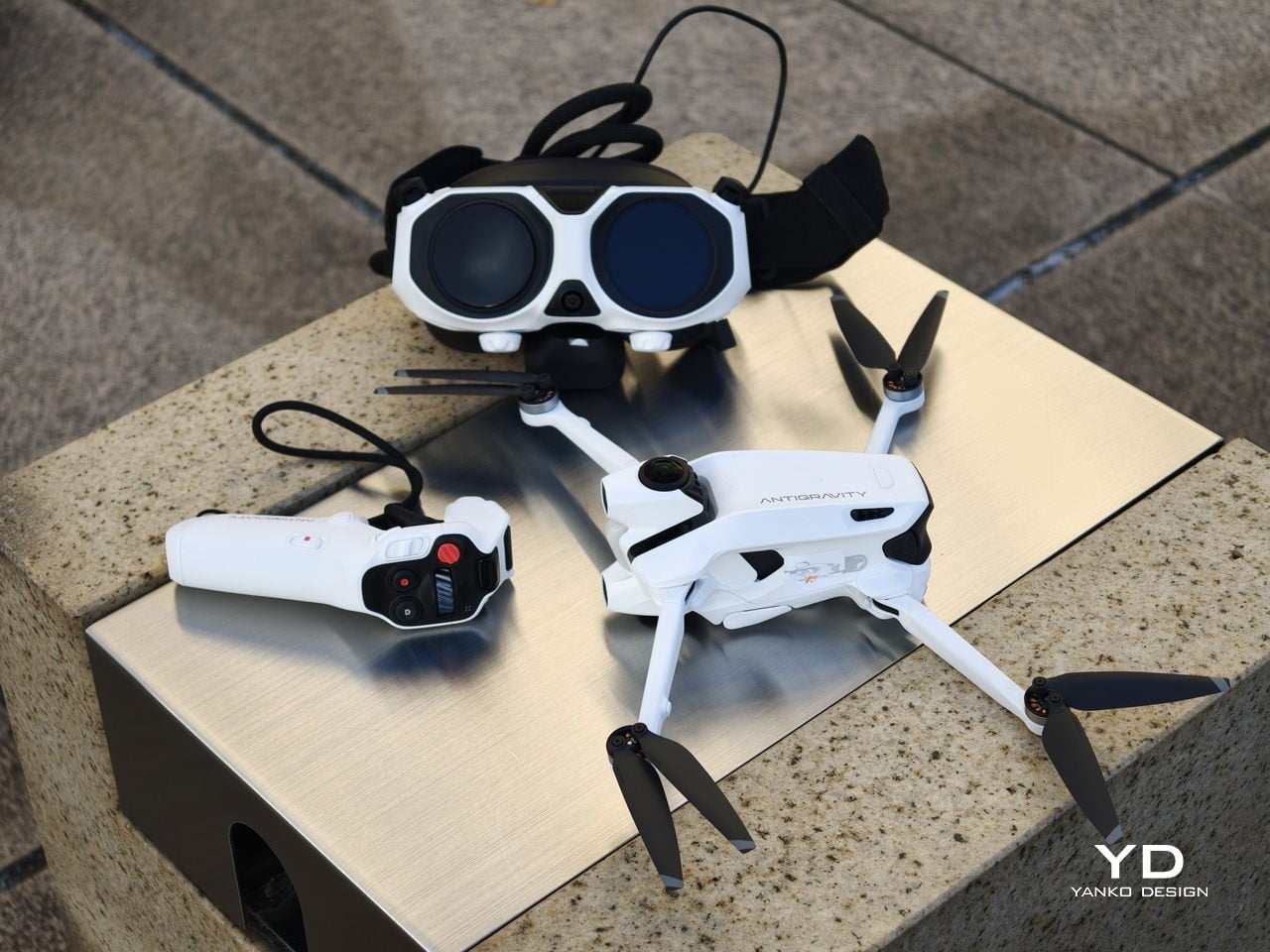
Antigravity A1 is the first expression of that idea. It is a compact 8K 360 drone that arrives as a complete kit, with Vision goggles and a single‑hand Grip controller that you steer with subtle tilts and gestures. You do not fly it by staring at a phone and juggling twin sticks. You put on the goggles, step into a 360‑degree bubble of imagery, and guide the drone by moving your hand in the direction you want to travel. What was the experience with Antigravity A1 like? We tested it to bring you that answer.
Designer: Antigravity
Aesthetics
