PROS:
- Distinctive material finishes feel intentional, tactile, and far removed from generic glass phones.
- Curved AMOLED display integrates seamlessly into the frame with excellent visual balance.
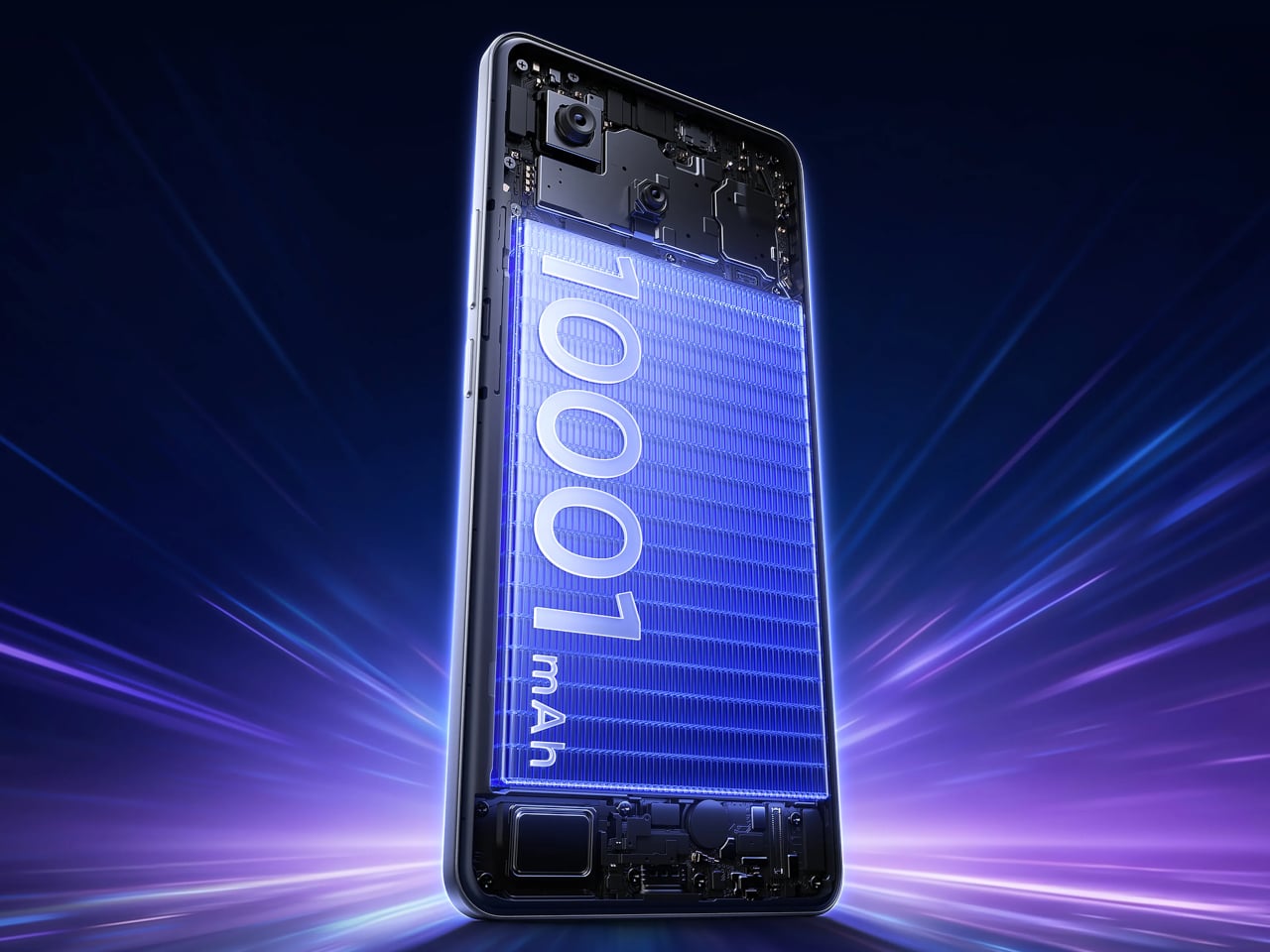
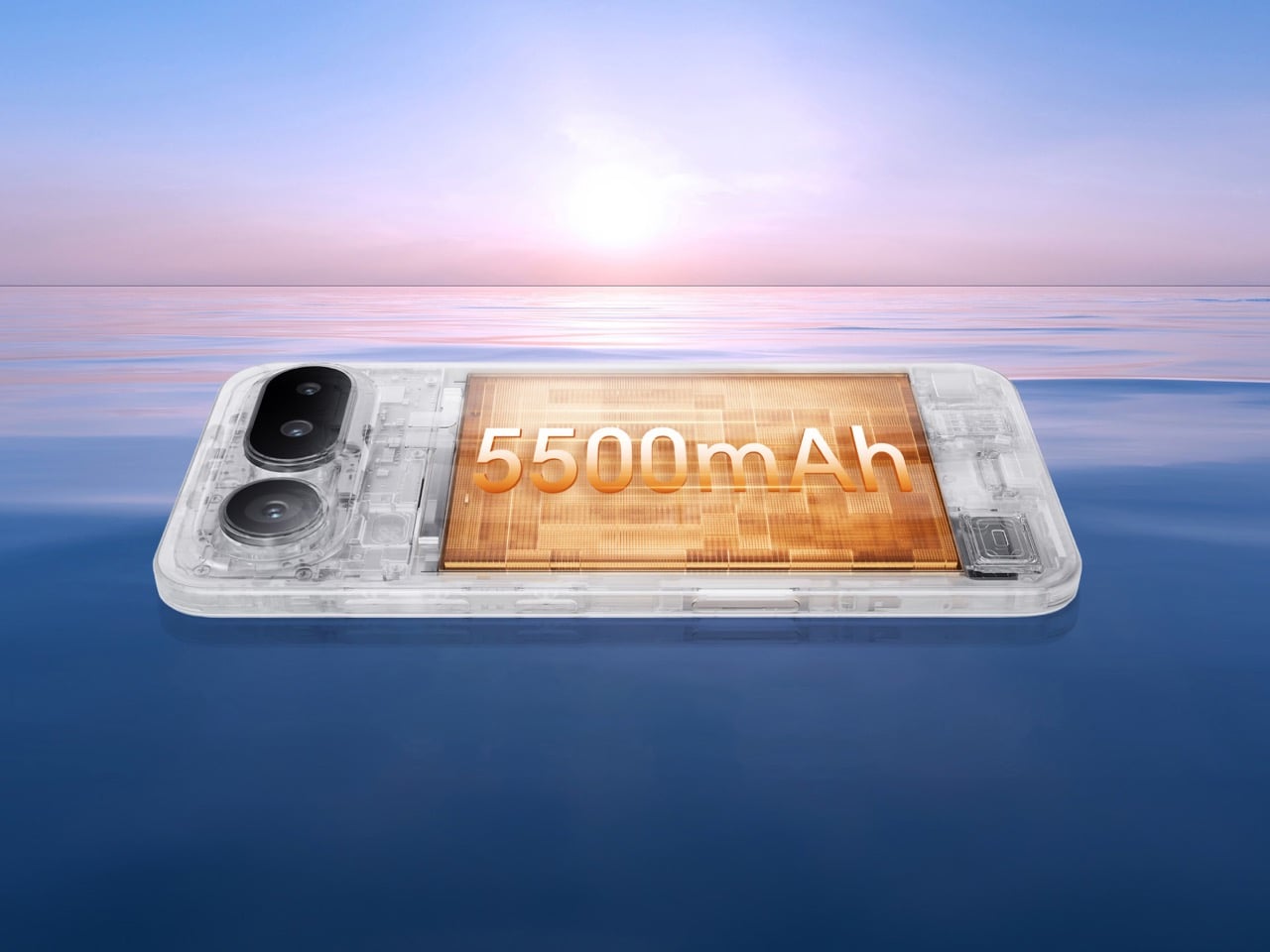
- Slim profile paired with large battery delivers comfort without sacrificing endurance.
- Weight distribution feels centered, stable, and comfortable during long daily use.
- Design language prioritizes subtle luxury over flashy, trend-driven aesthetics.
CONS:
- Performance prioritizes consistency over raw power for demanding mobile gaming.
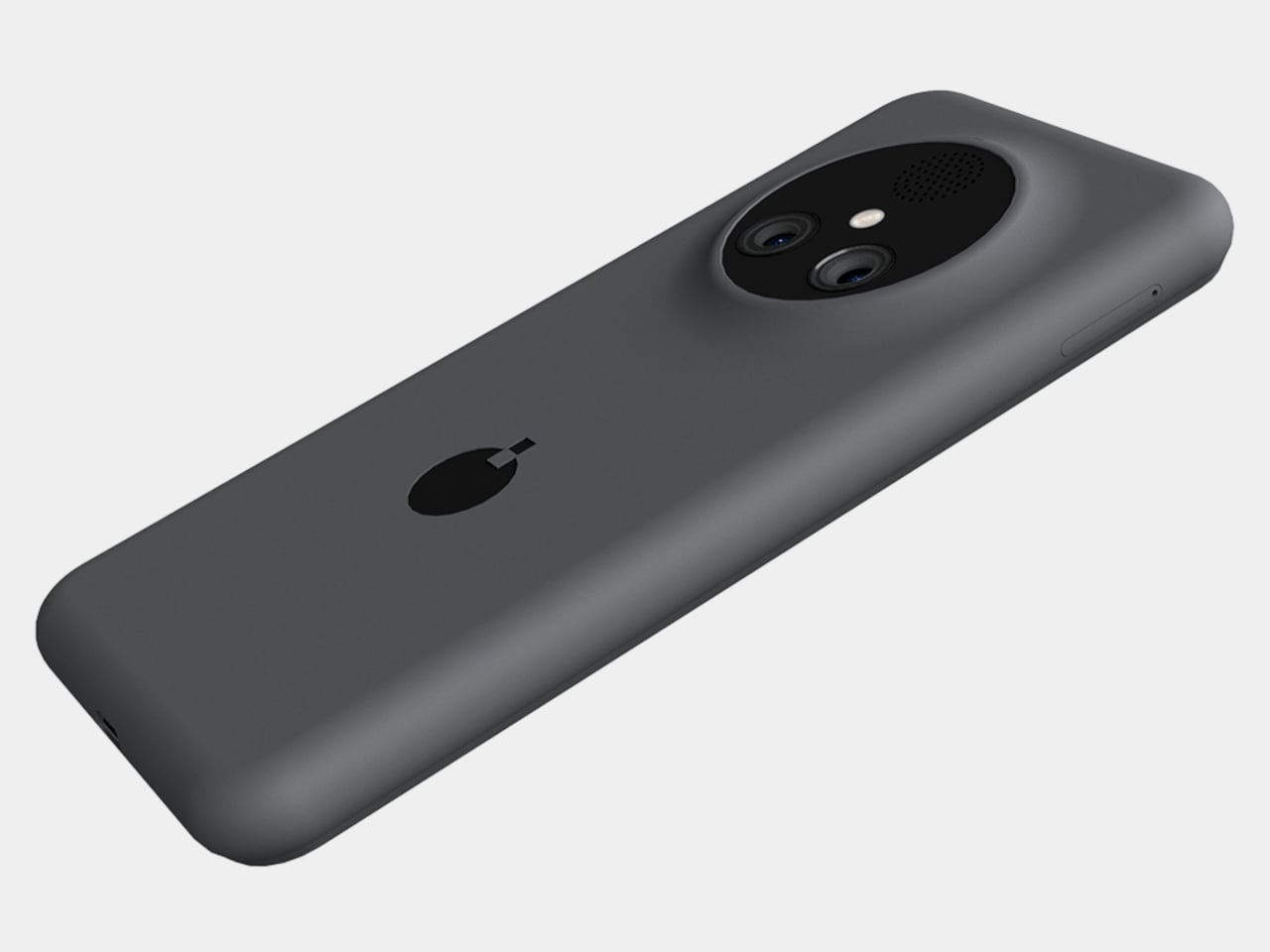
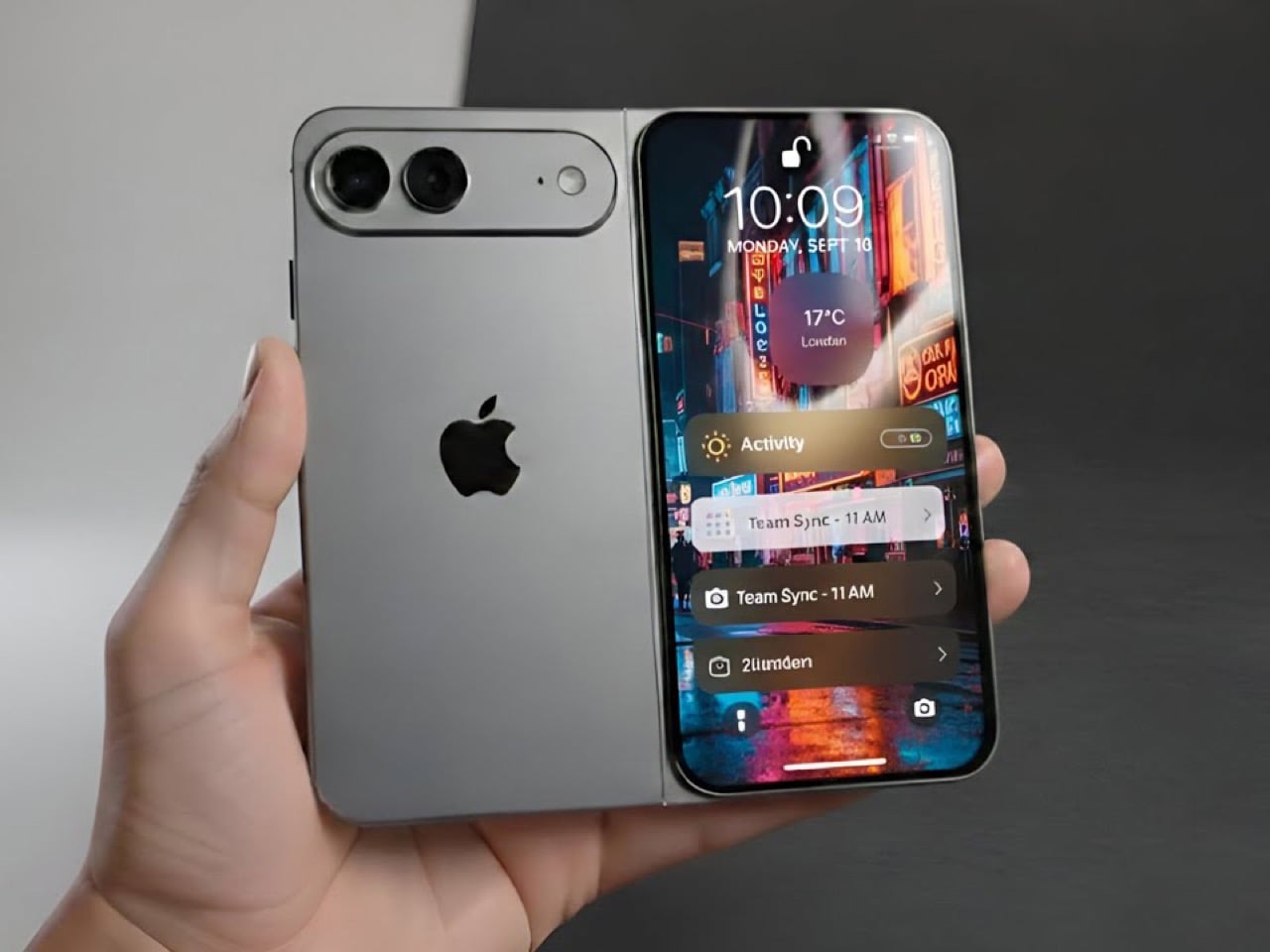
The Infinix NOTE Edge doesn’t announce itself through volume. It doesn’t rely on aggressive angles or oversaturated finishes to command attention. Instead, it arrives with a quieter confidence, the kind that reveals itself slowly as light shifts across its surface and the hand adjusts to its form.
