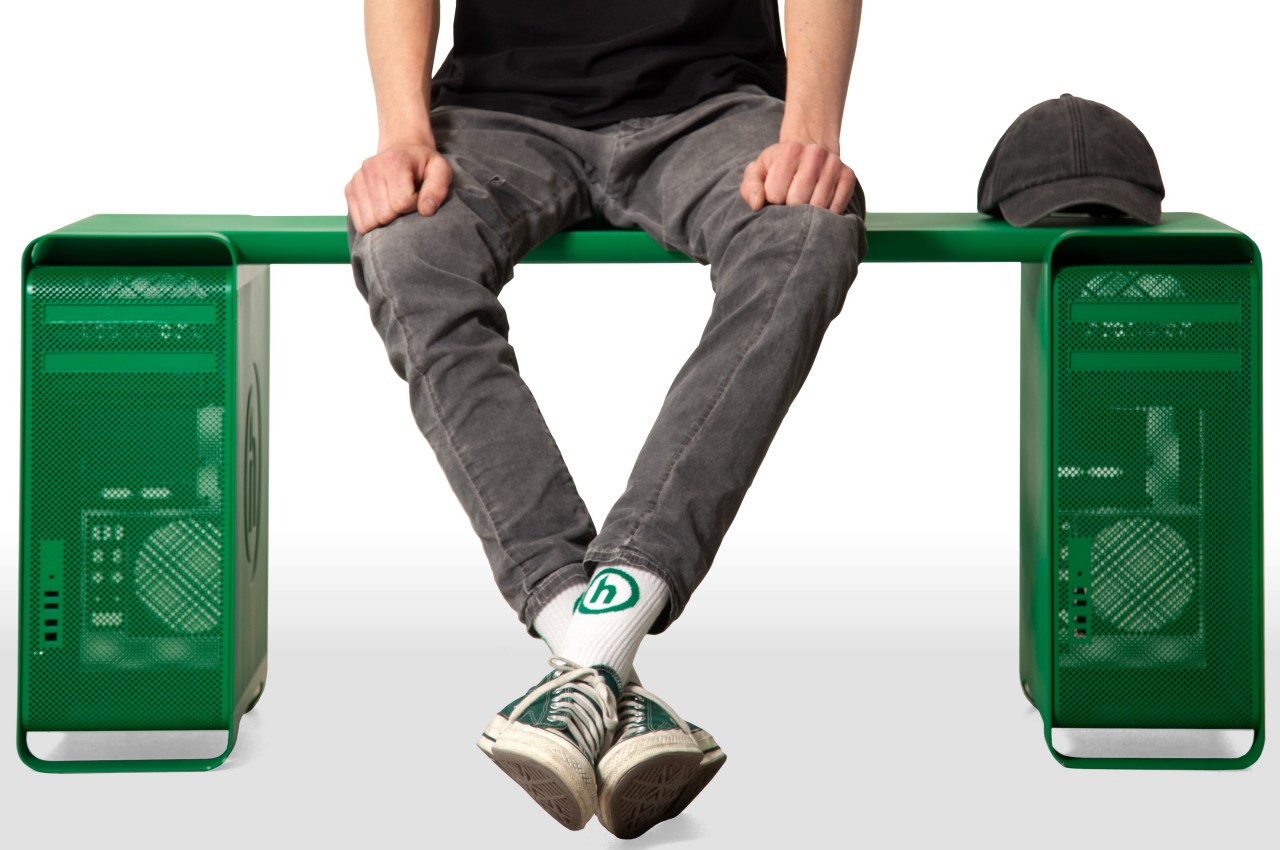
Apple is not a big fan of reusing its products for something else, at least something that is still close to the original function of the design. It probably won’t object to completely unrelated applications of those designs, especially when it’s for a creative and artistic purpose. The non-functional parts of an iPhone, for example, could be disassembled and framed to be displayed as a piece of tech history. Or one might simply take the empty shells of old Mac Pro and turn them into a piece of structural art, which is exactly what this rather striking metal bench tries to accomplish in a way that will probably make you wonder how strong those old Apple desktops might have been.
