There’s something deeply satisfying about watching a designer solve multiple problems at once. William Young’s Jigsaw Chess Set is one of those rare designs that makes you wonder why nobody thought of it sooner. It’s a chess set, yes, but it’s also a sculptural object, an accessibility tool, and a logistics solution all rolled into one beautifully executed package.
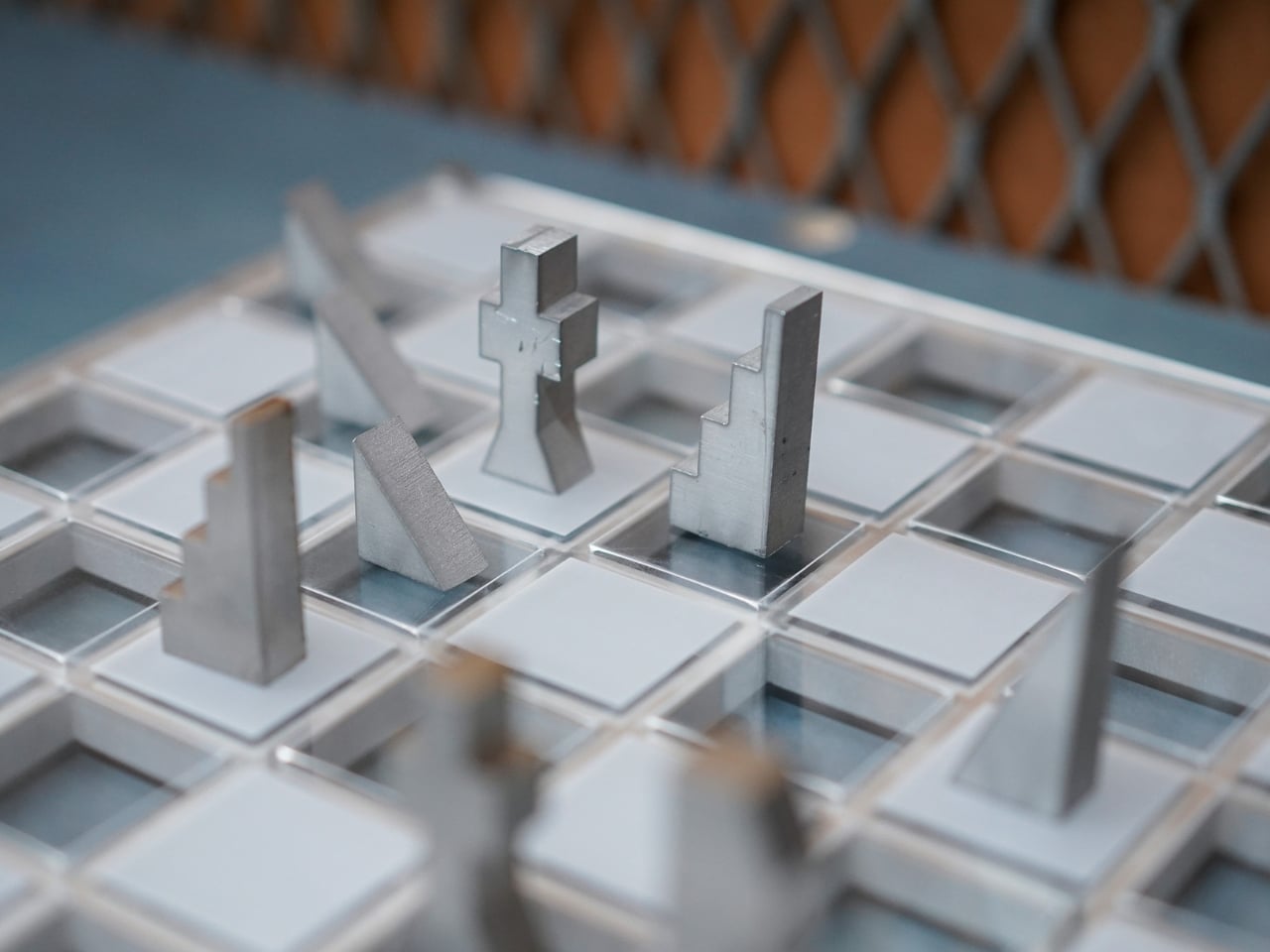
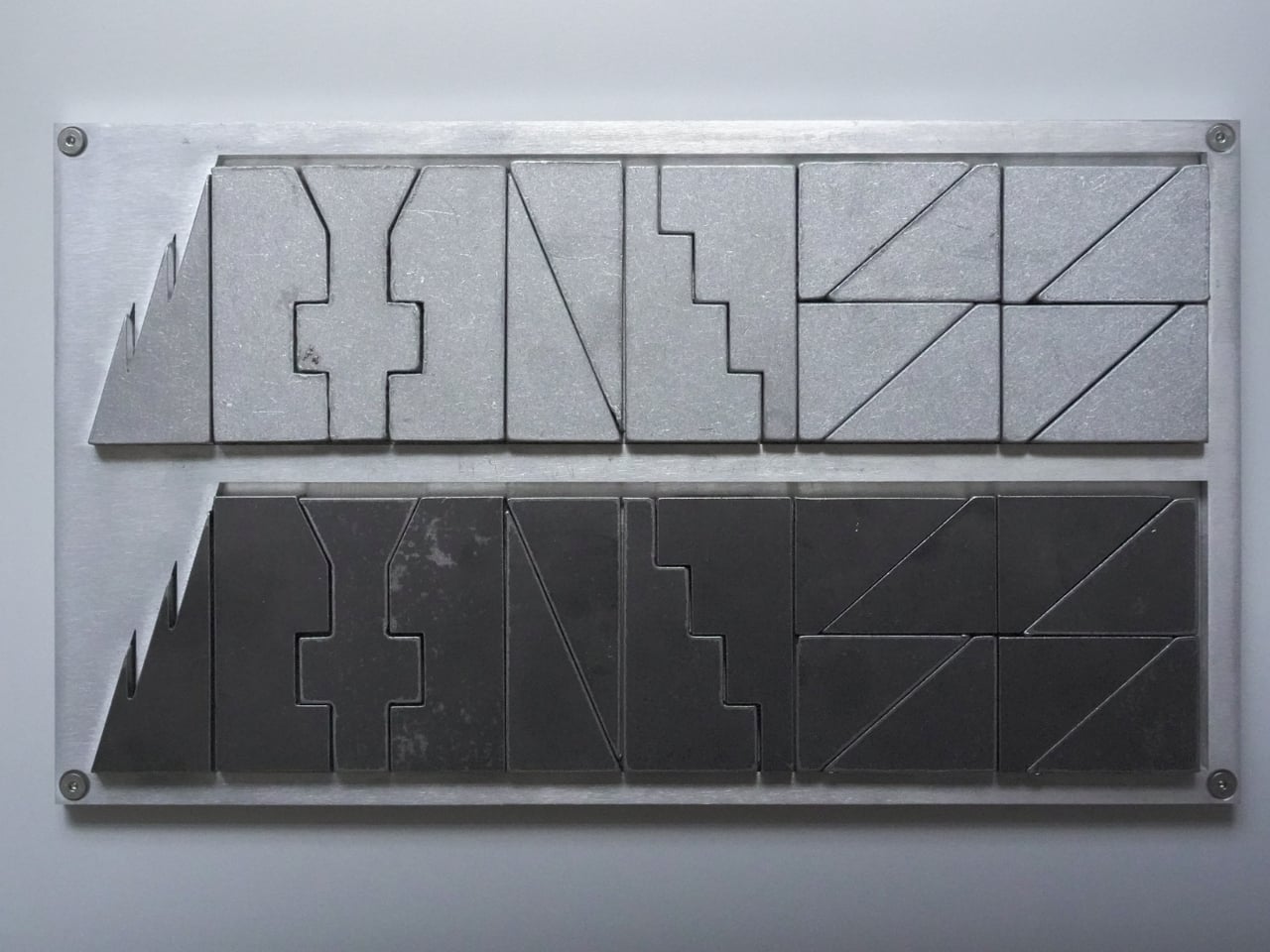
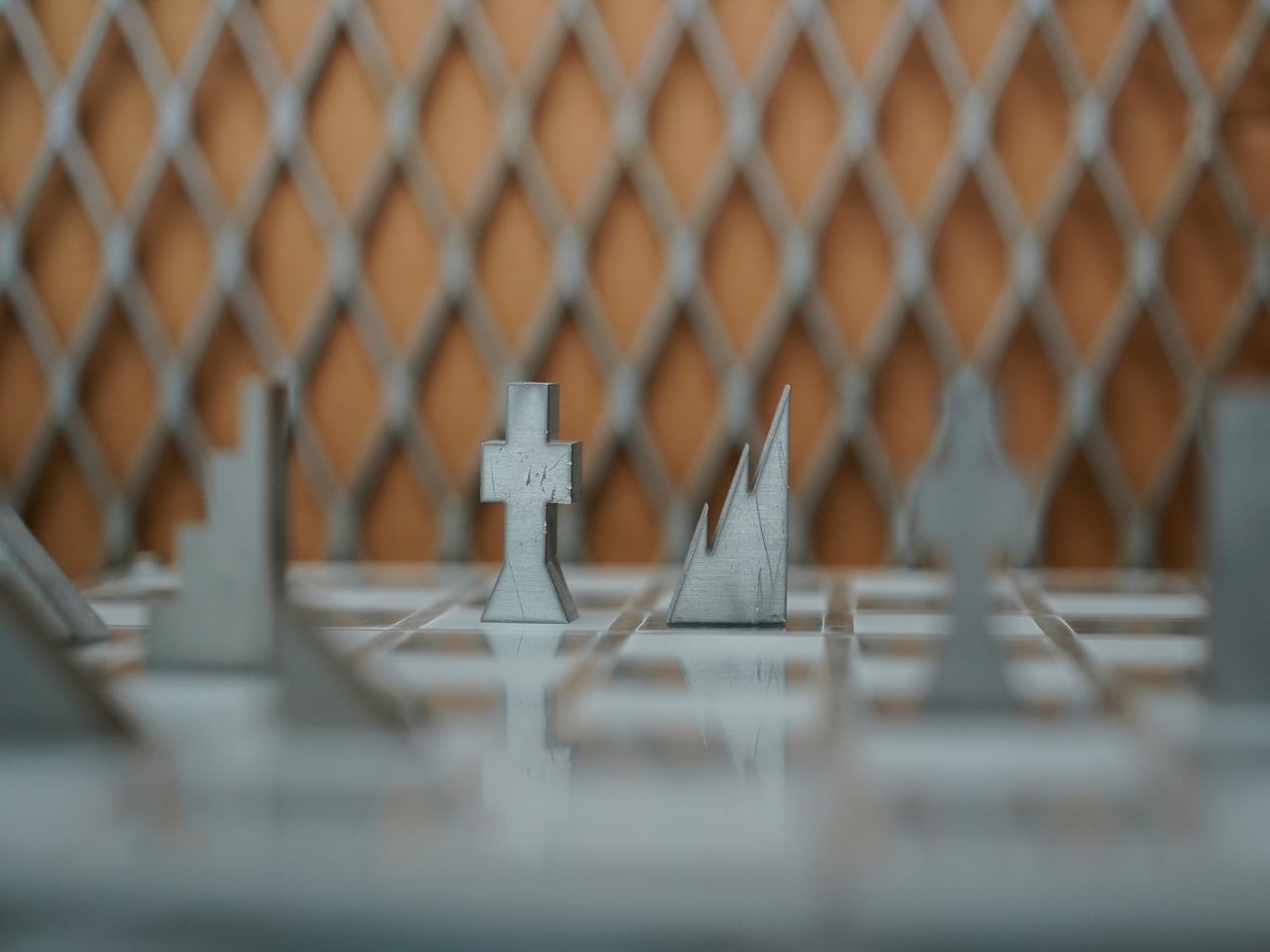
At first glance, the set looks like something you’d find in a modern art museum. The pieces are geometric, almost brutalist in their simplicity, fabricated from contrasting steel and aluminum. One side gets the cool, dark patina of steel, while the opposing army gleams in lighter aluminum. They’re angular, tessellated forms that look more like miniature architectural models than traditional chess pieces. But this isn’t just aesthetic posturing. Every design choice serves a purpose.