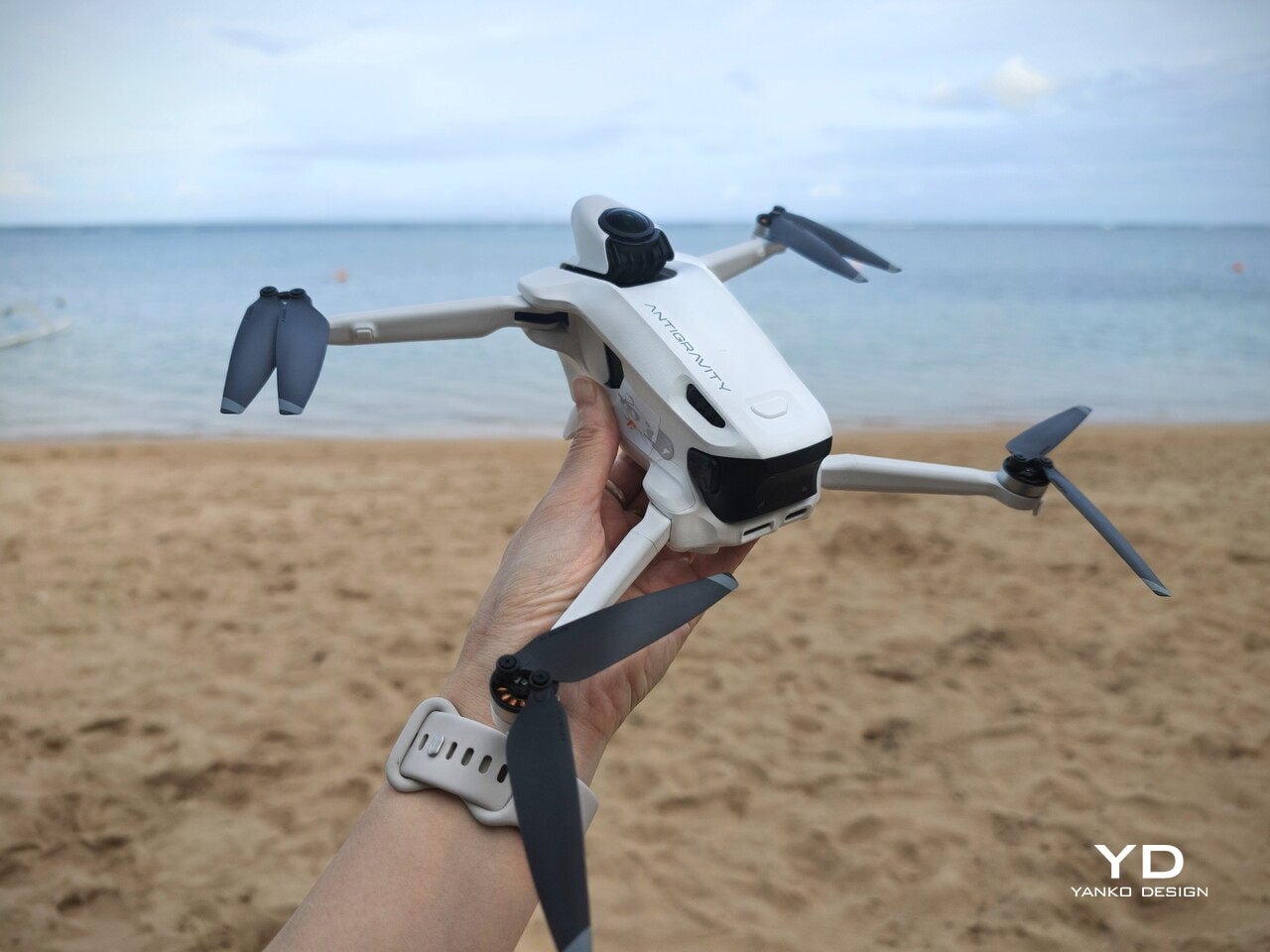

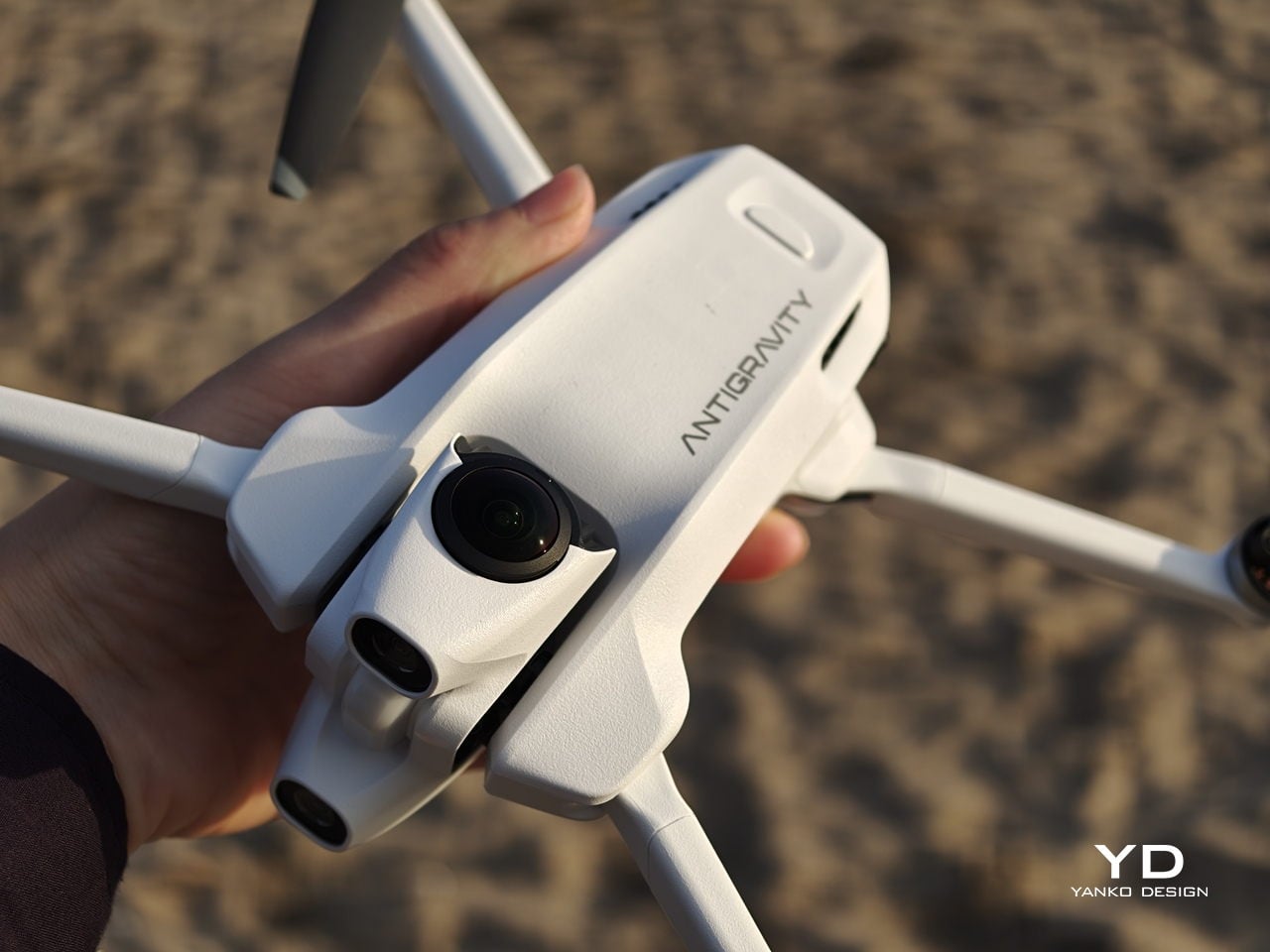
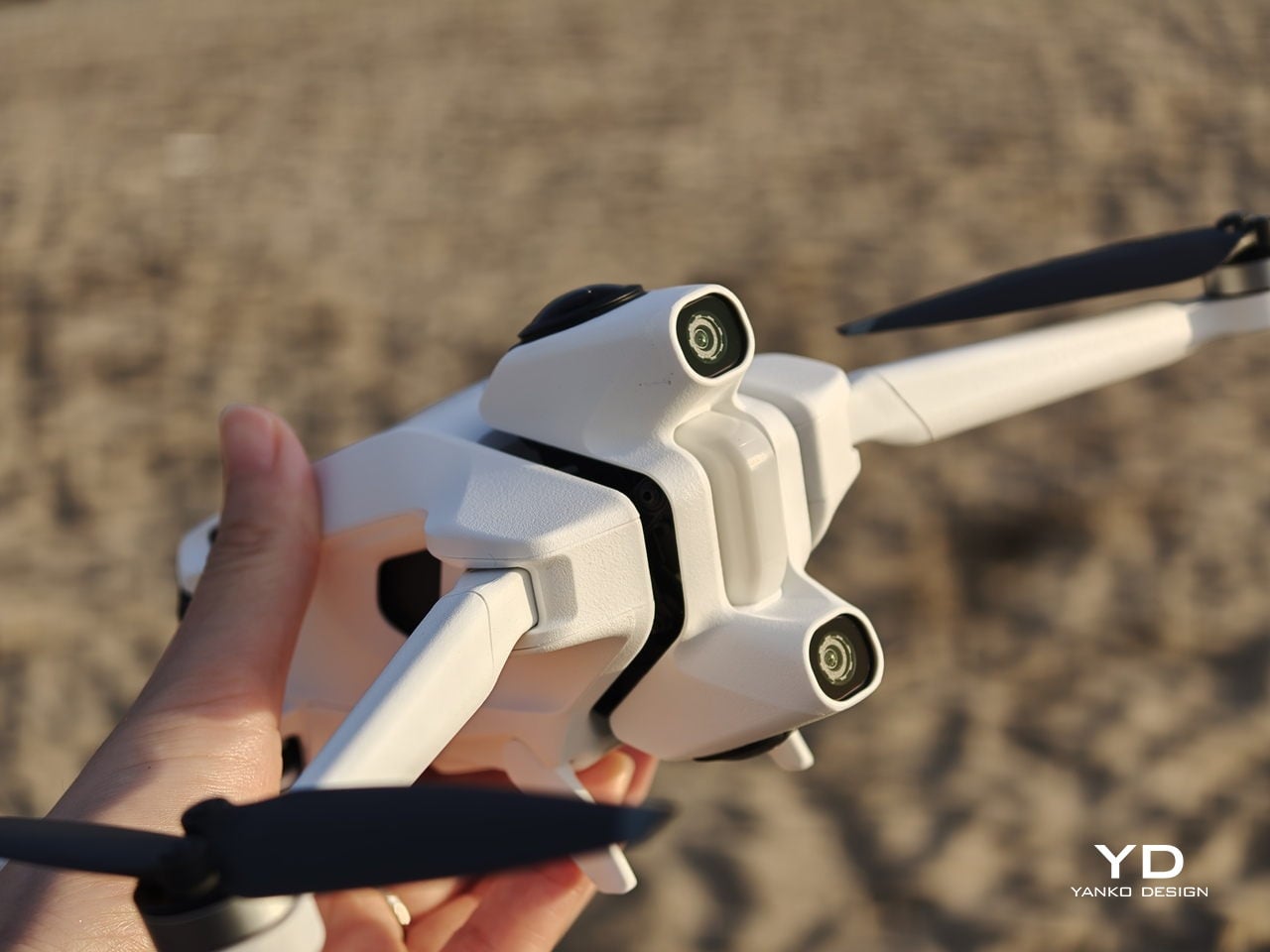
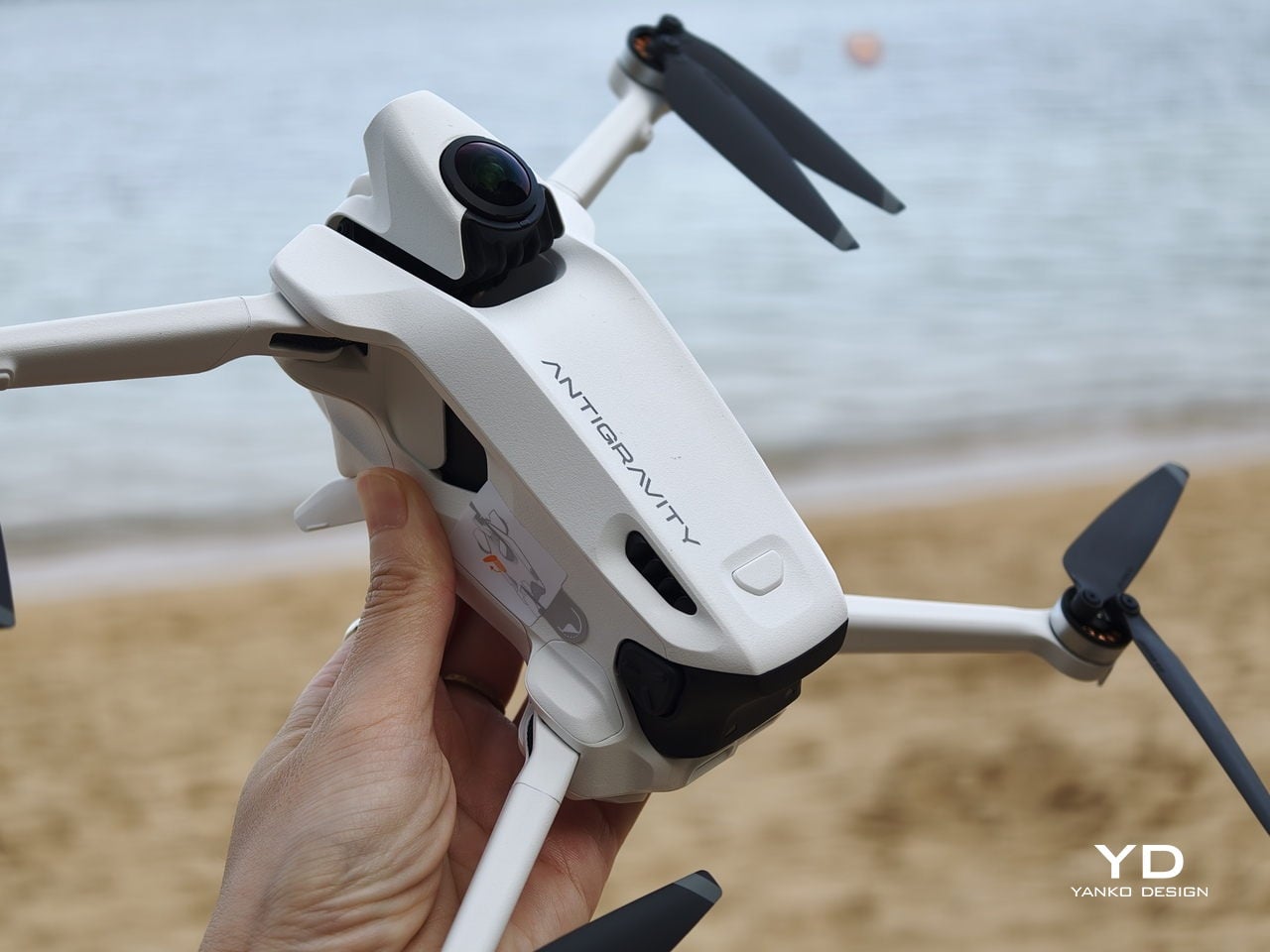
Antigravity A1 presents itself more as a system than a single object. There is the compact drone with its dual cameras, the Vision goggles, and the one‑hand Grip controller. Visually, the aircraft itself is quite understated. Aside from the two opposing lenses and the leg that shields the lower camera on the ground, it looks like a neat, functional quadcopter. The drama is reserved for what the system does, not how the airframe shouts for attention.

