
Historically, whenever man or beast's been bombarded with massive amounts of radiation the results have either been gruesome or wholly fantastical (see: any superhero origin story). But recent research out of Japan indicates that a barrage of electrons could actually help scientists revolutionize microbiology and, more excitingly, space travel. The experiment, conducted by a team from the Hamamatsu University of Medicine, found that the larvae of fruit flies hit with this electron rush were able to withstand an electron microscope's hostile vacuum unharmed and even grew to be healthy adults. The results weren't so rosy for the untreated group which, understandably, suffered a grislier fate: death by dehydration. The magic, it turns out, is in that subatomic spray, as the group treated with an electron shower benefited from a polymerizing effect or, more plainly, a bonding of molecules just above the skin's surface that yielded a tough, protective nano-layer measuring between 50- to 100-billionths of a meter thick. Finesse that technique some and it's easy to why one NASA scientist thinks this could lead to the creation of a super-thin "space shield... that could protect against dehydration and radiation."
The process is still far from foolproof, however, seeing as how an increase in the microscope's resolution requires an equal boost in radiation -- all of which is fatal to the insects. So, in order to go deeper and get a more close-up view of the larvae's internals, the team's currently exploring new methods of fabricating these "nano-suits" using an array of chemicals. If you're wondering just how far-off we are from practical human application, then consider this: the amount of radiation required to form the bonded layer is akin to "sunbathing naked on the top of Everest under a hole in the ozone." Which is to say, keep dreaming. And get Jeff Goldblum on the phone while you're at it... we have a promising idea for a Return of the Fly sequel.
Filed under: Science, Alt
Comments
Via: Wired
Source: ScienceNOW
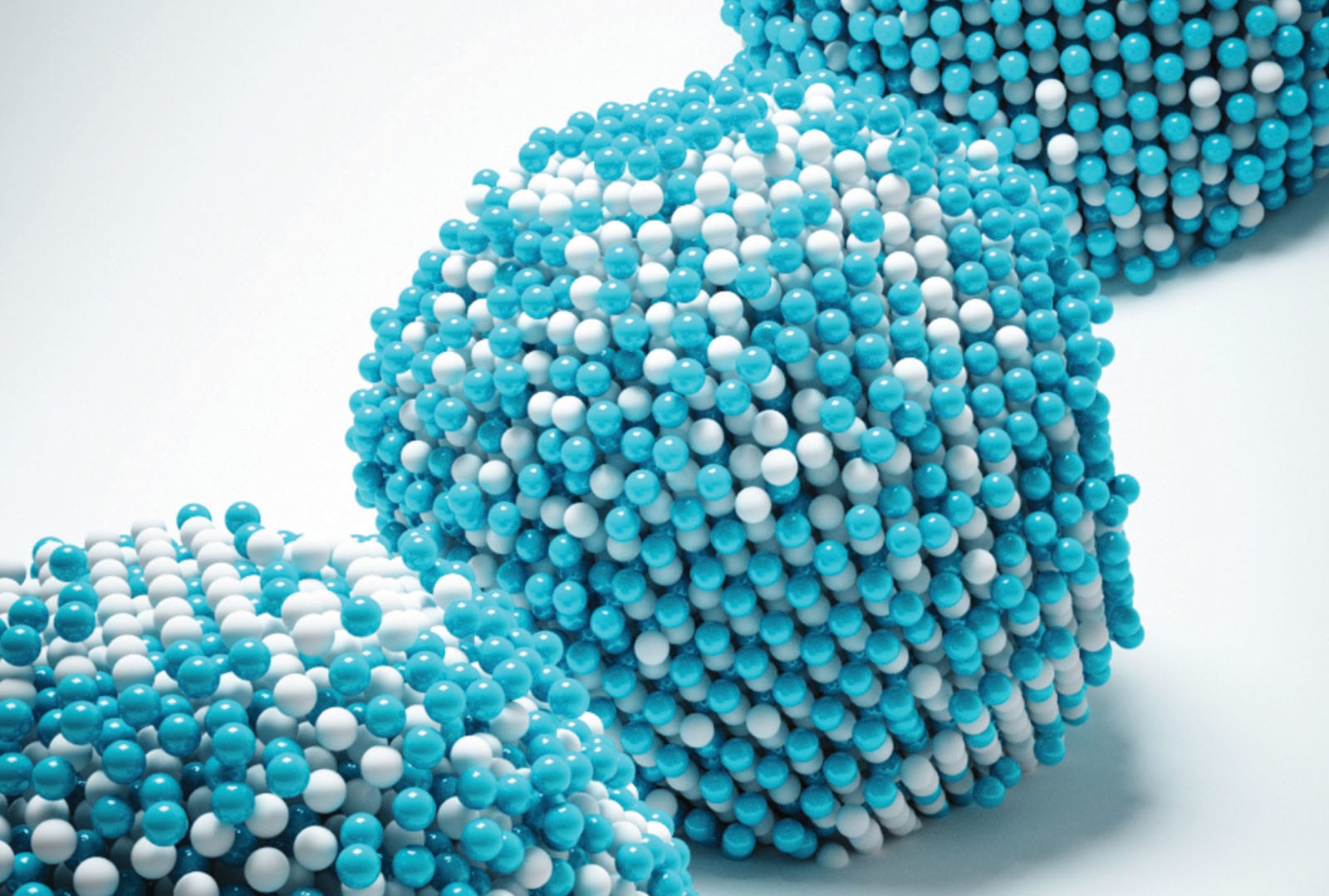 Long-held theories about how materials melt, freeze and evaporate may need to be tweaked thanks to some breakthrough research. A UCLA-led team of scientists have captured the 4D movement of atoms through time and 3D space as they changed states, repo...