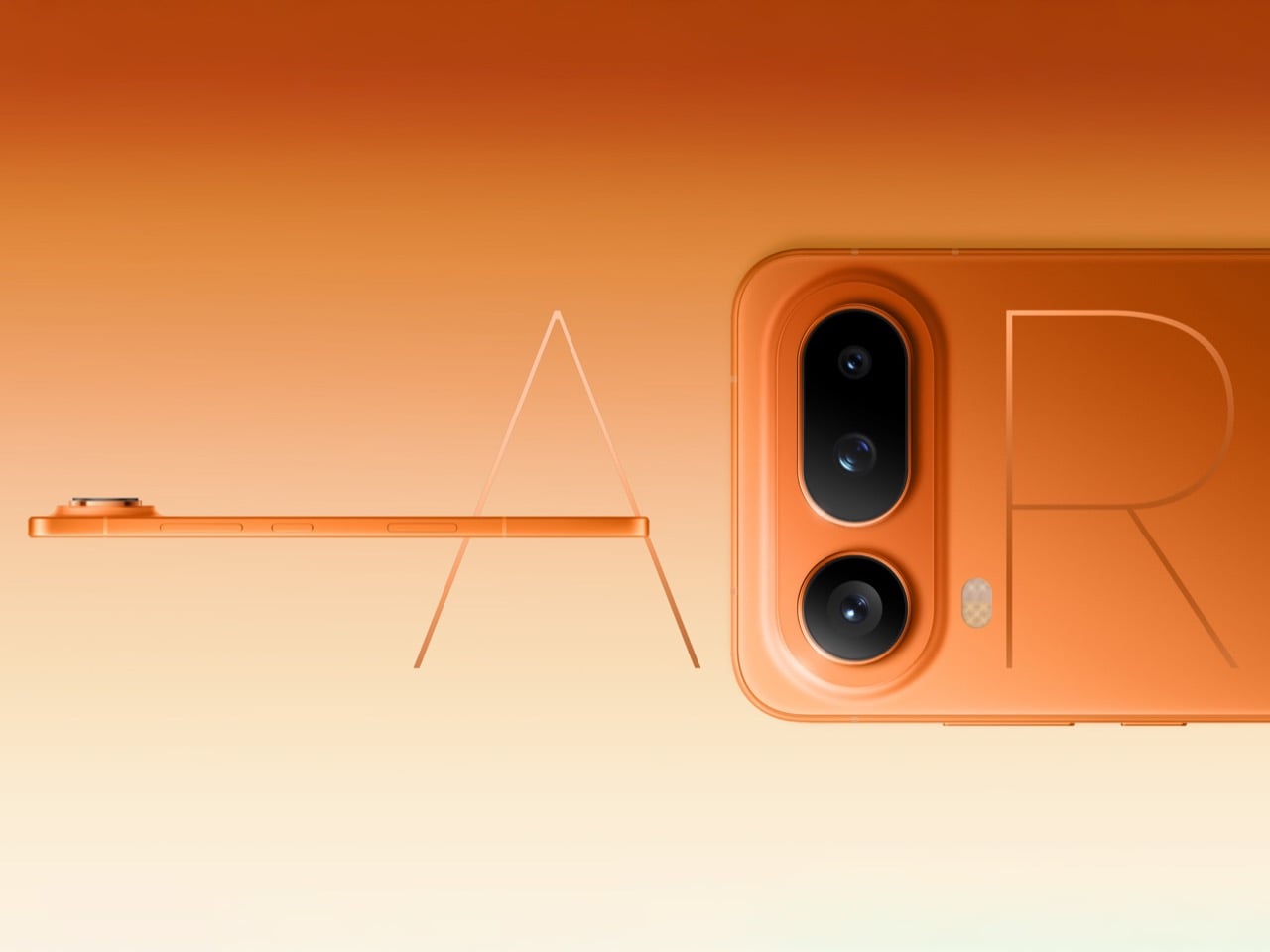
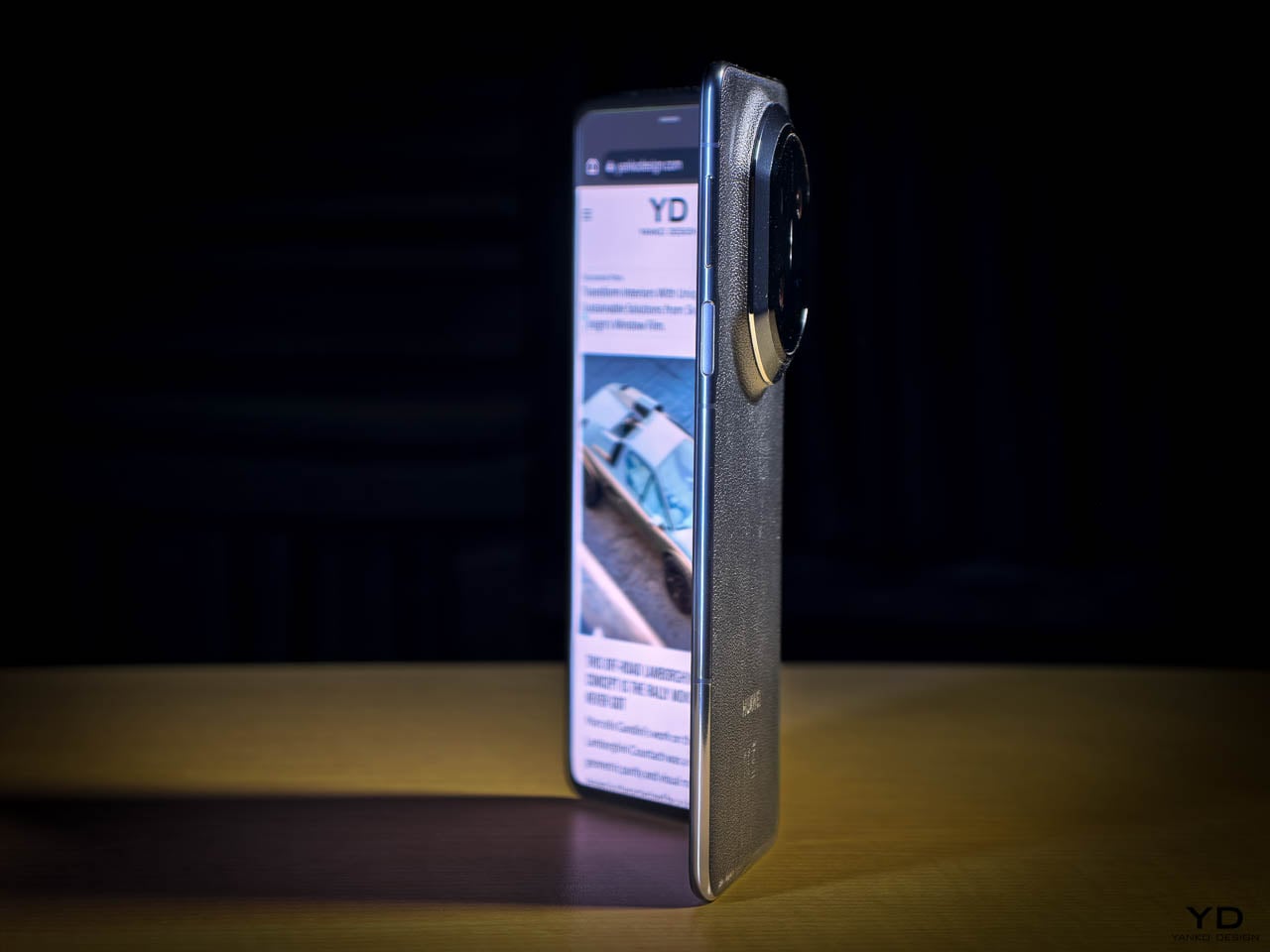
I’ve spent time with devices that prioritize specification lists over tactile experience, and the NOTE Edge represents a deliberate departure from that approach. Infinix has made choices here that suggest an understanding of what makes an object feel considered rather than merely assembled. The 7.2mm profile isn’t thin for the sake of a number on a spec sheet. It’s thin because that dimension allows the curved display to flow into the frame without creating awkward transitions or compromising grip. The fact that a 6,500mAh battery fits inside without adding bulk says something about the internal engineering priorities.