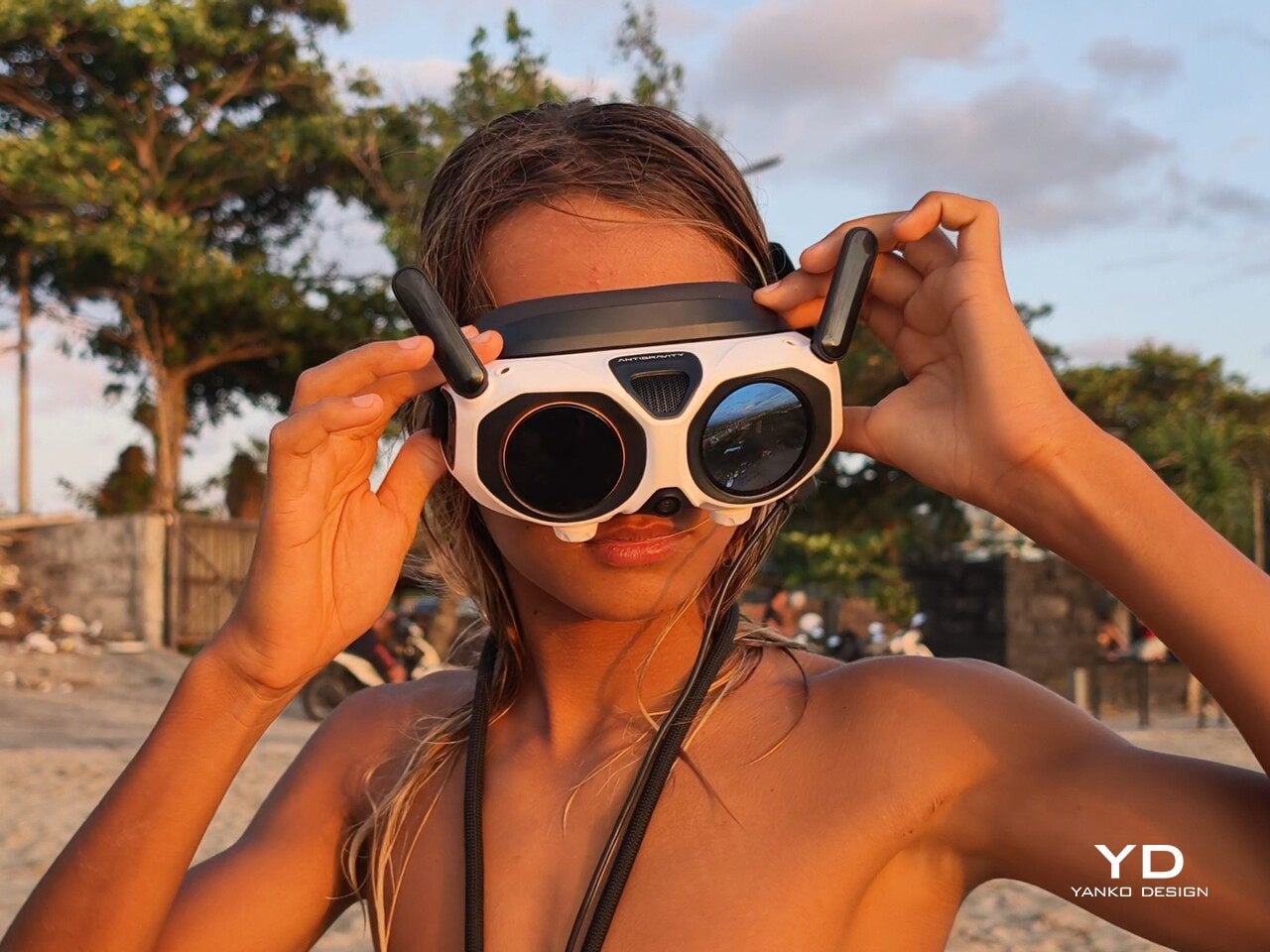
The Vision goggles lean into an almost character-like, even bug-like look, especially when you fold up the black antennas on each side that resemble insect feelers. The front shell is white with two large, dark circular eyes, giving the whole front a slightly cartoonish face. In between and just above those eyes sits an inverted triangle-shaped grille with a subtle Antigravity logo, adding a small technical accent without breaking the simplicity. The fabric strap and thick face padding sit behind this front mask. Wearing the goggles does look strange at first, but in a strangely cool way.

The Grip motion controller has a white plastic shell with buttons and a dial that uses color and icon cues to hint at their functions. On the back, a black trigger-style pull bar sits where your index finger naturally rests. There are additional buttons on each side. The mix of white body, black accents, and clearly marked controls makes the Grip look approachable rather than intimidating, which suits a controller that is meant to translate simple hand movements into flight.
Overall, the drone, goggles, and controller share a cohesive design language. They all use the same soft white shell, black accents, and gently rounded forms. The whole kit feels like a single, intentional system rather than three unrelated gadgets.
Ergonomics
The Vision goggles are where comfort really matters, and Antigravity has clearly spent time on fit. The goggles weigh 340 grams, yet the padding and strap geometry distribute that weight in a way that avoids obvious pressure points, even during longer sessions. The side that meets your face feels soft and accommodating, so the hardware never feels harsh. Once the 360-degree image appears, the headset fades faster than you might expect, which is exactly what you want from an immersive device. Optional corrective inserts mean many glasses wearers can enjoy a sharp view without wrestling frames under the band, which makes the experience more inclusive and less fussy.

Power for the goggles lives in a separate battery pack that you can wear on a lanyard around your neck. At 175 grams, it is not heavy, but over time, it can feel slightly cumbersome to have it hanging there, especially when you are moving around. Antigravity sells a 1.2 metre (3.9 foot) USB-C to DC power cable that lets you route the battery to a trouser pocket or bag instead, which makes the whole setup feel less dangly and more integrated.
You adjust the head strap with velcro, which works, but it is not perfect. A small buckle or hinge mechanism would make it much easier to put the goggles on or take them off while wearing a hat, without having to readjust the strap length every time. It is a minor detail, yet it shows how close the design already is. You start wishing for refinements, not fixes.