Long-held theories about how materials melt, freeze and evaporate may need to be tweaked thanks to some breakthrough research. A UCLA-led team of scientists have captured the 4D movement of atoms through time and 3D space as they changed states, repo...
 Long-held theories about how materials melt, freeze and evaporate may need to be tweaked thanks to some breakthrough research. A UCLA-led team of scientists have captured the 4D movement of atoms through time and 3D space as they changed states, repo...
Long-held theories about how materials melt, freeze and evaporate may need to be tweaked thanks to some breakthrough research. A UCLA-led team of scientists have captured the 4D movement of atoms through time and 3D space as they changed states, repo...
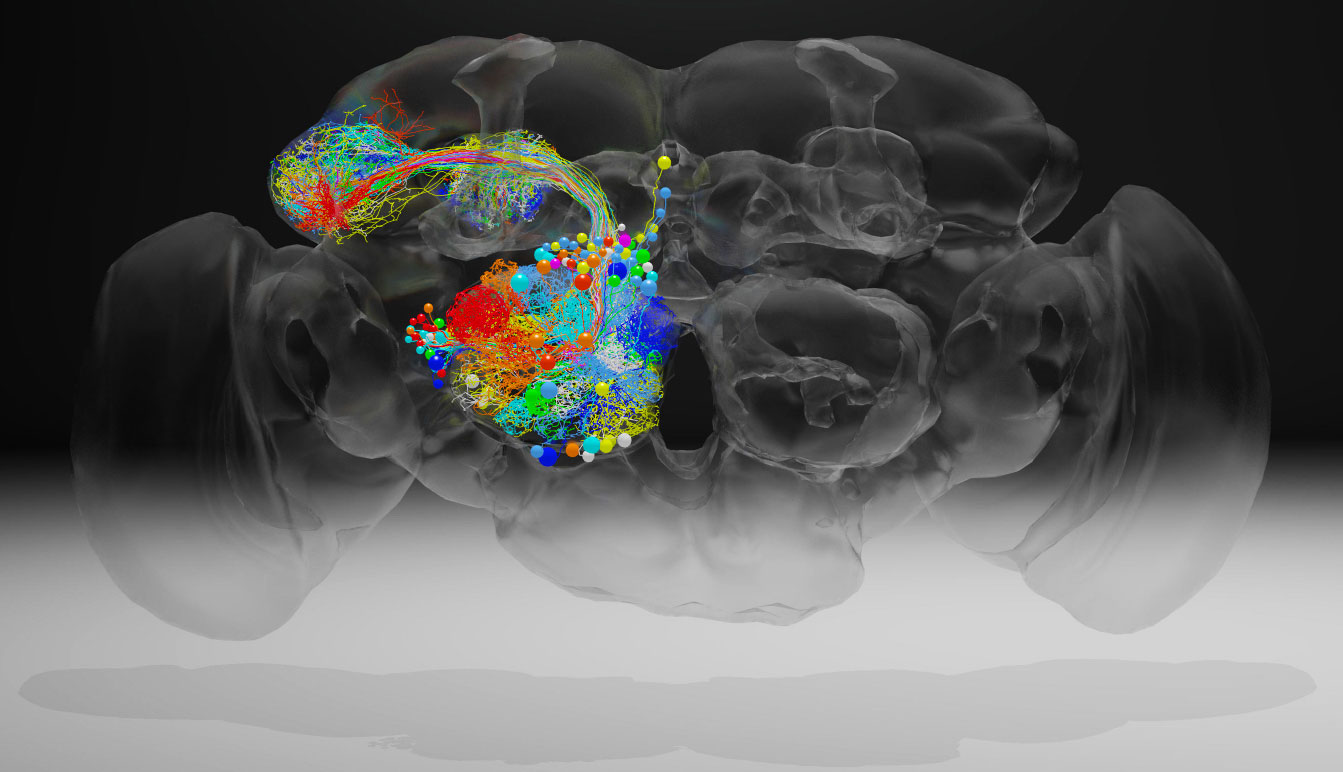 Scientists have created a high-resolution image of a fruit fly brain that will let researchers trace the connections of neurons throughout the brain. A team at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute's Janelia Research Campus led the work, which was rece...
Scientists have created a high-resolution image of a fruit fly brain that will let researchers trace the connections of neurons throughout the brain. A team at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute's Janelia Research Campus led the work, which was rece...