What interests me most about this device isn’t any single feature. It’s how Infinix has leaned into a specific material language, treating the phone less like a piece of consumer electronics and more like a fashion object, with finishes that reference gemstones, textiles, and luxury accessories rather than the gradient glass that dominates this category. The NOTE Edge wants to be noticed, but it doesn’t want to shout. That tension between presence and subtlety defines the entire experience.
Design and Ergonomics
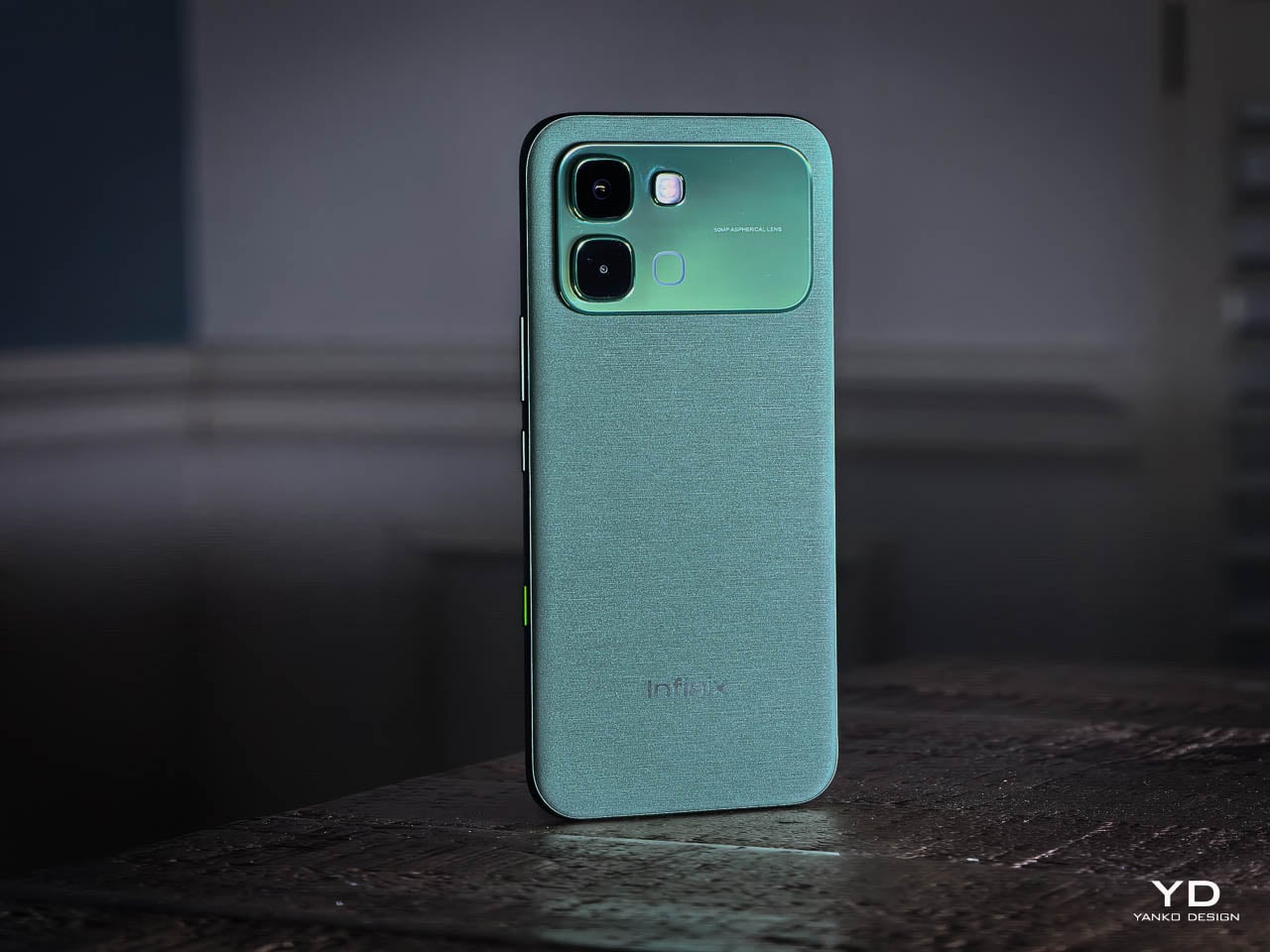
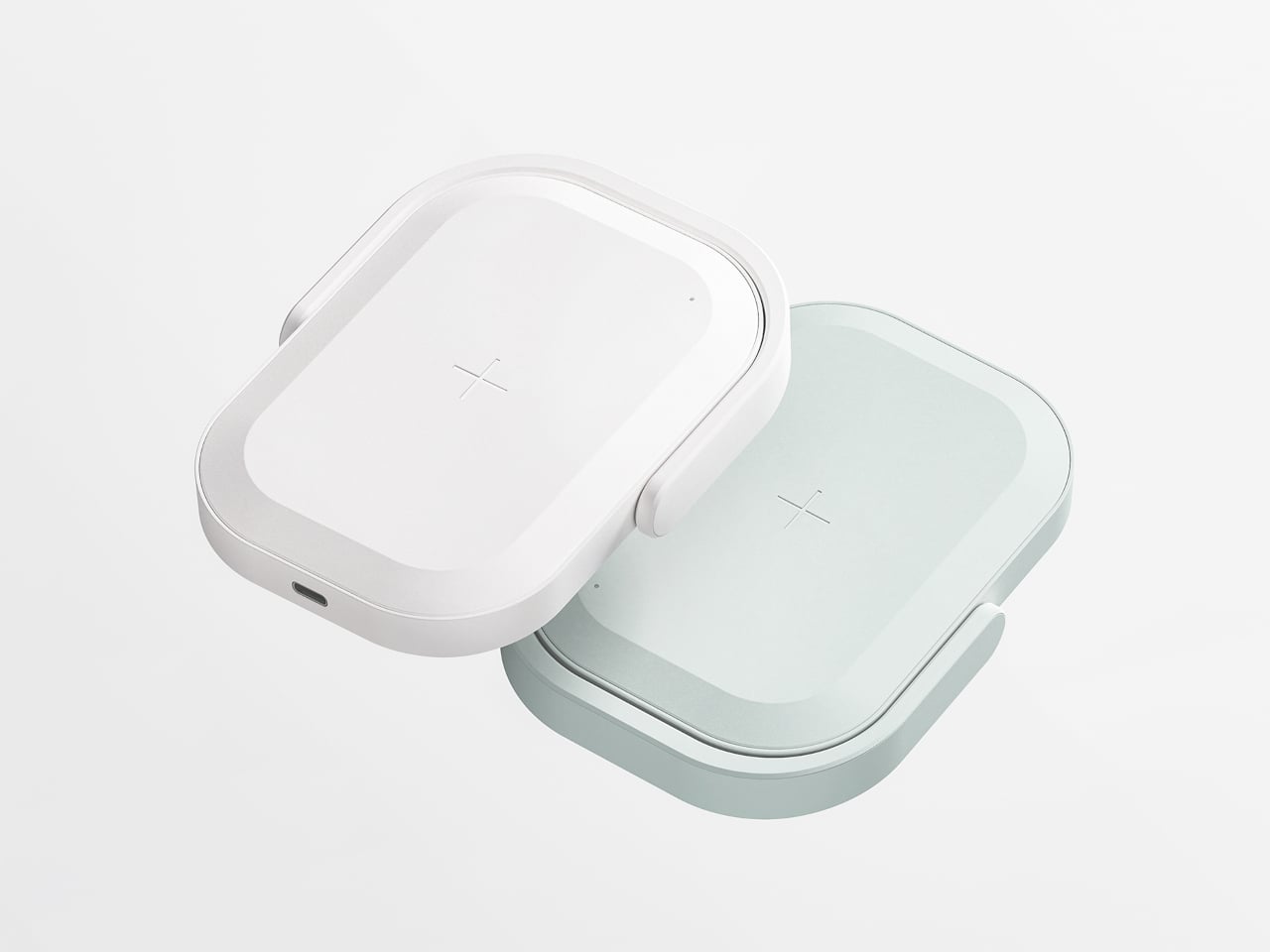
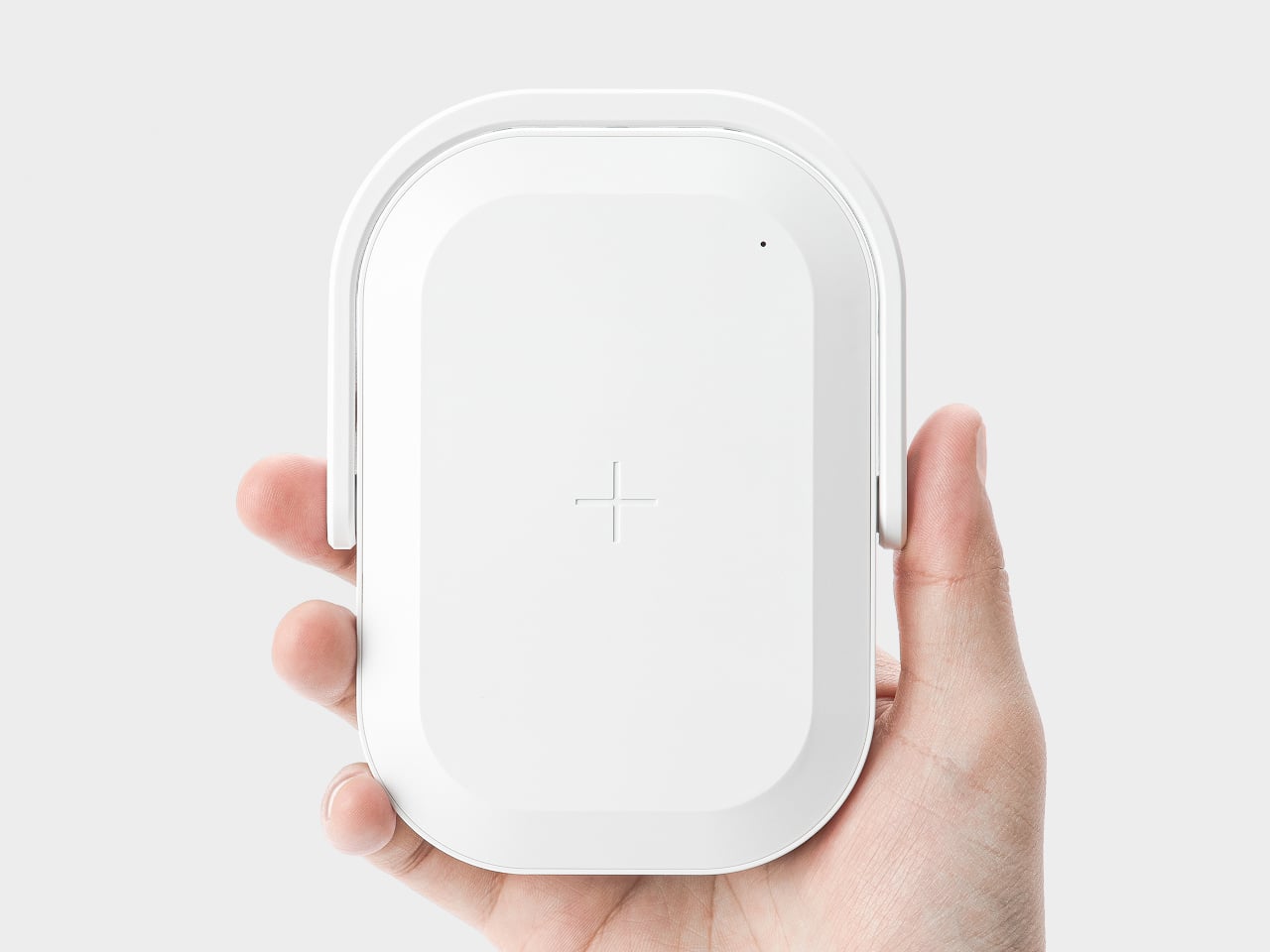
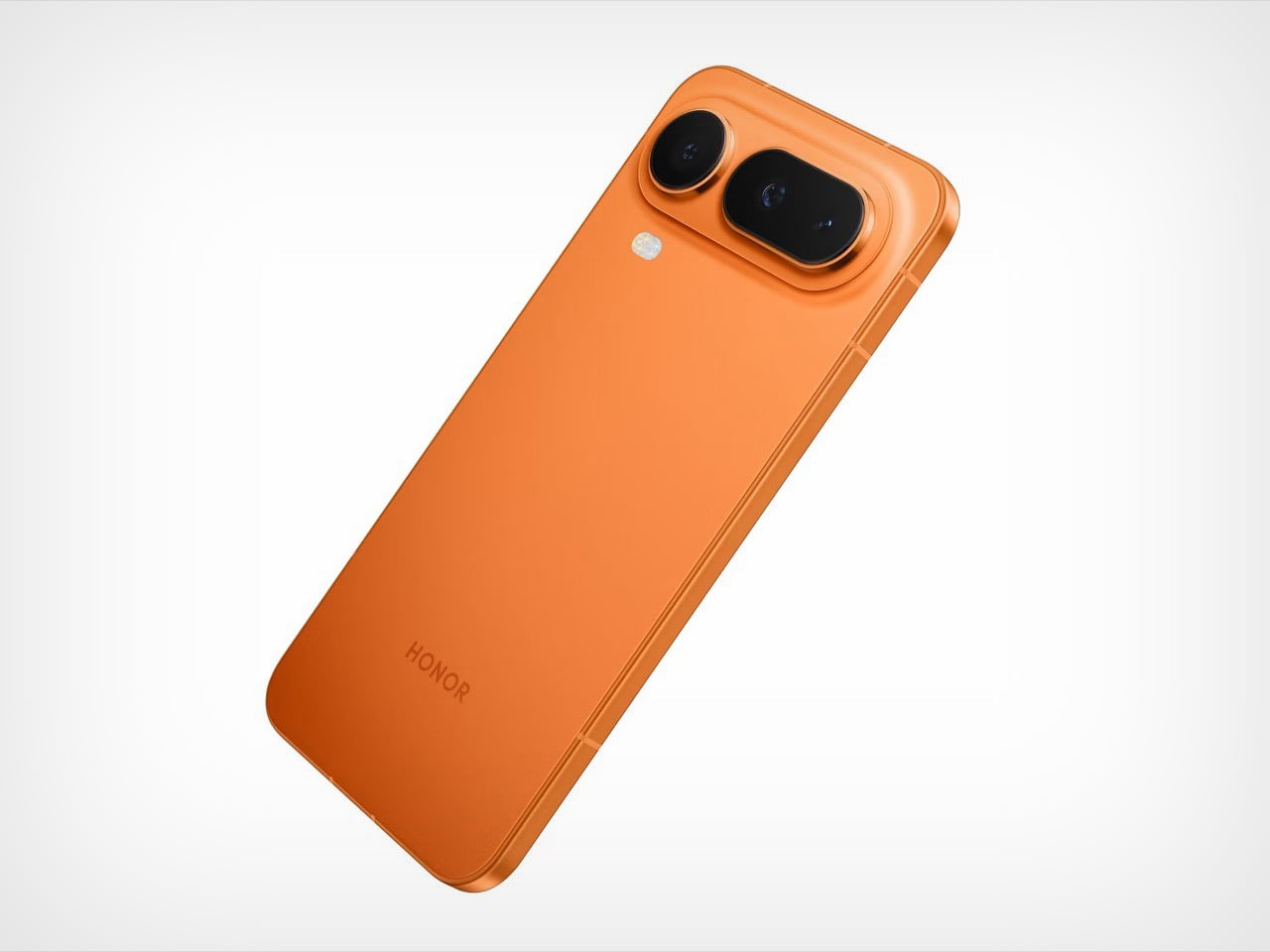
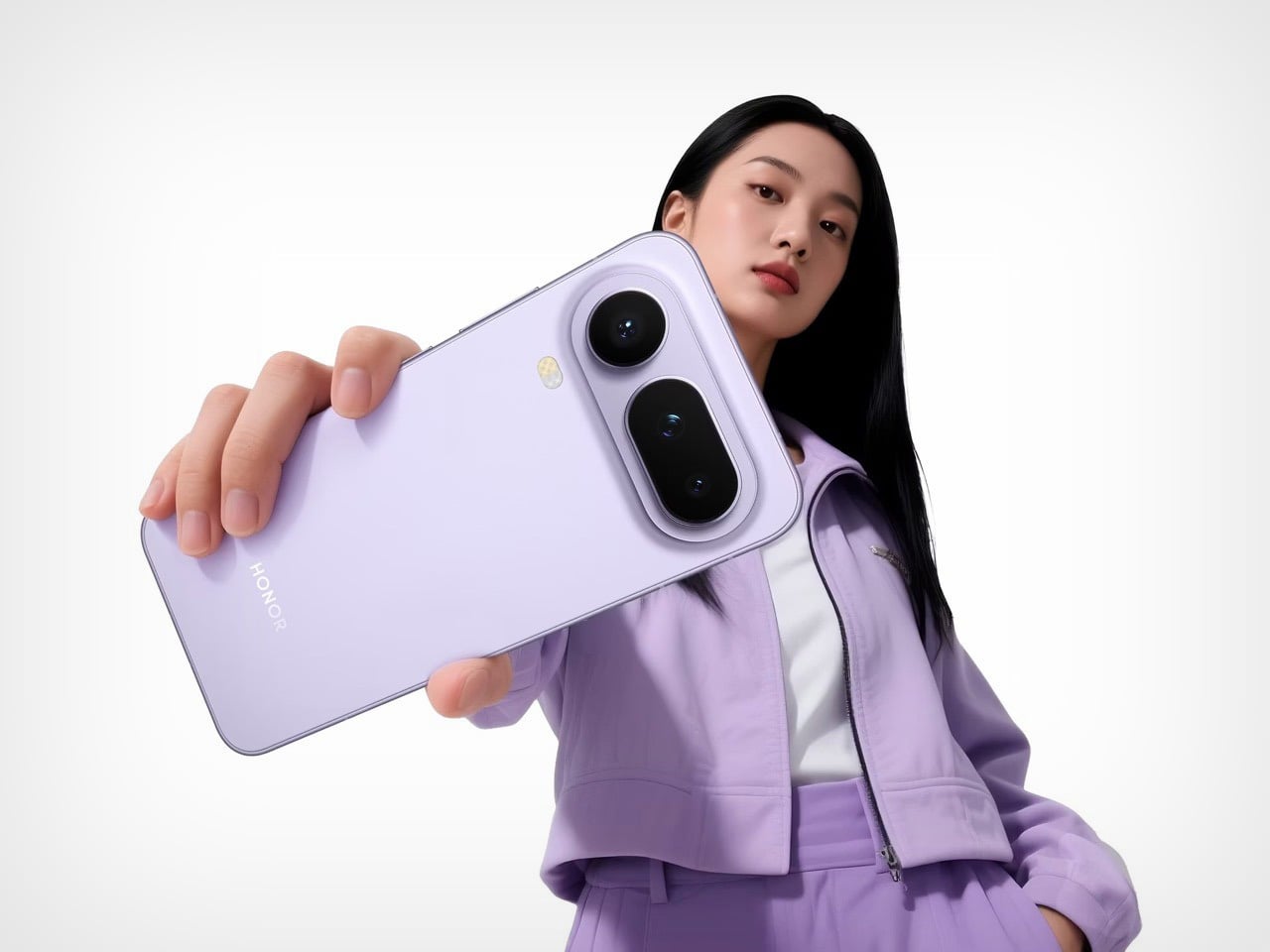
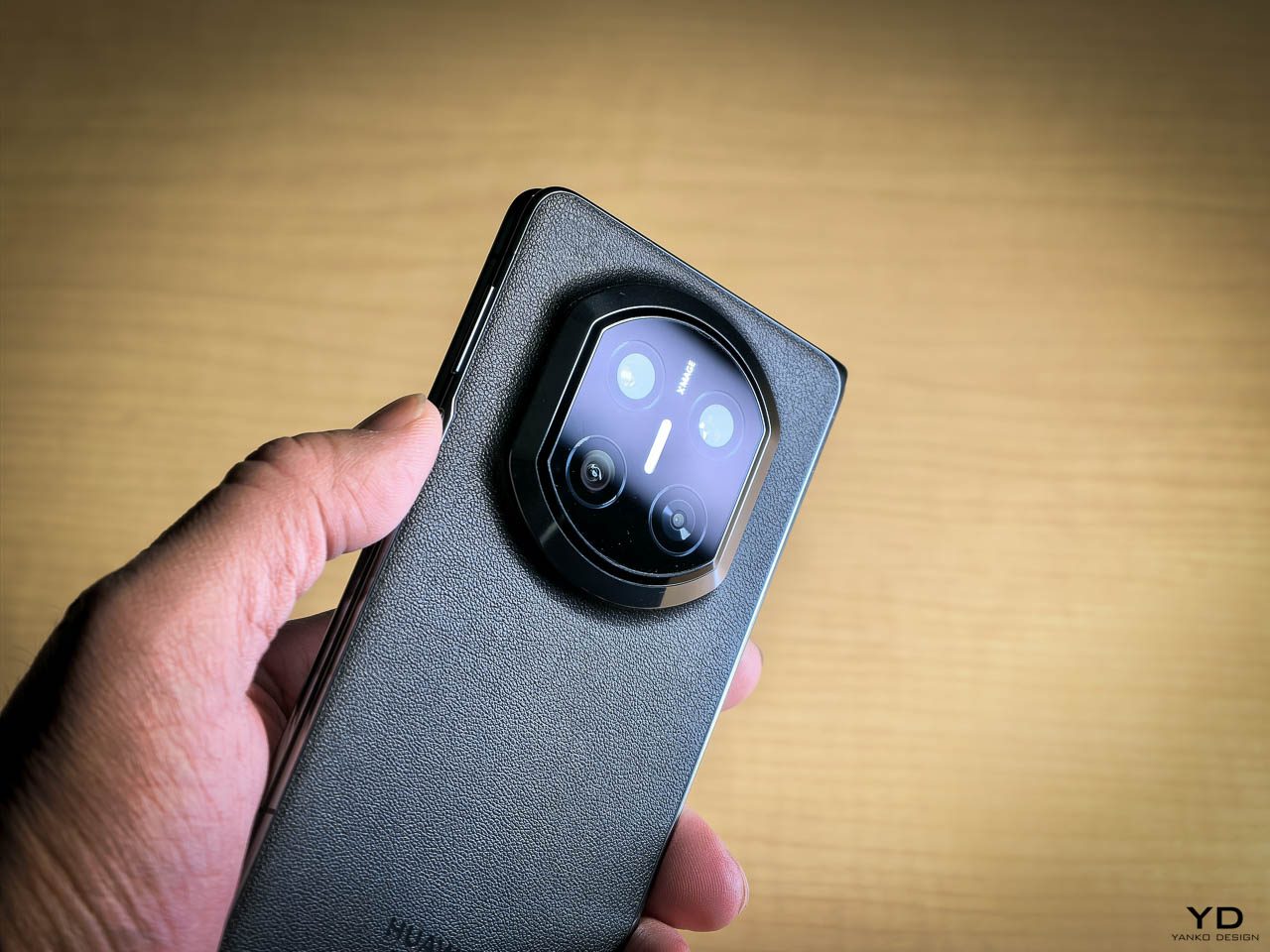
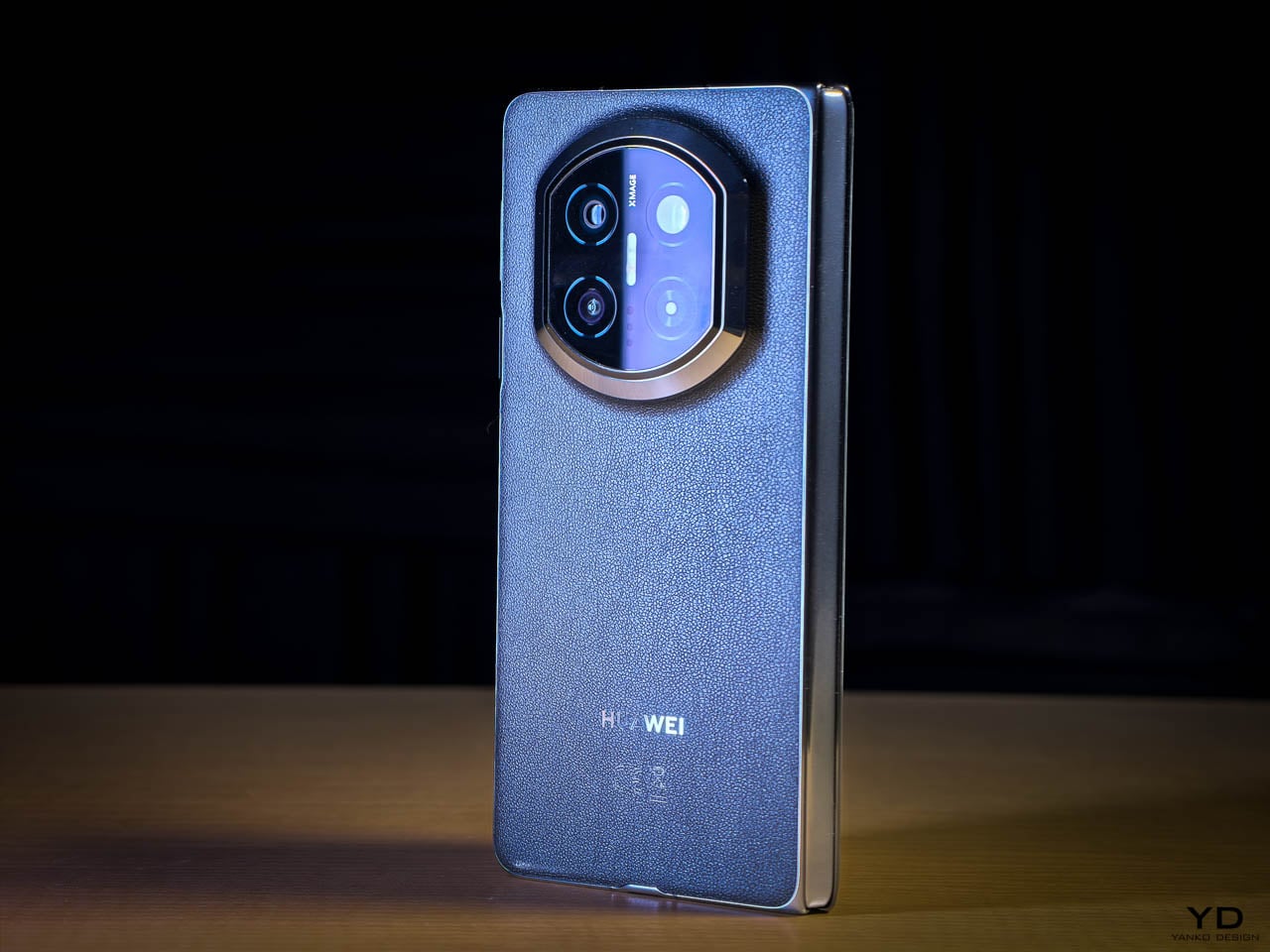
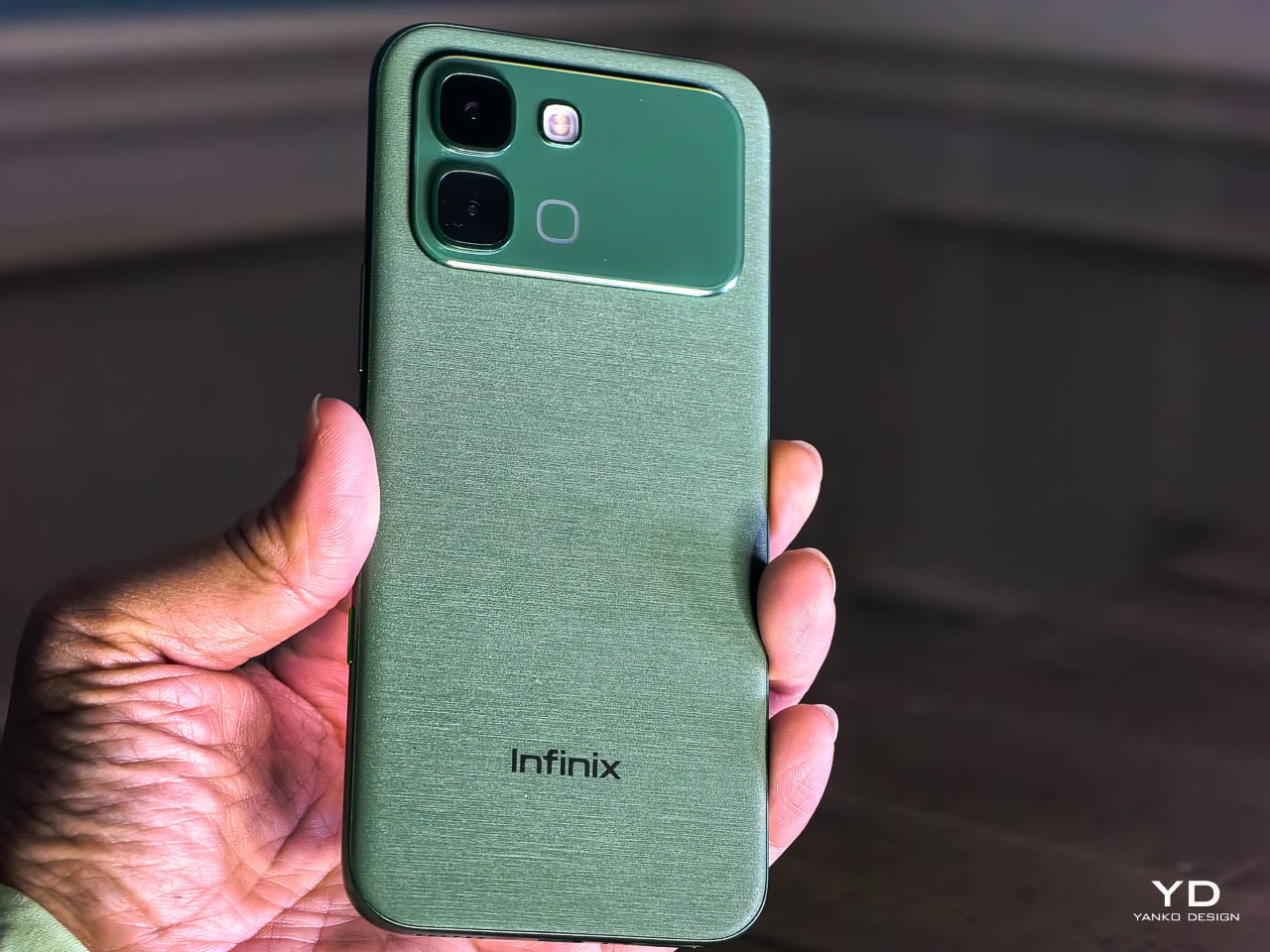