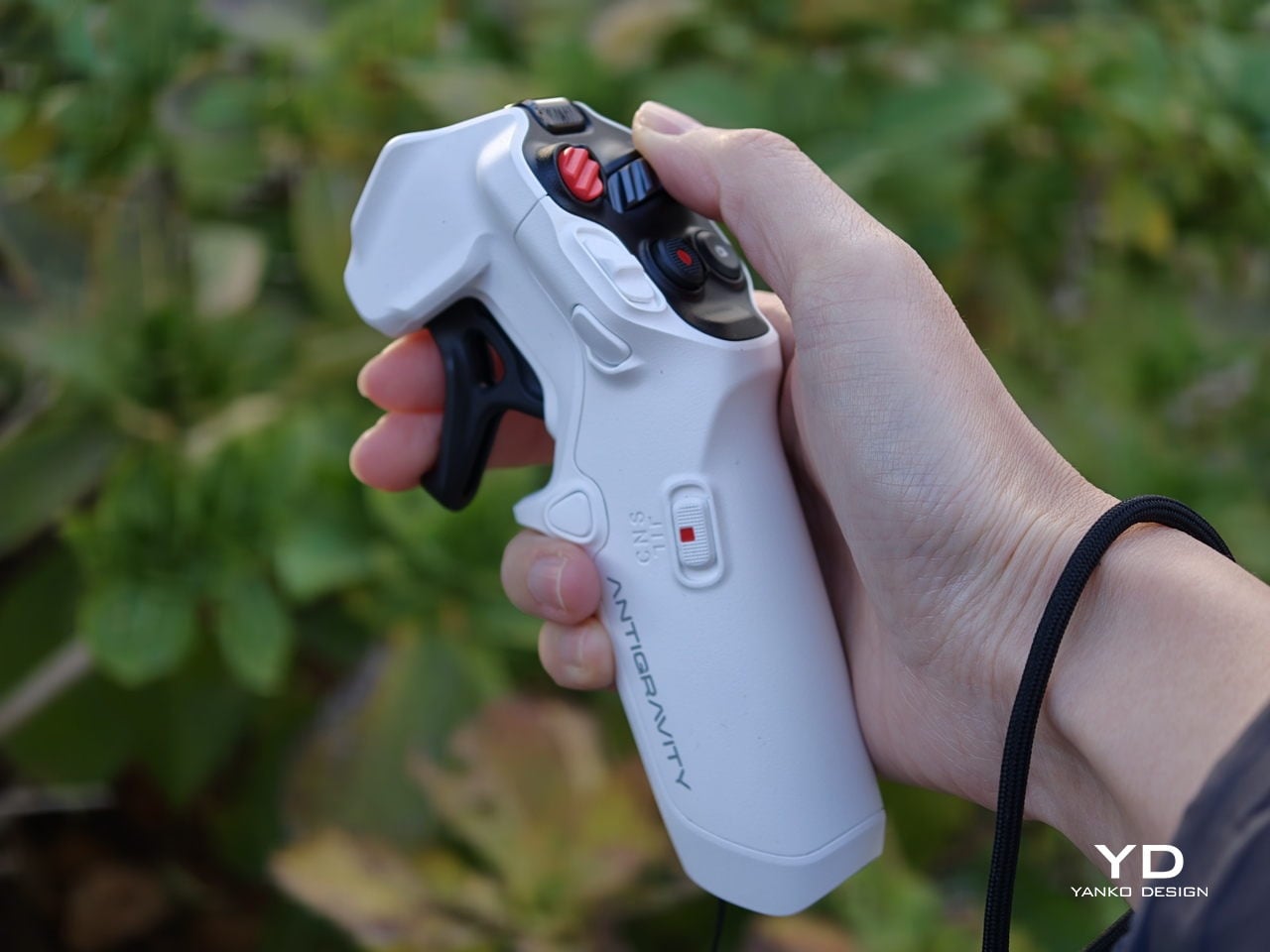

The Grip controller is where Antigravity’s ergonomic thinking really shows. It rests comfortably in one hand, with a form that supports a natural, slightly relaxed grip rather than a tense, clawed hold. For my hand, it is just a tiny bit on the large side, enough to notice but not enough to break the experience. This is very much nitpicking, and it actually underlines how well resolved the controller already is. When you are down to debating a few millimetres of girth, it means the fundamentals of comfort and control are in a very good place.
Performance
My experience with Antigravity A1 actually started at IFA in Berlin in early September. Outside the exhibition halls, I slipped on the Vision goggles while an Antigravity staff member flew the drone. As the A1 lifted and the IFA venue unfolded beneath me in every direction, my legs actually shivered a little, even though I like heights. Being wrapped in a live 360-degree view felt less like watching a screen and more like I was flying. That first taste was magical, which made me both excited and nervous to test the A1 myself later. I had almost crashed a friend’s drone years ago and had not flown since, so my piloting skills were close to none.

That magic comes with a setup phase that feels more like preparing a small system than turning on a single gadget. The first time you connect the drone, pair the Vision goggles, update firmware, and learn the grip controls, it can feel overwhelming. There are menus on the drone, options in the goggles, and status lights to decode, and they all compete for your attention at once. After a few sessions, it settles into a rhythm, but that initial ramp is something you feel before you ever lift off on your own.
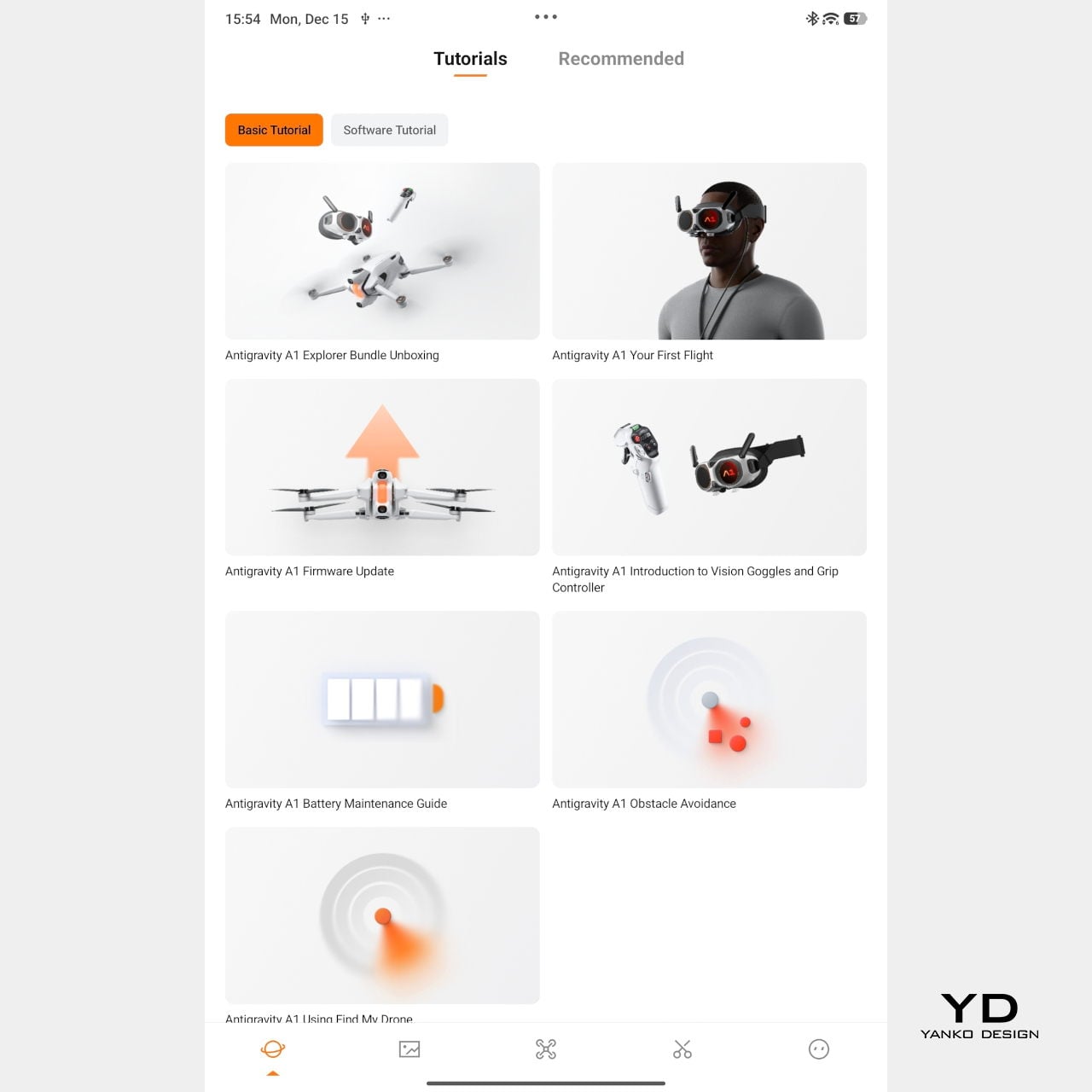
Mobile app – Tutorial
Packing the Antigravity A1 means finding room for the drone, the goggles and their separate battery, and the grip controller, often in a dedicated case or carefully arranged backpack. This nudges the whole experience away from “throw it in your bag just in case” and toward “plan a proper flying session.” The result is that the A1 feels more like a deliberate outing than a casual accessory.

On paper, the A1 looks quite sensible. With the standard battery, it weighs 249 g, staying just under the 250 g threshold that works nicely with regulations in many places, and it offers up to about 24 minutes of flight time in ideal conditions. Pop in the high-capacity battery, and the weight goes over 250 g, but Antigravity quotes up to around 39 minutes in the air. In reality, you get a solid single session per pack and will want spares if you plan to film seriously.
