Cory Doctorow coined the term “enshittification” to describe how internet platforms inevitably decay, prioritizing advertisers and shareholders over users who made them successful in the first place. What begins as a useful service gradually transforms into an advertising delivery system wrapped around minimal functionality. Websites that once loaded instantly now take seconds to render as they auction off your attention to the highest bidder. Social media feeds become algorithmic nightmares designed to maximize engagement with sponsored content rather than connections with actual people. This isn’t accidental degradation but a deliberate business model that treats users as products to be packaged and sold.
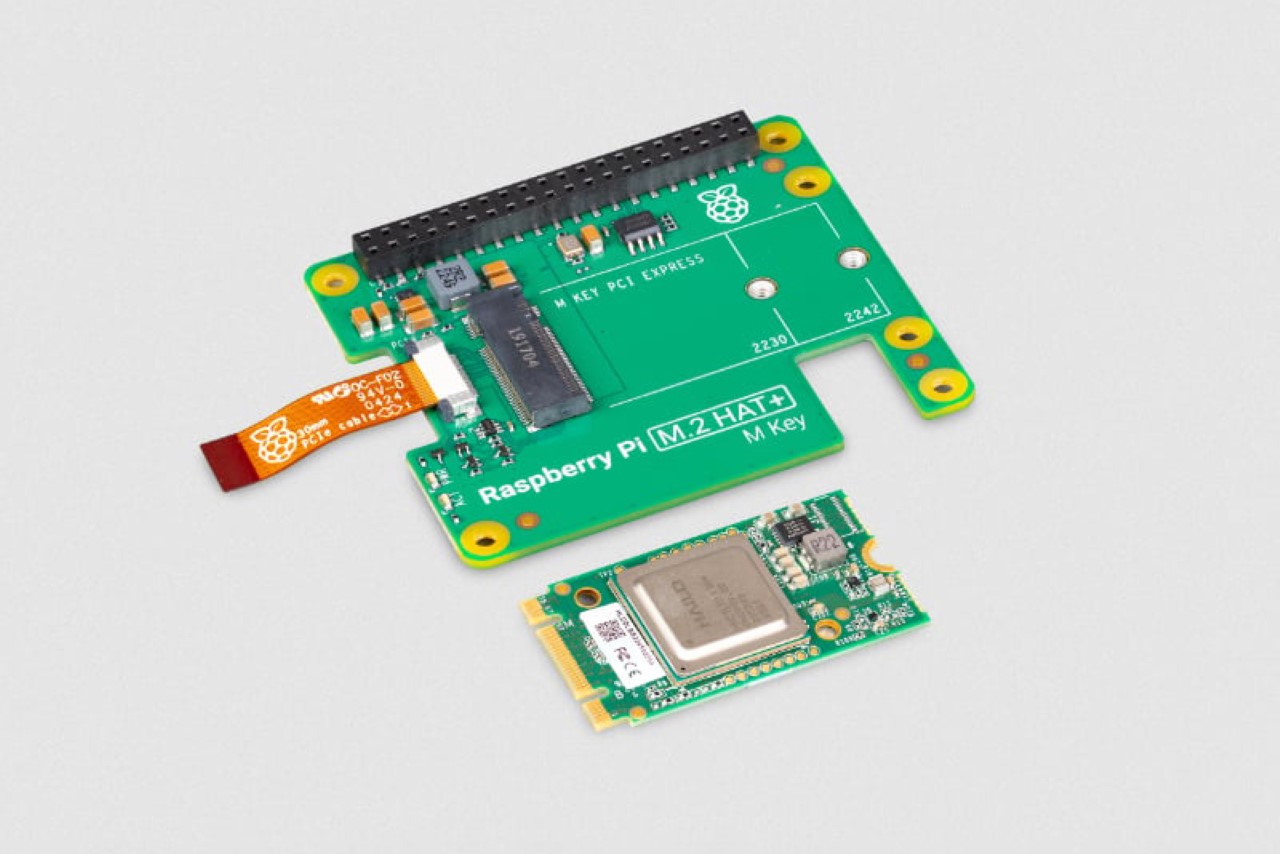
Fighting back against enshittification requires taking control of your own infrastructure rather than hoping platforms will respect your time and privacy. The Raspberry Pi Zero 2W running Pi-hole software represents a practical form of digital self-defense that costs less than $30 and works continuously in the background. This tiny computer sits on your home network and blocks advertising domains before they reach your devices, creating a cleaner internet experience across phones, tablets, computers, and smart TVs simultaneously. Adding Tailscale extends this protection beyond your home, ensuring that your browsing remains uncluttered whether you’re traveling or working remotely. The setup takes an evening and requires no programming expertise, just a willingness to reclaim your digital experience from platforms that have forgotten who they’re supposed to serve.