The Silk Green finish on our review unit operates differently than most smartphone surfaces. It’s a leather-like treatment with a texture evocative of luxury handbags, absorbing light rather than bouncing it back indiscriminately. Indoors, the color reads as deep and muted, almost forest-like in its saturation. Move outside, and the green opens up, revealing warmer undertones that shift depending on the angle of observation. This isn’t a static color. It’s a material that responds to its environment, and that responsiveness gives the phone a character that glass-backed devices simply can’t replicate.
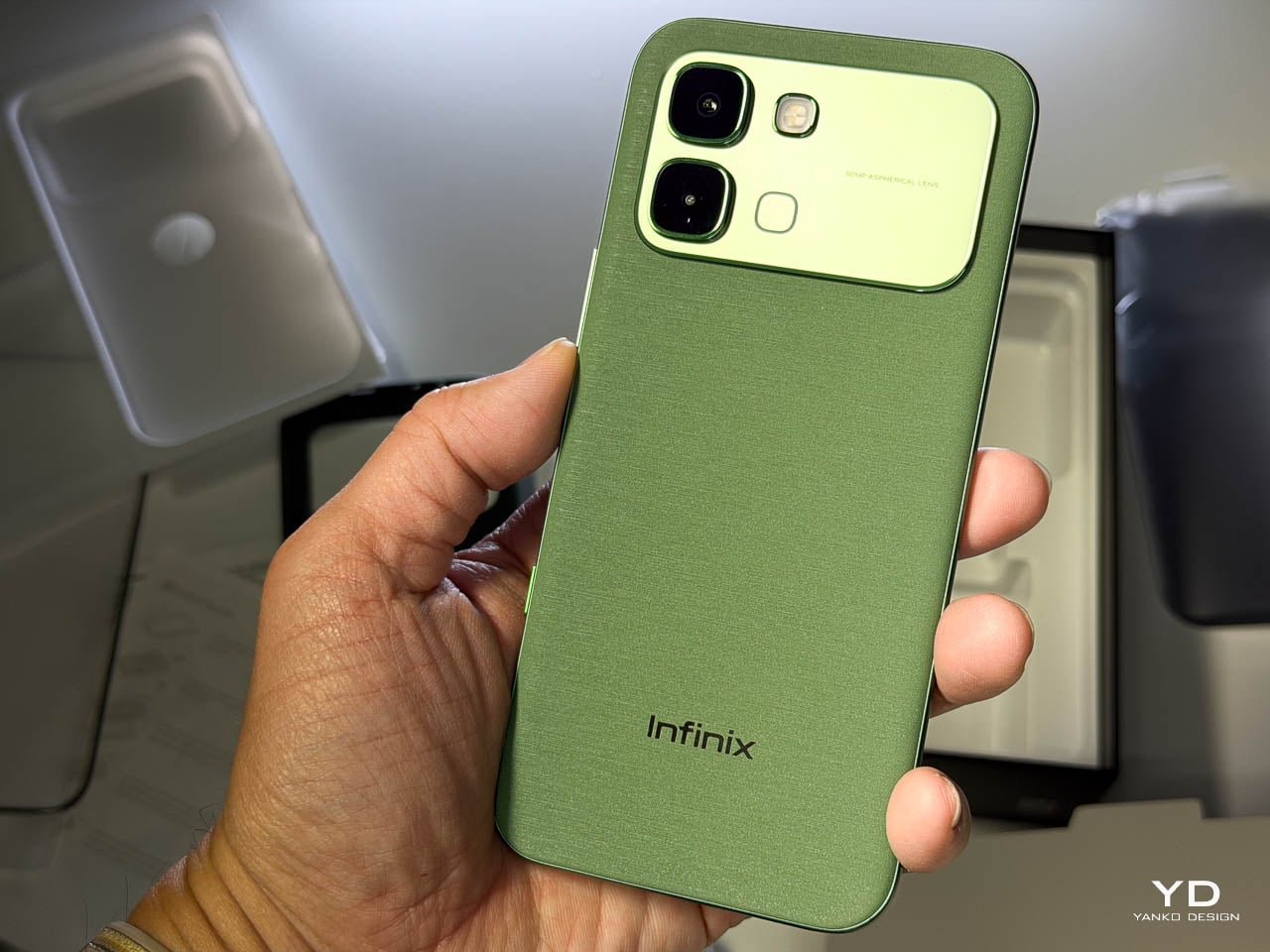

The texture matters as much as the color. There’s no cold shock when you pick it up from a table. Fingerprints don’t accumulate the way they do on glossy surfaces. After extended use, the back panel still looks intentional rather than smudged.