 Confocal microscopes are pretty wild. The instruments can capture cell division in realtime, but the downside is the lasers in existing ones tend to fry the cells they're studying. Researchers from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology m...
Confocal microscopes are pretty wild. The instruments can capture cell division in realtime, but the downside is the lasers in existing ones tend to fry the cells they're studying. Researchers from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology m...
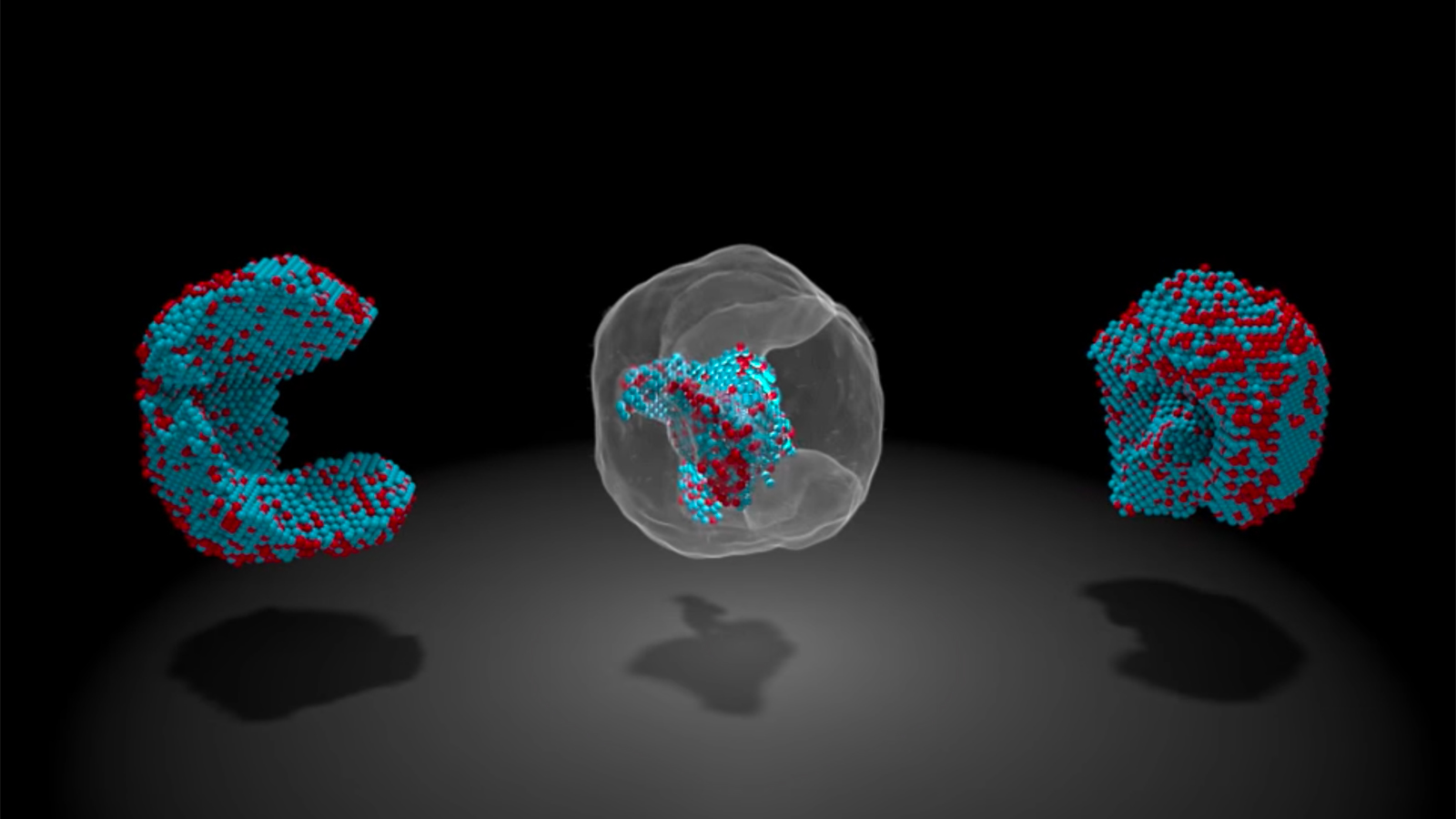 Even the smallest defects can create serious problems. It's a good thing, then, that researchers have found a way to map nanoparticles at an "unprecedented" level of detail -- they've located the 3D positions of all 23,000 atoms in an iron-platinum...
Even the smallest defects can create serious problems. It's a good thing, then, that researchers have found a way to map nanoparticles at an "unprecedented" level of detail -- they've located the 3D positions of all 23,000 atoms in an iron-platinum...