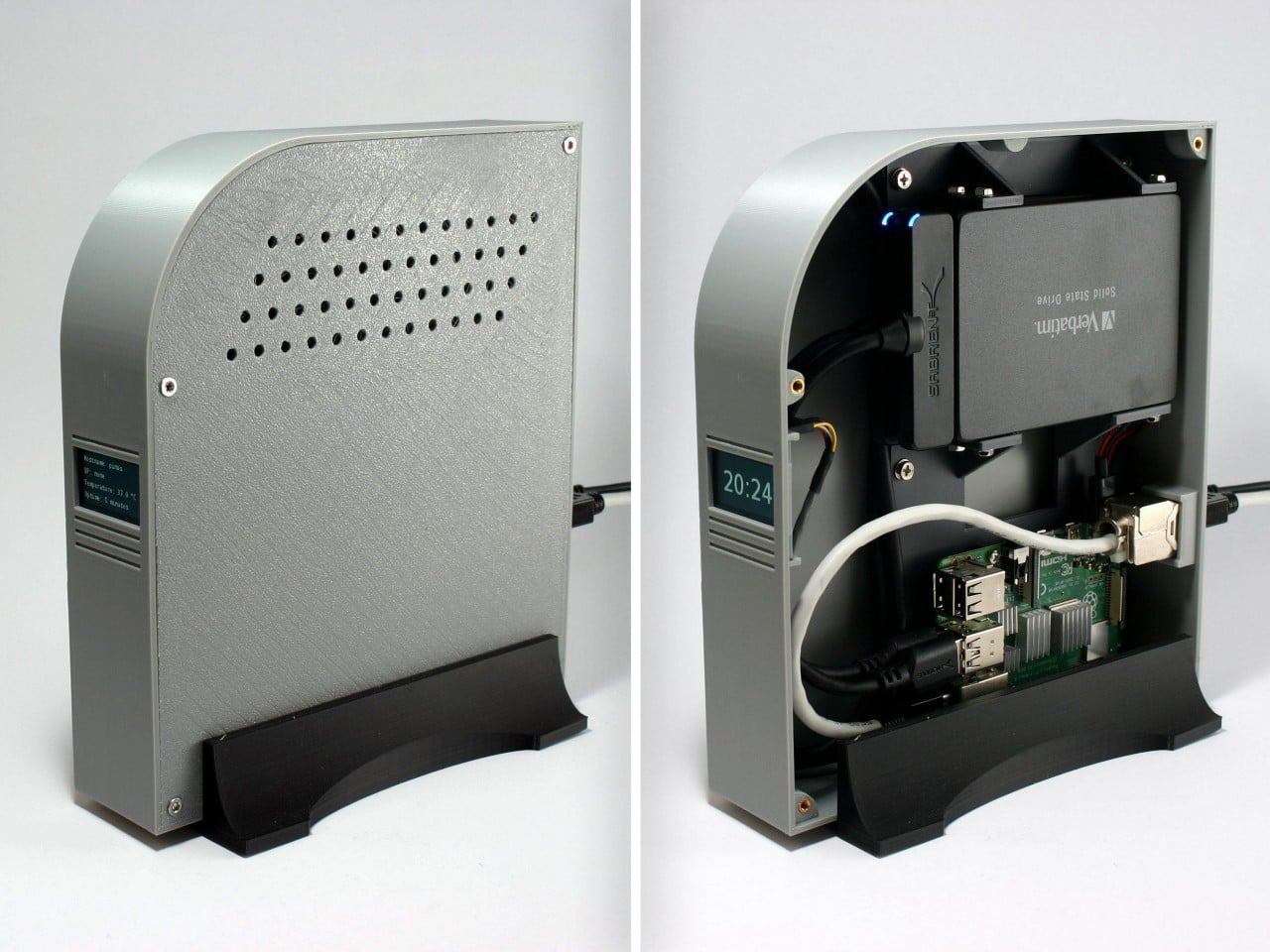
Designer: Enrique Neyra
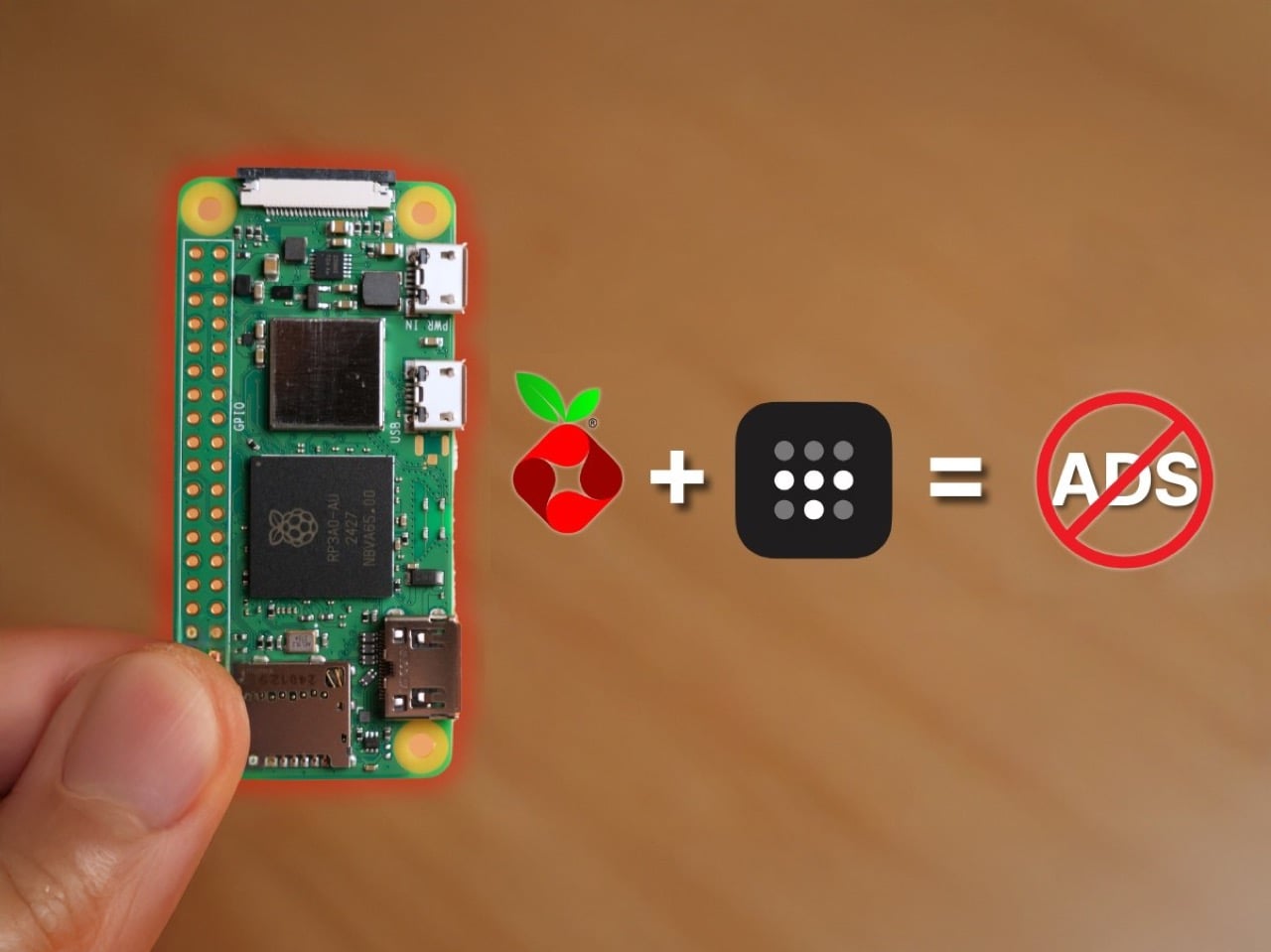

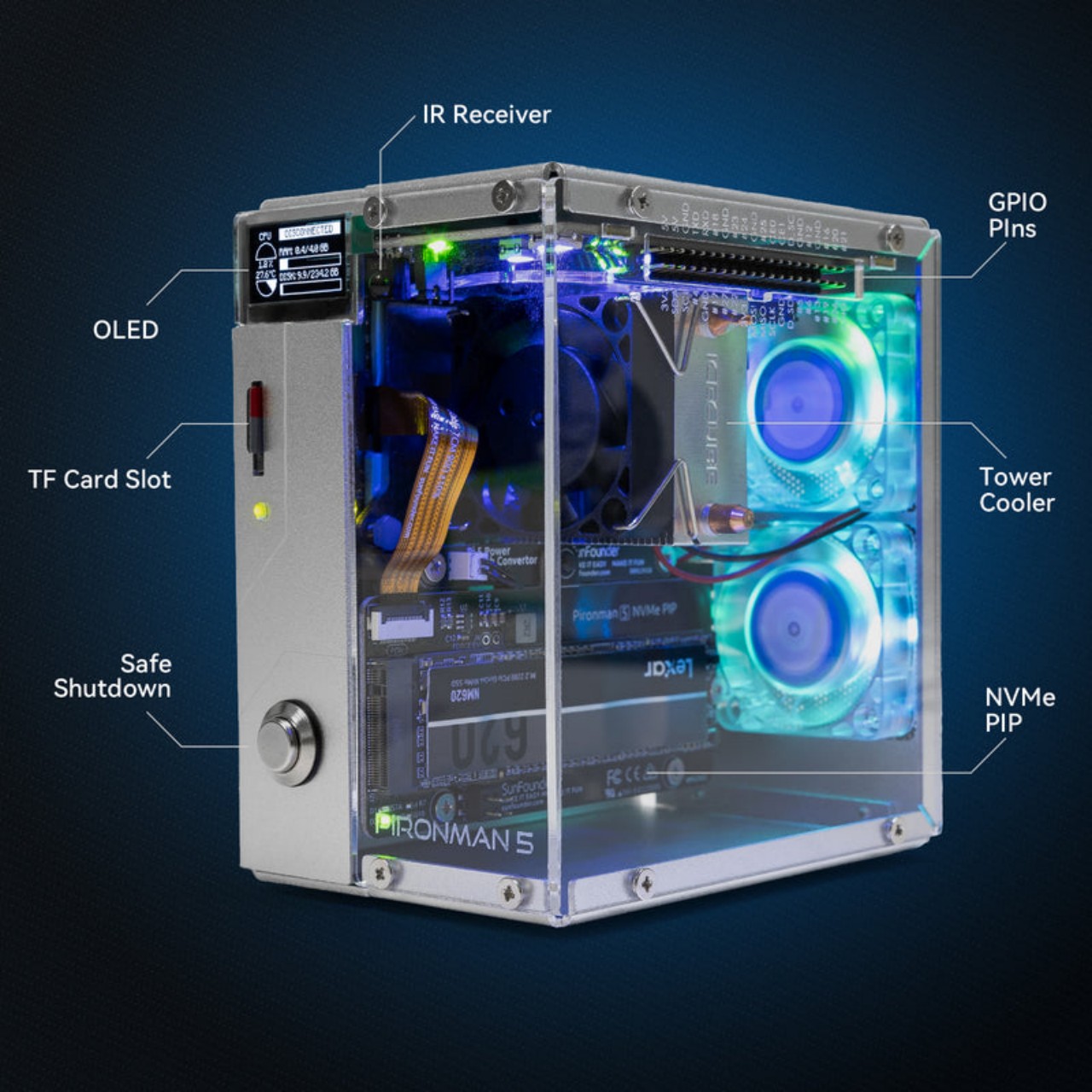
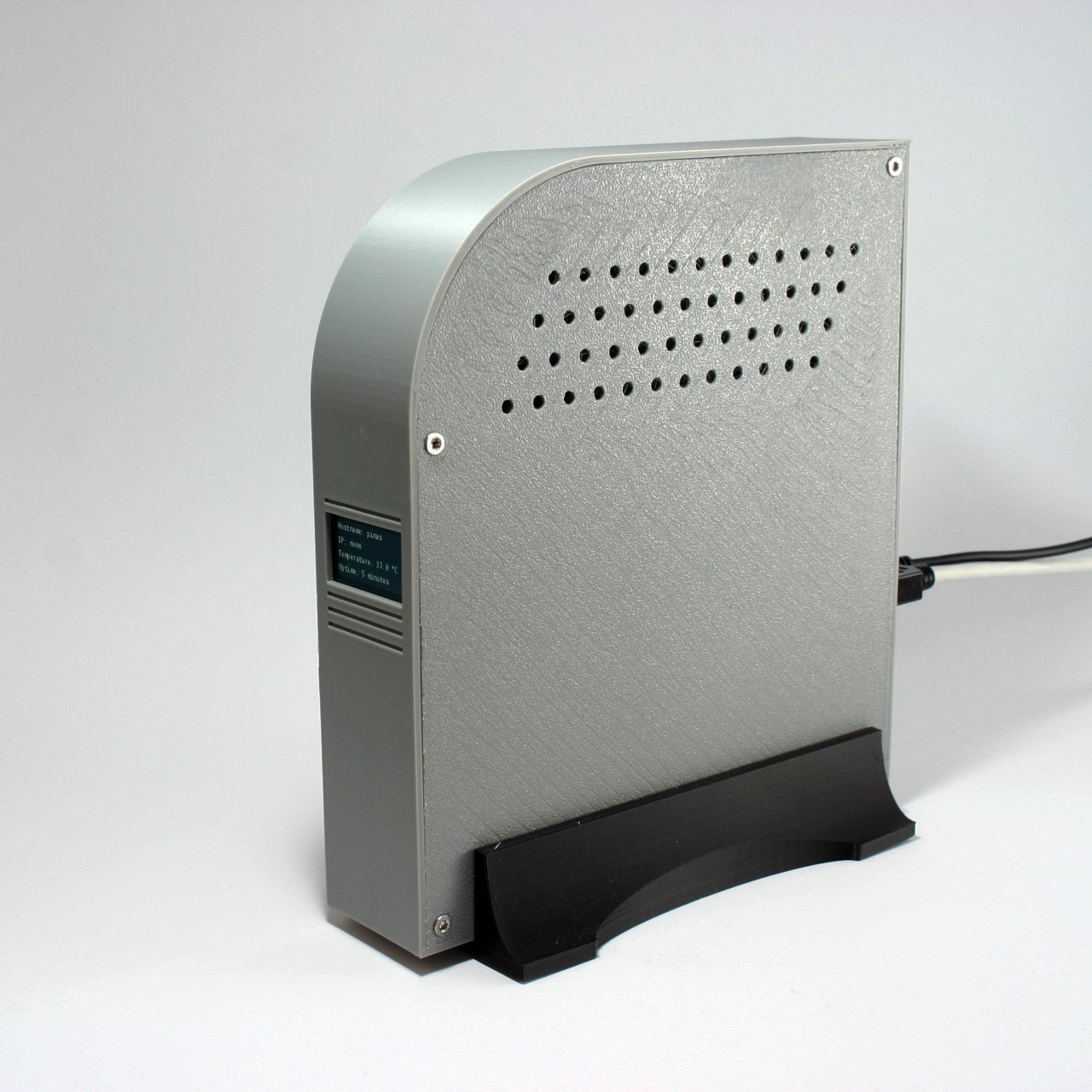