Designers: Quinner Baird, Alec Alborg, Ferb Liebana, Berit Levy, Jaime Uriarte (Caliper)
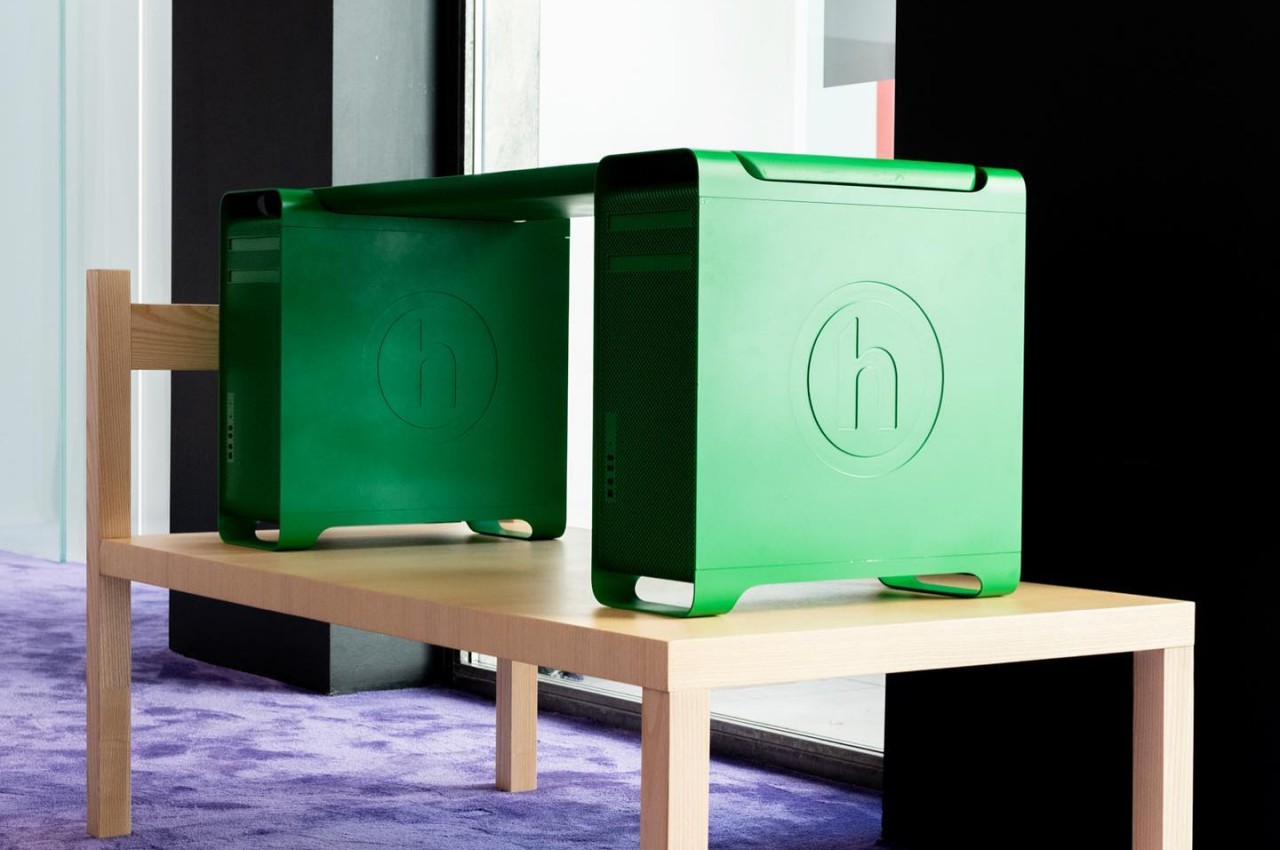


The designs for more recent Mac Pros have been rather controversial, to say the least. The cylindrical 2013 was derided for looking like a trash can, while the boxy 2019 design, though a bit more traditional, is jokingly called a cheese grater. Neither are good foundations for a stable piece of furniture, but the first-ever Mac Pro fortunately fits the bill perfectly. It was a minimalist brushed aluminum box with tapered legs on the front and back to raise it up and equally tapered handles on those same sides for easier lifting.