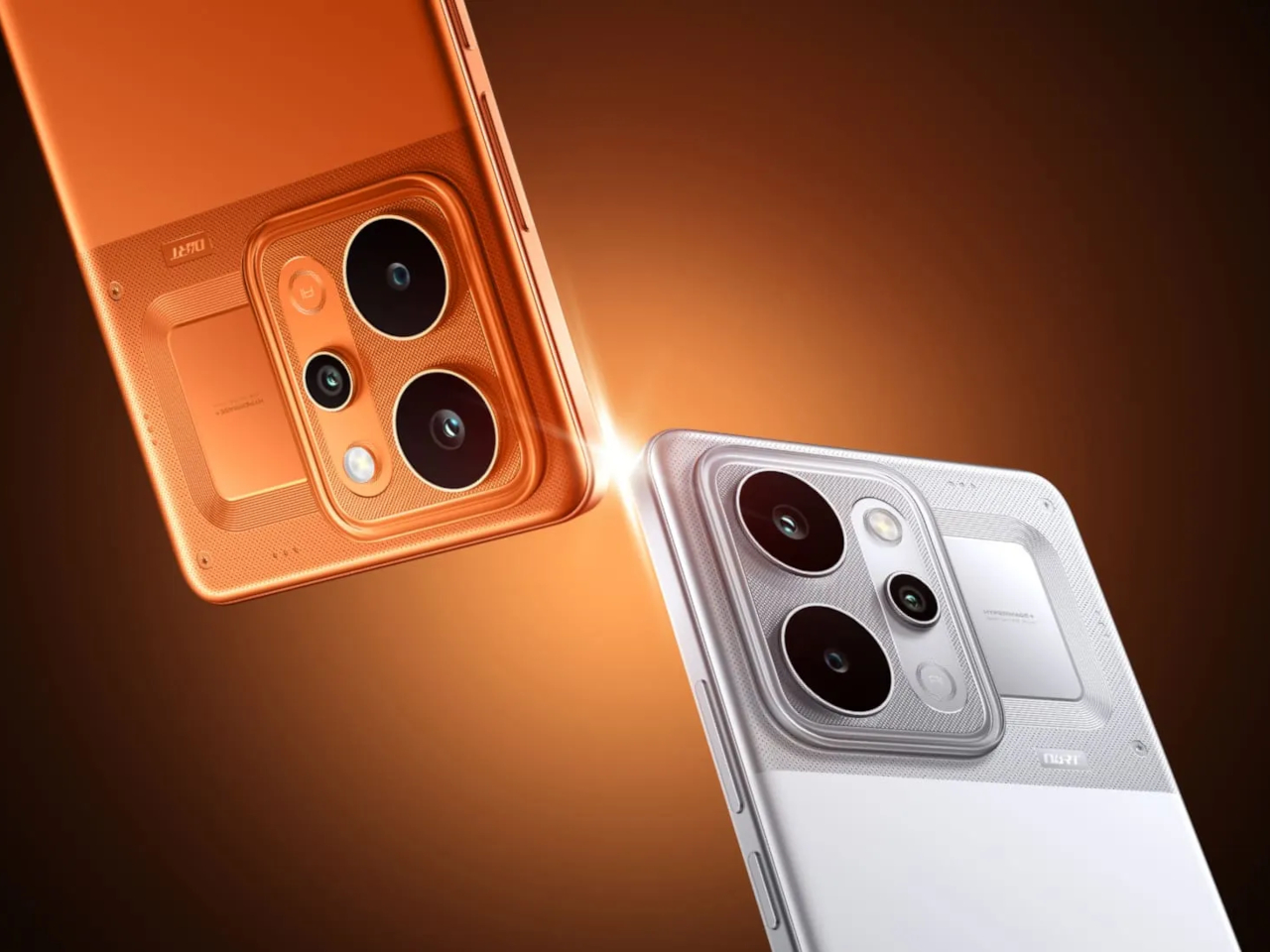
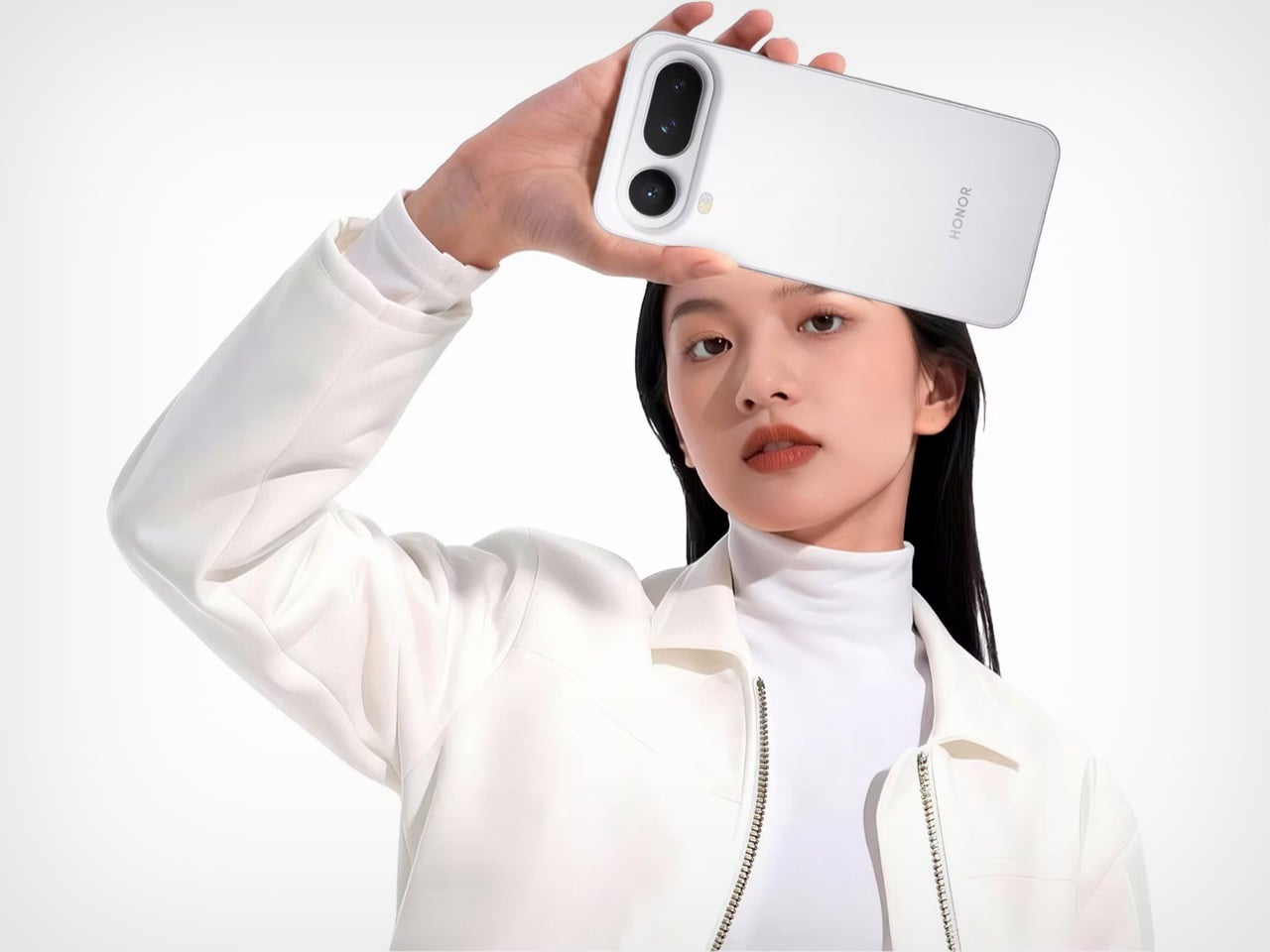
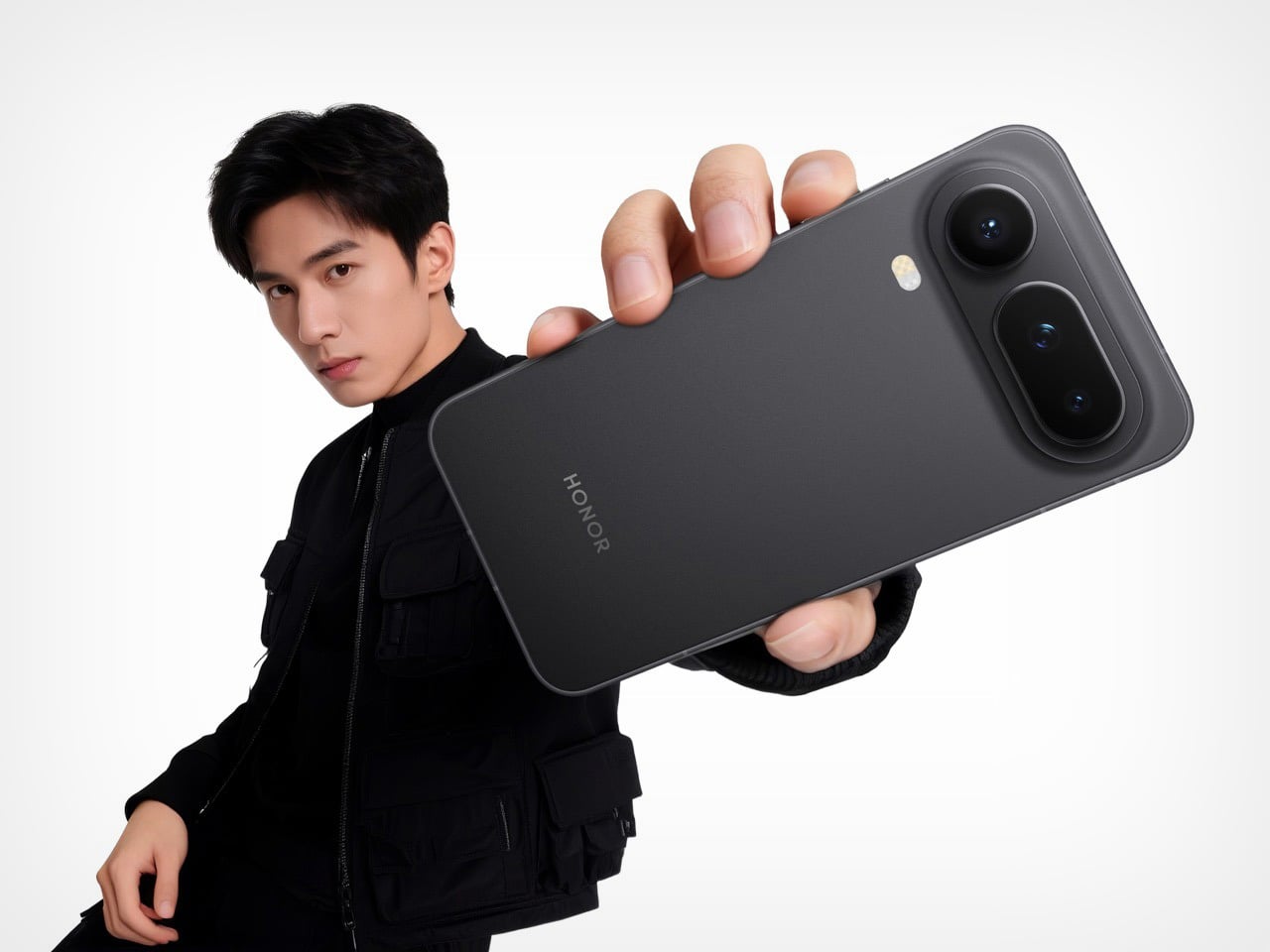
Infinix offers alternative finishes that pursue a different aesthetic entirely. The Lunar Titanium, Stellar Blue, and Shadow Black variants use a cat-eye stone inspired treatment that creates visible movement as the phone tilts. Light doesn’t just reflect from these surfaces. It travels across them, producing shifting patterns that never quite settle into a fixed appearance. The finish has enough grip to feel secure without becoming tacky, and it maintains that feel whether your hands are dry or slightly damp. The effect is dramatic without crossing into garish territory, and it demonstrates that Infinix isn’t limiting itself to a single design vocabulary.