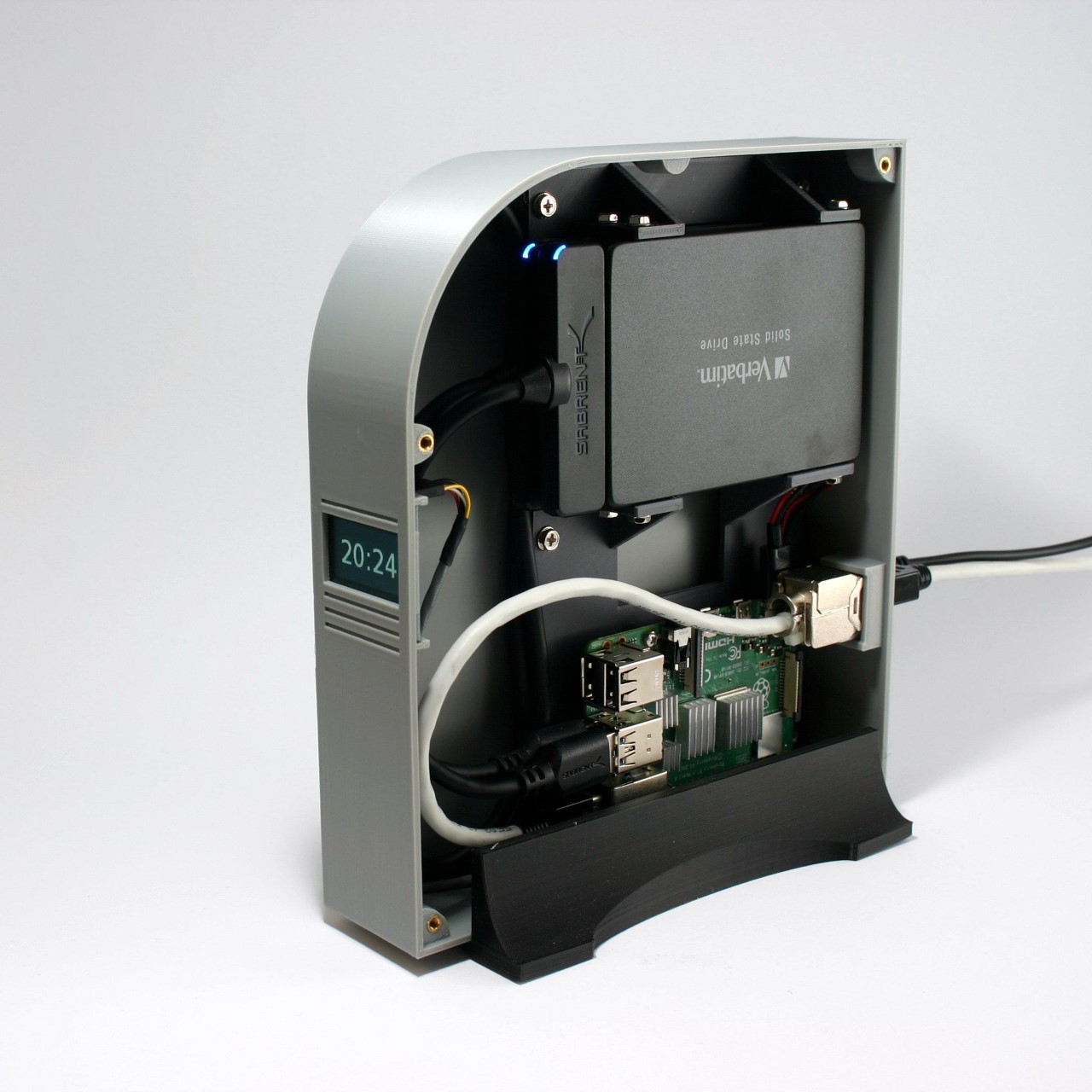
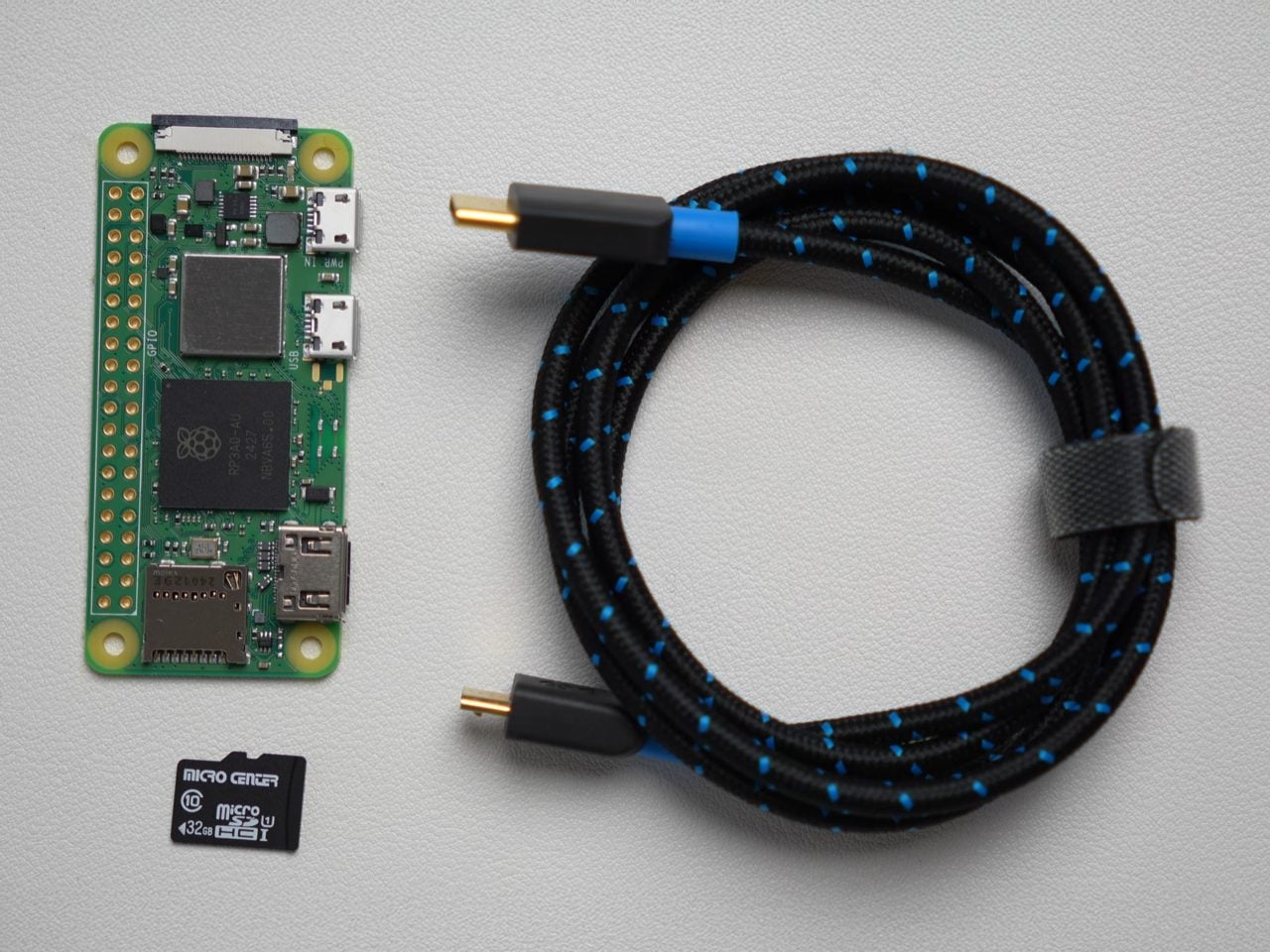
You’d expect an ad-blocker to be substantial on either the hardware or the software front, but this build proves just how small, easy, and cheap everything is. The Raspberry Pi Zero 2W running this entire thing measures 65mm by 30mm, smaller than most people’s wallets, drawing about 2 watts when it’s actually working. You could run this thing 24/7 for a year and spend less on electricity than a single trip to Starbucks. The whole shopping list is stupidly cheap too: the Pi itself runs $15, throw in an 8 dollar micro SD card and whatever USB cable you’ve got rattling around in a drawer. Thirty bucks max, and suddenly you’ve got hardware that can filter ads for every single device in your house.