Made for Manhattan clothing brand Hidden as part of store display, the Mac Pro Bench is exactly what it sounds like. It takes two first-gen Mac Pros, totally gutted of any and all electronic components, and has a folded aluminum plank attached on top. The plan has a tapered shape that fits perfectly between the front and back handles, making it feel as if the desktops were made for this very purpose. Two versions of the bench exist, one preserving the brushed aluminum aesthetic of the Mac Pro, and another thoroughly coated in Hidden’s green motif.
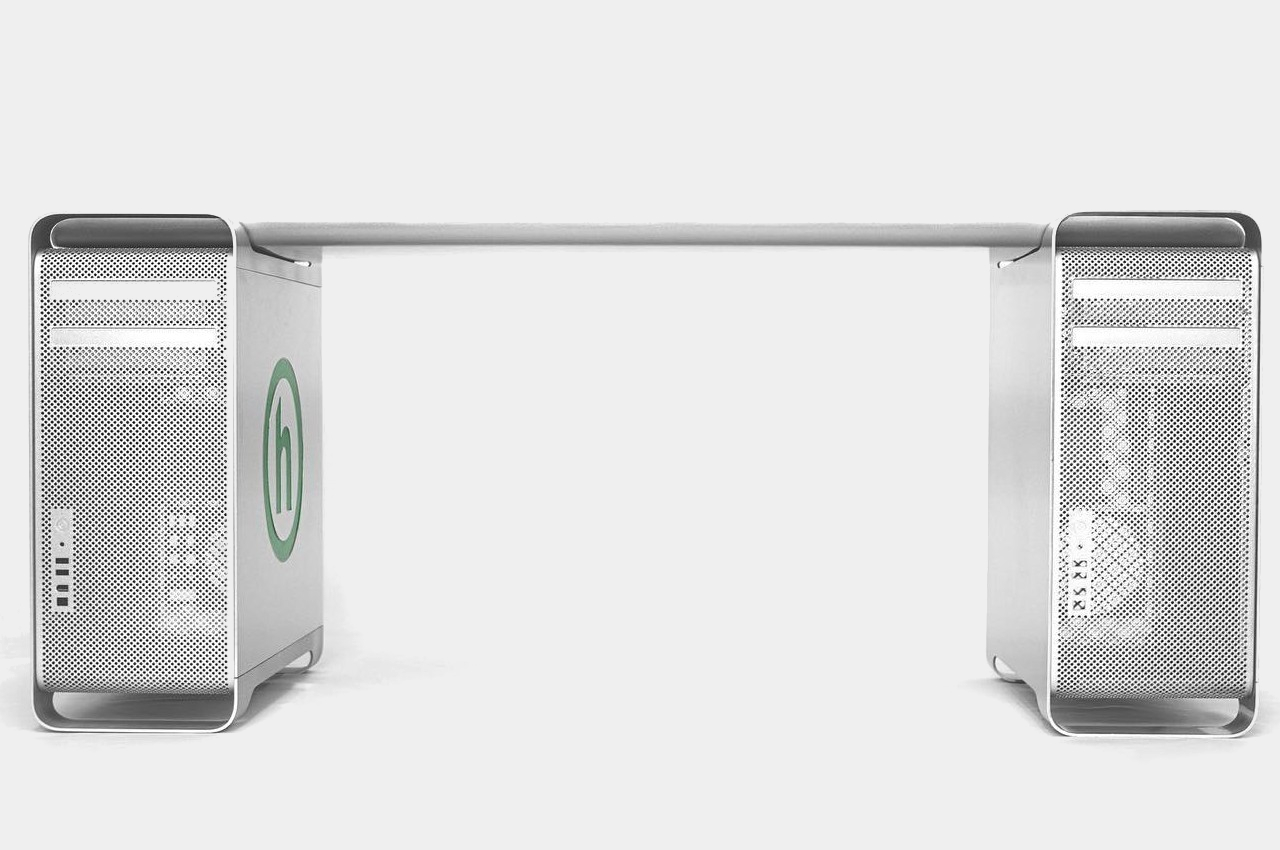