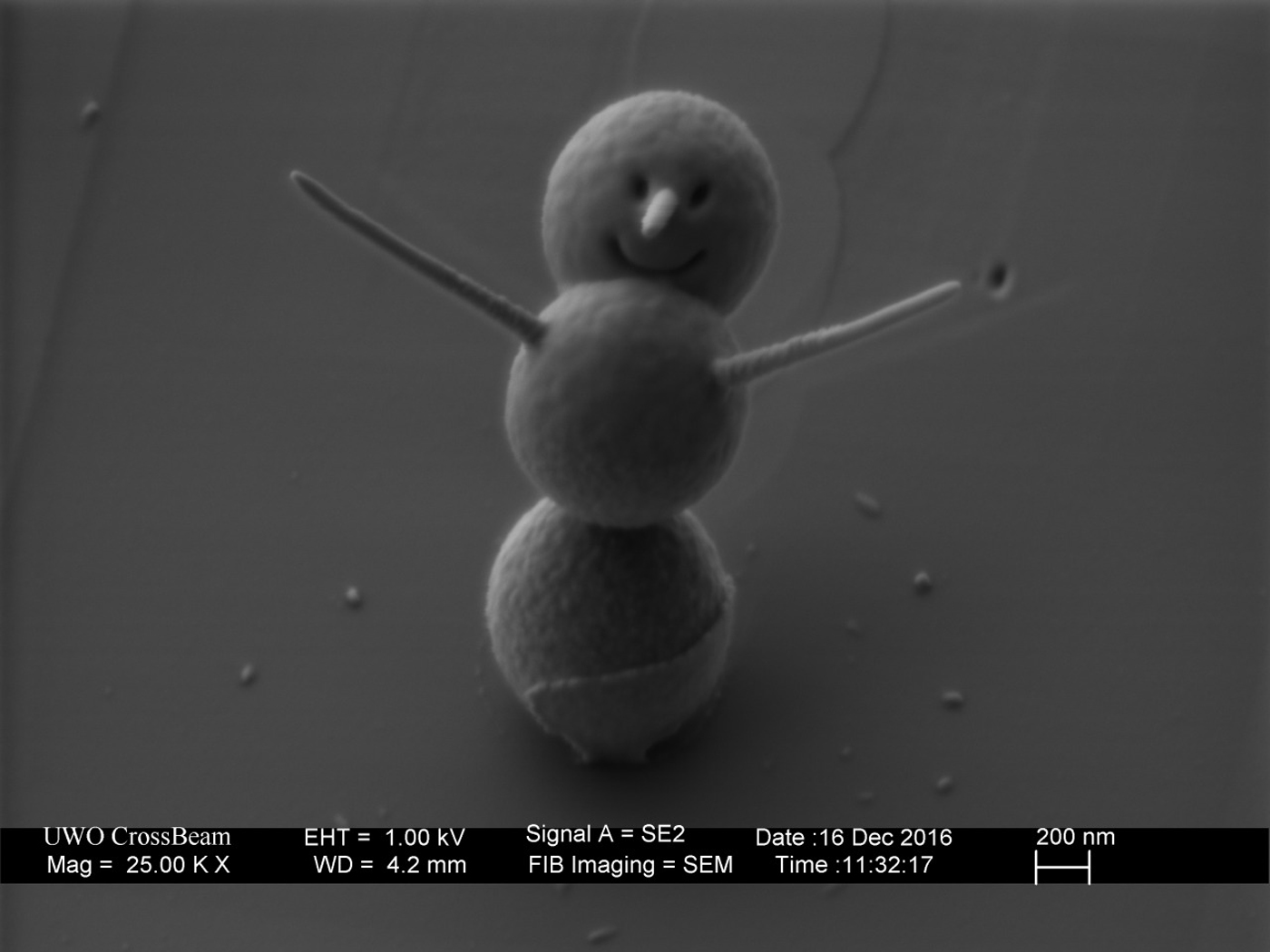 The holiday season gets bigger and more hectic every year -- and maybe you're looking for a smaller, more adorable way to celebrate. Here's one: the world's smallest snowman. This microscopic frosty was built by the nanofabrication lab at London's We...
The holiday season gets bigger and more hectic every year -- and maybe you're looking for a smaller, more adorable way to celebrate. Here's one: the world's smallest snowman. This microscopic frosty was built by the nanofabrication lab at London's We...