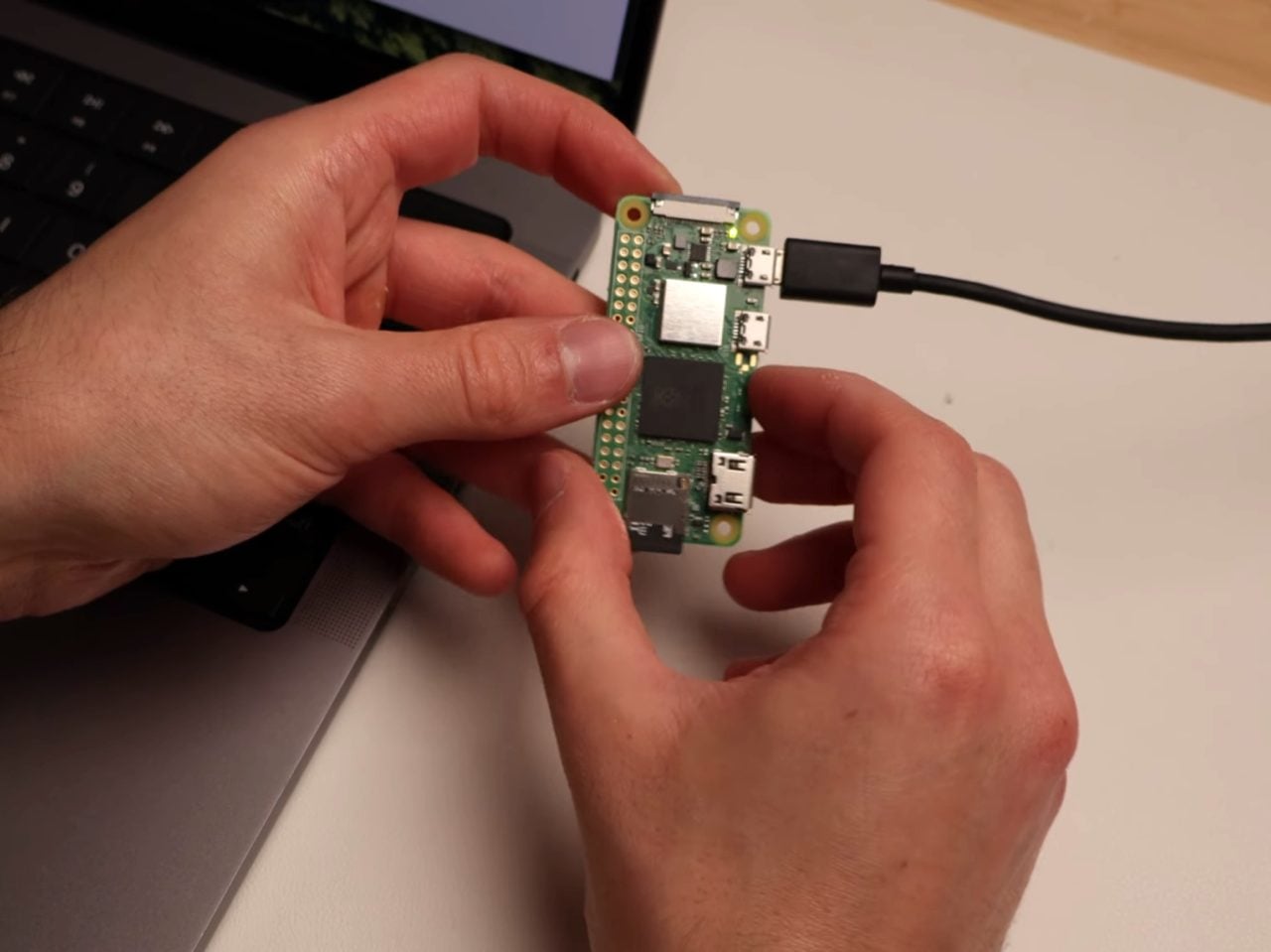
The Pi runs headless, meaning no monitor, no keyboard, just sitting there quietly doing DNS work in the background. You flash Raspberry Pi OS Light onto the SD card using their imaging tool, which strips out all the desktop environment bloat since you’ll never actually see a screen. During setup you punch in your WiFi credentials, enable SSH so you can talk to it remotely, and give it a hostname. Three minutes later the OS is ready and you’re plugging the card into the Pi. Boot it up, SSH in from your laptop, and you’re looking at a command prompt on a computer the size of a pack of gum.