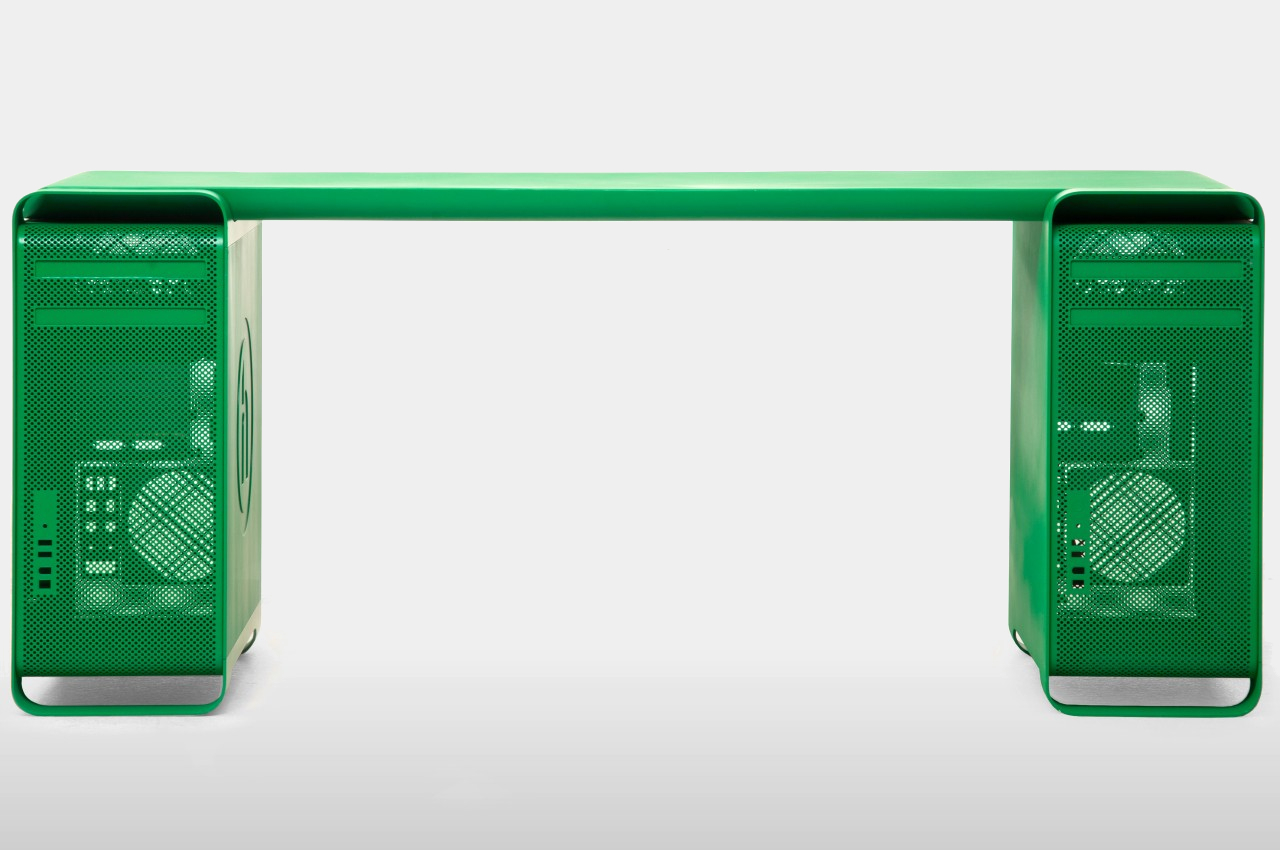


It’s not being sold en masse, which will probably keep Apple’s lawyers happy, though there are also ways to make your own. That said, it’s probably not a good idea outside of making it a decorative piece. It’s actually not tested how much weight the Mac Pros will be able to handle, especially with a bench meant to sit more than one person. The hollow legs of the desktop don’t look reassuring either, and it might have been more practical to have sawed those off, even if it meant ruining the original Mac Pro shape.
