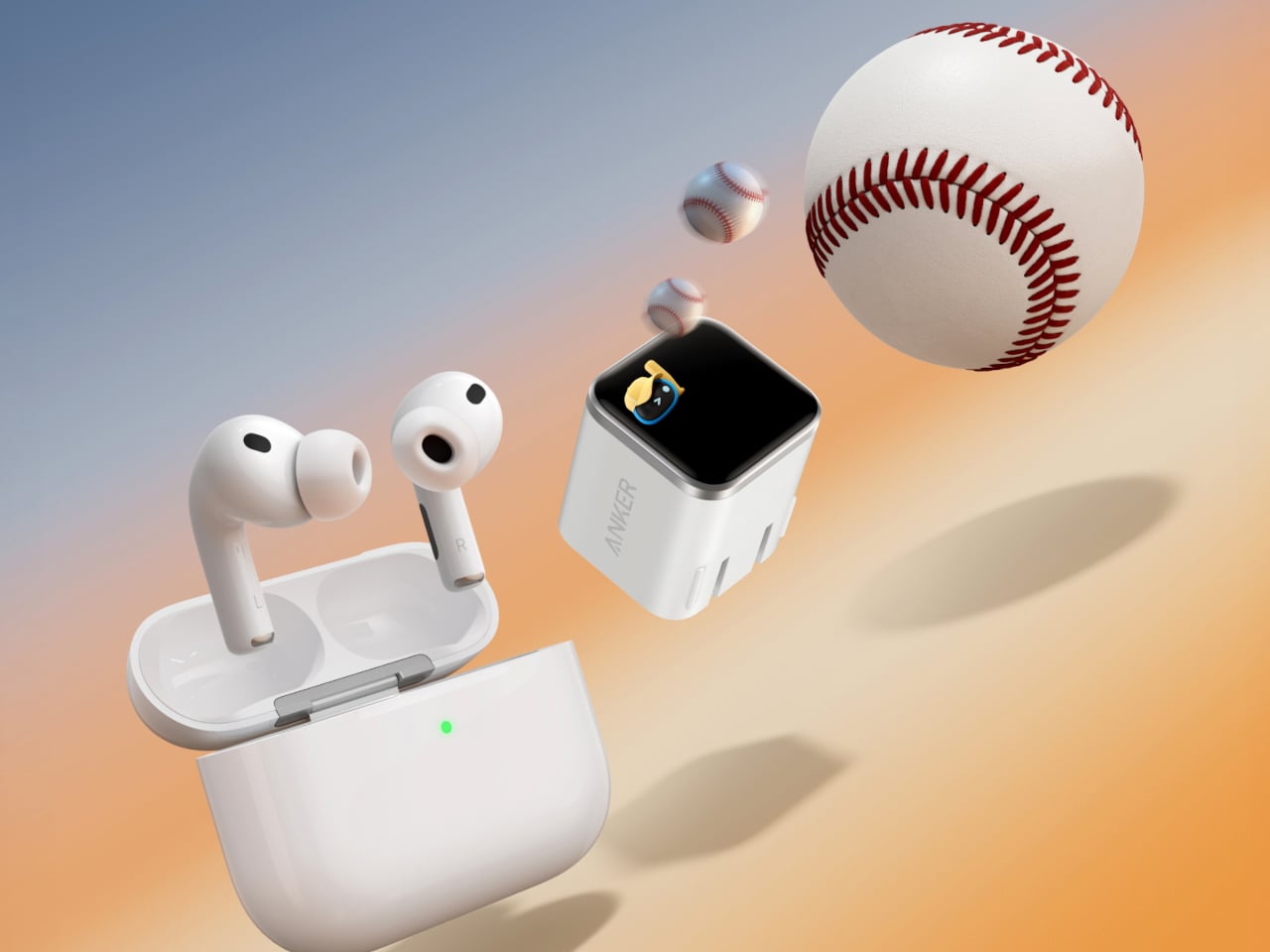
Charging has become a daily background task with a mix of wall bricks, wireless pads, power strips, and docks that rarely feel coordinated. As devices become faster and more power-hungry, the friction shifts from “do I have enough power?” to “how many adapters do I need without cluttering the desk?” The answer usually involves a drawer full of chargers that don’t talk to each other and rarely work where needed.
Anker’s CES 2026 portfolio treats this as a system. The Anker Charging lineup introduces four products, the Nano Charger, Prime Wireless Charging Station, Nano Power Strip, and Nano Docking Station, sharing ideas like smarter device recognition, Qi2 25 W wireless, AnkerSense View, and ActiveShield 5.0, but slotting into different moments where power is needed, wanted, or quietly essential to keeping momentum going without searching for another cable.