Flight behaviour is also adjustable. There are three flight modes, Cinematic, Normal, and Sport, so you can match how the drone responds to the scene you are flying in. Together with Free Motion and FPV, that gives the A1 enough range to feel relaxed and floaty when you want it, or more direct and energetic when the shot calls for it.
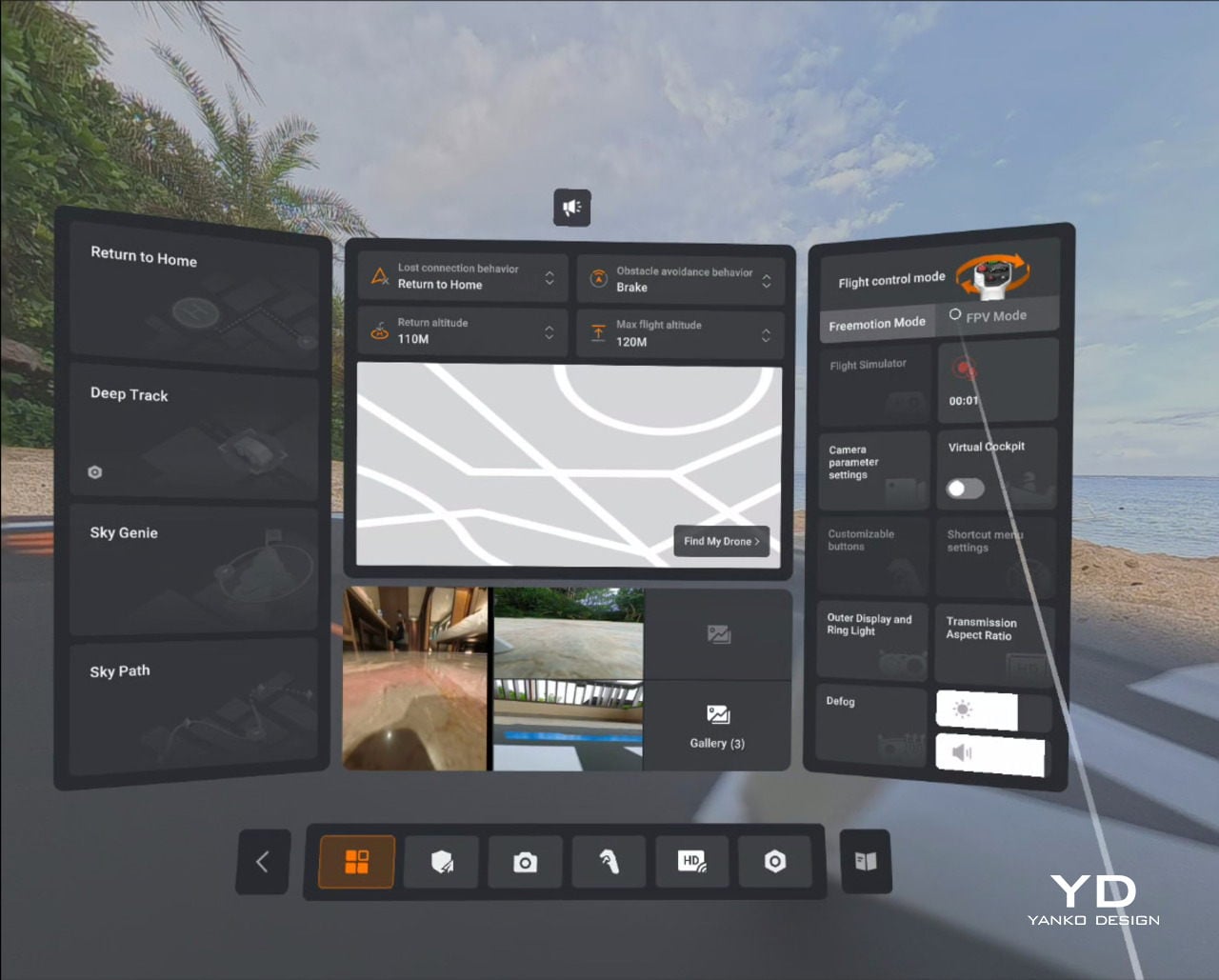
Vision goggles menu
On top of those basics, Antigravity adds automated tools like Sky Genie, Deep Track, and Sky Path. Sky Genie runs preprogrammed patterns that give you smooth, cinematic moves with minimal effort. Deep Track follows a chosen subject automatically, so you can focus more on timing than stick precision. Sky Path lets you record waypoints and have the A1 repeat the route on its own, which is handy for repeated takes or for nervous pilots.
Safety and workflow sit quietly in the background, which is exactly where they should be. Obstacle sensors on the top and bottom help protect the drone when you are close to structures or changes in elevation, and one click Return to Home acts as a psychological parachute. Knowing you can call the drone back with a single command does a lot to calm the nerves, especially if your last memory of drones involves a near crash.
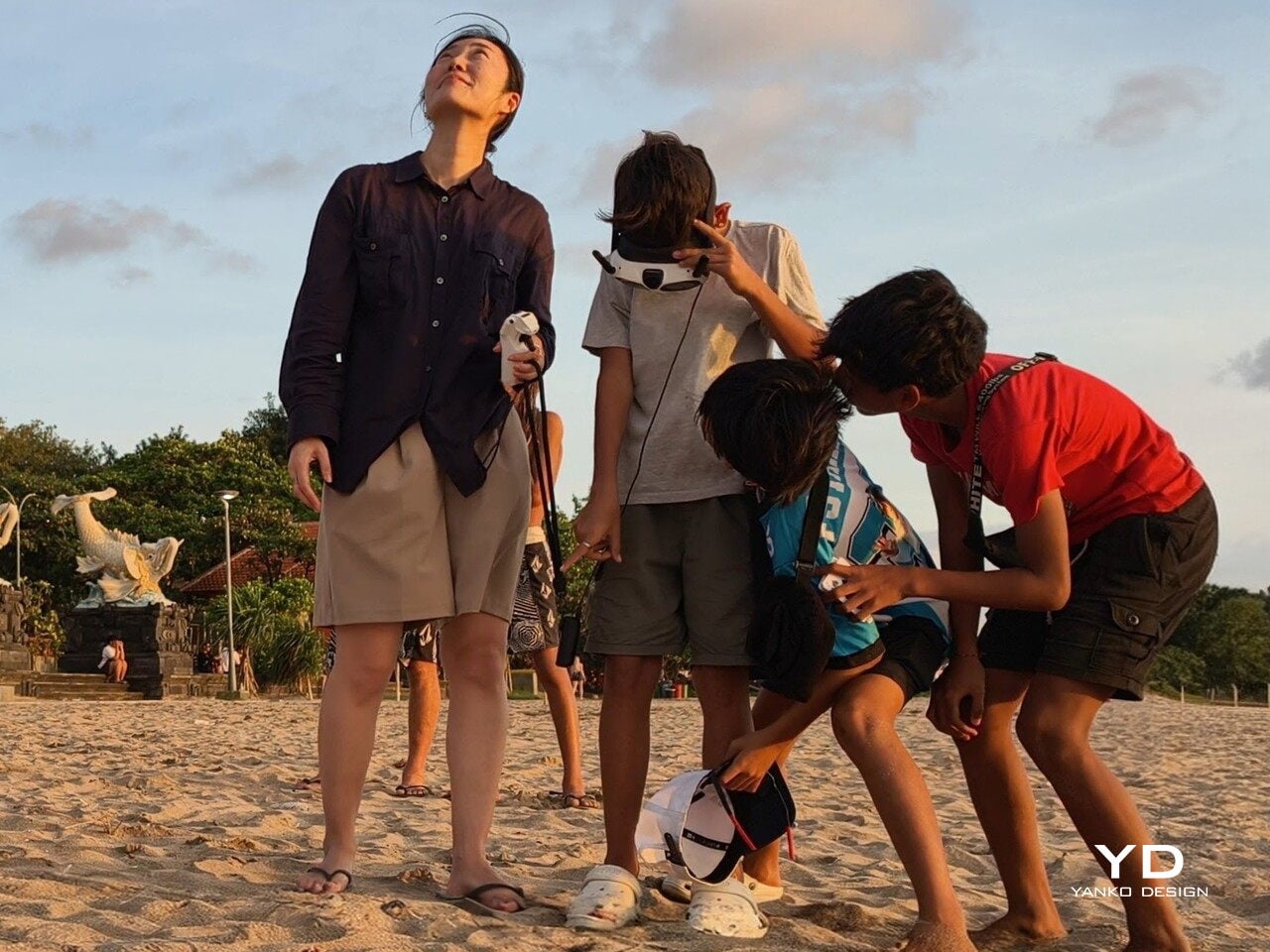

In the United States, FAA rules treat goggle-only flying as beyond visual line of sight, so you are meant to have a visual observer watching the drone while you are wearing the headset. That nudges the A1 away from solo, spur-of-the-moment flights and toward planned sessions with someone beside you acting as spotter.
On the imaging side, the A1 records up to 8K 360-degree video, with lower resolutions unlocking higher frame rates when you want smoother motion. Footage can be stored on internal memory or a microSD card, and you can offload it either by removing the card or plugging in via USB-C, so it slips neatly into most existing editing habits.