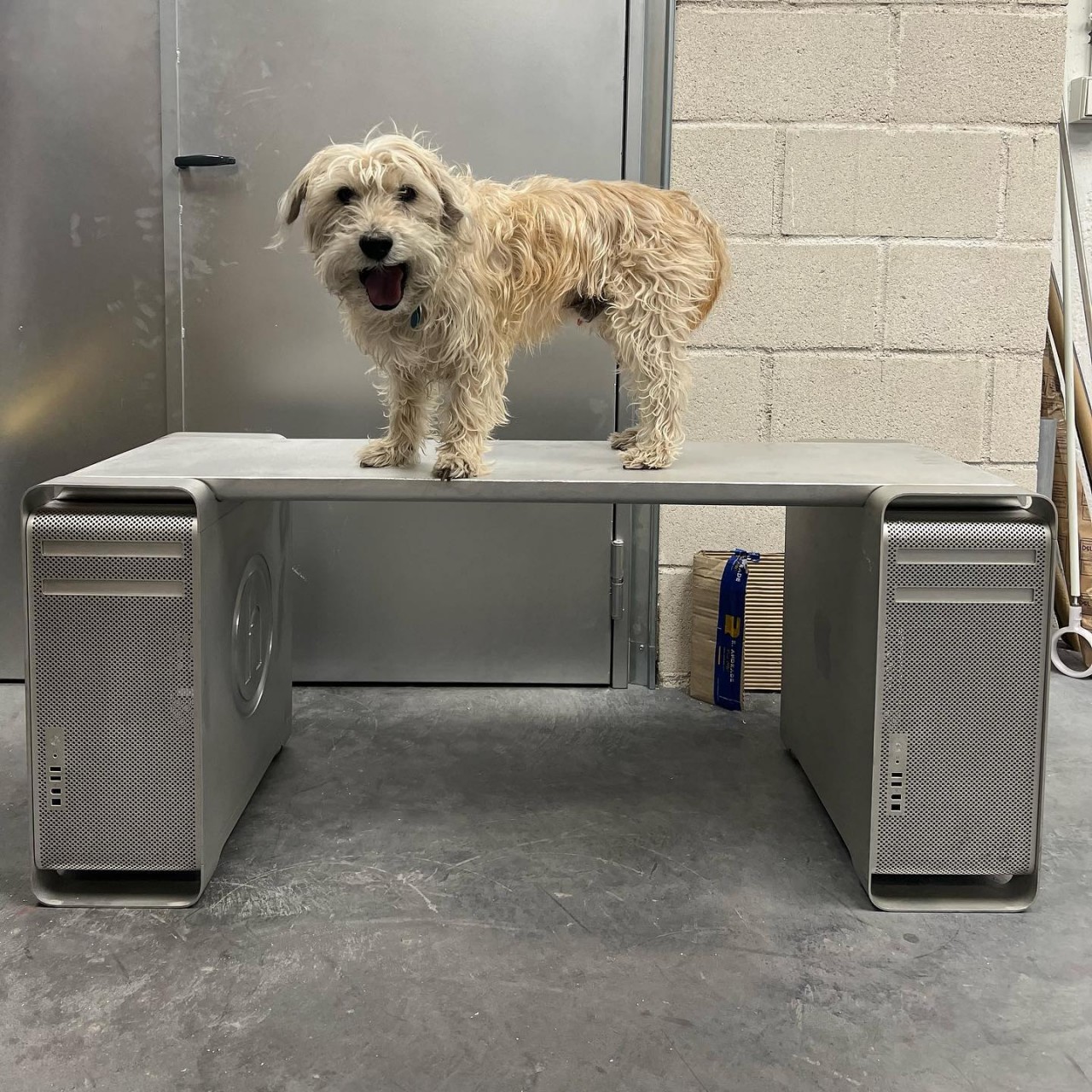

That said, it’s possible to reinforce the foundations of the Mac Pro Bench to make it a more usable piece of furniture. More importantly, however, the piece of art could also spark the imagination and creativity of others to make similar designs that reuse discarded desktop PCs in a less conventional and more interesting manner.