Designer: Anker
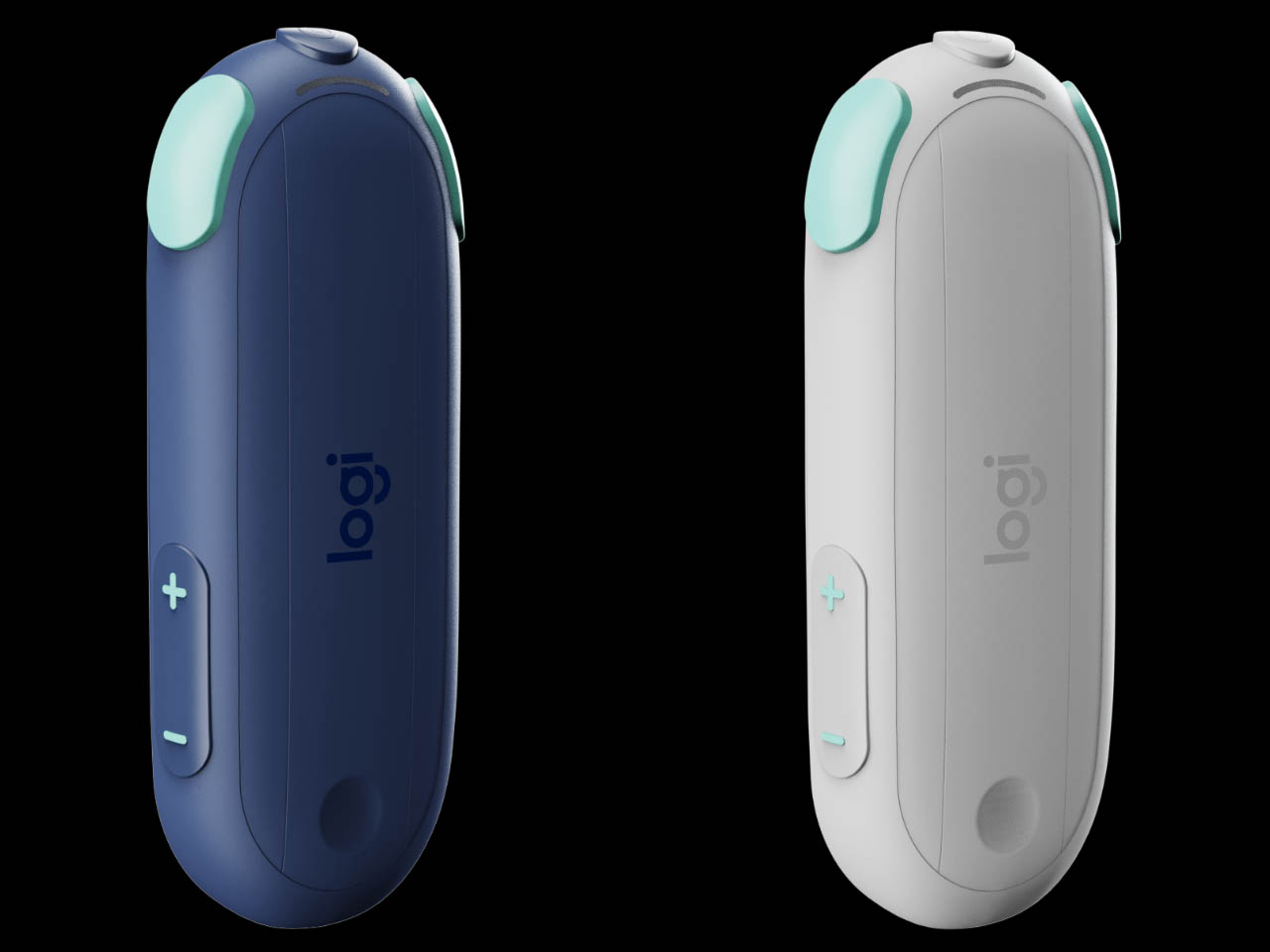
Anker Nano Charger (45W, Smart Display, 180° Foldable)
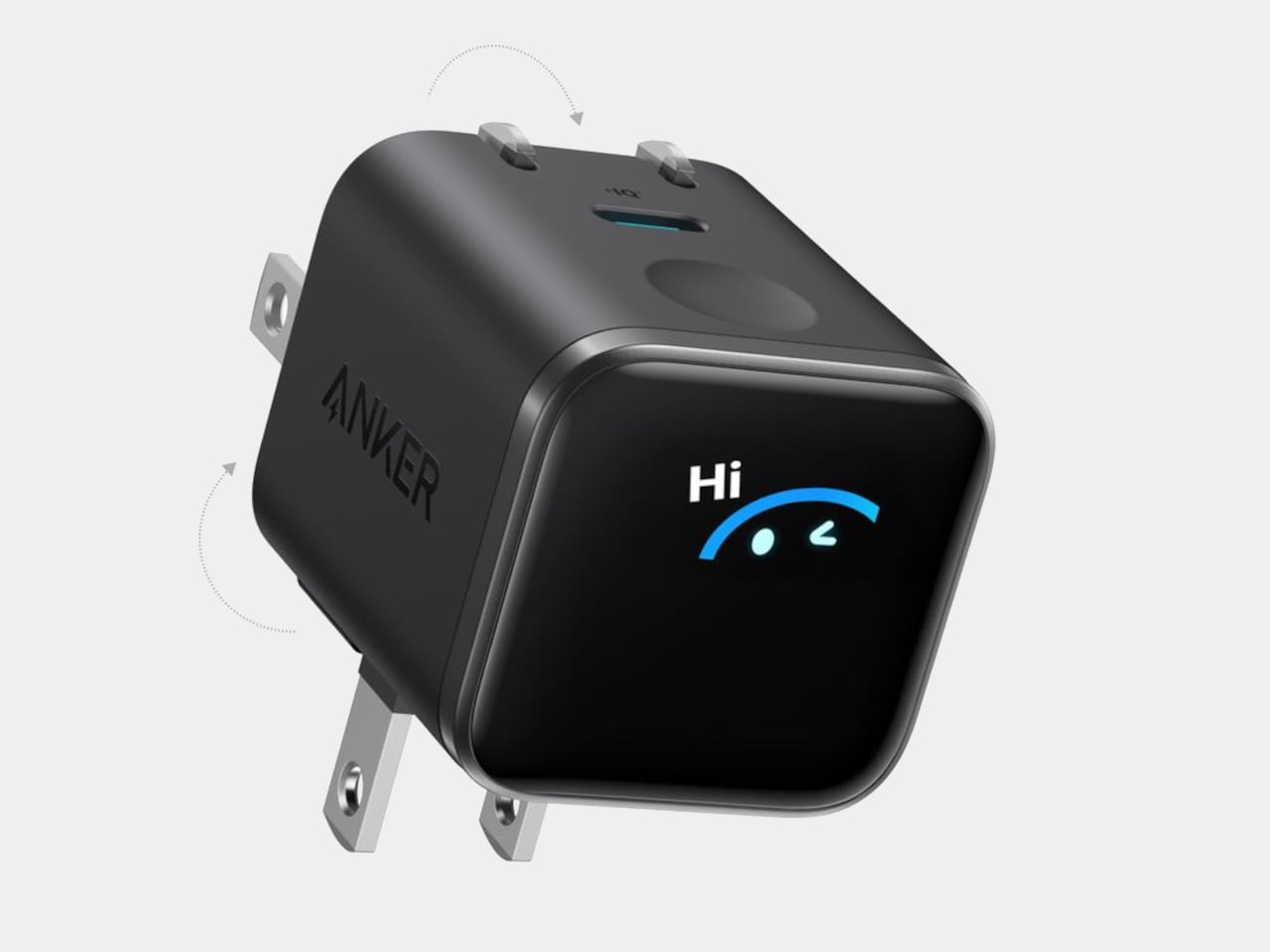

The Nano Charger recognizes recent iPhone and iPad Pro models in seconds, then uses a three-stage power profile to deliver up to 45 W tailored to the device. That auto-matching unlocks faster charging when the battery is low while easing off as it fills, avoiding overstressing batteries for people who charge overnight or keep devices plugged in during long work sessions without thinking about optimal timing.