Vision goggle screen recording
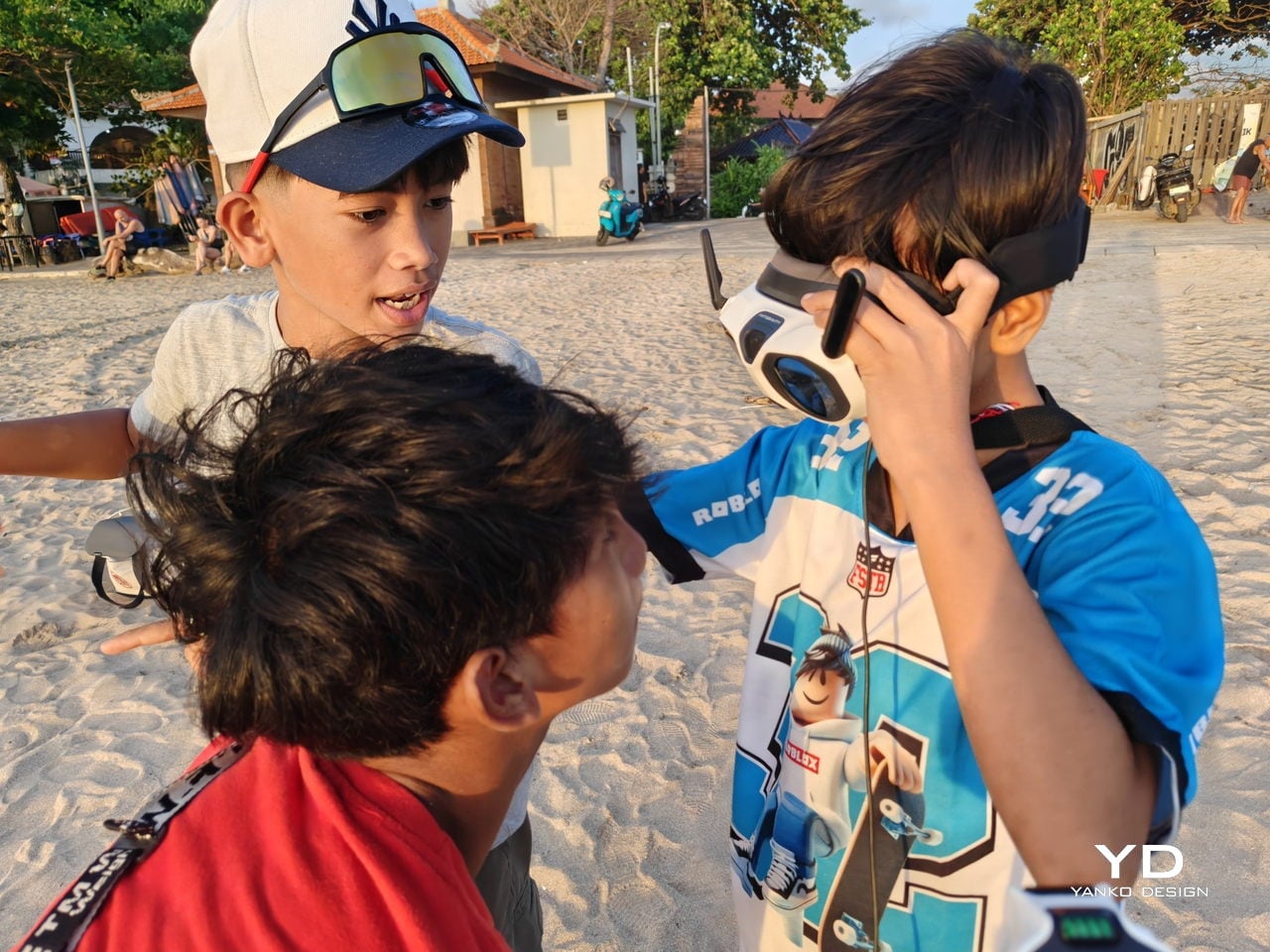
The real leap, though, comes from the goggles. They are the thing that truly sets A1 apart from almost every other consumer drone. Instead of glancing down at a phone, you step into an immersive 360-degree view that tracks your head and surrounds your vision. The drone feels less like a gadget in the sky and more like the spot your eyes and body are occupying. A double-tap on the side button flips you into passthrough view, so you can check your surroundings without pulling the headset off, and a tiny outer display mirrors a miniature version of the live feed for people nearby.

That small detail turned out to be important in Bali, where a group of local kids noticed the goggles and the moving image, wandered over, and suddenly found themselves taking turns “flying” above their own neighbourhood. Their gasps, laughter, and stunned silence were as memorable as the footage itself.
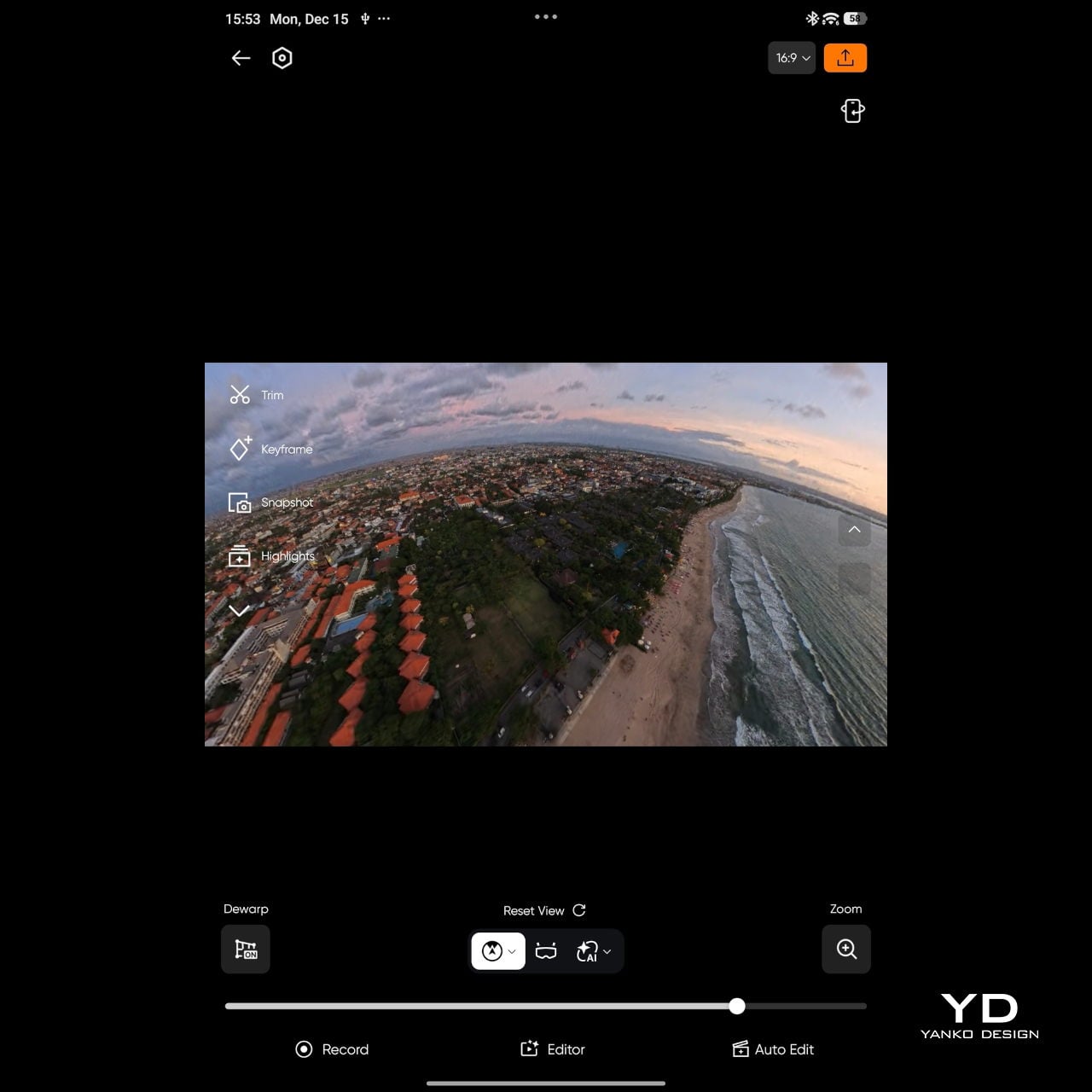
Mobile app
The magic continues even after you land. Because the A1 captures everything in 360 degrees, you can decide on your framing after the flight, which feels a bit like getting a second chance at every shot. Antigravity provides both mobile and desktop apps for this, so you can scrub through the sphere, mark angles, and carve out regular flat videos without having to nail every move in real time.