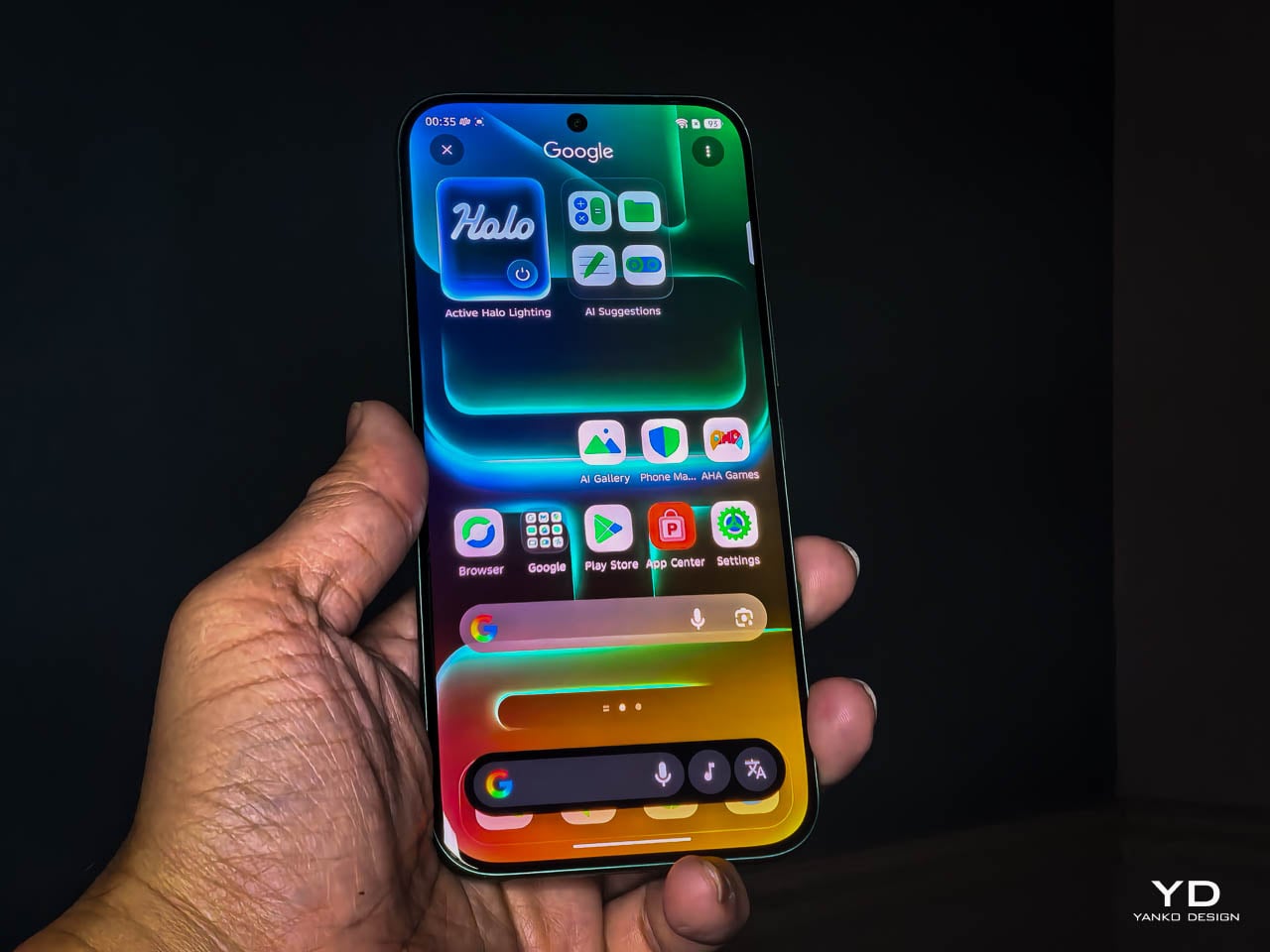
The 3D curved 1.5K AMOLED display integrates with the frame through a transition that eliminates the hard edge found on flat-screen devices. The curve is calibrated to reduce perceived width while maintaining usability across the entire display surface. Ultra-narrow bezels, with the bottom edge measuring just 1.87mm at its narrowest point, push content closer to the physical boundary of the device. The 6.78-inch panel feels immersive without forcing the body to expand beyond comfortable one-handed reach. A 120Hz refresh rate keeps motion smooth, 10-bit color depth renders gradients without visible banding, and 4500 nits of peak brightness means outdoor visibility doesn’t require cupped hands or squinting. Gamers benefit from a 2800Hz instant touch sampling rate that registers inputs faster than most users can perceive.
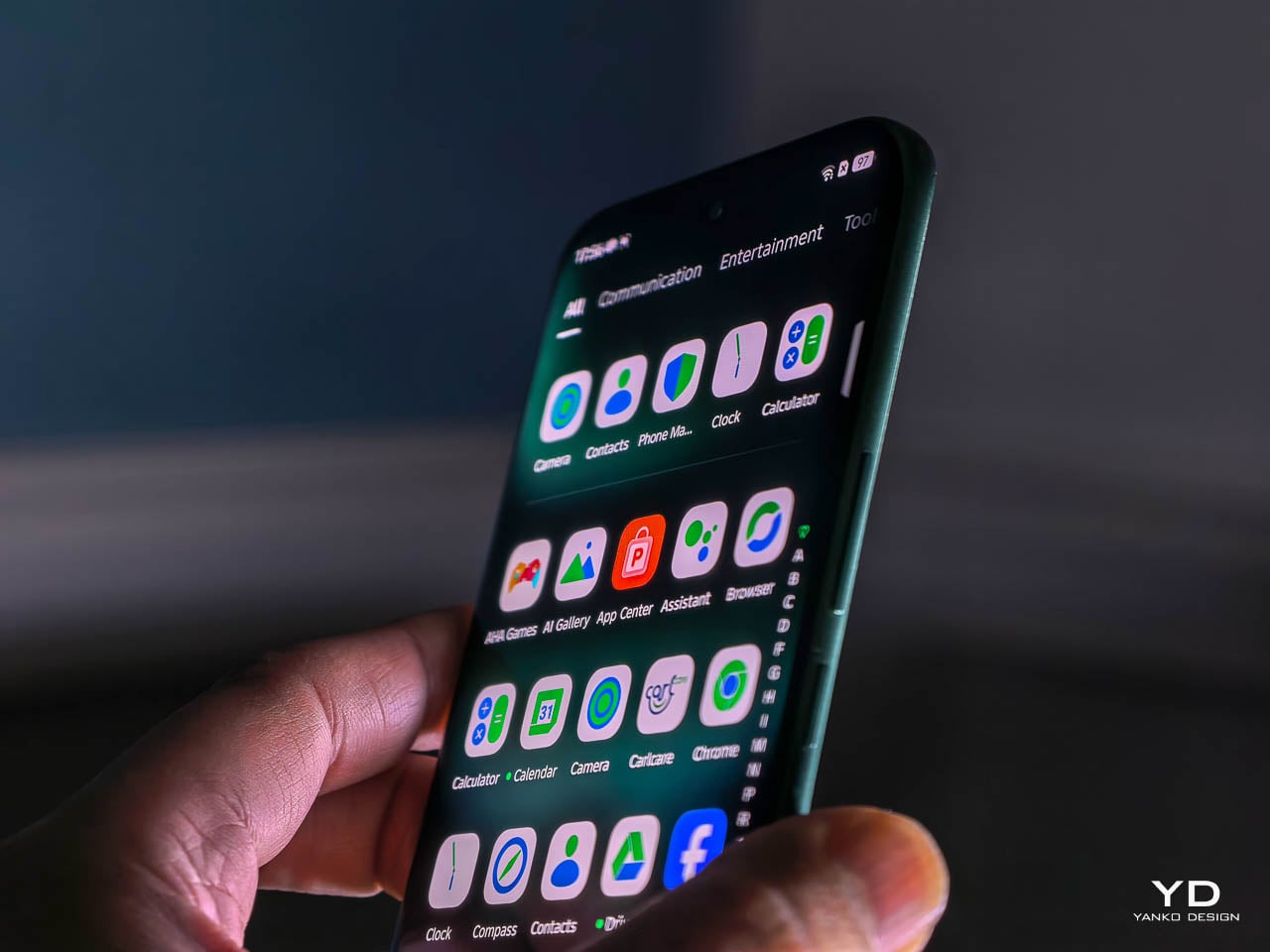

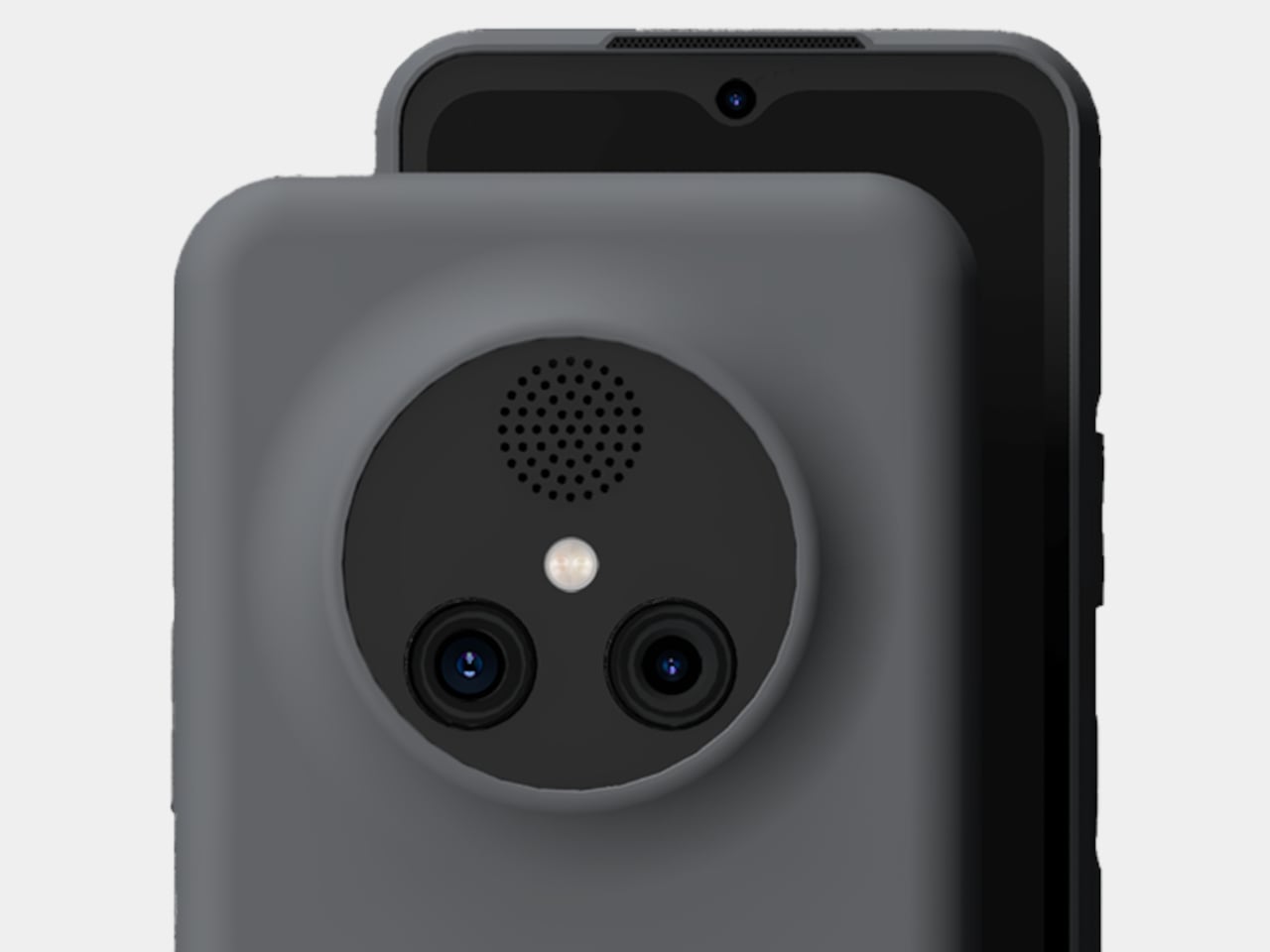
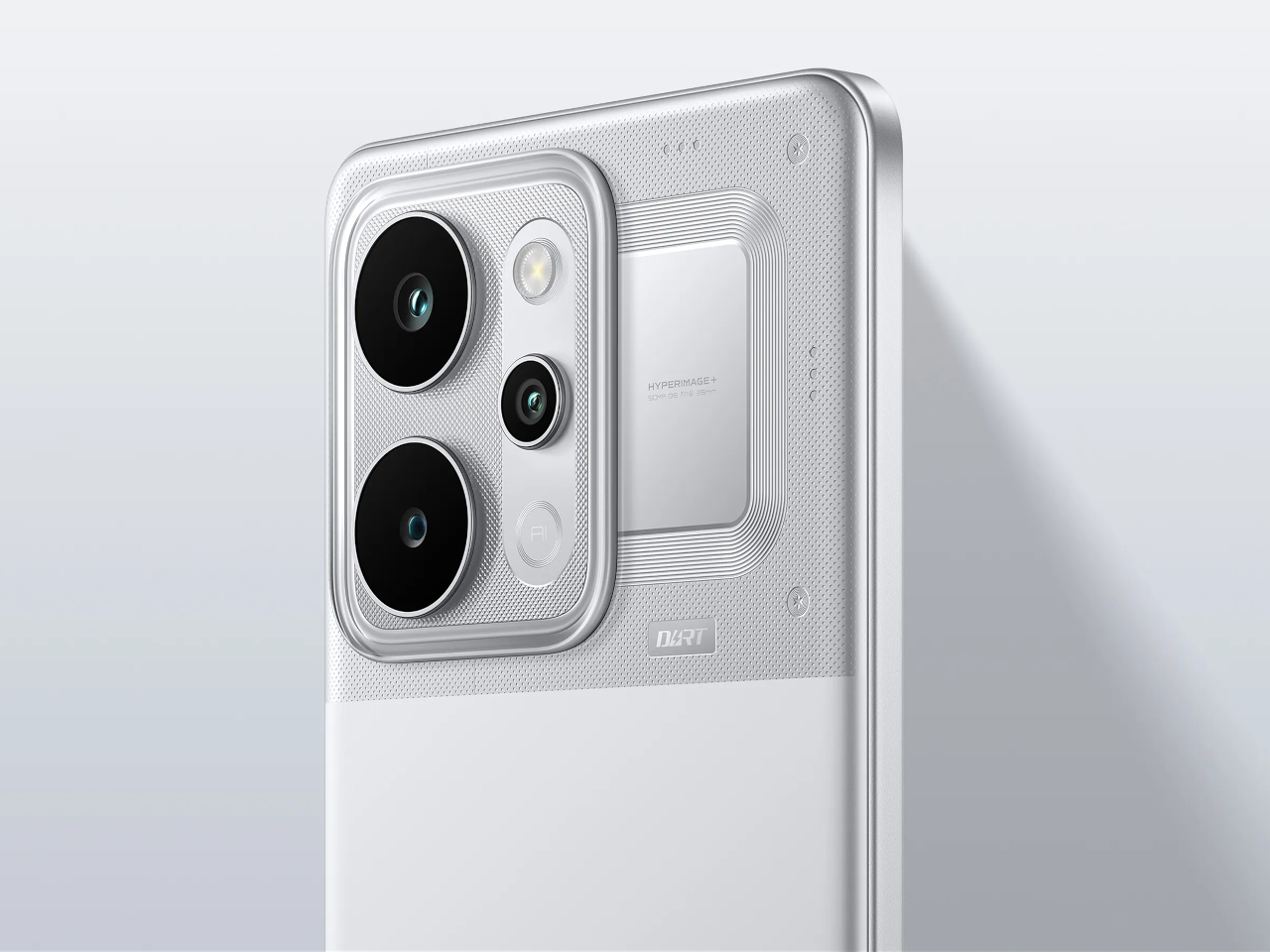
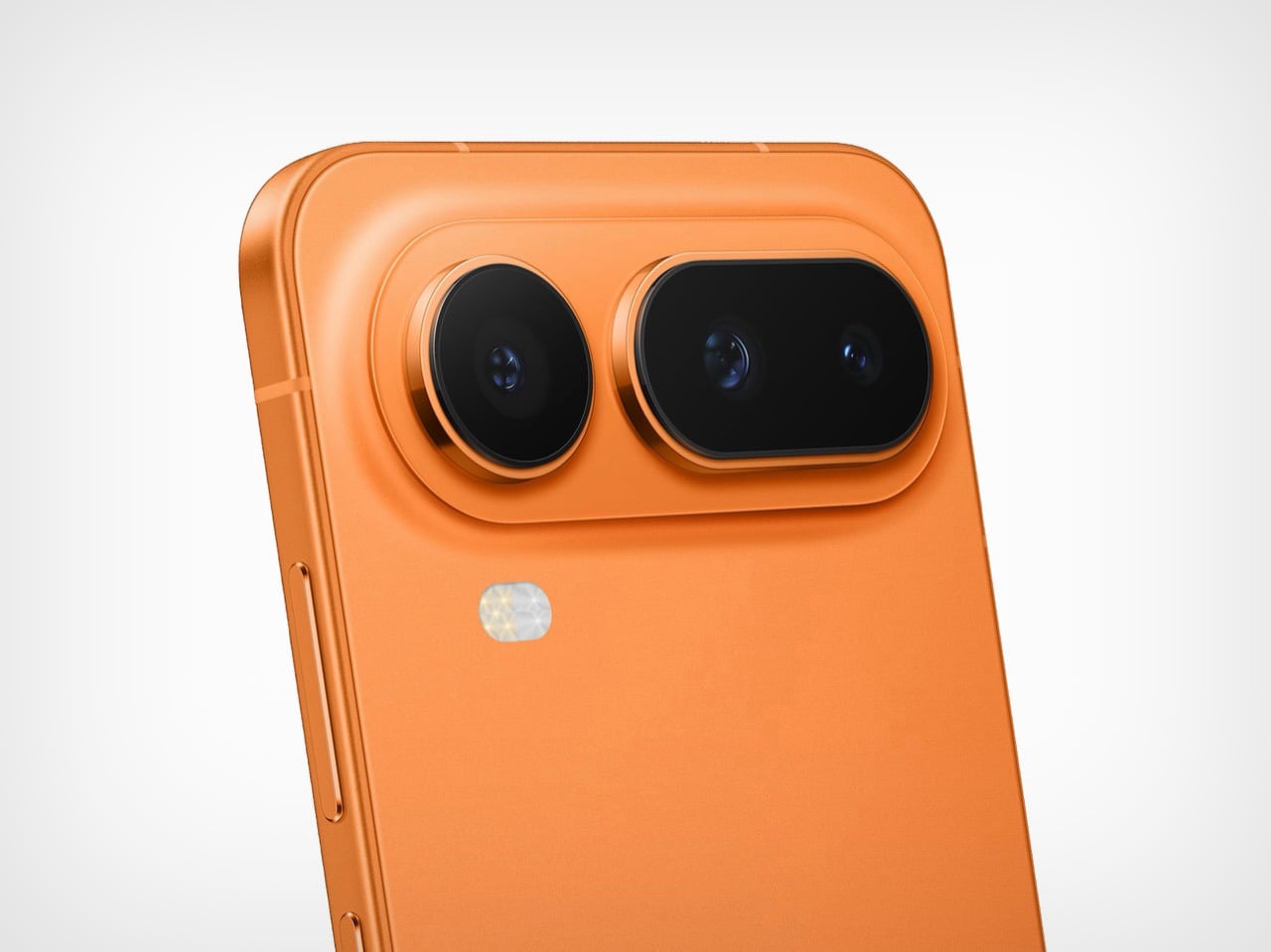
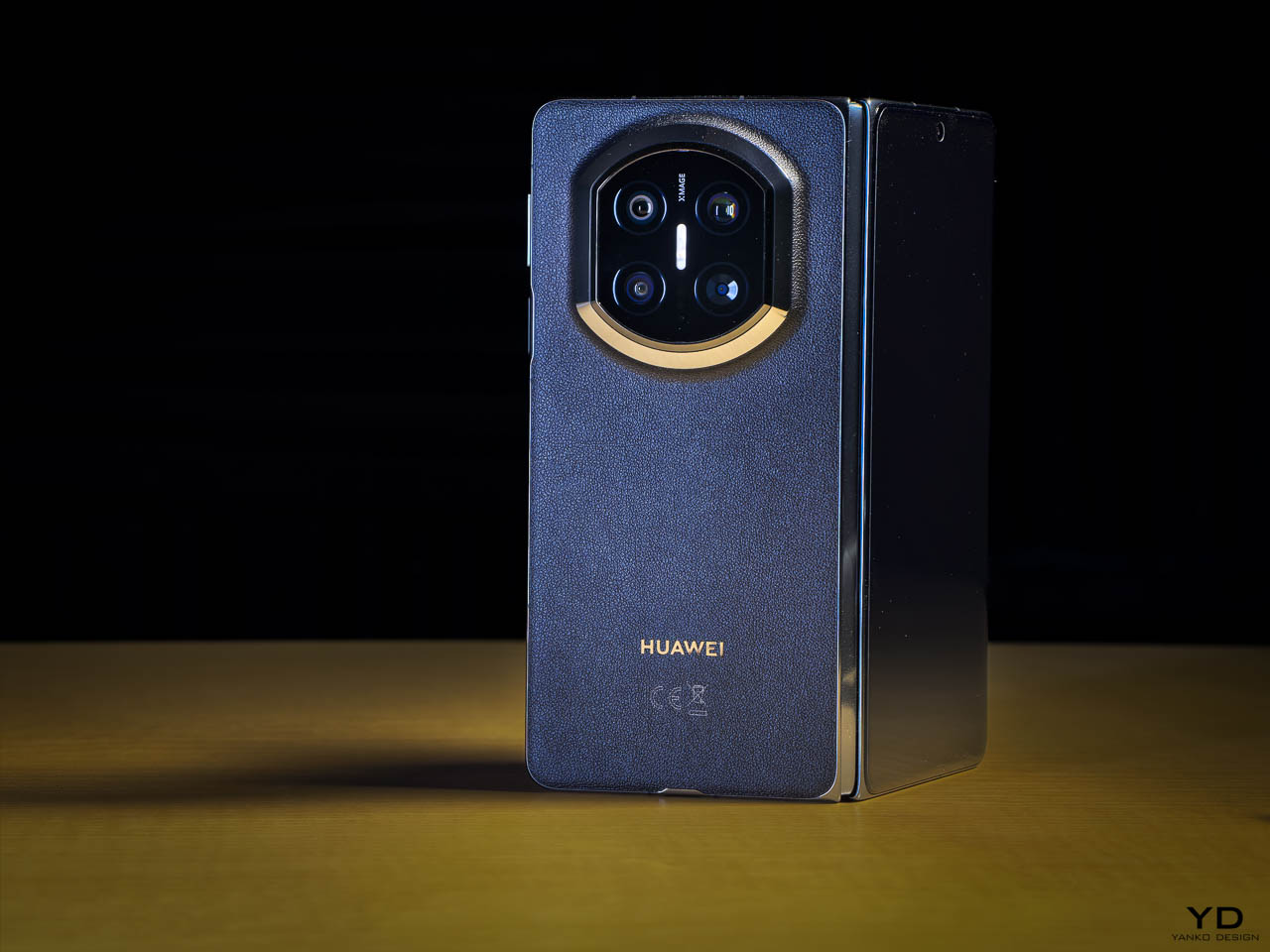
The interaction layer adds functional touches without cluttering the physical design. A dedicated One-Tap button on the frame provides customizable shortcuts to features like the flashlight, camera, or FOLAX AI assistant. The Active Halo Lighting around the rear camera module glows softly in response to notifications, calls, and charging status, with adjustable colors and stepless dimming. Neither element demands attention, but both reward users who engage with them. An integrated IR blaster lets you control TVs, air conditioners, and other appliances directly from the phone. eSIM support, a first for Infinix devices, adds flexibility for travelers and dual-SIM users who’d rather not swap physical cards. Availability varies by region and model, so check the official Infinix website to confirm eSIM support in your market.
Weight distribution deserves specific attention. A 6,500mAh battery creates density that could easily pull the phone off balance, making it feel top-heavy during vertical use or awkward during extended sessions. The NOTE Edge avoids this entirely, with mass centered in the chassis so scrolling, typing, and camera work all feel stable.

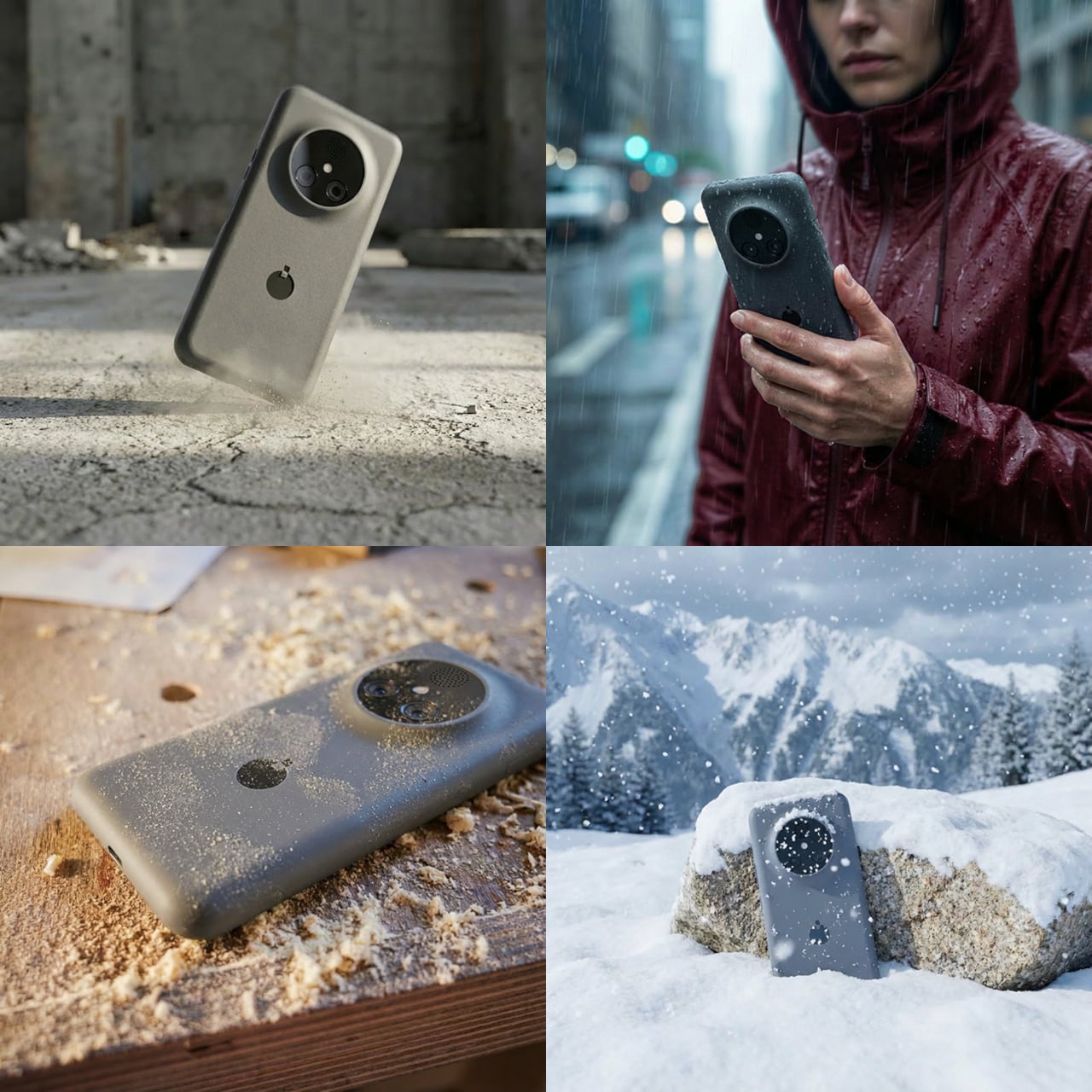