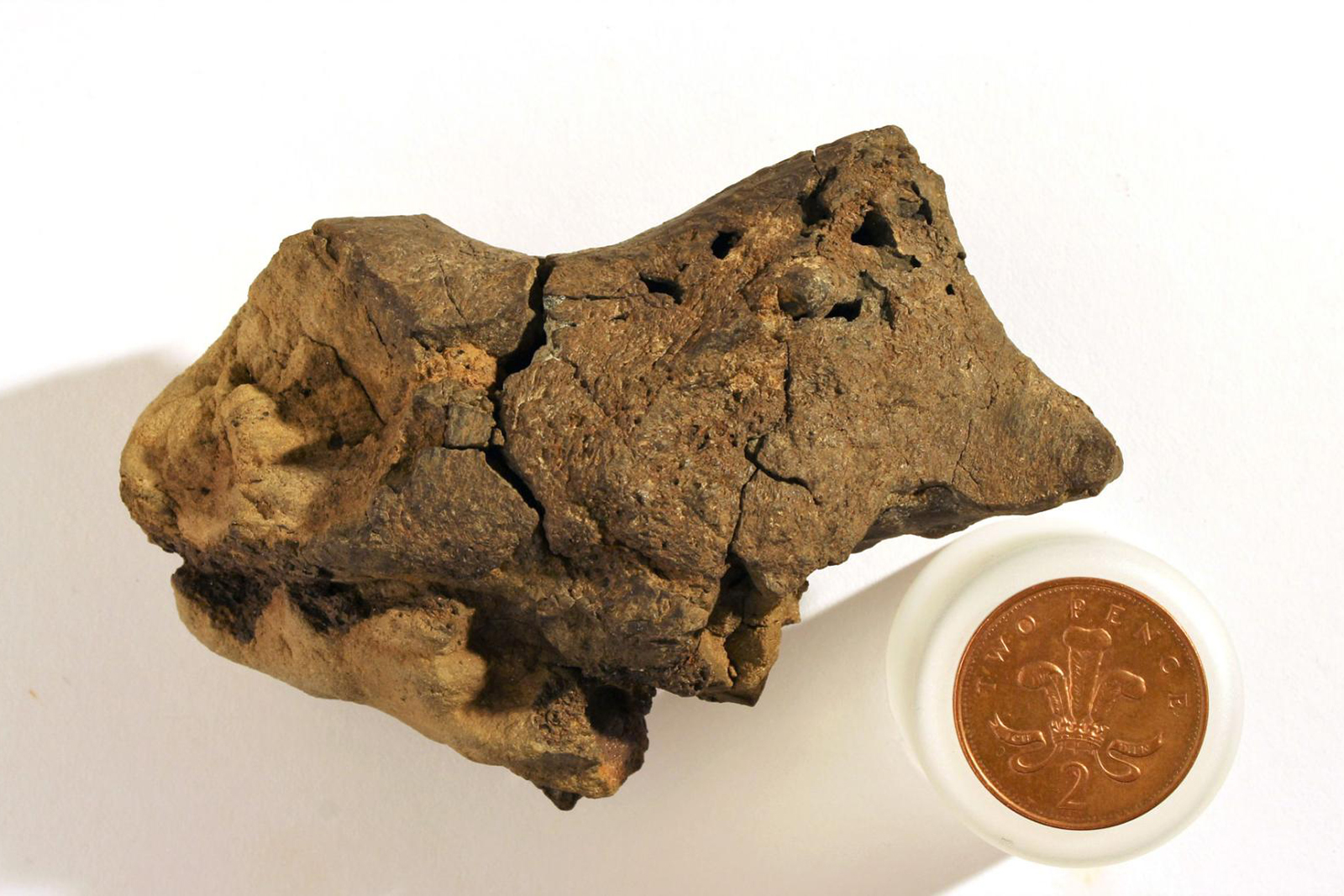 That lump you see above many not look like much at first blush, but it's a big deal for paleontology: scientists say they have discovered that the sample has the first known example of a dinosaur brain tissue fossil. The team used a scanning electron...
That lump you see above many not look like much at first blush, but it's a big deal for paleontology: scientists say they have discovered that the sample has the first known example of a dinosaur brain tissue fossil. The team used a scanning electron...