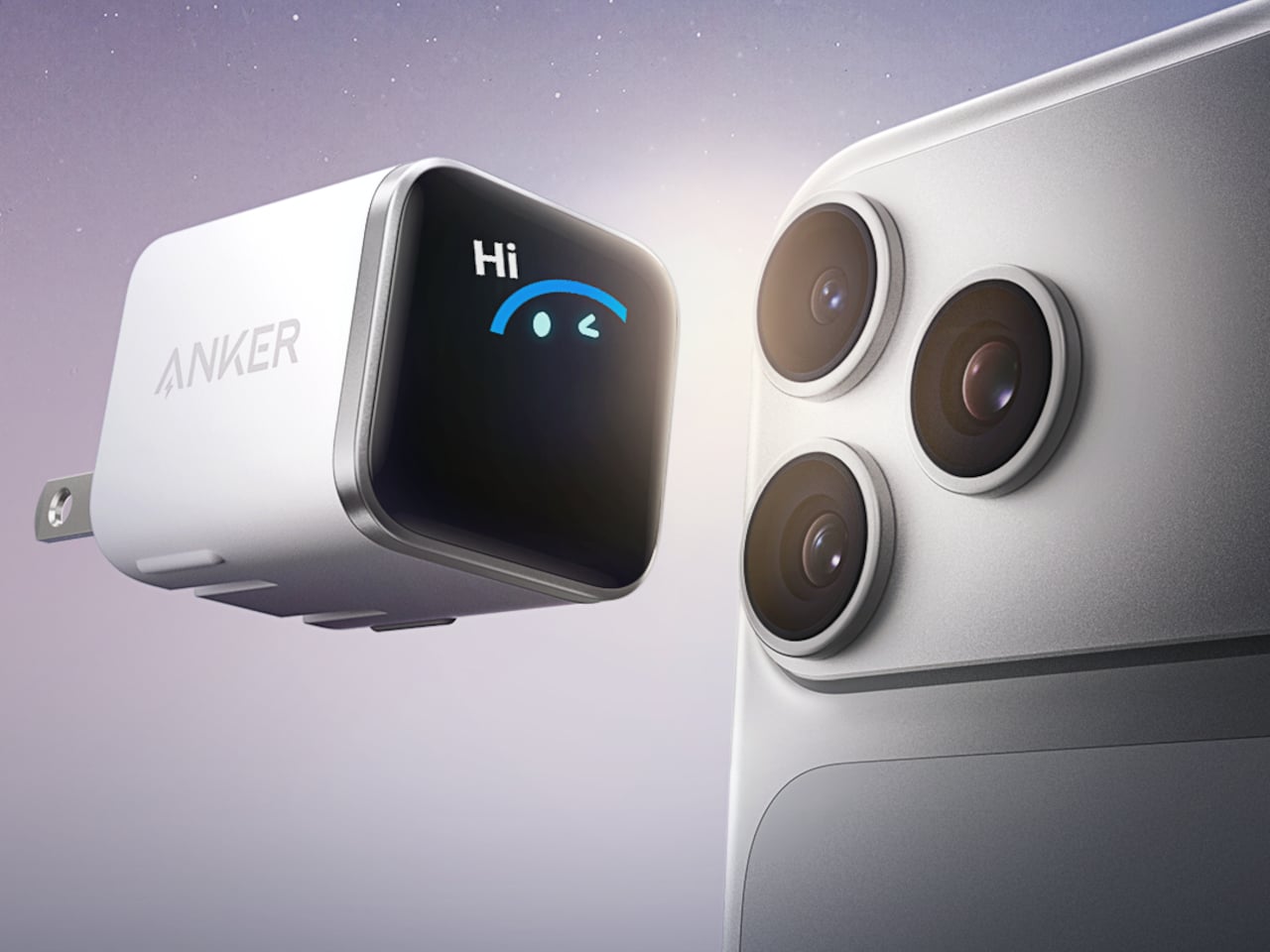

TÜV-certified Care Mode keeps the phone’s battery about 9 °F cooler than other 45 W chargers, a quiet win for long-term health. The small smart display shows real-time power and temperature with friendly icons, and the 180-degree foldable prongs let the charger sit in tight outlets while keeping the screen visible, fitting desk plugs, kitchen outlets, and behind-cabinets spaces where flat bricks fail.