The glass-to-frame transition reinforces that sense of cohesion. There’s no lip or ridge where materials meet. Your grip flows uninterrupted around the device, which matters more than it might seem during the first few minutes of handling. Over hours, that seamlessness translates to reduced fatigue. The phone disappears physically while remaining visually present, which is exactly the balance a design-forward device should achieve. Corning Gorilla Glass 7i protects the curved display surface, and IP65 dust and water resistance means the materials can handle exposure to the elements without requiring constant caution.
Software and User Experience (XOS 16)
XOS 16 plays a bigger role in how the NOTE Edge feels than you might expect. Built on Android 16, the interface doesn’t compete with the hardware for attention. It supports it. Transitions stay smooth, layouts feel intentional, and nothing about the experience pulls focus away from what you’re actually doing on the phone.
The Glow Space design language shows up in subtle ways rather than obvious visual tricks. Depth effects, layered wallpapers, and motion cues work especially well with the curved display, giving the interface a sense of dimension without becoming distracting. It pairs naturally with the phone’s physical form, which matters when you’re swiping one handed or shifting between apps quickly. After a few hours, the software fades into the background, which is exactly what good interface design should do.
Haptics feel restrained and precise. Taps register cleanly. Gestures feel confident without being exaggerated. There’s enough feedback to reinforce interaction, but not so much that it becomes noise. Combined with the curved edges and balanced weight, the software contributes directly to how comfortable the device feels over long sessions.
Infinix’s AI layer works best when it stays quiet. System level optimization, background task management, and two-way AI noise reduction operate without demanding attention. The noise cancellation works in both directions, cleaning up background sound on your end while also filtering what you hear from callers. That restraint fits the overall tone of the NOTE Edge.

Longevity is where XOS 16 quietly strengthens the value of the device. Infinix commits to three years of OS updates and five years of security patches, which changes how you think about living with the phone long term. This isn’t software designed to feel fresh for a few months and then age out. It’s built to remain stable, secure, and familiar well beyond the initial ownership window.
