
As NASA’s Kepler telescope searched for potentially habitable planets over the years, it also revealed many moons that could host life. Within the Solar System, Jupiter’s moon Europa is the most...
 It doesn't take hugely expensive space telescopes like the Hubble and future James Webb Space Telescope to hunt for habitable exoplanets. NASA and the University of Arizona will launch a small telescope the size of a cereal box called the Star-Planet...
It doesn't take hugely expensive space telescopes like the Hubble and future James Webb Space Telescope to hunt for habitable exoplanets. NASA and the University of Arizona will launch a small telescope the size of a cereal box called the Star-Planet...
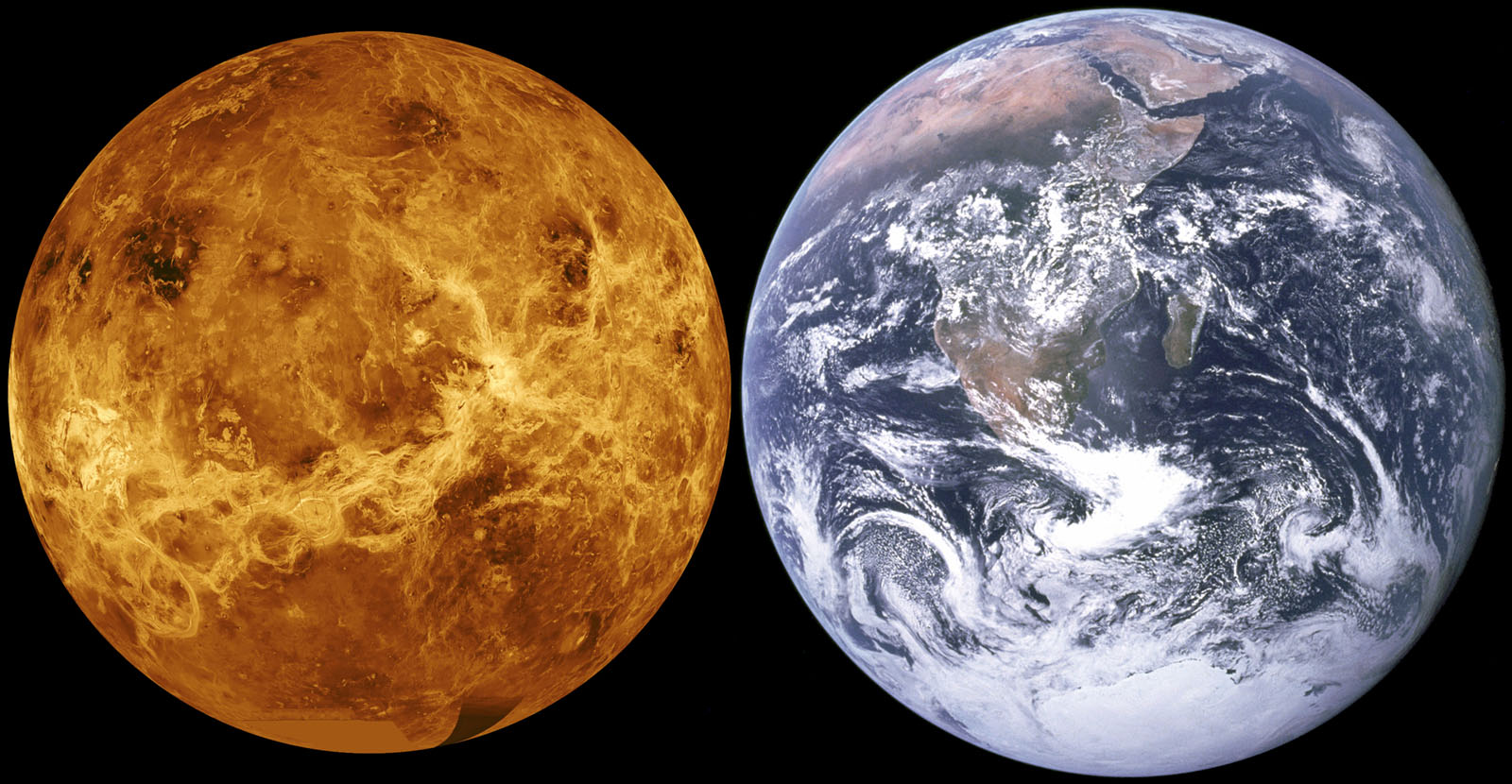 Venus is a hellhole. Despite being much closer to Earth than Mars, its climate is off-the-charts insane: Average temperatures of 864 degrees F, crushing barometric pressure, and did I mention the volcanoes? It's hard to believe that as little as 750...
Venus is a hellhole. Despite being much closer to Earth than Mars, its climate is off-the-charts insane: Average temperatures of 864 degrees F, crushing barometric pressure, and did I mention the volcanoes? It's hard to believe that as little as 750...