Anker Prime Wireless Charging Station (3-in-1, MagGo, AirCool, Foldable)
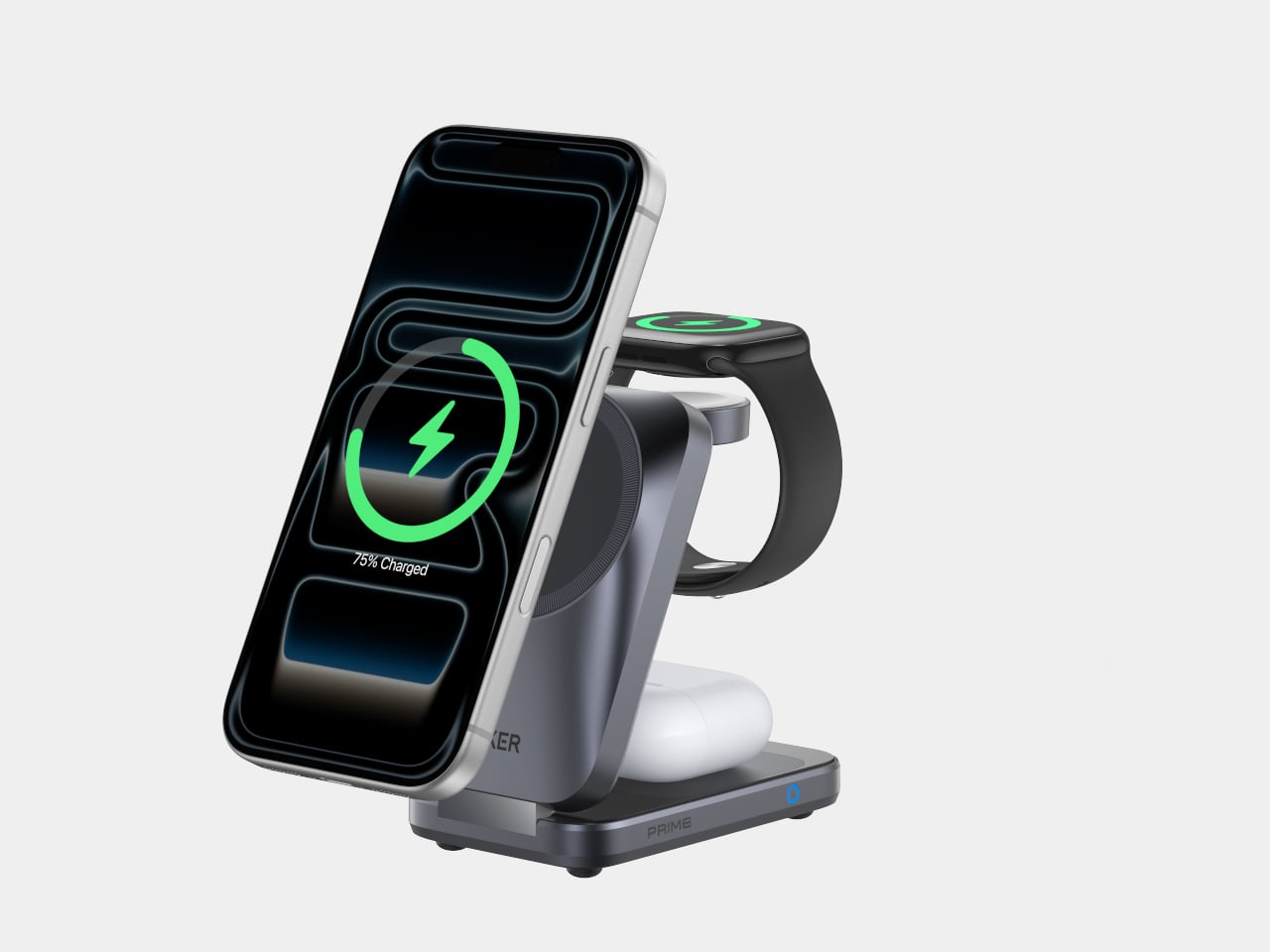

The Prime Wireless Charging Station handles an iPhone, earbuds, and a watch without three separate cables. It uses Qi2 25 W wireless charging to bring iPhone speeds close to wired, quoting 80% in about 55 minutes for an iPhone 17. The stand folds into a palm-sized block lighter than an iPhone 17 Pro Max, so it can live in a bag full-time, turning one USB-C input into a small charging island.