Designer: William Young

The most compelling aspect of the Jigsaw Chess Set is how it approaches accessibility. Most chess sets rely entirely on visual distinction. You know a knight from a bishop because you can see the carved horse head or the pointed mitre. But what if you can’t? Young’s design flips the script by making tactile identity the primary means of recognition. Each piece has a distinctive weight and texture that immediately identifies it in your hand. The king feels different from the rook, the pawn from the bishop. You could play this game with your eyes closed and know exactly what you’re moving across the board.

This isn’t a novelty feature. For visually impaired players, most chess sets require specialized modifications or Braille labels that still mark them as “other.” Young’s design makes accessibility intrinsic to the aesthetic, not an afterthought. The result is a set that works beautifully for everyone, regardless of visual ability. It’s inclusive design at its best, where accommodation becomes innovation.
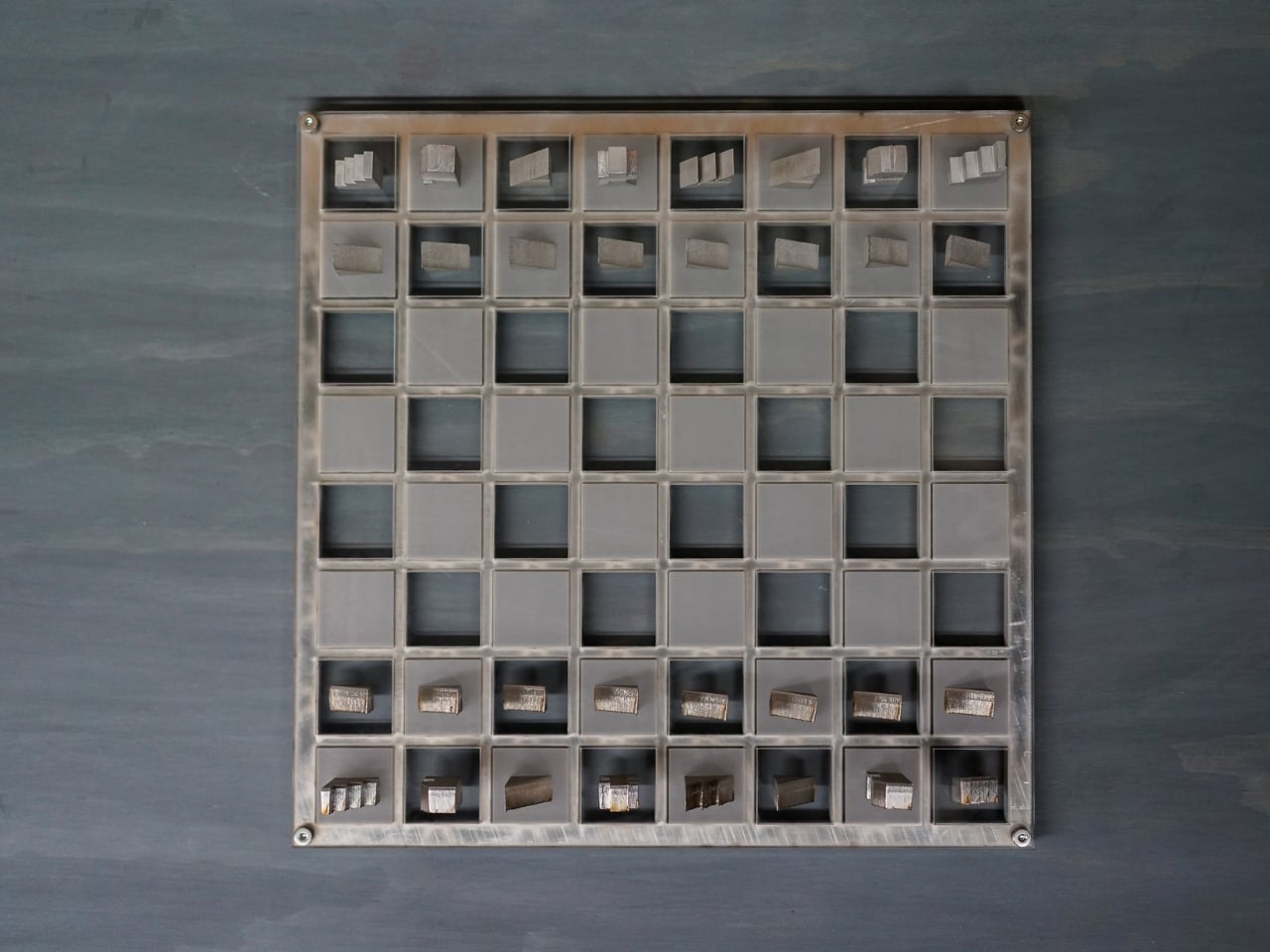

Then there’s the fabrication process, which deserves its own moment of appreciation. The pieces are created using a zero-waste cutting method. Picture a sheet of metal that gets sliced into interlocking forms, like a precision jigsaw puzzle where every cut produces a usable piece. Nothing gets tossed in the scrap bin. In an era where we’re increasingly aware of material waste and manufacturing impact, this approach feels refreshingly thoughtful. Each piece is then hand-finished, giving the set that tactile quality that makes it so satisfying to handle.
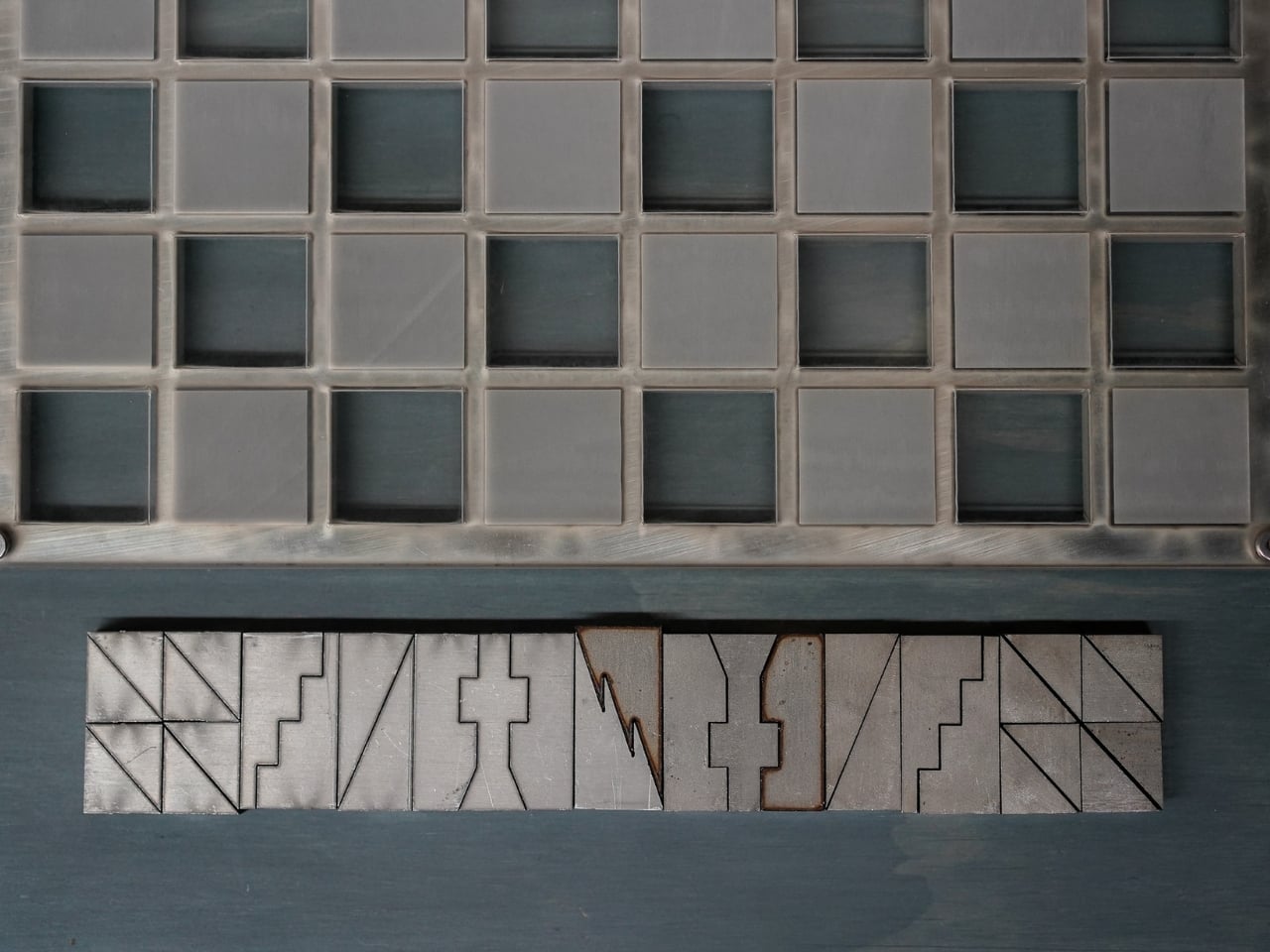

But wait, there’s more. (I know, I know, but genuinely, there’s more.) When you’re done playing, the entire set interlocks back into a dense, self-contained block. All 32 pieces fit together like a three-dimensional puzzle, creating a compact square that takes up minimal space. This is where the “jigsaw” name really earns its keep. The design is scalable too, meaning different size versions can be produced while maintaining the same interlocking logic.

From a shipping and storage perspective, this is genius. Traditional chess sets are bulky, awkward to pack, and wasteful in their use of space. Young’s design ships flat (well, flatish), reducing packaging materials and transportation costs. For consumers, it means easier storage when the set isn’t in use. For retailers, it means more efficient inventory management. Again, multiple problems solved with one elegant solution.
What really strikes me about the Jigsaw Chess Set is how it challenges our assumptions about what a chess set should be. The game is over 1,500 years old, and the basic design language of its pieces has remained relatively stable for centuries. Young doesn’t throw that all away, but he does ask: what if we started from scratch with contemporary materials, modern manufacturing techniques, and a genuine commitment to universal design?