Performance and Camera
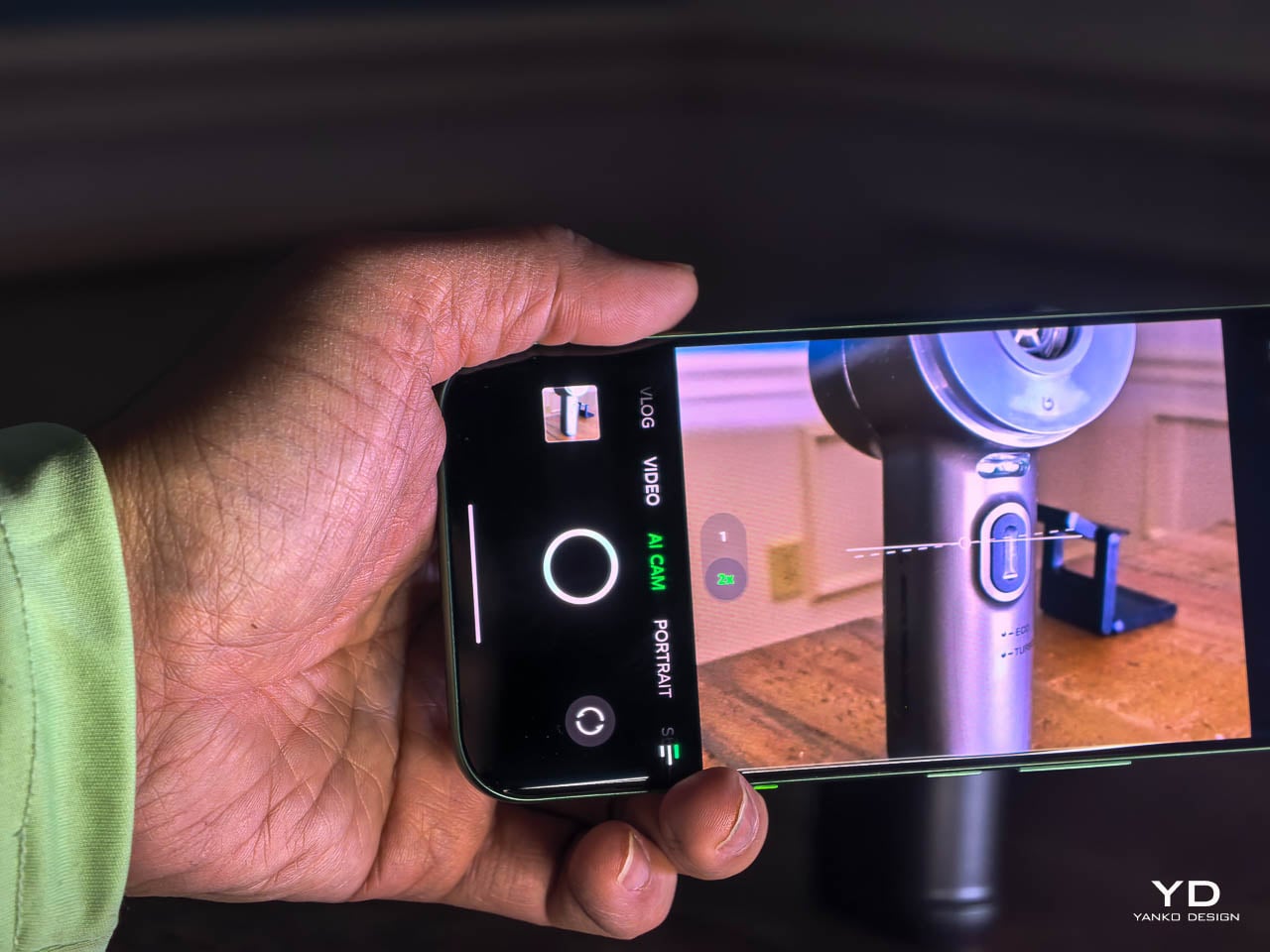
The MediaTek Dimensity 7100 5G handles daily use without calling attention to itself. Swiping, launching apps, and unlocking all register instantly. It’s the kind of platform that does its job and stays out of the way.

That consistency holds over longer sessions. I kept messaging, maps, and media apps running simultaneously and never felt the system hesitate or dump background processes. The interface stayed responsive after hours of mixed use, which matters more than benchmark numbers when you’re navigating an unfamiliar city or bouncing between work threads and personal messages. Heat management impressed me more than raw speed. Extended navigation, casual gaming, and heavy browsing didn’t produce the kind of warmth that makes you shift your grip or set the phone down. The chassis stayed comfortable against my palm throughout full afternoon sessions. Infinix clearly tuned this device for sustained operation rather than brief bursts of peak performance.

Signal stability reinforces that dependability. Infinix’s UPS 3.0 Super Signal Technology focuses on low-frequency cellular bands, the 615 to 960 MHz range that travels farther and penetrates obstacles better than higher frequencies. These are the signals that actually reach you in elevators, underground parking garages, and concrete-heavy buildings when everything else drops off.
The engineering behind it involves physically larger antenna components. Infinix increased the radiation arm area of the main low-frequency antenna by 50 percent and the auxiliary antenna’s radiation wall by 30 percent. That translates to a 1.5 to 2 dB gain in low-frequency reception, which sounds modest on paper but shows up clearly in practice. Calls held steady in places where I normally expect a brief dropout. Data kept flowing in basement-level parking where other phones tend to stall while searching for signal.
It’s the kind of reliability you only notice when it’s missing.
The camera follows that same practical mindset. It’s built to produce usable results without demanding expertise.

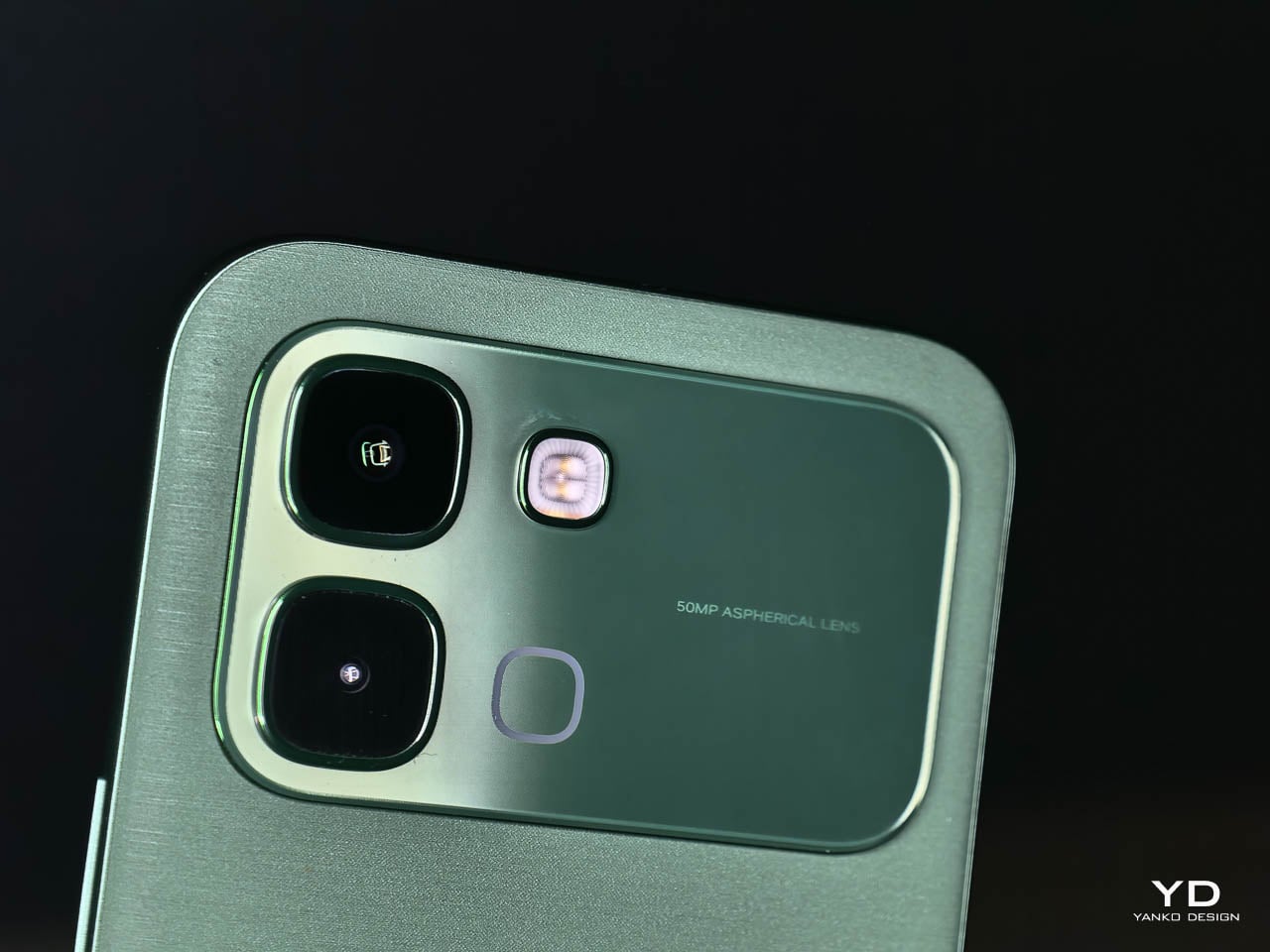
This is a dual camera setup. The 50MP main sensor handles all meaningful imaging work, while the secondary lens exists for depth separation in portrait shots.
The 50MP main sensor handles everyday situations with consistent color accuracy from shot to shot. Outdoor images retain detail without oversaturating, and indoor shots keep skin tones natural under mixed lighting. Low light performance benefits from Infinix’s AI RAW imaging algorithm, which lifts shadow detail without flattening contrast or blowing highlights. Texture stays intact where other processing tends to smooth everything into mush. You don’t need to fight the camera or babysit settings. Point, shoot, and move on works more often than not.



Live Photo Mode captures a three-second window around each shutter press, giving you motion instead of a single frozen frame. It’s useful for candid moments, pets, or scenes where timing matters. Exporting as GIFs, setting captures as live wallpapers, or sharing to iPhones via NFC makes the feature feel integrated rather than bolted on. The implementation suggests Infinix thought about how people actually use these clips rather than just checking a feature box.

Video recording stays predictable and clean. Footage looks solid in good light, motion doesn’t introduce distracting jitter, and audio capture handles casual recording without issues. Nothing here feels experimental or unfinished.
Audio and Sound Performance
Sound is handled by a dual stereo speaker system co-engineered with JBL, and it’s immediately noticeable once you stop defaulting to headphones. Volume comes up without harshness, and the tonal balance stays intact even when you push it higher than you normally would for casual listening. There’s actual separation here, with dialogue staying forward in videos and podcasts while music doesn’t collapse into a single flat plane.
Infinix leans on a five-magnet acoustic system and a high-elasticity silicone rubber diaphragm, which sounds technical until you use it. Bass has presence without rattling, mids stay clean, and highs don’t spike in a way that fatigues your ears over longer sessions. The diaphragm flexibility contributes to that balanced output, absorbing vibrations that would otherwise muddy the low end. The 360-degree symmetrical sound field matters more than I expected, especially when you’re watching something without holding the phone perfectly straight. Audio stays consistent whether the phone is resting on a table, propped up, or held casually in one hand. That positional flexibility makes the speakers feel genuinely usable rather than an afterthought.
Sustainability and Longevity
Battery capacity tells only part of the endurance story. The 6,500mAh cell in our review unit (6,150mAh in certain regional configurations) provides multi-day operational potential under moderate use patterns. This isn’t about chasing screen-on time records. It’s about eliminating the anxiety that comes with uncertainty around whether a device will last through an unpredictable day.
In practice, that translates to roughly 22 hours of continuous video playback or 26 hours of outdoor navigation before you need to reach for a cable. When you do need to refuel, 45W All-Round FastCharge gets you to 50% in about 27 minutes and a full charge in just over an hour. Bypass Charging routes power directly to the system board during gaming or navigation, which keeps the battery out of the thermal loop and reduces heat buildup during extended plugged-in sessions.

Long-term battery health becomes relevant when capacity numbers reach this scale. Infinix claims the battery retains more than 80% capacity after 2,000 full charge cycles, equivalent to over six years of typical daily use. The company also cites self-healing technology that repairs micro-damage through dynamic recrystallization during low-current recovery. These aren’t marketing abstractions. They’re engineering claims with testable outcomes, and they suggest the multi-day endurance you experience initially should hold over the ownership cycle rather than eroding within the first year. The durability framing extends beyond just the battery. Material choices across the device suggest consideration for how surfaces age, how components withstand repeated stress, and how the phone maintains its character over months rather than weeks.
XOS 16, built on Android 16, runs the software side. Infinix commits to three years of OS updates and five years of security patches, which represents the longest support window the NOTE series has offered. That commitment matters for a device positioned around longevity.
Value
The NOTE Edge occupies a market position that doesn’t get enough attention. It’s a design-forward midrange device, which means it competes on material quality and user experience rather than processor benchmarks or camera sensor counts. For users who prioritize how a phone looks and feels over how it performs in synthetic tests, the value proposition here is substantial.

What you receive for the price includes premium-feeling materials, balanced ergonomics, multi-day battery endurance, and a display that rivals more expensive devices in clarity and immersion. The Dimensity 7100 5G provides capable daily performance without generating the heat or power consumption of flagships processors. The camera handles real-world scenarios reliably. None of these elements represents a compromise.
The fashion-led color palette means the NOTE Edge appeals to users who want their technology to reflect personal aesthetic preferences. This isn’t a device that disappears into generic smartphone uniformity. It makes a statement.
Wrap Up
The Infinix NOTE Edge succeeds because it understands what it’s trying to be. It’s a considered object that prioritizes material quality, ergonomic refinement, and visual identity over the metrics that dominate most smartphone conversations.
The Silk Green finish exemplifies the approach. It’s a material choice that affects how the phone looks, how it feels, how it ages, and how it responds to its environment. Nothing about it exists in isolation. Every decision connects to a broader vision of what a design-forward smartphone should offer. That coherence is rare, and it’s what separates the NOTE Edge from devices that feel like committees designed them.

For users who’ve grown tired of phones that feel like interchangeable glass rectangles, the NOTE Edge represents an alternative worth serious consideration. Infinix has demonstrated that visible luxury and practical usability can coexist in the midrange segment. The result is a device that you’ll want to use, want to look at, and want to keep using long after the initial appeal of any new purchase typically fades.
The post Infinix NOTE Edge Review: Visible Luxury first appeared on Yanko Design.