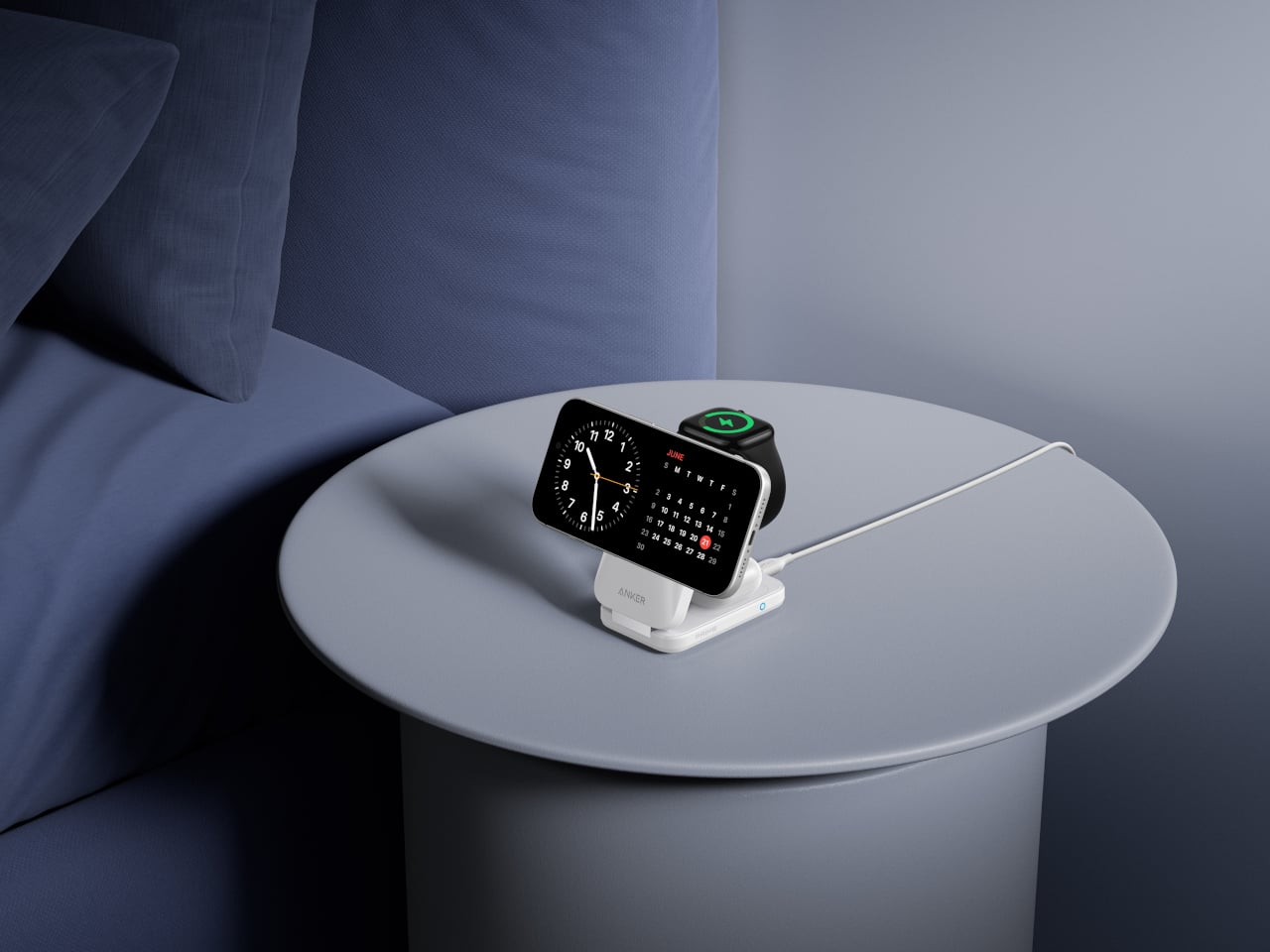


The AirCool airflow system keeps the charger and devices at stable temperatures when everything is stacked overnight or during work sessions, important when running 25 W to a phone while also topping up a watch and earbuds. That thermal management keeps the 3-in-1 from becoming uncomfortably hot on a nightstand or desk, and the foldable form clears cable clutter from hotel rooms and home offices, making it the kind of charger that actually gets packed for every trip.