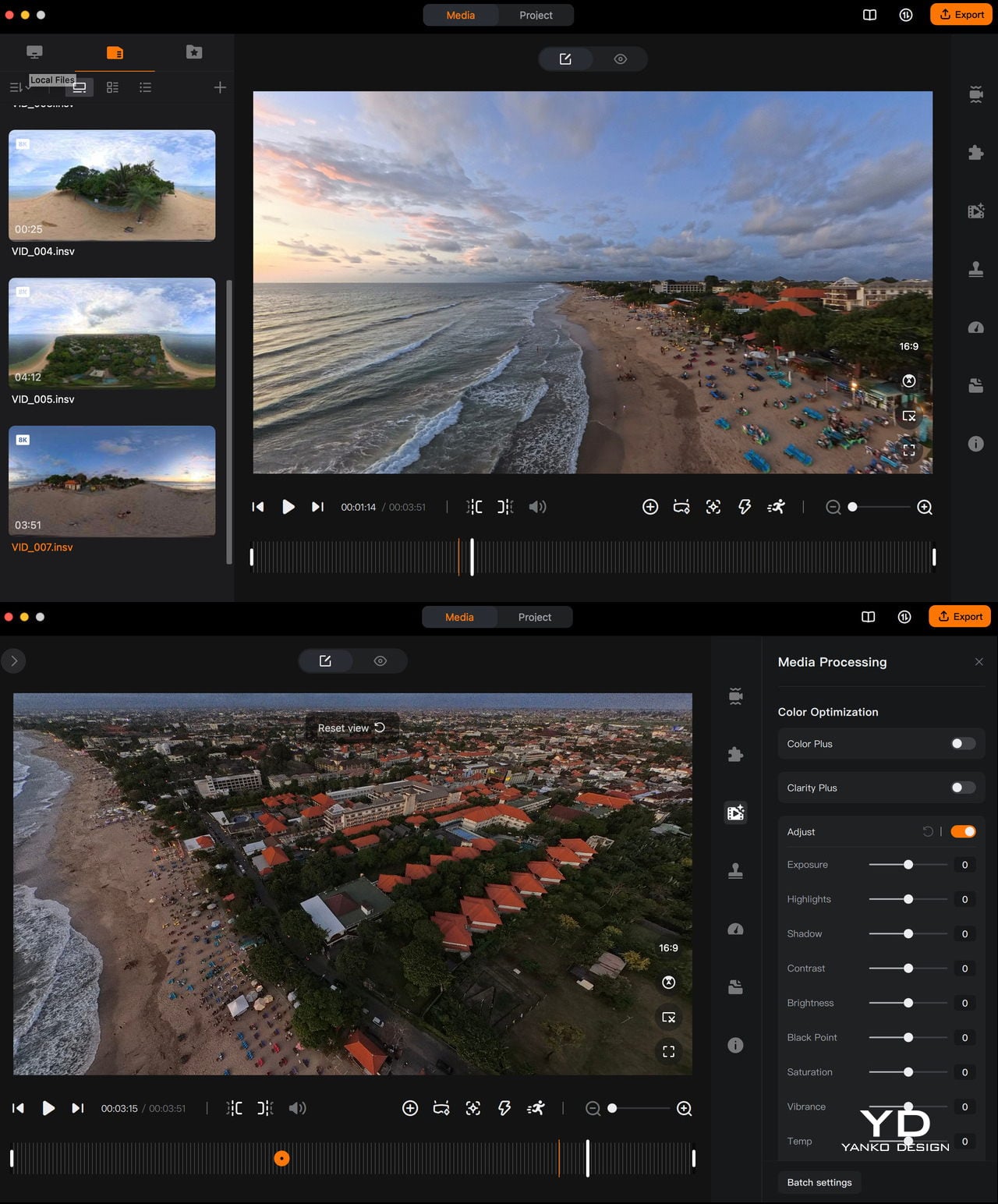
Desktop app
If you have used the Insta360 app, the Antigravity app will feel instantly familiar, with similar timelines, keyframes, and swipe-to-pan gestures. Even if you have not, it is straightforward to learn, helped by clear icons and responsive previews. There is also an AI auto-edit mode that can assemble quick cuts for you, which is handy when you just want something shareable without sinking an evening into manual reframing.
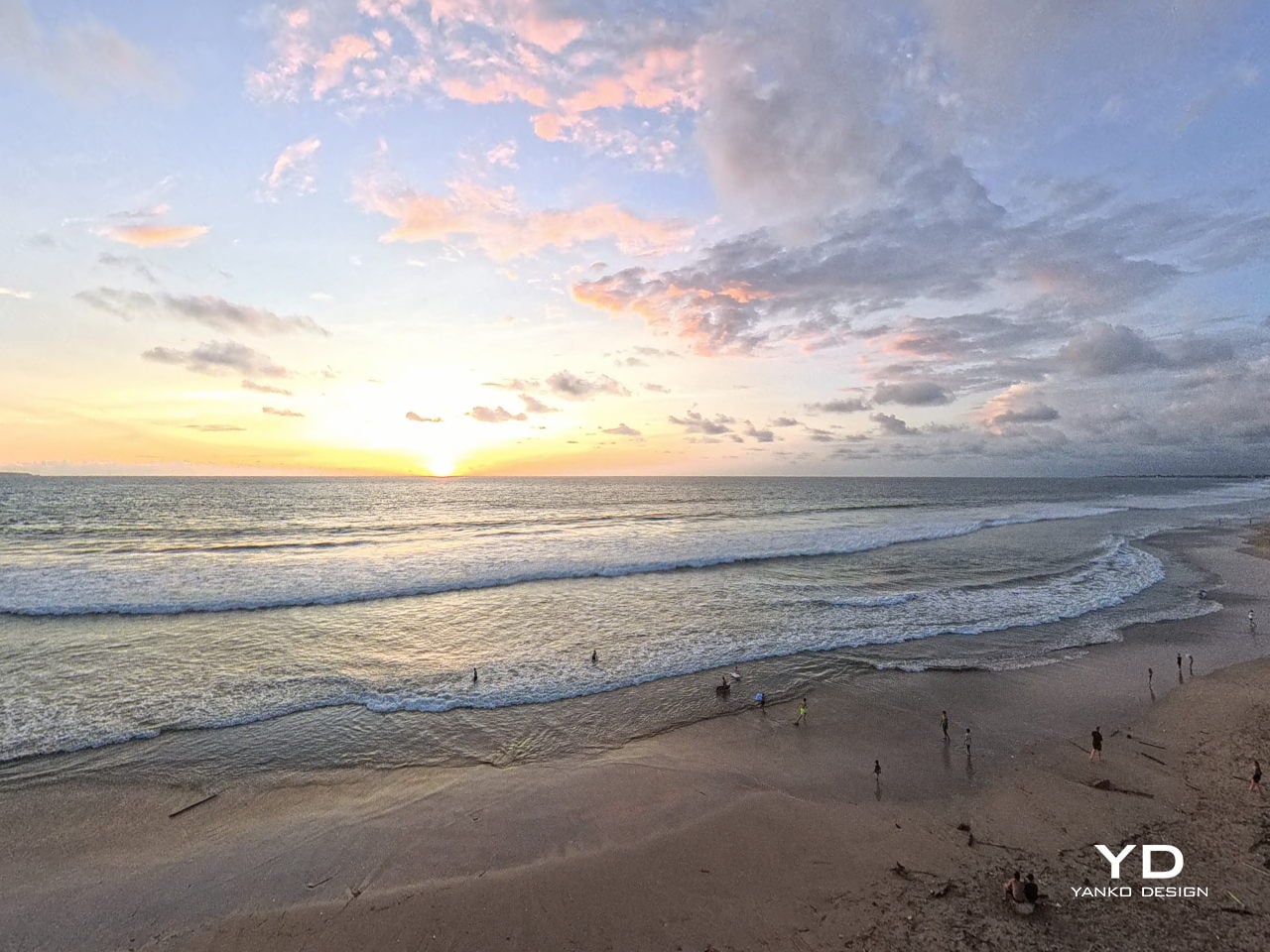
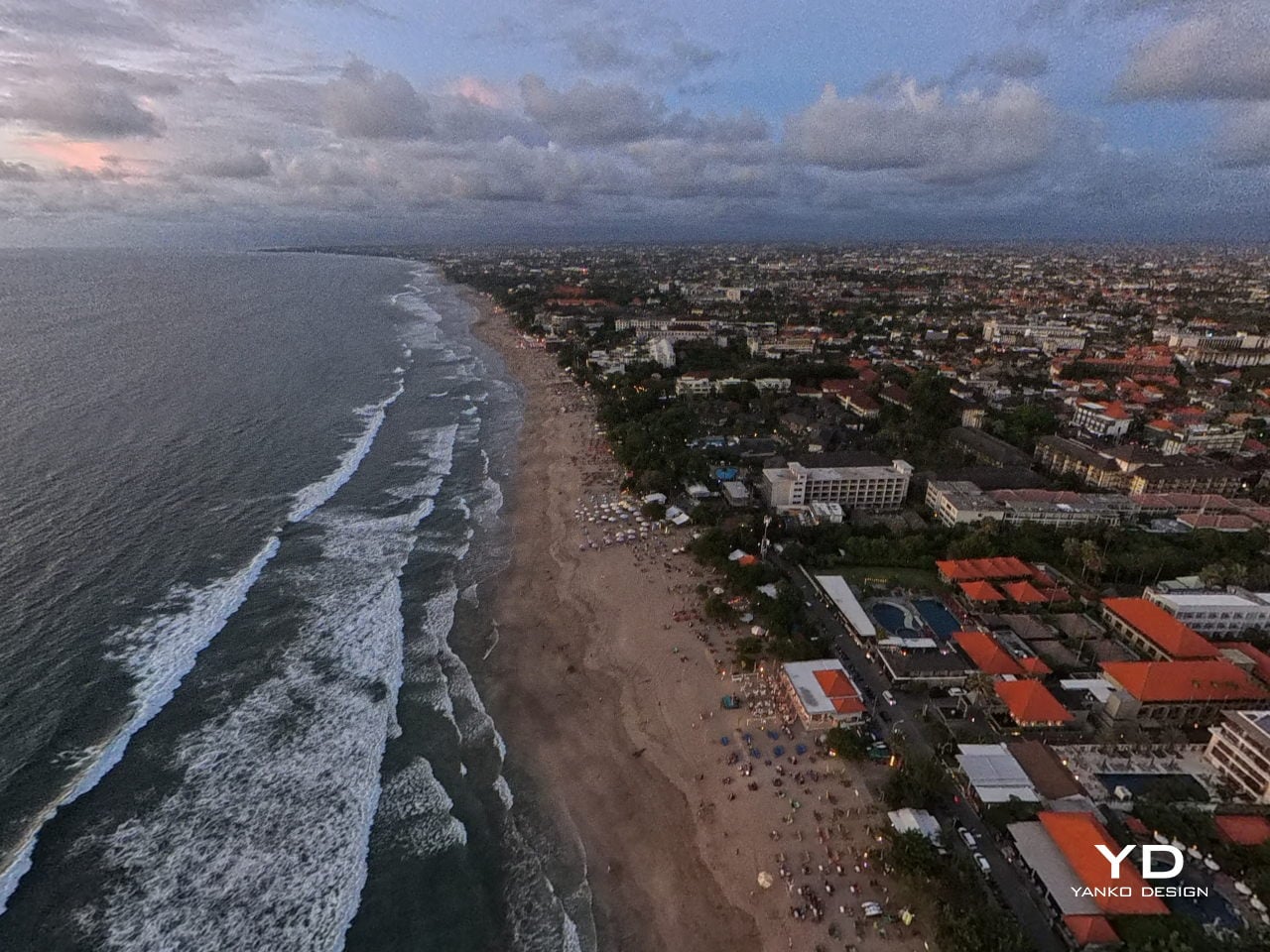


In the end, A1’s performance is not just about how long it stays in the air or how many modes it offers. Those pieces matter, and they are solid, but what you remember is the feeling of lifting off inside the goggles and the ease with which you can hand that experience to someone else. It still behaves like a well-mannered compact drone on the spec sheet, yet in use it edges closer to a shared flying machine, one that turns a patch of ground into a small, temporary viewing platform in the sky.
Sustainability
Antigravity does not make any big sustainability claims with the A1. There is no mention of recycled materials or lower-impact manufacturing, and the packaging and hardware feel very much in line with a typical consumer drone. This is not a product that sells itself on being green, and the company does not pretend otherwise.

What you do get is some support for repairing rather than replacing. The A1 ships with spare propellers in the box, which encourages you to swap out damaged blades instead of treating minor knocks as the end of the drone. Antigravity also sells replacement lenses, so a scratched front element does not automatically become a total write-off. It is a small step, but it nudges the A1 slightly toward a longer, more fixable life rather than a purely disposable gadget.
Value
