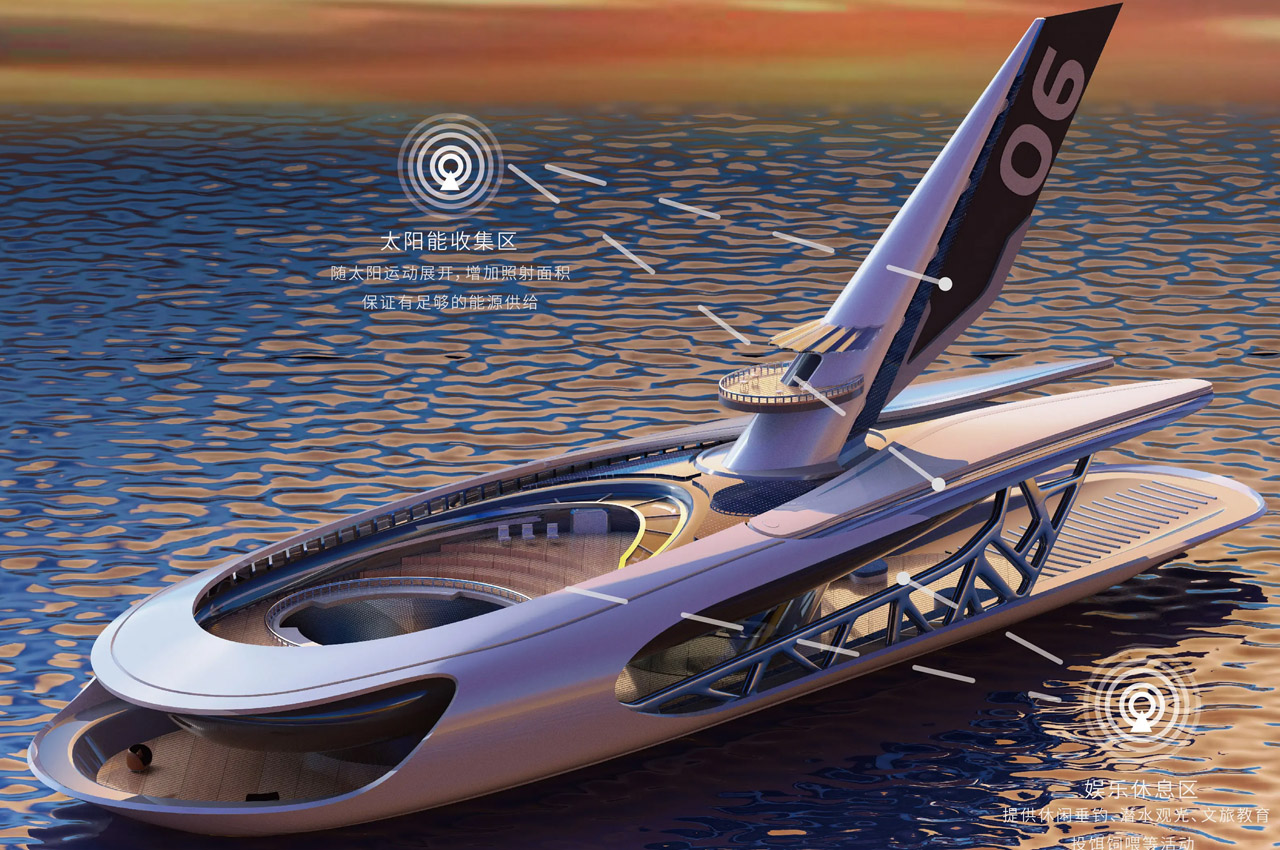
The walk from the Las Vegas Convention Center to Tacos El Gordo may only be seven-tenths of a mile but under the blazing sun of a Nevada winter, the trip can seem an eternity. Lucky for us Al Pastor enthusiasts, this traditional CES taco trek is now far more convenient as the Boring Company and Resorts World Las Vegas announced the official opening of the latest Loop station at Las Vegas Convention Center.
This spur off of the Boring Company's existing Loop network (which runs underneath the North and South halls of the LVCC) connects the convention center directly to a sister station underneath the World Resorts property on the other side of South Las Vegas Blvd. Boring expects the trip between the two to take just a few minutes — assuming nothing goes wrong — and plans to eventually expand the underground vehicle network to more than 55 stops along the Strip.
“Today marks a monumental moment not only for our resort, but for Las Vegas,” Scott Sibella, president of Resorts World Las Vegas, said in a Thursday press relea. “Our passenger station will make a visit to our resort from the Las Vegas Convention Center easier than ever, and eventually connect us to key destinations throughout the city.”
The Boring Company began work on the initial $47 million tunnels running under the LVCC back in 2019, completed excavation the following May, and opened for service — because of course it did — on April 20th, 2022. In October, 2021 Las Vegas approved the Boring Company's plans to expand its Loop network to encompass more than 29 miles of tunnel. That figure grew to 34 miles in June, 2022 to include stations at Harry Reid International Airport and Allegiant Stadium following approval from the Clark County Commissioners. However, despite Boring CEO Elon Musk's claims of superior passenger capacity — up to 4,400 people every hour! — the system so far has only managed to move around 575 people in that time.