With potential oceans flowing below its icy surface, NASA thinks Jupiter's Europa moon is promising candidate to harbor organic life. As such, the space agency and its JPL laboratory are looking to send a lander there within a decade, and have detailed what it wants it to explore in a new paper. Key goals include measuring the organic content of surface and near-surface chemistry, exploring mineralogy, measuring the thickness and salinity of the oceans and ice, imaging surface formations and looking at microscopic ice and non-ice grains. Researchers also looked at potential landing sites, and were torn between a more interesting, active site like "Thera Macula" and a more stable location with ancient geology. NASA's Juno mission, launched in August 2011, is expected to help settle such issues when it probes Europa from orbit starting in 2016. Though it'd be hard to top Curiosity's setdown, a Europa landing could be even more dramatic, considering the moon is over 10 times farther away than Mars and never gets above minus 370 degrees Fahrenheit.
Via: The Register
Source: NASA (paper)
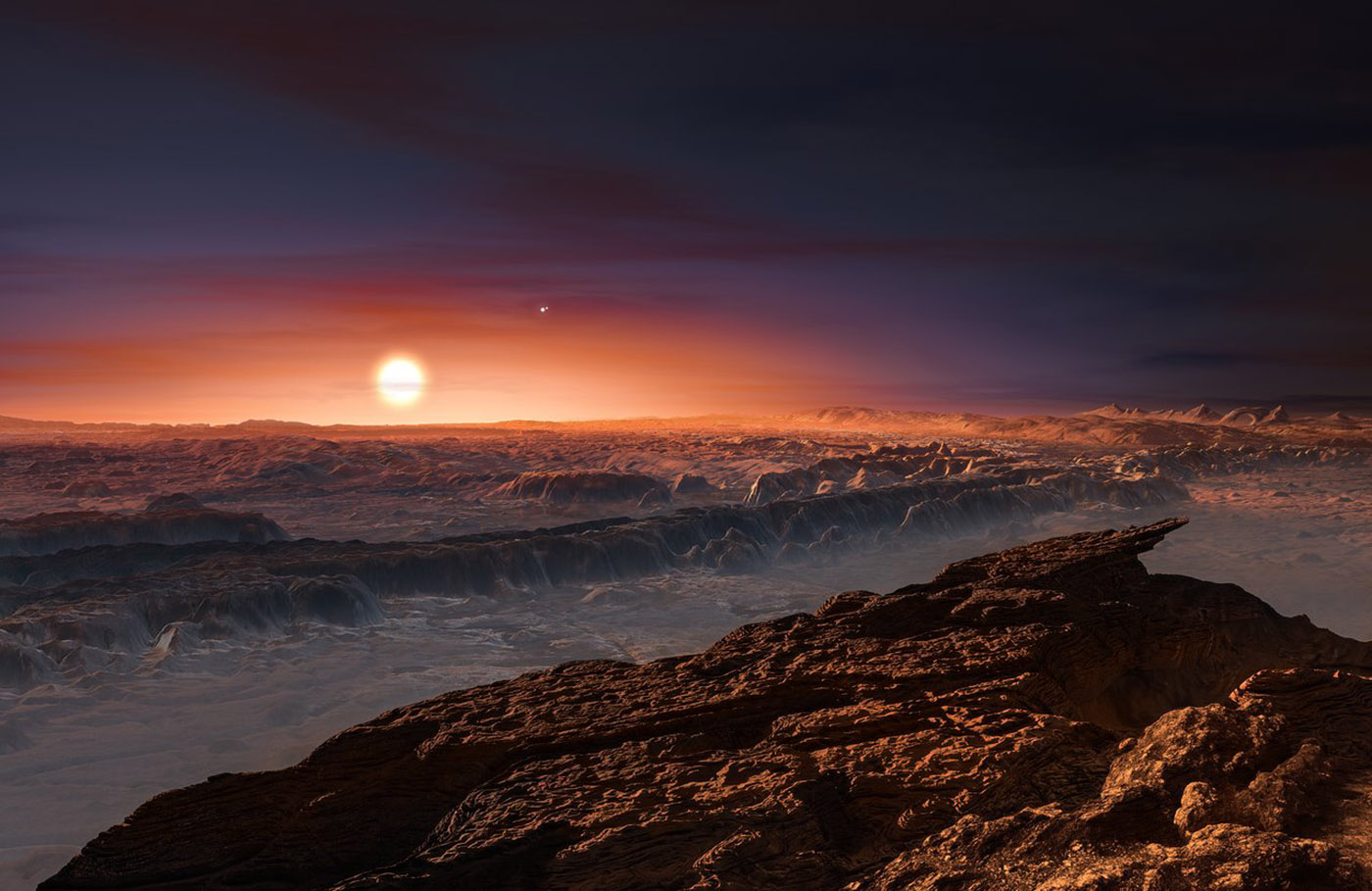
Astronomers have a good day when they detect one planet inside a star system's habitable zone. A mostly European team of researchers must be giddy, then, as it just found three of those ideally located planets around Gliese 667C. The group has combined existing observations from the ESO's Very Large Telescope with new HARPS telescope data to spot the trio of super-Earths, all of which could theoretically support liquid water. As long as the discovery holds up, it may have a big impact on exoplanetary research: it shows both that three super-Earths can exist in one system and that more than one survivable planet can orbit a low-mass star. We can only do so much with the findings when Gliese 667C is 22 light-years away, but it's good to learn that space could be more human-friendly than we once thought.
Source: ESO