Pi-hole (an open-source software that blocks ads across the entire network) installs with one command. Literally paste it into the terminal and the script handles everything, walking you through prompts about which DNS provider you want upstream and whether you want query logging enabled. You absolutely want the web admin interface because that’s where you’ll watch the magic happen in real time. The trickier bit is the static IP assignment, which sounds intimidating but really just means logging into your router and clicking a button that says “reserve this IP for this device.” Most modern routers make this dead simple. ISPs like Spectrum have apps where you just scroll through connected devices, find your Pi, and hit reserve. Done.
Once the Pi has its permanent address, you point your router’s DNS settings at it instead of whatever your ISP provides by default. Every device on your network now funnels DNS requests through Pi-hole before connecting to anything. Pi-hole maintains these massive blocklists of known advertising and tracking domains, thousands of entries that get updated regularly. Your phone tries to load an ad from doubleclick.net? Blocked. Facebook wants to ping its analytics server? Blocked. The actual content you’re trying to see loads normally while all the parasitic garbage just vanishes. The Pi-hole dashboard shows you this happening in real time, queries flying in and getting either allowed or blocked based on the lists.
The really clever part is Tailscale, which turns your home setup into something you can use anywhere. Tailscale creates this encrypted mesh network between all your devices using WireGuard under the hood, and it’s shockingly easy to configure. Install it on the Pi with another single command, authenticate through their web console by clicking a link, and boom, your Pi appears in the Tailscale admin panel. Then you tell Tailscale to use your Pi’s IP as the DNS server for everything connected to your account. Now your laptop routes through your home Pi-hole whether you’re at a coffee shop in Brooklyn or an airport in Singapore. The VPN overhead adds maybe 10 milliseconds, completely imperceptible during actual browsing.
What you get is immediate and obvious. News sites that normally assault you with autoplaying video ads and popup overlays suddenly render clean. Mobile apps stop shoving interstitials between every interaction. Your smart TV’s interface becomes less cluttered with sponsored content tiles. Pi-hole typically blocks 20 to 30 percent of all DNS queries, which translates directly into faster page loads because your devices skip downloading megabytes of ad scripts and tracking pixels. Battery life improves on phones and laptops since they’re not constantly rendering and refreshing ad content in the background. The internet feels faster because it actually is faster when you’re not waiting for seventeen different ad networks to respond.

Now, the limitations. DNS blocking works great until it doesn’t, and the main place it fails is when ads come from the same domain as the content you want. YouTube is the classic example because Google serves ads from youtube.com subdomains that the platform needs for actual video playback. Block those domains and you break the whole site. Some news organizations have gotten smarter about this too, serving ads from their own CDNs to sidestep DNS filters. You’re looking at maybe 95 percent effectiveness across the broader web, which is substantial but leaves gaps. For the stubborn stuff you still need browser extensions (or use the Brave browser that even blocks YouTube ads) or just simply accept some ads will slip through. If you’ve reached this far, the latter clearly sounds like it isn’t an option.
The other consideration is dependency. If your home internet goes down and you’re traveling somewhere relying on Tailscale to route back through your Pi-hole, you lose DNS resolution entirely. You can mitigate this by configuring a secondary DNS server like Google’s 8.8.8.8 as a fallback, though that partially defeats the privacy angle. Some people solve this by running Pi-hole in the cloud on something like Google Cloud’s free tier, which gives you better uptime but requires more sophisticated networking to avoid creating an open DNS resolver that attackers can hijack for DDoS amplification. That’s a whole different level of complexity that I’m frankly not equipped to even explain.
The upside, even with this regular build, is massive. For thirty bucks and an evening of tinkering, you get network-wide ad blocking that follows you everywhere and works on every device you own without individual configuration. That’s precisely the practical digital self-defense Doctorow addresses about when he describes taking back control from platforms designed to extract value rather than provide it. The web becomes usable again, and I know that shouldn’t sound like a massive deal… but honestly, after seeing ads in Google, Gmail, Instagram, YouTube, Uber, heck, even ChatGPT, it kinda does feel game-changing.
The post DIY $15 Raspberry Pi Device Blocks Every Ad on Your Phone, TV, and Laptop Automatically first appeared on Yanko Design.