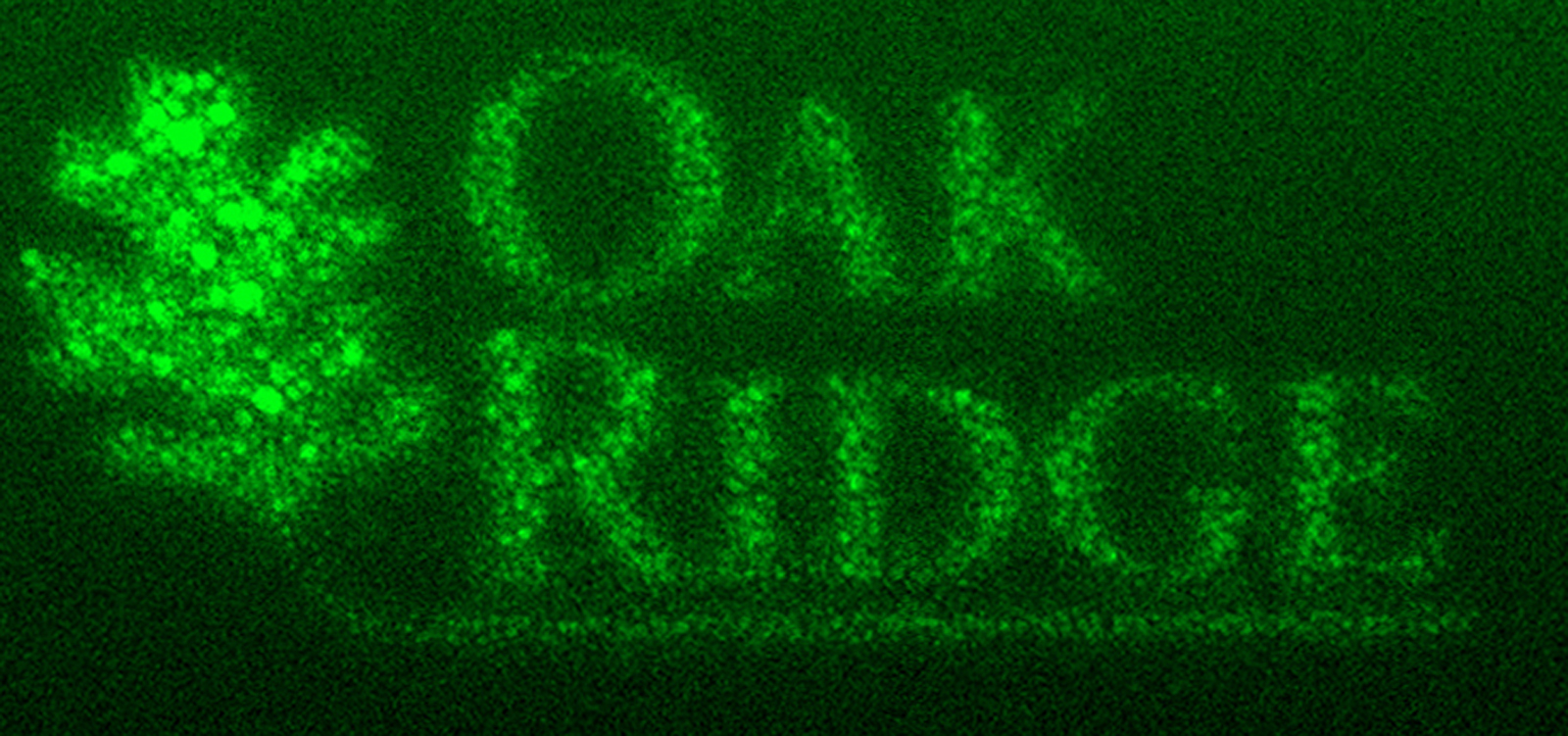 One of the greatest challenges in designing electronics is drawing very fine details. You normally need lithography, which complicates the process by requiring masks. However, Oak Ridge National Laboratory has now found a way to write at an extreme...
One of the greatest challenges in designing electronics is drawing very fine details. You normally need lithography, which complicates the process by requiring masks. However, Oak Ridge National Laboratory has now found a way to write at an extreme...