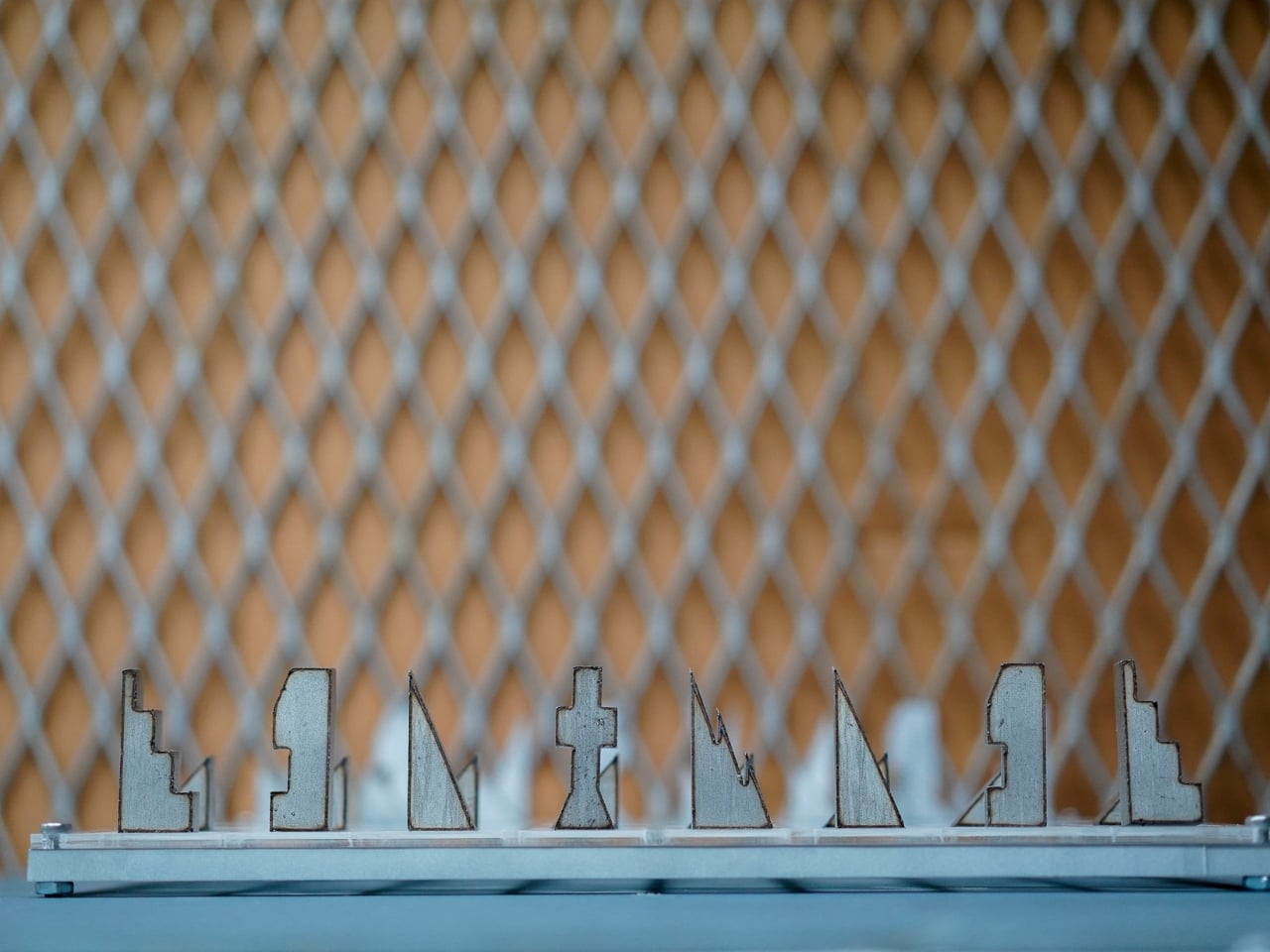

The answer is something that feels both familiar and radically new. You can still play chess exactly as you always have, but now you’re doing it with an object that works harder, thinks smarter, and includes more people in the experience. It’s a reminder that even the most traditional games have room for innovation when designers are willing to question the fundamentals. Whether you’re a chess enthusiast, a design collector, or someone who simply appreciates objects that do multiple things exceptionally well, the Jigsaw Chess Set deserves your attention. It’s proof that good design isn’t about adding features. It’s about rethinking everything from the ground up.
The post The Chess Set That Plays By Touch, Ships Flat, Wastes Nothing first appeared on Yanko Design.