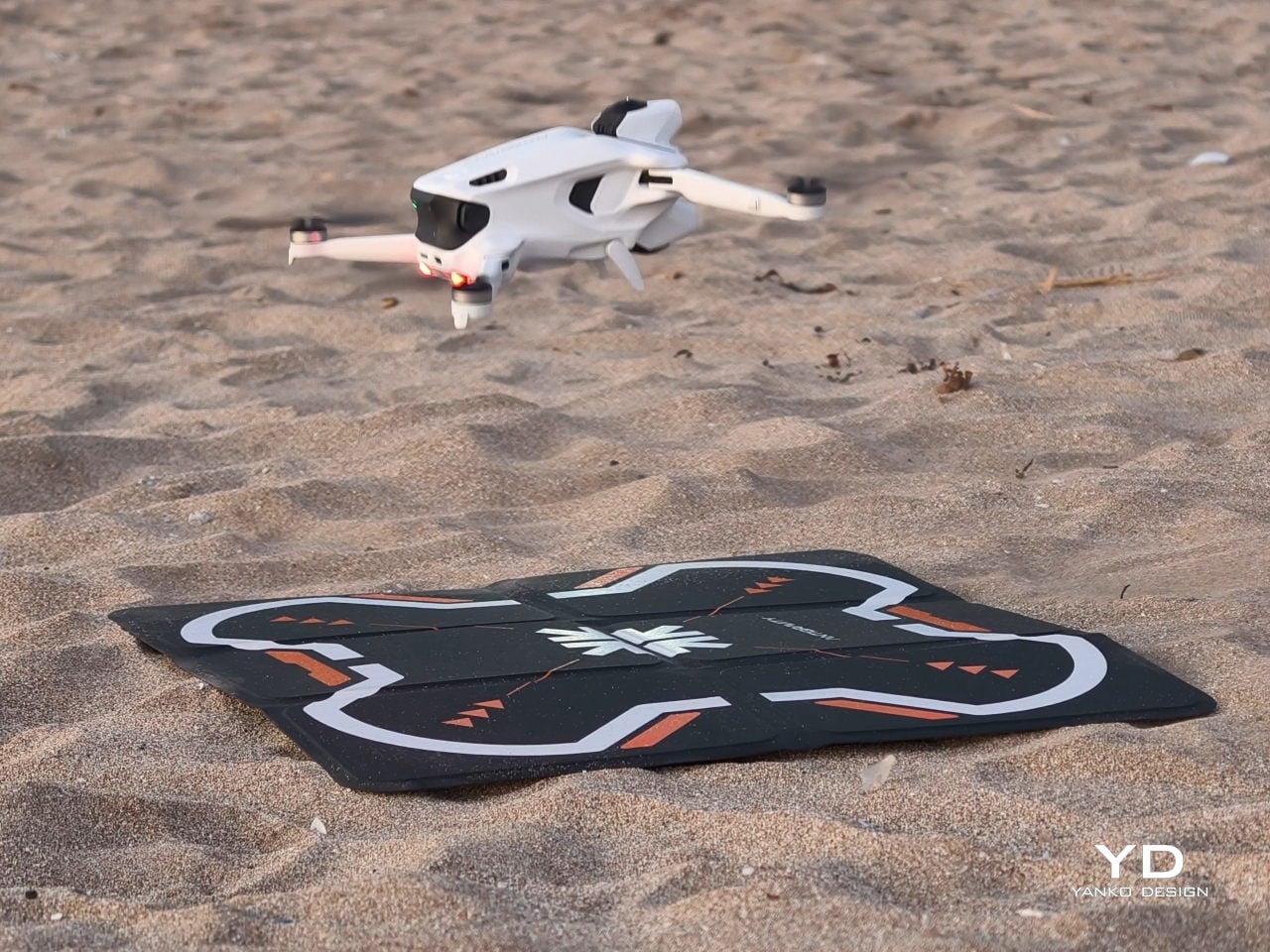
The standard Antigravity A1 bundle starts at 1599 USD, with Explorer and Infinity bundles stepping up battery count and accessories for longer, more serious flying. It is undeniably an expensive system, especially compared to regular camera drones that only give you a phone view.

At the same time, what you are really paying for is the experience of being inside the flight and reframing your shots after the fact. That sense of presence and flexibility is hard to put a number on, and for me, it nudges the A1 from “costly gadget” toward something closer to a priceless experience machine, if you know you will actually use it.
Verdict
Antigravity A1 is not the simplest drone in terms of equipment. You are managing goggles, a grip controller, multiple batteries, and in some places, you also need a visual observer if regulations require it. On top of that, the price sits firmly in premium territory. In return, you get a very different kind of flying. At first, setup and piloting can feel overwhelming, but it becomes natural surprisingly quickly, and there are plenty of automated features to help you keep the drone under control and capture cool shots. Combined with 360-degree capture and post-flight reframing in the Antigravity app, it feels less like operating hardware and more like stepping into a movable viewpoint.

If you just want straightforward aerial clips, the A1 is probably more than you need. If you care about immersive perspective and shared experiences, the mix of kit, software, and feeling it delivers starts to justify the cost. It is fussy, ambitious, and occasionally awkward, yet when you are inside that live 360-degree view, it really does reimagine what a drone can feel like to fly.
The post Antigravity A1 Review: Reimagining What a Drone Feels Like to Fly first appeared on Yanko Design.