Anker Nano Power Strip (10-in-1, 70W, Clamp)
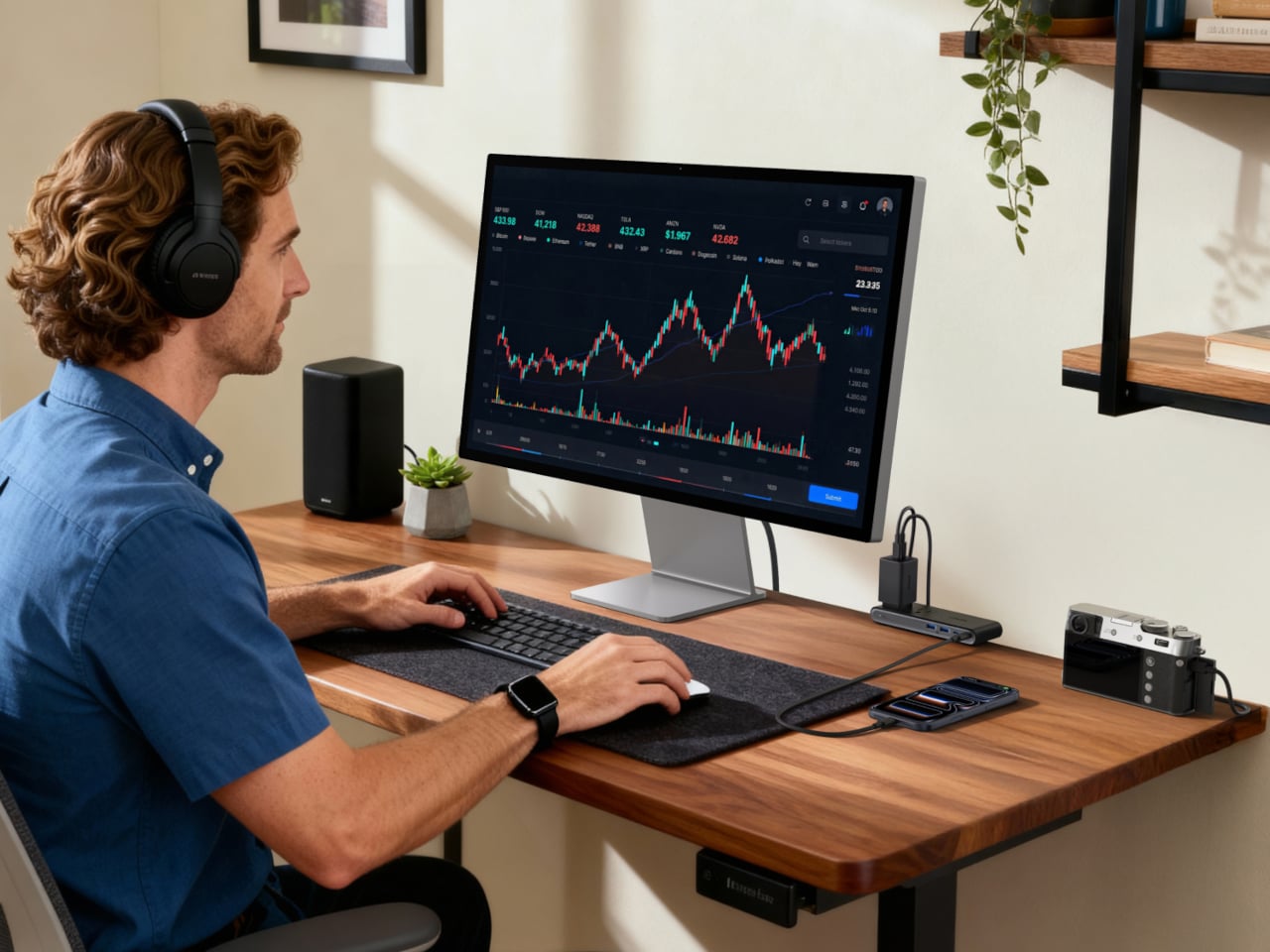
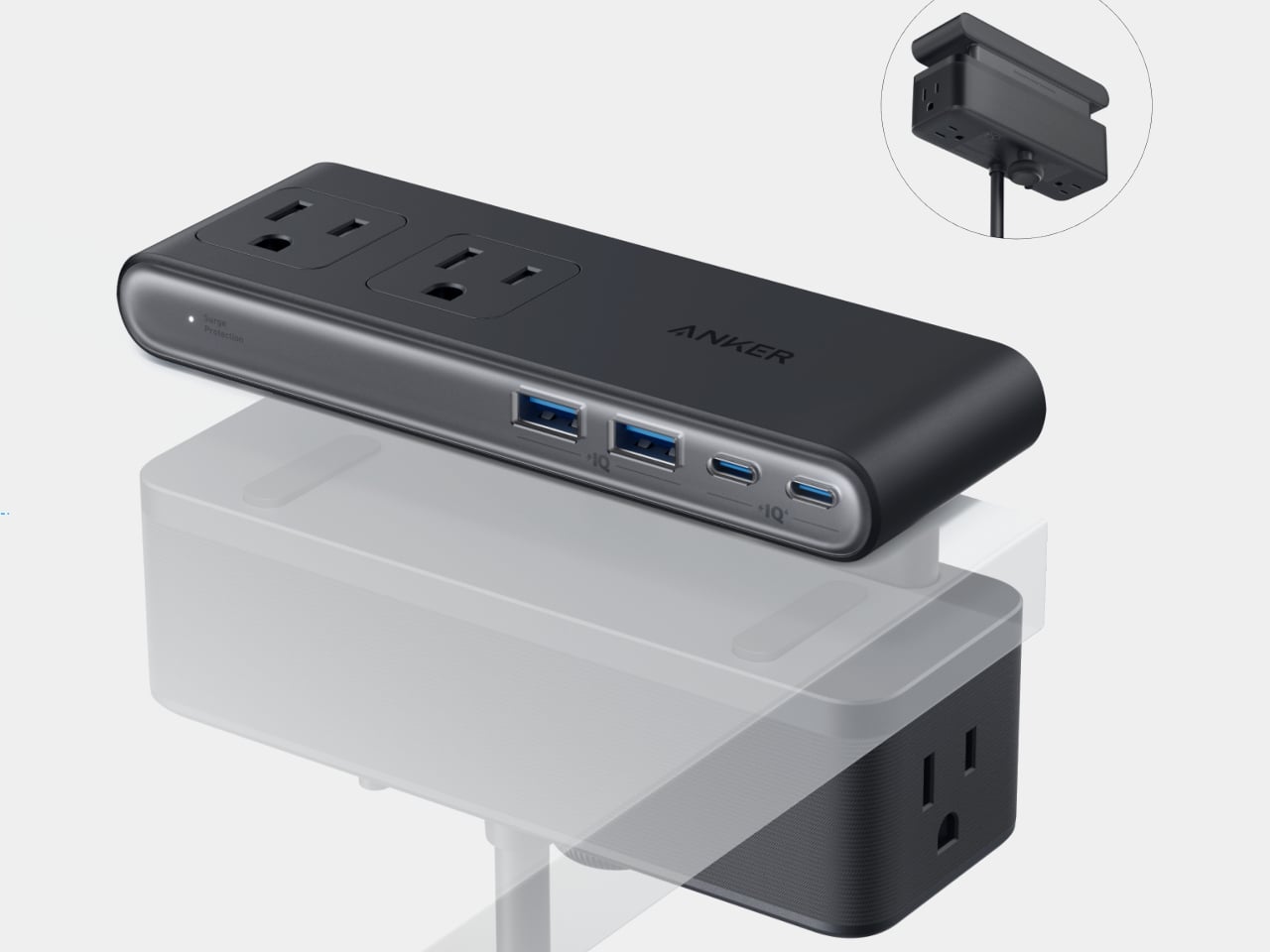


The Nano Power Strip is a dual-zone power bar that lives at the desk edge instead of under it. It combines six AC outlets with two USB-C and two USB-A ports, with a single USB-C delivering up to 70 W, enough to run a laptop or gaming handheld directly. The clamp-on design keeps the strip fixed in place while making ports easy to reach, so you stop crawling under desks to plug in temporary devices.
The built-in 1,500 J surge protection shields connected gear from spikes, which matters when monitors, desktop PCs, and audio equipment all share one outlet. Having the USB ports face forward and the AC outlets below the desk creates a cleaner visual line and makes it easier to manage cable runs, turning the strip into permanent desk infrastructure that handles both power and data charging without sprawling across the surface or tangling behind a monitor stand.

Anker Nano Docking Station (13-in-1, Triple Display, Built-In Removable Hub)
The Nano Docking Station is a 13-in-1 dock for people who treat a laptop as their main machine but want a desktop-class workspace. It supports triple-display output with up to 4K resolution on a single monitor, up to 100 W upstream charging, and USB-C, USB-A, HDMI, DisplayPort, Ethernet, and SD / TF 3.0 card slots, all running at up to 10 Gbps, where it counts for fast file transfers and external storage.

The built-in 6-in-1 removable hub slides out, letting someone leave the desktop cable tree intact while taking key ports and card readers on the road with a single, slim module. That bridging between permanent and mobile workflows makes the dock feel less like a fixed base station and more like a system that adapts to whether you are spending the day at a desk or heading to a meeting with just a laptop and the small hub in a bag.
Anker at CES 2026: Charging as a Coherent System
These four products sketch out Anker’s view of charging in 2026, not as isolated bricks and pads, but as coordinated tools that follow people from pocket to bedside to desk. Instead of chasing ever-higher wattage alone, the lineup leans into smarter interfaces, cooler operation, and forms that respect the spaces they live in, the kind of thinking Yanko Design readers expect from everyday hardware that earns its place by working better and quieter.

The post Anker’s CES 2026 Charging Lineup Treats Power as a Coordinated System first appeared on Yanko Design.