
Imaging has been defined by glass lenses for centuries, and even fiber optics haven't entirely escaped the material's clutch. Harvard's School of Engineering and Applied Sciences might have just found a way to buck those old (and not-so-old) traditions. A new 60-nanometer thick silicon lens, layered with legions of gold nanoantennas, can catch and refocus light without the distortion or other artifacts that come with having to use the thick, curved pieces of glass we're used to -- it's so accurate that it nearly challenges the laws of diffraction. The lens isn't trapped to bending one slice of the light spectrum, either. It can range from near-infrared to terahertz ranges, suiting it both to photography and to shuttling data. We don't know what obstacles might be in the way to production, which leads us to think that we won't be finding a gold-and-silicon lens attached to a camera or inside a network connection anytime soon. If the technology holds up under scrutiny, though, it could ultimtately spare us from the big, complicated optics we often need to get just the right shot.
Filed under: Cameras, Science
Harvard makes distortion-free lens from gold and silicon, aims for the perfect image (or signal) originally appeared on Engadget on Sat, 25 Aug 2012 00:00:00 EDT. Please see our terms for use of feeds.
Permalink  Phys.org
Phys.org |
 Harvard University
Harvard University |
Email this |
Comments
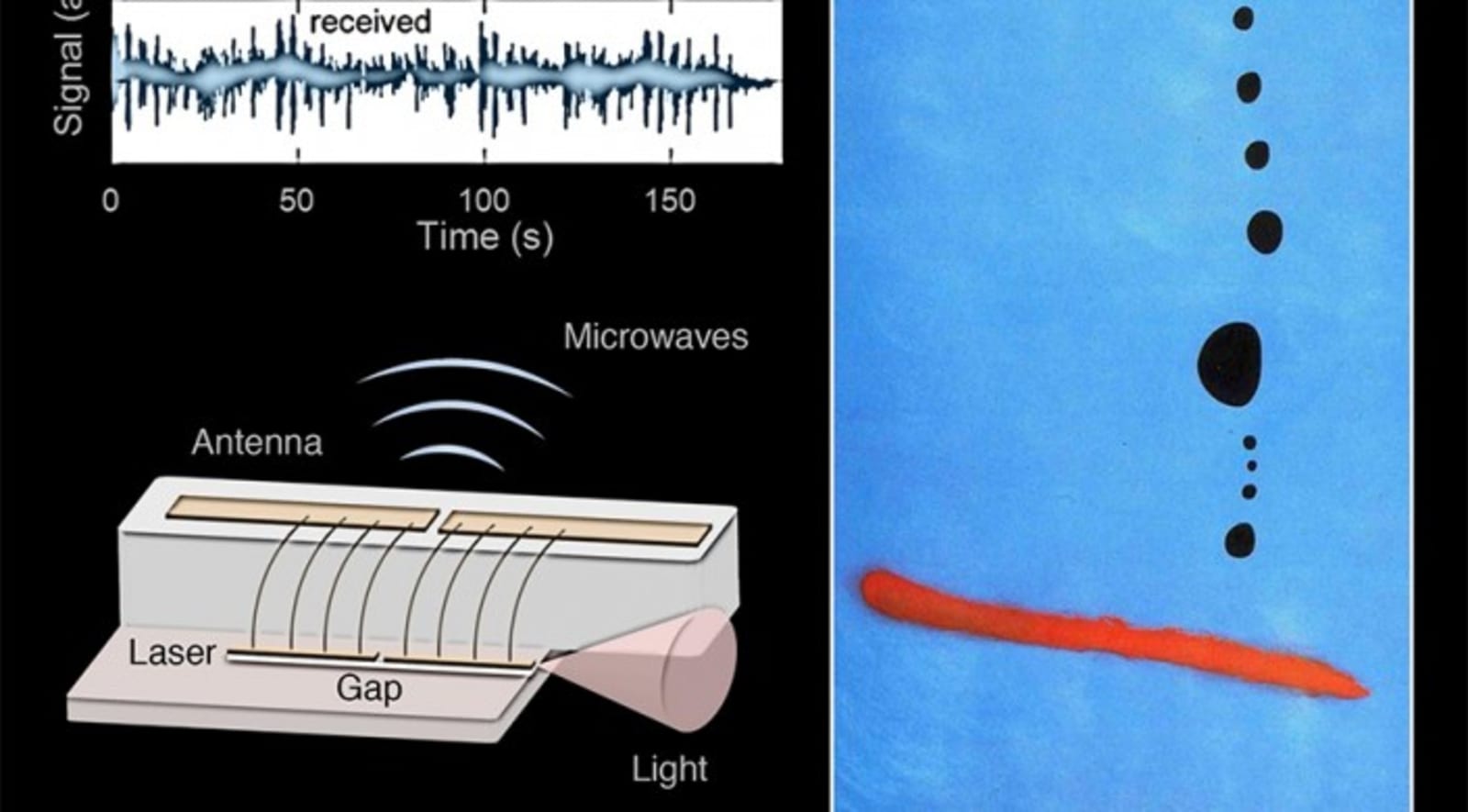 Researchers at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences have developed a method to wirelessly transmit radio frequency via a semiconductor laser. The breakthrough, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, is a marke...
Researchers at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences have developed a method to wirelessly transmit radio frequency via a semiconductor laser. The breakthrough, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, is a marke...
 Researchers at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences have developed a method to wirelessly transmit radio frequency via a semiconductor laser. The breakthrough, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, is a marke...
Researchers at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences have developed a method to wirelessly transmit radio frequency via a semiconductor laser. The breakthrough, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, is a marke...