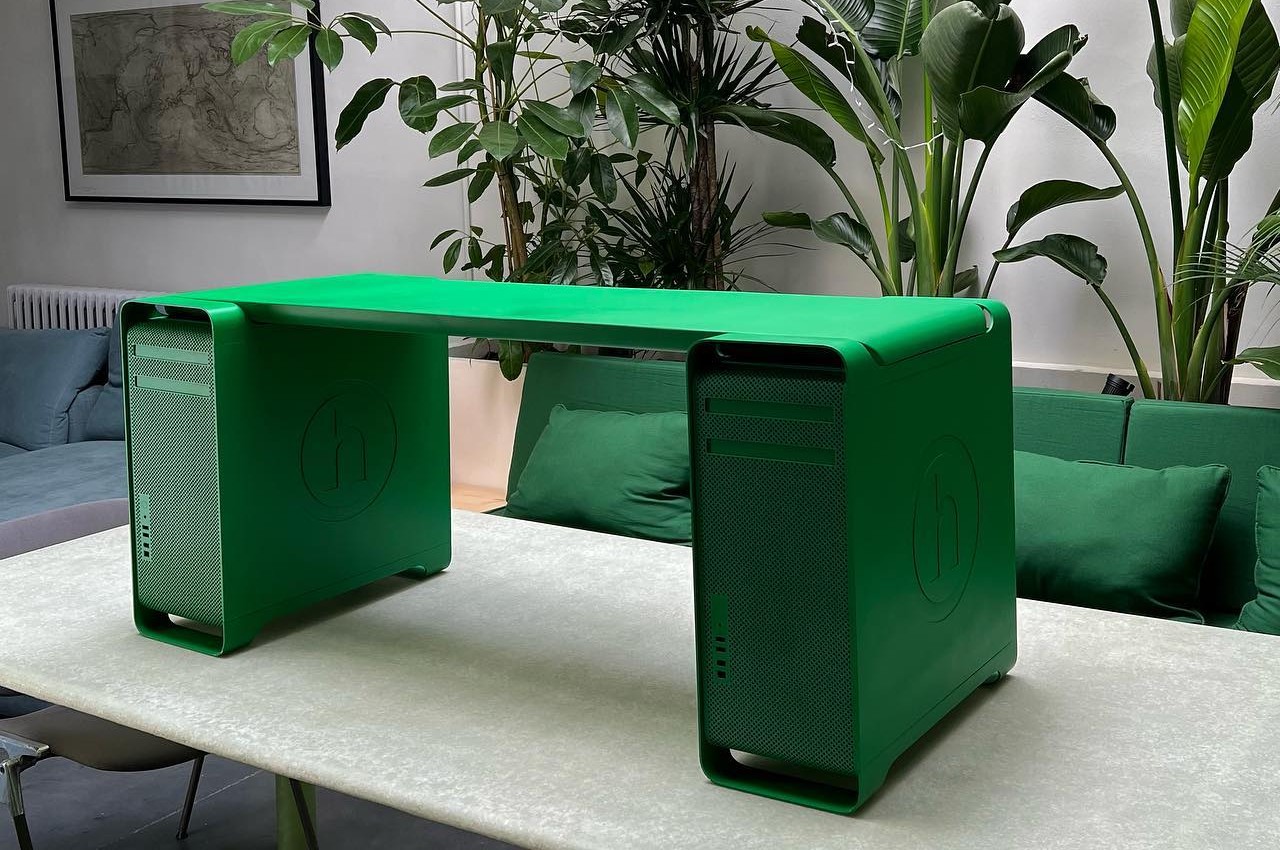



The post This aluminum bench stands on the shoulders of discarded Mac Pro cases first appeared on Yanko Design.